java 反射详解
定义
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
用途
在日常的第三方应用开发过程中,经常会遇到某个类的某个成员变量、方法或是属性是私有的或是只对系统应用开放,这时候就可以利用Java的反射机制通过反射来获取所需的私有成员或是方法。当然,也不是所有的都适合反射,之前就遇到一个案例,通过反射得到的结果与预期不符。阅读源码发现,经过层层调用后在最终返回结果的地方对应用的权限进行了校验,对于没有权限的应用返回值是没有意义的缺省值,否则返回实际值起到保护用户的隐私目的。
一、java反射
1、反射:动态获取类的信息,以及动态调用对象的方法的功能。可以理解为动态看透类的能力。
2、主要功能:
①在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类;
②在运行时构造任意一个类的对象;
③在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法;
④在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法;
⑤生成动态代理。
通过java反射机制,可以在程序中访问已经装载到JVM中的java对象的描述,实现访问、检测和修改描述java对象本身信息的功能。java反射机制的功能十分强大,java.lang.reflect包中提供了对该功能的支持。
二、通过反射获取类的三种方法
//1、第一种方式-->Class.forName("类名字符串");
//注:类名字符串是"包名+类名" 返回Class的对象。(这种是最常用的方法)
Class c1=Class.forName("csdn.Student");
//2、第二种方式-->先创建对象,再用对象调用getClass()方法,即实例对象.getClass().返回运行时类。
//任何一个java对象都有getClass()方法
Student s=new Student();
Class c2 = s.getClass();
//3、第三种方式-->类名.class。返回Class的对象。(每个类都有class属性)
Class c3=Student.class;三、通过反射可以获取到的主要描述信息
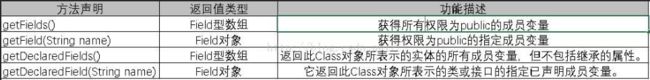
1、获得属性
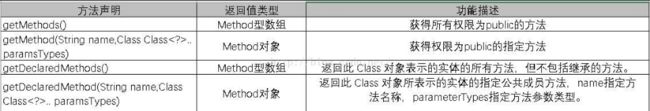
2、获得方法:
3、获得构造方法:
4、获得其他信息:
四、具体演示反射
父类:Person类
package com.liuxd.reflection;
/**
* Created by Liuxd on 2018/8/14.
*/
public class Person {
public String name;// 姓名
public int age;// 年龄
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String showInfo() {
return "name=" + name + ", age=" + age;
}
}子类:Student类
package com.liuxd.reflection;
/**
* Created by Liuxd on 2018/8/14.
*/
public class Student extends Person implements Study {
public String className;// 班级
private String address;// 住址
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age, String className, String address) {
super(name, age);
this.className = className;
this.address = address;
}
public Student(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public String toString() {
return "姓名:" + name + ",年龄:" + age + ",班级:" + className + ",住址:"
+ address;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
接口:study
package com.liuxd.reflection;
/**
* Created by Liuxd on 2018/8/14.
*/
public interface Study {
//仅为了演示获得接口,就没有写抽象方法
}1、获得属性:
package com.liuxd.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* Created by Liuxd on 2018/8/14.
*/
public class TestAttributes {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class stu = null;
try {
stu = Class.forName("com.liuxd.reflection.Student");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 获取对象的所有公有属性。
Field[] fields = stu.getFields();
for (Field f : fields) {
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println("---------------------");
// 获取对象所有属性,但不包含继承的。
Field[] declaredFields = stu.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field ff : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(ff);
}
}
}运行结果:
public java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Student.className
public java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Person.name
public int com.liuxd.reflection.Person.age
---------------------
public java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Student.className
private java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Student.address
2、获得方法:
package com.liuxd.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Created by Liuxd on 2018/8/14.
*/
public class TestMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class stu = null;
try {
stu = Class.forName("com.liuxd.reflection.Student");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 获取对象的所有公共方法
Method[] methods = stu.getMethods();
for (Method m : methods) {
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println("---------------------");
// 获取对象所有方法,但不包含继承的
Method[] declaredMethods = stu.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method ms : declaredMethods) {
System.out.println(ms);
}
}
}运行结果:
public java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Student.toString()
public java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Student.getAddress()
public void com.liuxd.reflection.Student.setAddress(java.lang.String)
public java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Person.showInfo()
public final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long,int) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long) throws java.lang.InterruptedException
public boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)
public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()
public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()
public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()
public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()
---------------------
public java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Student.toString()
public java.lang.String com.liuxd.reflection.Student.getAddress()
public void com.liuxd.reflection.Student.setAddress(java.lang.String)
3、获得构造方法:
为了演示区别,将Student类中参数为className的构造方法的public修饰符改为protected,查看效果。
package com.liuxd.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
/**
* Created by Liuxd on 2018/8/14.
*/
public class TestConstructor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class stu = null;
try {
stu = Class.forName("com.liuxd.reflection.Student");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 获取对象所有的公共构造方法
Constructor[] constructors = stu.getConstructors();
for (Constructor c : constructors) {
System.out.println(c);
}
System.out.println("---------------------");
// 获取对象所有的构造方法
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = stu.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor con : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(con);
}
}
}运行结果为:
public com.liuxd.reflection.Student(java.lang.String)
public com.liuxd.reflection.Student(java.lang.String,int,java.lang.String,java.lang.String)
public com.liuxd.reflection.Student()
---------------------
public com.liuxd.reflection.Student(java.lang.String)
public com.liuxd.reflection.Student(java.lang.String,int,java.lang.String,java.lang.String)
public com.liuxd.reflection.Student()
4、获得其他:
package com.liuxd.reflection;
/**
* Created by Liuxd on 2018/8/14.
*/
public class TestOther {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class stu = null;
try {
stu = Class.forName("com.liuxd.reflection.Student");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(stu.getName());//获取对象全限定名称
System.out.println(stu.getPackage());// 获取包名
Class[] interfaces = stu.getInterfaces();//获取该类实现的所有接口
for (Class in : interfaces) {
System.out.println(in);
}
}
}运行结果为:
com.liuxd.reflection.Student
package com.liuxd.reflection
interface com.liuxd.reflection.Study
5、通过反射实例化对象,调用对象方法
package com.liuxd.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Created by Liuxd on 2018/8/14.
*/
public class TestReflect {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//获取class对象
Class c = Class.forName("com.liuxd.reflection.Student");
Student stu1 = (Student) c.newInstance();
// 第一种方法,实例化默认构造方法,调用set赋值
stu1.setAddress("深圳南山");
System.out.println(stu1);
// 第二种方法 取得全部的构造函数 使用构造函数赋值
Constructor constructor = c.getConstructor(String.class,
int.class, String.class, String.class);
Student stu2 = (Student) constructor.newInstance("李四", 18, "七班", "深圳");
System.out.println(stu2);
/**
* 獲取方法并执行方法
*/
Method show = c.getMethod("showInfo");//获取showInfo()方法
Object object = show.invoke(stu2);//调用showInfo()方法
System.out.println(object);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 运行结果为:
姓名:null,年龄:0,班级:null,住址:深圳南山
姓名:李四,年龄:18,班级:七班,住址:深圳
name=李四, age=18