注: 此文章为转载类型 为防止博客地址失效 特此备份
原文地址:http://www.madmalls.com/blog/post/deploy-flask-gunicorn-nginx-supervisor-on-centos7/
Synopsis: 当你用Flask框架在本地完全开发好一个应用程序后,想部署到服务器上,让互联网用户可以访问它,这与搭建本地开发环境还是有一些不一样的地方。首先,我们假设在服务器上安装了CentOS-7系统,使用git来上传和后续更新程序源代码,由于Flask自带的开发Web服务器性能不足以应对生产环境的并发访问,所以我们使用Gunicorn来替代它,同时,整个Web应用有许多静态资源,而Nginx非常善于处理这类请求,所以在Gunicorn前面再部署Nginx来提供静态资源服务,将其它请求反向代理给后面的Flask应用服务器Gunicorn。最后,为保证我们的Web应用持续提供服务,使用Supervisor来监控MongoDB/Gunicorn/Nginx的服务状态,当某一服务意外停止后,它会自动重启它。另外,我们也可以用Fabric实现这整个生产环境的部署过程自动化
- Git客户端
Win10安装git for windows
1.1 设置Git全局参数
打开Git Bash
$ git config --global user.name "Alice-HomePC"
$ git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
1.2 生成SSH Key
打开Git Bash,可使用-C选项指定公钥的说明信息
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "Alice-HomePC"
一直回车确认即可,秘钥对默认保存在C:\Users\你的Win10用户名.ssh目录下,其中id_rsa是私钥(Private Key),要小心保管;id_rsa.pub是公钥(Public Key),待会要上传到VPS上,实现基于SSH无密码登录VPS。同理,如果你在Github或Coding上有代码仓库,也是先要将公钥上传过去,才能无密码使用Git命令操作远程仓库。
- 配置VPS
2.1 修改主机名
# hostnamectl set-hostname CentOS
或者:
# vi /etc/hostname
# hostnamectl
重新登录.
2.2 修改SSH端口
# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.bak
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
将默认22端口改为你指定的, 例如
Port 12345
# systemctl restart sshd
2.3 禁用SSH密码认证,改为秘钥认证
首先需要将步骤1中生成的公钥上传到服务器,可以使用xmanager套件中的xftp上传,假设上传到/root目录
1. 添加公钥
# cd /root
# mkdir ~/.ssh && chmod 700 ~/.ssh
# touch ~/.ssh/authorized_keys && chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
# cat id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
2. 修改SSH配置文件
# vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
修改几处地方,最终内容如下:
# 禁用root登录
PermitRootLogin no
# 启用密钥验证
RSAAuthentication yes
PubkeyAuthentication yes
# 指定公钥数据库文件
AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys
# 禁用密码验证
PasswordAuthentication no
3. SSH重新加载配置文件
# systemctl reload sshd
此时,Win10可以通过xshell,无密码登录VPS了,且只能使用私钥认证通过。
- 安装Python3
CentOS-7.3默认安装的是Python-2.7, 我的Flask程序是基于Python3写的,所以要再安装Python3
1. 准备编译环境
# yum -y install gcc make readline-devel sqlite-devel openssl openssl-devel zlib*
2. 编译安装
# wget -P /root http://python.org/ftp/python/3.6.4/Python-3.6.4.tar.xz
# tar xf Python-3.6.4.tar.xz
# cd Python-3.6.4/
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/python-3.6
# make && make install
# ln -s /usr/local/python-3.6/bin/python3.6 /usr/bin/python3
# ln -s /usr/local/python-3.6/bin/pip3.6 /usr/bin/pip3
更改pip安装源为国内的源,比如aliyun
# mkdir ~/.pip
# vi ~/.pip/pip.conf
添加内容如下:
[global]
index-url = http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple/
[install]
trusted-host=mirrors.aliyun.com
(可选)安装IPython
- Home Page
- GitHub Project
- Installing Jupyter Notebook
1. pip方式安装(推荐), 该方式会有语法高亮等特性
# pip3 --version
# pip3 install --upgrade pip
# pip3 install ipython
# ln -s /usr/local/python-3.6/bin/ipython3 /usr/bin/ipython3
2. 编译安装
# tar xf ipython-0.13.1.tar.gz
# cd ipython-0.13.1/
# python3 setup.py install
# ln -s /usr/local/python-3.6/bin/ipython3 /usr/bin/ipython3
4. 安装MongoDB
官方文档
1. 配置repo源
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-3.6.repo
内容如下:
[mongodb-org-3.6]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/3.6/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-3.6.asc
2. 安装并启动服务
# yum install -y mongodb-org
# systemctl start mongod.service
# systemctl enable mongod.service
- Git服务端
1. 安装
# yum install -y git
2. 创建裸仓库
# mkdir /home/git && cd /home/git
# git init --bare flask_project.git
我在Win10上已经开发好了Flask程序,待会上传到此git仓库中,应用程序代码准备部署到/home/www/flask_project,并通过git的hooks当客户端每次提交代码后,自动同步仓库中的代码到应用部署的位置 Simple automated GIT Deployment using GIT Hooks
1. 创建代码部署目录
# mkdir -pv /home/www/flask_project
2. 创建hooks
# vi /home/git/flask_project.git/hooks/post-receive
内容如下:
#!/bin/bash
TRAGET="/home/www/flask_project"
GIT_DIR="/home/git/flask_project.git"
BRANCH="master"
while read oldrev newrev ref
do
# only checking out the master (or whatever branch you would like to deploy)
if [[ $ref = refs/heads/$BRANCH ]];
then
echo "Ref $ref received. Deploying ${BRANCH} branch to production…"
git --work-tree=$TRAGET --git-dir=$GIT_DIR checkout -f
else
echo "Ref $ref received. Doing nothing: only the ${BRANCH} branch may be deployed on this server."
fi
done
3. 赋权
# chmod +x /home/git/flask_project.git/hooks/post-receive
- 上传代码
打开Git Bash,准备把服务器上的flask_project.git仓库(目前为空)克隆下来。Git默认使用SSH协议且端口22,由于我们刚修改了服务器的SSH端口,所以克隆时要指定修改后的端口号
6.1 克隆远程仓库
方法1:
$ git clone ssh://root@VPS的IP或域名:VPS的SSH端口号//home/git/flask_project.git
方法2: 在Win10保存SSH秘钥对的目录下创建配置文件 C:\Users\你的Win10用户名.ssh\config
host VPS的IP或域名
port VPS的SSH端口
然后执行克隆命令:
$ git clone root@VPS的IP或域名:/home/git/flask_project.git
6.2 提交代码
克隆后会在当前目录下生成 flask_project 目录,把开发好的flask代码拷贝到这里面,并指定哪些文件不提交到git仓库,在git bash中运行:
$ cd flask_project
$ vi .gitignore
比如我的规则:
.idea/
__pycache__/
uploads/
venv3/
提交代码:
$ git add .
$ git commit -m "initial"
$ git push
你会发现/home/www/flask_project目录下会自动拷贝git仓库中master分支的最新代码过来。
- 调试程序
7.1 准备virtualenv环境
# pip3 install virtualenv
# ln -s /usr/local/python-3.6/bin/virtualenv /usr/bin/virtualenv
# cd /home/www/flask_project
# virtualenv --no-site-packages --python=/usr/bin/python3 venv3
7.2 安装相关python包
# source venv3/bin/active
(venv3)# pip install flask
依次安装完所有的依赖包后,
(venv3)# pip freeze > requirements.txt
7.3 测试用Flask自带的服务器能否运行
(venv3)# python manage.py runserver -h 0.0.0.0 -p 80
如果你能通过VPS的IP正常访问Flask应用,那么就可以进行下一步,使用Gunicorn替代Flask自带的开发服务器
8. Gunicorn
- 官网
- 文档
8.1 安装
(venv3)# pip install gunicorn
8.2 创建包含应用入口app的模块文件
一般我们开发时,都是使用manage.py,里面有flask-script方便调试,生产环境要再创建一个模块,比如:
# vi wsgi.py
内容如下:
import os
from app import create_app
###
# 调用工厂函数,初始化Flask程序实例,默认使用生产环境配置
###
app = create_app(os.getenv('FLASK_CONFIG') or 'production')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host='0.0.0.0')
那么使用gunicorn命令行来启动Flask非常简单:
(venv3)# gunicorn -w 3 wsgi:app -b 0.0.0.0:80
说明:
-w 3 是启用3个进程,建议是CPU核数*2 + 1
wsgi:app 其中wsgi代表当前目录下的wsgi.py模块,后面的app代表wsgi.py模块里面的Flask应用app
如果你能通过VPS的IP正常访问Flask应用,那么通过指定gunicorn配置文件来启动Flask,比如:
# mkdir deploy
# vi deploy/gunicorn.conf.py
内容如下:
import multiprocessing
# bind = '127.0.0.1:8001'
bind = 'unix:/run/gunicorn.sock'
workers = multiprocessing.cpu_count() * 2 + 1
# daemon = True
pidfile = '/run/gunicorn.pid'
loglevel = 'info'
errorlog = '/tmp/gunicorn-error.log'
accesslog = '/tmp/gunicorn-access.log'
access_log_format = '%(h)s %(l)s %(u)s %(t)s "%(r)s" %(s)s %(b)s "%(f)s" "%(a)s"'
更详细的配置可以参考Gunicorn官方示例
那么,此时启动Flask变成:
(venv3)# gunicorn wsgi:app -c deploy/gunicorn.conf.py
- Redis
使用Flask-Caching缓存页面,测试环境用默认的simple,生产环境用redis
9.1 安装Redis
1. Redis需要EPEL源
# yum install epel-release
2. 安装
# yum install -y redis
3. 启动与开机自启
# systemctl start redis.service
# systemctl enable redis.service
9.2 设置Redis
编辑/etc/redis.conf,确保只有本机能够访问Redis,即bind 127.0.0.1没有被注释掉。默认没有密码。
9.3 验证是否启用缓存
wsgi.py中是使用production配置,确保config.py中ProductionConfig的配置项CACHE_TYPE = 'redis'
1. 用gunicorn启动Flask
# gunicorn -w 3 wsgi:app -b 0.0.0.0:5000
2. 用浏览器访问 VPS的IP:5000, 测试是不是缓存生效了
3. 输入 keys * ,查看redis中所有的key
# redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "flask_cache_view//blog/?page=1"
10. Nginx
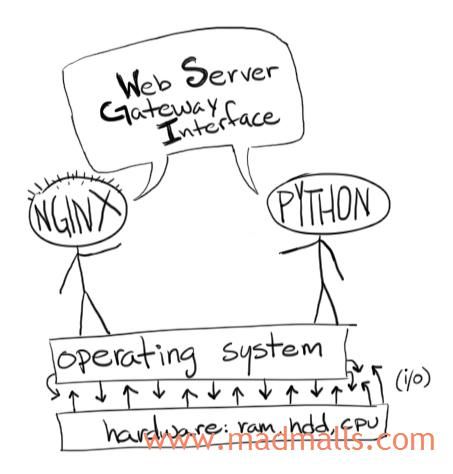
WSGI服务器没有Nginx处理静态文件的性能好,所以我们安装nginx,把我们应用程序中像logo.png这类静态资源变给nginx处理响应。而客户端的那些不是请求静态资源的request,会被nginx反向代理给后端的gunicorn,gunicorn生成html响应后,交回给nginx,再由nginx返回给客户端。
10.1 安装
官方文档
1. 添加repo源
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo
内容如下:
[nginx]
name=nginx repo
baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/$basearch/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
2. 安装
# yum install -y nginx
3. 启动
# systemctl start nginx
# systemctl enable nginx
10.2 响应静态资源
1. 增加配置文件
# vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/flask_project.conf
内容如下:
server {
listen 80;
# server_name www.madmalls.com;
location /static {
alias /home/www/flask_project/static/;
}
}
2. 重启
# mv /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf.bak
# nginx -t
# systemctl restart nginx
如果步骤8中没有停止gunicorn,先stop它:
# pkill gunicorn
此时,你用VPS的IP访问/static目录下的logo.png,如果能正常访问,说明是nginx在提供服务(因为此时我们已经关闭gunicorn了)
10.3 反向代理
1. 修改配置文件
# vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/flask_project.conf
内容如下:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.madmalls.com;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://unix:/run/gunicorn.sock;
}
location /static {
alias /home/www/flask_project/app/static/;
}
}
2. 重启
# nginx -t
# systemctl restart nginx
启动gunicorn:
(venv3)# gunicorn wsgi:app -c deploy/gunicorn.conf.py
此时,用VPS的IP访问Flask应用,应该一切正常。
11. Supervisor
使用supervisor来管理gunicorn进程的启停
11.1 安装
CentOS可以通过yum安装
# yum install -y supervisor
# systemctl start supervisord.service
# systemctl enable supervisord.service
11.2 增加配置文件
要监控gunicorn进程,只需要添加/etc/supervisord.d/gunicorn.ini配置文件,详细配置参考gunicorn的官方示例
# vi /etc/supervisord.d/gunicorn.ini
内容如下:
[program:gunicorn]
command=/home/www/flask_project/venv3/bin/gunicorn wsgi:app -c deploy/gunicorn.conf.py
directory=/home/www/flask_project
user=root
autostart=true
autorestart=true
redirect_stderr=true
说明:
command 即启动gunicorn的命令,此处要写绝对路径
directory 项目部署目录,不然没办法知道command中wsgi模块在哪
11.3 管理gunicorn
1. 增加配置文件后,更新
# supervisorctl reread
# supervisorctl update
2. 查看状态
# supervisorctl status
3. 启动/停止
# supervisorctl start gunicorn
# supervisorctl stop gunicorn
# supervisorctl restart gunicorn
12. Fabric
官网
假如现在修复了一个bug,要重新部署代码,先在Win10上git push代码到仓库,自动同步到部署目录,用supervisor重启gunicorn,步骤不多,所以没必要用fabric 如果你的应用比较复杂,数据库层、缓存层、服务层、Web层都是分布式架构,那么可以用fabric自动部署,省得登录这么多台服务器去做一些枯燥费时的重复操作。