1、+load 方法的顺序
已知分类添加的方法与本类方法重名时的调用顺序是优先分类的方法,当 +load 方法主类分类中同时实现时,其加载顺序是什么呢?
执行工程(源码地址),输出结果如下:
func: +[MyPerson load]
func: +[MyPerson(cateTwo) load]
func: +[MyPerson(cateMore) load]
可看到主类load方法优先调用。2个分类的 load 加载顺序是如何呢?
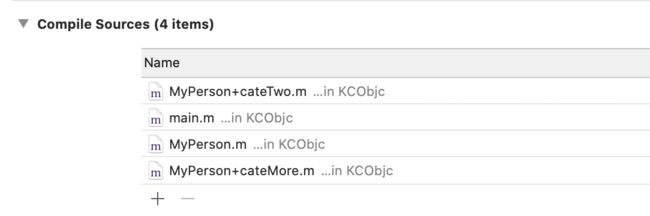
上面的输出结果时,2个分类的 Compile Sources编译资源 的顺序如下图,cateTwo 在前:
我们将
cateTwo移动到
cateMore之前,再次运行:
func: +[MyPerson load]
func: +[MyPerson(cateMore) load]
func: +[MyPerson(cateTwo) load]
由上可知,分类的 load方法的调用顺序和Compile Sources中一致。
下面进行详细探究。
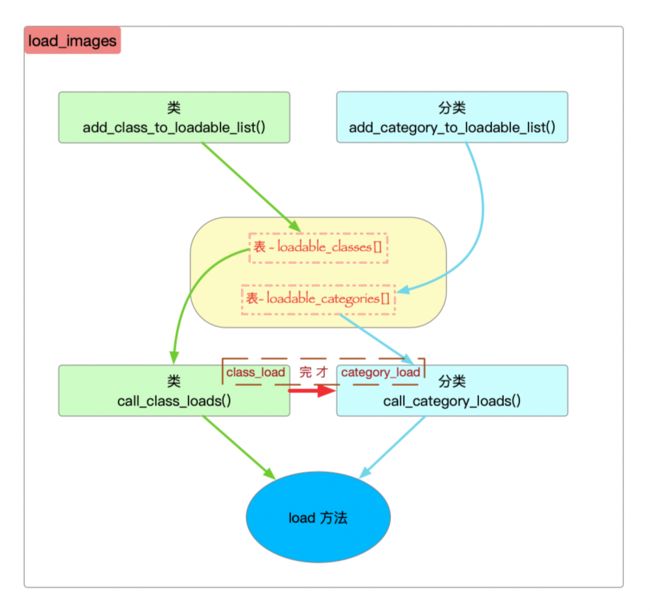
load_images 源码:
/***********************************************************************
* load_images
* Process +load in the given images which are being mapped in by dyld.
*
* Locking: write-locks runtimeLock and loadMethodLock
**********************************************************************/
extern bool hasLoadMethods(const headerType *mhdr);
extern void prepare_load_methods(const headerType *mhdr);
// 在 load 中处理images镜像文件 - 这些文件是通过 dyld 映射进去的
void
load_images(const char *path __unused, const struct mach_header *mh)
{
if (!didInitialAttachCategories && didCallDyldNotifyRegister) {
didInitialAttachCategories = true;
loadAllCategories();
}
// Return without taking locks if there are no +load methods here.
if (!hasLoadMethods((const headerType *)mh)) return;
recursive_mutex_locker_t lock(loadMethodLock);
// Discover load methods 找到所有 load 方法们
// 准备
{
mutex_locker_t lock2(runtimeLock);
prepare_load_methods((const headerType *)mh);
}
// Call +load methods (without runtimeLock - re-entrant)
// 调用
call_load_methods();
}
1)prepare_load_methods()源码:
void prepare_load_methods(const headerType *mhdr)
{
size_t count, i;
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
// 类 list
// 为何是 Nonlazy 非懒加载 --> 实现 load 方法了呀
classref_t const *classlist =
_getObjc2NonlazyClassList(mhdr, &count);// 取非懒加载的 classList
// 遍历,将 cls 加到 loadable_classes[] 表中
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
// schedule_class_load:处理镜像文件中类的 loads 方法
schedule_class_load(remapClass(classlist[i]));
}
// 分类 list - 处理流程和类相似
category_t * const *categorylist = _getObjc2NonlazyCategoryList(mhdr, &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++) {
category_t *cat = categorylist[i];
Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
if (!cls) continue; // category for ignored weak-linked class
if (cls->isSwiftStable()) {
_objc_fatal("Swift class extensions and categories on Swift "
"classes are not allowed to have +load methods");
}
realizeClassWithoutSwift(cls, nil);// class需要实现
ASSERT(cls->ISA()->isRealized());
// 将 cat 加到 loadable_categories[] 表中
add_category_to_loadable_list(cat);
}
}
1.1)schedule_class_load()源码,类的方法的准备:
/***********************************************************************
* prepare_load_methods
* Schedule +load for classes in this image, any un-+load-ed
* 对 镜像文件中 任何 未加载的类 的 +load 进行安排处理
* superclasses in other images, and any categories in this image.
**********************************************************************/
// Recursively schedule +load for cls and any un-+load-ed superclasses.
// cls must already be connected.
static void schedule_class_load(Class cls)
{
if (!cls) return;
ASSERT(cls->isRealized()); // _read_images should realize
if (cls->data()->flags & RW_LOADED) return;
// Ensure superclass-first ordering
schedule_class_load(cls->superclass);// 递归
// 把 cls 添加到 loadable 列表里面
add_class_to_loadable_list(cls);
cls->setInfo(RW_LOADED); // 标记为有 load 方法 - data->setFlags()
}
1.1.1)add_class_to_loadable_list() 源码,cls 添到表中:
/***********************************************************************
* add_class_to_loadable_list
* Class cls has just become connected. Schedule it for +load if
* it implements a +load method.
**********************************************************************/
void add_class_to_loadable_list(Class cls)
{
IMP method;
loadMethodLock.assertLocked();
method = cls->getLoadMethod();
/** 拿到 load 方法 - if (0 == strcmp(name, "load")) { return meth.imp; }
// objc_class::getLoadMethod
// fixme
// Called only from add_class_to_loadable_list.
// Locking: runtimeLock must be read- or write-locked by the caller.
IMP
objc_class::getLoadMethod()
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
const method_list_t *mlist;
ASSERT(isRealized());
ASSERT(ISA()->isRealized());
ASSERT(!isMetaClass());
ASSERT(ISA()->isMetaClass());
mlist = ISA()->data()->ro()->baseMethods();
if (mlist) {
// 遍历方法列表 methodLists,取到 load
for (const auto& meth : *mlist) {
const char *name = sel_cname(meth.name);
if (0 == strcmp(name, "load")) {// name是否j和load同
return meth.imp;
}
}
}
return nil;
}
*/
if (!method) return; // Don't bother if cls has no +load method
if (PrintLoading) {
_objc_inform("LOAD: class '%s' scheduled for +load",
cls->nameForLogging());
}
// 当前使用的和正在开辟的 是否是表里面的同一个,是 --> 扩容
if (loadable_classes_used == loadable_classes_allocated) {
// 扩容
loadable_classes_allocated = loadable_classes_allocated*2 + 16;
// realloc 重新开辟空间
loadable_classes = (struct loadable_class *)
realloc(loadable_classes,
loadable_classes_allocated *
sizeof(struct loadable_class));
}
// 将 cls 和 method 加到 loadable_classes 表的 loadable_classes_used 位置
loadable_classes[loadable_classes_used].cls = cls;
loadable_classes[loadable_classes_used].method = method;
loadable_classes_used++;// 后移
}
2)call_load_methods() 源码:
/***********************************************************************
* call_load_methods
* Call all pending class and category +load methods.
* Class +load methods are called superclass-first.
* Category +load methods are not called until after the parent class's +load.
* 先调 主类,直到 class 的 load 调完后才分类
* This method must be RE-ENTRANT, because a +load could trigger
* more image mapping. In addition, the superclass-first ordering
* must be preserved in the face of re-entrant calls. Therefore,
* only the OUTERMOST call of this function will do anything, and
* that call will handle all loadable classes, even those generated
* while it was running.
*
* The sequence below preserves +load ordering in the face of
* image loading during a +load, and make sure that no
* +load method is forgotten because it was added during
* a +load call.
* Sequence:
* 1. Repeatedly call class +loads until there aren't any more
* 2. Call category +loads ONCE.
* 3. Run more +loads if:
* (a) there are more classes to load, OR
* (b) there are some potential category +loads that have
* still never been attempted.
* Category +loads are only run once to ensure "parent class first"
* ordering, even if a category +load triggers a new loadable class
* and a new loadable category attached to that class.
*
* Locking: loadMethodLock must be held by the caller
* All other locks must not be held.
**********************************************************************/
void call_load_methods(void)
{
static bool loading = NO;
bool more_categories;
loadMethodLock.assertLocked();
// Re-entrant calls do nothing; the outermost call will finish the job.
if (loading) return;
loading = YES;
void *pool = objc_autoreleasePoolPush();
do {
// 1. Repeatedly call class +loads until there aren't any more
while (loadable_classes_used > 0) {
call_class_loads();// 类的 load 调用
}
// 2. Call category +loads ONCE
more_categories = call_category_loads();// 分类的 load 调用
// 3. Run more +loads if there are classes OR more untried categories
} while (loadable_classes_used > 0 || more_categories);
objc_autoreleasePoolPop(pool);
loading = NO;
}
先调主类 load,直到 parent's class 全调完,再分类.
2.1)call_class_loads() 类的 load 调用
/***********************************************************************
* call_class_loads
* Call all pending class +load methods.
* If new classes become loadable, +load is NOT called for them.
*
* Called only by call_load_methods().
**********************************************************************/
static void call_class_loads(void)
{
int i;
// Detach current loadable list.
struct loadable_class *classes = loadable_classes;
int used = loadable_classes_used;
loadable_classes = nil;
loadable_classes_allocated = 0;
loadable_classes_used = 0;
// Call all +loads for the detached list.
for (i = 0; i < used; i++) {
Class cls = classes[i].cls;
load_method_t load_method = (load_method_t)classes[i].method;
if (!cls) continue;
if (PrintLoading) {
_objc_inform("LOAD: +[%s load]\n", cls->nameForLogging());
}
// 指针的调用 - 函数调用
// 两个参数:load 的隐藏参数 id self 和 SEL cmd
(*load_method)(cls, @selector(load));
}
// Destroy the detached list. 销毁已分离的 list
if (classes) free(classes);
}
2.2)call_category_loads() 分类 load 调用
它包含了call_load_methods()中死循环的出口条件处理。
/***********************************************************************
* call_category_loads
* Call some pending category +load methods.
* The parent class of the +load-implementing categories has all of
* its categories attached, in case some are lazily waiting for +initalize.
* Don't call +load unless the parent class is connected.
* If new categories become loadable, +load is NOT called, and they
* are added to the end of the loadable list, and we return TRUE.
* Return FALSE if no new categories became loadable.
*
* Called only by call_load_methods().
**********************************************************************/
static bool call_category_loads(void)
{
int i, shift;
bool new_categories_added = NO;
// Detach current loadable list.
struct loadable_category *cats = loadable_categories;
int used = loadable_categories_used;
int allocated = loadable_categories_allocated;
loadable_categories = nil;
loadable_categories_allocated = 0;
loadable_categories_used = 0;
// Call all +loads for the detached list.
for (i = 0; i < used; i++) {
Category cat = cats[i].cat;
load_method_t load_method = (load_method_t)cats[i].method;
Class cls;
if (!cat) continue;
cls = _category_getClass(cat);
if (cls && cls->isLoadable()) {
if (PrintLoading) {
_objc_inform("LOAD: +[%s(%s) load]\n",
cls->nameForLogging(),
_category_getName(cat));
}
(*load_method)(cls, @selector(load));
cats[i].cat = nil;// 调用后解除关联,防止多次调
}
}
// call_load_methods() 的 do{}while() 死循环的出口处理 : 表走到了第0个走完
// Compact detached list (order-preserving)
shift = 0;
for (i = 0; i < used; i++) {
if (cats[i].cat) {
cats[i-shift] = cats[i];
} else {
shift++;
}
}
used -= shift;
// Copy any new +load candidates from the new list to the detached list.
new_categories_added = (loadable_categories_used > 0);
for (i = 0; i < loadable_categories_used; i++) {
if (used == allocated) {
allocated = allocated*2 + 16;
cats = (struct loadable_category *)
realloc(cats, allocated *
sizeof(struct loadable_category));
}
cats[used++] = loadable_categories[i];
}
// Destroy the new list.
if (loadable_categories) free(loadable_categories);
// Reattach the (now augmented) detached list.
// But if there's nothing left to load, destroy the list.
if (used) {
loadable_categories = cats;
loadable_categories_used = used;
loadable_categories_allocated = allocated;
} else {
if (cats) free(cats);
loadable_categories = nil;
loadable_categories_used = 0;
loadable_categories_allocated = 0;
}
if (PrintLoading) {
if (loadable_categories_used != 0) {
_objc_inform("LOAD: %d categories still waiting for +load\n",
loadable_categories_used);
}
}
return new_categories_added;
}
流程总结:
2、+initialize 初始化
给主类和分类都添加 +initialize 方法,运行 输出结果如下:
func: +[MyPerson load]
func: +[MyPerson(cateTwo) load]
func: +[MyPerson(cateMore) load]
func: +[MyPerson(cateMore) initialize]
只有 分类后编译的 cateMore调用,为何? --> 苹果关于 +initialize 的注释解释:
CLS_INITIALIZED 一旦设置就永不会清除。 send +initialize,即initialize 是通过消息发送调用的。
/***********************************************************************
* objc-initialize.m
* +initialize support
**********************************************************************/
/***********************************************************************
* Thread-safety during class initialization (GrP 2001-9-24)
*
* Initial state: CLS_INITIALIZING and CLS_INITIALIZED both clear.
* During initialization: CLS_INITIALIZING is set
* After initialization: CLS_INITIALIZING clear and CLS_INITIALIZED set.
* CLS_INITIALIZING and CLS_INITIALIZED are never set at the same time.
* CLS_INITIALIZED is never cleared once set.
*
* Only one thread is allowed to actually initialize a class and send
* +initialize. Enforced by allowing only one thread to set CLS_INITIALIZING.
*
* Additionally, threads trying to send messages to a class must wait for
* +initialize to finish. During initialization of a class, that class's
* method cache is kept empty. objc_msgSend will revert to
* class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache, which checks CLS_INITIALIZED before
* messaging. If CLS_INITIALIZED is clear but CLS_INITIALIZING is set,
* the thread must block, unless it is the thread that started
* initializing the class in the first place.
*
* Each thread keeps a list of classes it's initializing.
* The global classInitLock is used to synchronize changes to CLS_INITIALIZED
* and CLS_INITIALIZING: the transition to CLS_INITIALIZING must be
* an atomic test-and-set with respect to itself and the transition
* to CLS_INITIALIZED.
* The global classInitWaitCond is used to block threads waiting for an
* initialization to complete. The classInitLock synchronizes
* condition checking and the condition variable.
**********************************************************************/
2.1)简单验证下:
去掉全部load方法的实现,重新运行工程,断点调试查看堆栈信息,见下图:
objc_alloc(cls=MyPerson)--> 消息发送
_objc_msgSend_uncached -->
lookUpImpOrFoeward .
2.1.1)initialize方法和 load方法类似
readClass()中读取 data():
// 执行到 readClass() 方法中读取数据
// 我加的调试代码
const char *myPersonName = "MyPerson";
if (strcmp(mangledName, myPersonName) == 0) {
auto my_ro = (const class_ro_t *)cls->data();
printf("%s 函数 func: %s\n",__func__,mangledName);
}
// lldb 调试数据如下:
(lldb) p my_ro
(const class_ro_t *) $0 = 0x0000000100003238
(lldb) p *$0
(const class_ro_t) $1 = {
flags = 388
instanceStart = 8
instanceSize = 24
reserved = 0
ivarLayout = 0x0000000100001d91 "\x01"
name = 0x0000000100001d88 "MyPerson"
baseMethodList = 0x0000000100003048
baseProtocols = 0x0000000000000000
ivars = 0x0000000100003280
weakIvarLayout = 0x0000000000000000
baseProperties = 0x00000001000032c8
_swiftMetadataInitializer_NEVER_USE = {}
}
(lldb) p $1.baseMethodList
(method_list_t *const) $2 = 0x0000000100003048
(lldb) p *$2
(method_list_t) $3 = {
entsize_list_tt = {
entsizeAndFlags = 24
count = 11
first = {
name = "helloObj1"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001a10 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson(cateOne) helloObj1])
}
}
}
(lldb) p $3.get(1)
(method_t) $4 = {
name = "helloCateOneInstance"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001a40 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson(cateOne) helloCateOneInstance])
}
(lldb) p $3.get(2)
(method_t) $5 = {
name = "helloObj1"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x00000001000018a0 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson(cateTwo) helloObj1] at MyPerson+cateTwo.m:28)
}
(lldb) p $3.get(3)
(method_t) $6 = {
name = "helloCateTwoInstance"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x00000001000018d0 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson(cateTwo) helloCateTwoInstance] at MyPerson+cateTwo.m:32)
}
(lldb) p $3.get(4)
(method_t) $7 = {
name = "funcInstanceTest"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001ae0 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson funcInstanceTest])
}
(lldb) p $3.get(5)
(method_t) $8 = {
name = "helloObj1"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001b10 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson helloObj1])
}
(lldb) p $3.get(6)
(method_t) $9 = {
name = ".cxx_destruct"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001b40 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson .cxx_destruct])
}
(lldb) p $3.get(7)
(method_t) $10 = {
name = "testpName"
types = 0x0000000100001da9 "@16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001b70 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson testpName])
}
(lldb) p $3.get(8)
(method_t) $11 = {
name = "setTestpName:"
types = 0x0000000100001db1 "v24@0:8@16"
imp = 0x0000000100001ba0 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson setTestpName:])
}
(lldb) p $3.get(9)
(method_t) $12 = {
name = "age"
types = 0x0000000100001dbc "q16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001bd0 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson age])
}
(lldb) p $3.get(10)
(method_t) $13 = {
name = "setAge:"
types = 0x0000000100001dc4 "v24@0:8q16"
imp = 0x0000000100001bf0 (KCObjc`-[MyPerson setAge:])
}
*/
2.1.2)继续执行到 realizeClassWithoutSwift()方法
通过 lldb 读数据发现methodLists中有6个方法了,是包含initialize的类方法们 --> "元类":
// 我加的调试代码
const char *mangledName = ro->name;
const char *myPersonName = "MyPerson";
if (strcmp(mangledName, myPersonName) == 0) {
printf("%s 函数 func: %s\n",__func__,mangledName);
}
// lldb 读数据如下:
(lldb) p ro
(const class_ro_t *) $14 = 0x00000001000031f0
(lldb) p *$14
(const class_ro_t) $15 = {
flags = 389
instanceStart = 40
instanceSize = 40
reserved = 0
ivarLayout = 0x0000000000000000
name = 0x0000000100001d88 "MyPerson"
baseMethodList = 0x0000000100003158
baseProtocols = 0x0000000000000000
ivars = 0x0000000000000000
weakIvarLayout = 0x0000000000000000
baseProperties = 0x0000000000000000
_swiftMetadataInitializer_NEVER_USE = {}
}
(lldb) p $15.baseMethodList
(method_list_t *const) $16 = 0x0000000100003158
(lldb) p *$16
(method_list_t) $17 = {
entsize_list_tt = {
entsizeAndFlags = 24
count = 6
first = {
name = "initialize"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001980 (KCObjc`+[MyPerson(cateOne) initialize])
}
}
}
(lldb) p $15.get(1)
error: no member named 'get' in 'class_ro_t'
(lldb) p $17.get(1)
(method_t) $18 = {
name = "helloCateOneClass"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x00000001000019e0 (KCObjc`+[MyPerson(cateOne) helloCateOneClass])
}
(lldb) p $17.get(2)
(method_t) $19 = {
name = "initialize"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001810 (KCObjc`+[MyPerson(cateTwo) initialize] at MyPerson+cateTwo.m:19)
}
(lldb) p $17.get(3)
(method_t) $20 = {
name = "helloCateTwoClass"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001870 (KCObjc`+[MyPerson(cateTwo) helloCateTwoClass] at MyPerson+cateTwo.m:35)
}
(lldb) p $17.get(4)
(method_t) $21 = {
name = "initialize"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001a70 (KCObjc`+[MyPerson initialize])
}
(lldb) p $17.get(5)
(method_t) $22 = {
name = "funcClassTest"
types = 0x0000000100001d93 "v16@0:8"
imp = 0x0000000100001ab0 (KCObjc`+[MyPerson funcClassTest])
}
(lldb)
2.2)initialize流程:
_read_images()->readClass()数据取自data
-->realizeClassWithoutSwift() -- (auto isMeta = ro->flags & RO_META)为true,此时menthodLists有6个类方法
-->_objc_msgSend_uncached-->objc_alloc(cls=MyPerson)-->lookUpImpOrForward没有初始化 去初始化
-->initializeAndLeaveLocked()-->initializeAndMaybeRelock() -->initializeNonMetaClass()有必要的话(未初始化)去初始化非元类(cls->isInitializing = true) --> initializingFinish
--> 跳转到 realizeClassWithoutSwift(),此时isMeta为 false,menthodLists数量为11. --> methodizeClass() (此流程和load方法相同 - method 的整理)
--> 继续执行realizeClassMaybeSwiftMaybeRelock--> initializeNonMetaClass()-->callInitialize()
--> 打印输出func: +[MyPerson(cateOne) initialize]
callInitialize() 代码如下:
void callInitialize(Class cls)
{
// 我加的调试代码
const char *mangledName = cls->mangledName();
const char *myPersonName = "MyPerson";
if (strcmp(mangledName, myPersonName) == 0) {
printf("%s 函数 func: %s\n",__func__,mangledName);
}
// objc_msgSend 发送消息
// cls: MyPerson
// SEL: initialize
((void(*)(Class, SEL))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(initialize));
asm("");
}
总结:
initialize
-
initialize方法是通过msg_send触发执行的; -
initialize调用顺序:后编译的分类>先编译的分类>主类; -
initialize相较于load,对于同一个主类(不论是否包含分类或子类)只会调用一次,优先调用规则遵循第2条;
- Tip --> 注意一点:子类的
initialize是不会调用的(MySubPerson中的initialize并不会被调用)。
load:
-
load直接函数指针调用; -
load只要实现不论是谁都会走一遍load流程;-->方法list都要搞一遍,耗时、影响启动; -
load调用优先级:本类>子类>先编译的分类>后编译的分类。