SpringSecurity和Shiro学习笔记
SpringSecurity和Shiro学习笔记
适用与SpringSecurity和Shiro的初学者,入门学习。
文章目录
- SpringSecurity和Shiro学习笔记
- 一、安全简介
- 二、SpringSecurity
-
- 1、SpringSecurity简介
- 2、认识SpringSecurity
- 3、实战测试
-
- 3.1、实验环境搭建
- 3.2、认证和授权
- 3.3、权限控制和注销
-
- 1、注销
- 2、权限控制
- 3.4、"记住我"功能
- 3.5、定制自己的登录页
-
- 1、问题
- 2、实现
- 4、所有代码归总
- 三、Shiro
-
- 1.简介
-
- 1.1、什么是Shiro
-
- 1.2、shiro能干嘛
- 1.3、shiro架构(外部)
- 1.4、shiro结构(内部)
- 2、HelloWord
-
- 2.1、快速开始
- 3、整合 SpringBoot
-
- 3.1、准备基本环境
- 3.2、增加验证请求
- 3.3、增加登陆功能
-
- 1、使用内存数据模拟用户
- 2、使用数据库中数据进行的验证
- 3.4、请求、用户增加访问权限
-
- 1、给请求增加访问权限
- 2、给用户添加能够访问的权限
- 3.5、thymeleaf和shiro的整合
- 四、代码汇总链接。
一、安全简介
- 在 Web 开发中,安全一直是非常重要的一个方面。安全虽然属于应用的非功能性需求,但是应该在应用开发的初期就考虑进来。如果在应用开发的后期才考虑安全的问题,就可能陷入一个两难的境地:一方面,应用存在严重的安全漏洞,无法满足用户的要求,并可能造成用户的隐私数据被攻击者窃取;另一方面,应用的基本架构已经确定,要修复安全漏洞,可能需要对系统的架构做出比较重大的调整,因而需要更多的开发时间,影响应用的发布进程。因此,从应用开发的第一天就应该把安全相关的因素考虑进来,并在整个应用的开发过程中。
- 市面上存在比较有名的安全框架:Shiro,Spring Security !
二、SpringSecurity
1、SpringSecurity简介
- 每一个框架的出现都是为了解决某一问题而产生了,那么Spring Security框架的出现是为了解决什么问题呢?
- Spring Security是一个功能强大且高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架。它实际上是保护基于Spring的应用程序的标准。
- Spring Security是一个框架,侧重于为Java应用程序提供身份验证和授权。与所有Spring项目一样,Spring安全性的真正强大之处在于它可以轻松地扩展以满足定制需求。
- 想我们之前做项目是没有使用框架是怎么控制权限的?对于权限 一般会细分为功能权限,访问权限,和菜单权限。代码会写的非常的繁琐,冗余。
- 怎么解决之前写权限代码繁琐,冗余的问题,一些主流框架就应运而生而Spring Scecurity就是其中的一种。
- Spring 是一个非常流行和成功的 Java 应用开发框架。Spring Security 基于 Spring 框架,提供了一套 Web 应用安全性的完整解决方案。一般来说,Web 应用的安全性包括用户认证(Authentication)和用户授权(Authorization)两个部分。
- 用户认证指的是验证某个用户是否为系统中的合法主体,也就是说用户能否访问该系统。用户认证一般要求用户提供用户名和密码。系统通过校验用户名和密码来完成认证过程。
- 用户授权指的是验证某个用户是否有权限执行某个操作。在一个系统中,不同用户所具有的权限是不同的。比如对一个文件来说,有的用户只能进行读取,而有的用户可以进行修改。一般来说,系统会为不同的用户分配不同的角色,而每个角色则对应一系列的权限。
- 对于上面提到的两种应用情景,Spring Security 框架都有很好的支持。在用户认证方面,Spring Security 框架支持主流的认证方式,包括 HTTP 基本认证、HTTP 表单验证、HTTP 摘要认证、OpenID 和 LDAP 等。在用户授权方面,Spring Security 提供了基于角色的访问控制和访问控制列表(Access Control List,ACL),可以对应用中的领域对象进行细粒度的控制。
2、认识SpringSecurity
- Spring Security 是针对Spring项目的安全框架,也是Spring Boot底层安全模块默认的技术选型,他可以实现强大的Web安全控制,对于安全控制,我们仅需要引入 spring-boot-starter-security 模块,进行少量的配置,即可实现强大的安全管理!
- 记住几个类:
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter:继承这个类,自定义Security策略
- AuthenticationManagerBuilder:自定义认证策略
- @EnableWebSecurity:给配置类标记注解,即开启WebSecurity模式
- Spring Security的两个主要目标是 “认证” 和 “授权”(访问控制)。
-
“认证”(Authentication):身份验证是关于验证您的凭据,如用户名/用户ID和密码,以验证您的身份。身份验证通常通过用户名和密码完成,有时与身份验证因素结合使用。
-
“授权” (Authorization):授权发生在系统成功验证您的身份后,最终会授予您访问资源(如信息,文件,数据库,资金,位置,几乎任何内容)的完全权限。这个概念是通用的,而不是只在Spring Security 中存在。
-
3、实战测试
3.1、实验环境搭建
-
新建一个初始的springboot项目web模块,thymeleaf模块
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId> dependency> -
编写静态资源
- 1、index.html
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>indextitle> head> <body> <div> <a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登陆a> div> <div> <div>vip1div> <a th:href="@{/vip1/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip1/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip1/3}">3.htmla> div> <br/> <div> <div>vip2div> <a th:href="@{/vip2/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip2/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip2/3}">3.htmla> div> <br/> <div> <div>vip3div> <a th:href="@{/vip3/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip3/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip3/3}">3.htmla> div> body> html> - 2、login.html页面
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>logintitle> head> <body> <h1>自己的登录页面h1> <form th:action="@{/login}"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br/> 密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br/> <input type="checkbox" name="remeberme">记住我<br/> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> form> body> html> - 3、 各个vip文件下的页面(只写一个,其他都类似,只要显示不同内容区分不同页面即可)
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>vip1/1title> head> <body> <h1>vip1/1h1> body> html> - 4、目录结构

- 1、index.html
-
controller跳转各个页面!
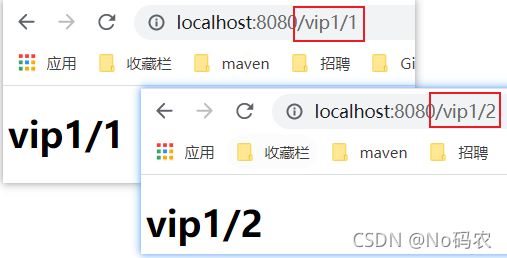
/** * 去往各个页面 */ @Controller public class ToPageController { @GetMapping({ "/","index"}) public String index(){ return "index"; } @GetMapping("toLogin") public String toLogin(){ return "login"; } /* 通过id参数,去往不同的vip1下的不同页面 */ @GetMapping("/vip1/{id}") public String goVip1(@PathVariable("id") String id){ return "/vip1/"+id; } @GetMapping("/vip2/{id}") public String goVip2(@PathVariable("id") String id){ return "/vip2/"+id; } @GetMapping("/vip3/{id}") public String goVip3(@PathVariable("id") String id){ return "/vip3/"+id; } }
3.2、认证和授权
- 上面的测试环境,是谁都可以访问的,没有登陆也可以访问各个模块。我们使用 Spring Security 增加上认证和授权的功能。
- 引入 Spring Security 模块 。版本已经自动仲裁了。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId> dependency> - 编写 Spring Security 配置类
- 官网的配置类。

package com.example.securingweb; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager; @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .formLogin() .loginPage("/login") .permitAll() .and() .logout() .permitAll(); } @Bean @Override public UserDetailsService userDetailsService() { UserDetails user = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder() .username("user") .password("password") .roles("USER") .build(); return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user); } } - 自定义配置类
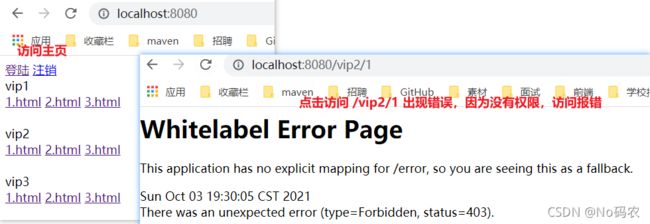
/** * 安全配置类 * WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 适配器类 */ @EnableWebSecurity // 开启WebSecurity模式 public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // 定制请求的授权规则 // 首页所有人可以访问,其他页面,不登录不能访问 http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/","index").permitAll()//排出 / index 请求所有人可以访问 // .antMatchers("/**").hasAnyRole() //hasAnyRole 所有人都可访问 // .anyRequest().authenticated() //所有其他路径都必须经过身份验证。 .antMatchers("/vip1/**").hasRole("vip1") //将vip1下的请求 标记为vip1d的授权规则 只有用户有vip1这个权限才可以访问下面的请求 .antMatchers("/vip2/**").hasRole("vip2") .antMatchers("/vip3/**").hasRole("vip3"); } } - 测试一下:发现除了首页都进不去了!因为我们目前没有登录的角色,因为请求需要登录的角色拥有对应的权限才可以!
- 官网的配置类。
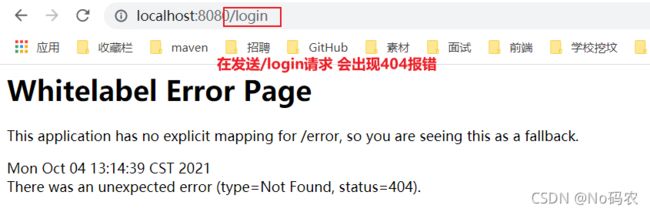
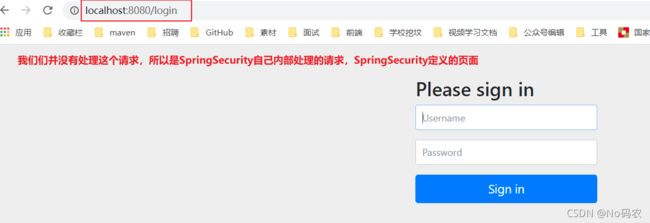
- 在configure()方法中加入以下配置,开启自动配置的登录功能!没有权限访问就会自动发送/login请求,跳转到他自定义的登陆界面。
// 开启自动配置的登录功能 // 会发送login 请求,跳转到它自定义的登录页 // /login?error 重定向到这里表示登录失败 http.formLogin(); - 测试一下:没有权限的时候,都会跳转到登录的页面!
- 查看 http.formLogin();源代码的注释信息;

- 可以定义认证规则,在配置类中重写configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)方法。(定义认证规则:jdbc简单实现案例)
/** * 定义认证规则:即哪些用户能访问哪些请求 * @param auth * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { //在内存中定义用户,但实际是去jdbc中去拿 auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("pj").password("123456").roles("vip1","vip2")//添加一个用户,设置密码,添加能够访问授权规则为vip1,vip2的请求 .and() .withUser("root").password("123456").roles("vip1","vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("guest").password("123456").roles("vip1"); } - 测试,可以使用这些账号登录进行测试!发现会报错!
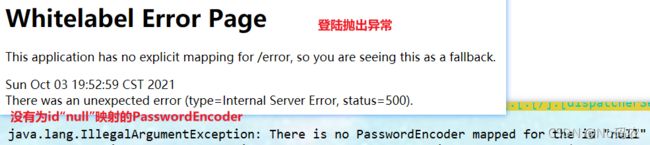
- 原因,我们要将前端传过来的密码进行某种方式加密,否则就无法登录(因为我们没做密码的加密 ,SpringSecurity,会认为通过明文密码登陆,不安全,所以报错),所以需要给密码进行加密。
/** * 定义认证规则:即哪些用户能访问哪些请求 * @param auth * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { //在内存中定义用户,但实际是去jdbc中去拿.... /* Spring security 5.0中新增了多种加密方式,也改变了密码的格式。 要想我们的项目还能够正常登陆,需要修改一下configure中的代码。我们要将前端传过来的密码进行某种方式加密 spring security 官方推荐的是使用bcrypt加密方式。 */ BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(bCryptPasswordEncoder) .withUser("pj").password(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2")//添加一个用户,设置密码,添加能够访问授权规则为vip1,vip2的请求 .and() .withUser("root").password(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("guest").password(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123456")).roles("vip1"); } - 测试,发现可以登录成功,并且每个角色只能访问自己认证下的授权规则!
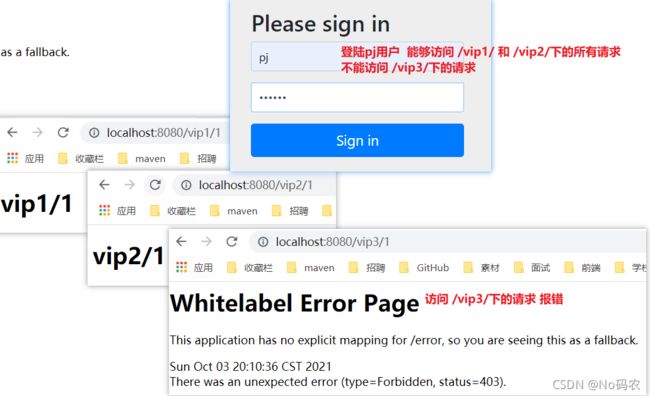
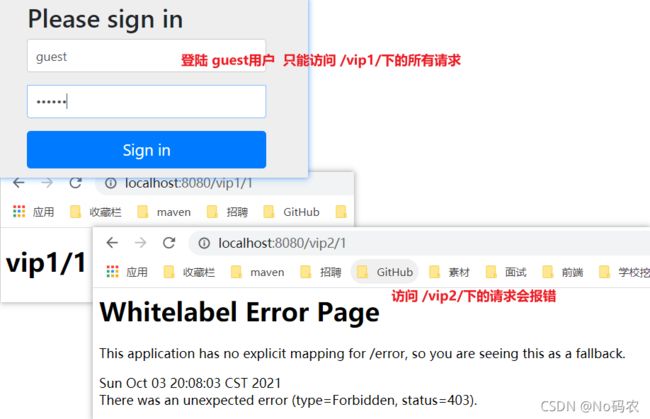
3.3、权限控制和注销
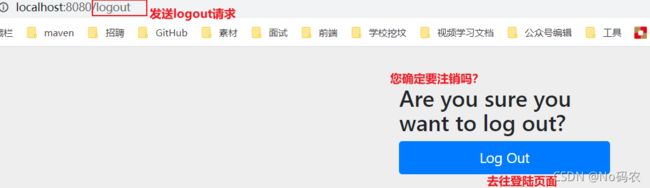
1、注销
-
开启自动配置的注销的功能
//定义请求的授权规则:那些请求需要身份验证 @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //.... //开启自动配置的注销的功能 // 注销时,会发送/logout 注销的请求 http.logout(); } -
注销的按钮,index.html中,点击时,发送 /logout请求。
<a th:href="@{/logout}">注销a> -
想让他注销成功后,依旧可以跳转到首页,该怎么处理呢。在配置类找中添加如下代码。
//定义请求的授权规则:那些请求需要身份验证 @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { //.... // 注销时,会发送/logout 注销的请求 .logoutSuccessUrl("/"); 注销成功来到发送 / 请求 去往首页 http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/"); }
2、权限控制
-
需求:我们需要结合thymeleaf中的一些功能。
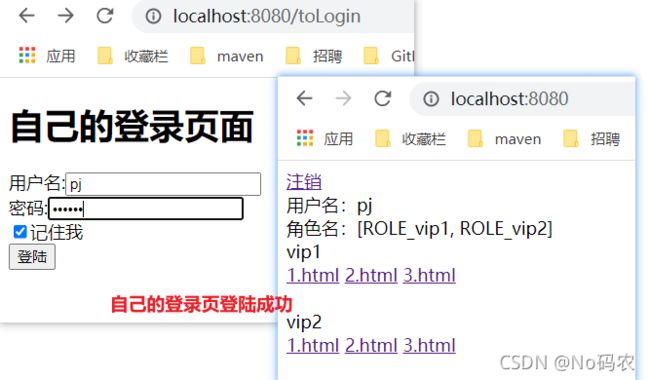
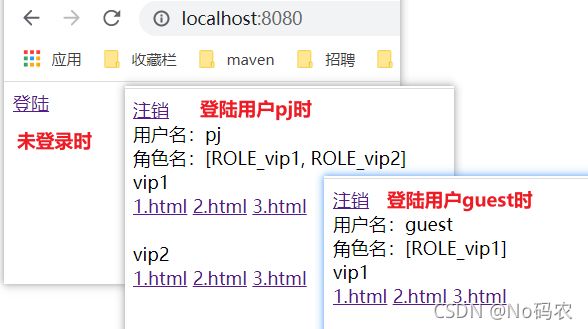
- 1、用户没有登录的时候,导航栏上只显示登录按钮,用户登录之后,导航栏可以显示登录的用户信息及注销按钮。
- 2、pj这个用户,它只有 vip2,vip3功能,那么登录则只显示这两个功能,而vip1的功能菜单不显示!这个就是真实的网站情况了!
-
需求功能1实现:使用sec:authorize="isAuthenticated():是否认证登录!来显示不同的页面。
- maven需要引入thymeleaf整合springsecurity的依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf.extrasgroupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5artifactId> dependency> - 修改index.html页面。(记得引入命令空间: xmlns:sec=“http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3”)
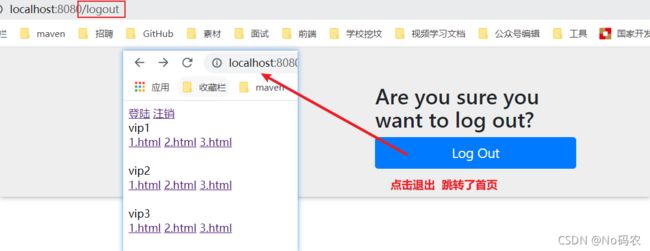
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>indextitle> head> <body> <div> <div sec:authorize="!isAuthenticated()"> <a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登陆a> div> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a th:href="@{/logout}">注销a> 用户名:<span sec:authentication="principal.username">span> 角色名:<span sec:authentication="principal.authorities">span> div> div> <div> <div>vip1div> <a th:href="@{/vip1/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip1/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip1/3}">3.htmla> div> <br/> <div> <div>vip2div> <a th:href="@{/vip2/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip2/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip2/3}">3.htmla> div> <br/> <div> <div>vip3div> <a th:href="@{/vip3/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip3/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip3/3}">3.htmla> div> body> html> - 测试,不登录时页面和登录成功后的页面。
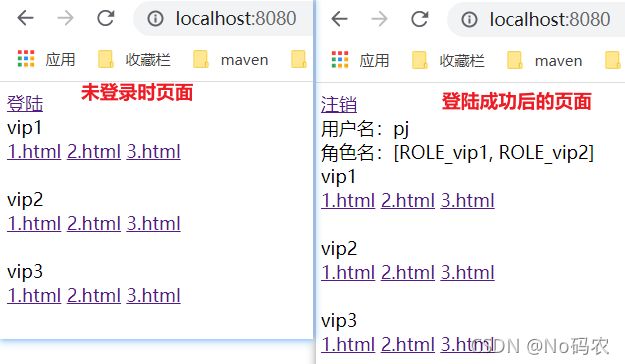
- 如果点击注销,出现了404了,就是因为它默认防止csrf跨站请求伪造,因为会产生安全问题,我们可以将请求改为post表单提交,或者在spring security中关闭csrf功能;在配置中增加 http.csrf().disable();关闭了scrf功能。
http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能:跨站请求伪造,默认只能通过post方式提交logout请求
- maven需要引入thymeleaf整合springsecurity的依赖。
-
需求功能2实现。展示各个用户的可见模块。
- 修改index.html页面。修改各个模块能被不同权限的人给访问。
<div sec:authorize="hasRole('vip1')"> <div>vip1div> <a th:href="@{/vip1/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip1/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip1/3}">3.htmla> div> <br/> <div sec:authorize="hasRole('vip2')"> <div>vip2div> <a th:href="@{/vip2/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip2/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip2/3}">3.htmla> div> <br/> <div sec:authorize="hasRole('vip3')"> <div>vip3div> <a th:href="@{/vip3/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip3/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip3/3}">3.htmla> div> - 测试一下。
- 修改index.html页面。修改各个模块能被不同权限的人给访问。
3.4、"记住我"功能
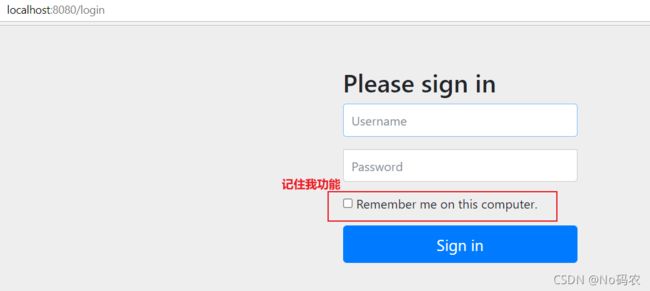
- 现在的情况,我们只要登录之后,关闭浏览器,再登录,就会让我们重新登录,但是很多网站的情况,就是有一个记住密码的功能。
- 实现
- 在配置类中开启记住我功能 。
//定制请求的授权规则 @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { ...... //记住我的功能 http.rememberMe(); } - 我们再次启动项目测试一下,发现登录页多了一个记住我功能,我们登录之后关闭浏览器,然后重新打开浏览器访问,发现用户依然在登陆状态。
- 我们点击注销的时候,可以发现,spring security 帮我们自动删除了这个 cookie。
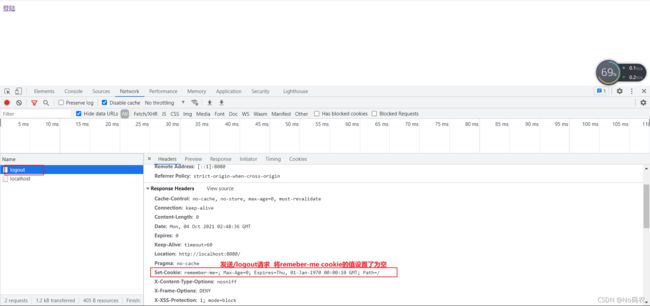
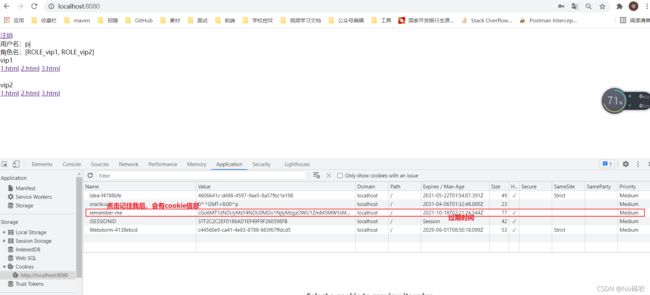
- 实现原理:点击记住我功能后,登录成功后,会将cookie发送给浏览器保存,以后登录带上这个cookie,只要通过检查就可以免登录了。如果点击注销,则会删除这个cookie。
- 在配置类中开启记住我功能 。
3.5、定制自己的登录页
1、问题
- 现在这个登录页面都是spring security 默认的,怎么样可以使用我们自己写的Login界面呢。
2、实现
-
在配置类中,刚才的登录页配置后面指定 loginpage。
/** * 定义请求的授权规则:那些请求需要身份验证 * @param http * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { ..... // 开启自动配置的登录功能 // 会发送login 请求,跳转到它自定义的登录页 // /login?error 重定向到这里表示登录失败 //loginPage("/toLogin"); 自定义登录页的url,默认为/login //所以在发送/login请求去往登录页会报404错 http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin"); .... } -
前端index.html页面也需要指向我们自己定义的 toLogin请求
<div sec:authorize="!isAuthenticated()"> <a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登陆a> div> -
login.html 必须配置提交请求方式,方式必须为post提交。

修改login.html页面。改成post提交<h1>自己的登录页面h1> <form th:action="@{/toLogin}" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br/> 密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br/> <input type="checkbox" name="remember-me">记住我<br/> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> form> -
这个请求提交上来,还需要验证处理,怎么做呢?我们可以查看formLogin()方法的源码!如果是默认的参数名:username、passwor、remember-me,可以不用配置,如果参数名不是,就需要配置接收登陆的用户名和密码等参数。

-
如果参数不一样,需要配置,在配置类中添加代码。
/** * 定义请求的授权规则:那些请求需要身份验证 * @param http * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { .... // 开启自动配置的登录功能 // 会发送login 请求,跳转到它自定义的登录页 // /login?error 重定向到这里表示登录失败 //loginPage("/toLogin"); 指定自定义登录页的url,默认为/login http.formLogin() .usernameParameter("user") //指定用户名的参数名称 .passwordParameter("paw") //指定密码的参数名称 .loginPage("/toLogin") .loginProcessingUrl("/login"); // 更改登陆表单提交登陆时的请求 更改后 表单的提交的登陆请求必须指定为这个 ........ http.rememberMe()//开启记住我的功能 .rememberMeParameter("remember"); //指定"记住我"的参数名称 }<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="user"><br/> 密码:<input type="password" name="paw"><br/> <input type="checkbox" name="remember">记住我<br/> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> form>
4、所有代码归总
-
WebSecurityConfig配置类代码。
/** * 安全配置类 * WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 适配器类 */ @EnableWebSecurity // 开启WebSecurity模式 public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { /** * 定义请求的授权规则:那些请求需要身份验证 * @param http * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { // 首页所有人可以访问,其他页面,不登录不能访问 http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/","index").permitAll()//排出 / index 请求所有人可以访问 // .antMatchers("/**").hasAnyRole() //hasAnyRole 所有人都可访问 //.anyRequest().authenticated(); //除了上面排出的,其他所有其他路径都必须经过身份验证。 .antMatchers("/vip1/**").hasRole("vip1") //将vip1下的请求 标记为vip1的授权规则 只有用户有vip1这个权限才可以访问下面的请求 .antMatchers("/vip2/**").hasRole("vip2") .antMatchers("/vip3/**").hasRole("vip3"); // 开启自动配置的登录功能 // 会发送login 请求,跳转到它自定义的登录页 // /login?error 重定向到这里表示登录失败 //loginPage("/toLogin"); 自定义登录页的url,默认为/login http.formLogin() .usernameParameter("user") //指定用户名的参数名称 .passwordParameter("paw") //指定密码的参数名称 .loginPage("/toLogin") .loginProcessingUrl("/login"); // 更改登陆表单提交登陆时的请求 更改后 登陆的请求必须指定这个 http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能:跨站请求伪造,默认只能通过post方式提交logout请求 //开启自动配置的注销的功能 // 注销时,会发送/logout 注销的请求 .logoutSuccessUrl("/"); 注销成功来到首页 http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/"); http.rememberMe()//开启记住我的功能 .rememberMeParameter("remember"); //指定"记住我"的参数名称 } /** * 定义认证规则:即哪些用户能访问哪些请求 * @param auth * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { /* //在内存中定义用户,但实际是去jdbc中去拿.... auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("pj").password("123456").roles("vip1","vip2")//添加一个用户,设置密码,添加能够访问授权规则为vip1,vip2的请求 .and() .withUser("root").password("123456").roles("vip1","vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("guest").password("123456").roles("vip1");*/ //在内存中定义用户,但实际是去jdbc中去拿.... /* Spring security 5.0中新增了多种加密方式,也改变了密码的格式。 要想我们的项目还能够正常登陆,需要修改一下configure中的代码。我们要将前端传过来的密码进行某种方式加密 spring security 官方推荐的是使用bcrypt加密方式。 */ BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(bCryptPasswordEncoder) .withUser("pj").password(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2")//添加一个用户,设置密码,添加能够访问授权规则为vip1,vip2的请求 .and() .withUser("root").password(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3") .and() .withUser("guest").password(bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123456")).roles("vip1"); } } -
ToPageController代码。
/** * 去往各个页面 */ @Controller public class ToPageController { @GetMapping({ "/","index"}) public String index(){ return "index"; } @GetMapping("/toLogin") public String toLogin(){ return "login"; } @GetMapping("/vip1/{id}") public String goVip1(@PathVariable("id") String id){ return "/vip1/"+id; } @GetMapping("/vip2/{id}") public String goVip2(@PathVariable("id") String id){ return "/vip2/"+id; } @GetMapping("/vip3/{id}") public String goVip3(@PathVariable("id") String id){ return "/vip3/"+id; } } -
login.html页面。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>logintitle> head> <body> <h1>自己的登录页面h1> <form th:action="@{/login}" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="user"><br/> 密码:<input type="password" name="paw"><br/> <input type="checkbox" name="remember">记住我<br/> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> form> body> html> -
index.html页面。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>indextitle> head> <body> <div> <div sec:authorize="!isAuthenticated()"> <a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登陆a> div> <div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()"> <a th:href="@{/logout}">注销a> <br/> 用户名:<span sec:authentication="principal.username">span> <br/> 角色名:<span sec:authentication="principal.authorities">span> div> div> <div sec:authorize="hasRole('vip1')"> <div>vip1div> <a th:href="@{/vip1/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip1/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip1/3}">3.htmla> div> <br/> <div sec:authorize="hasRole('vip2')"> <div>vip2div> <a th:href="@{/vip2/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip2/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip2/3}">3.htmla> div> <br/> <div sec:authorize="hasRole('vip3')"> <div>vip3div> <a th:href="@{/vip3/1}">1.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip3/2}">2.htmla> <a th:href="@{/vip3/3}">3.htmla> div> body> html>
三、Shiro
1.简介
1.1、什么是Shiro
- Apache Shiro是- 一个Java的安全(权限)框架。
- Shiro 可以非常容易的开发出足够好的应用,其不仅可以用在JavaSE环境(在小环境也可以用),也可以用在JavaEE环境。
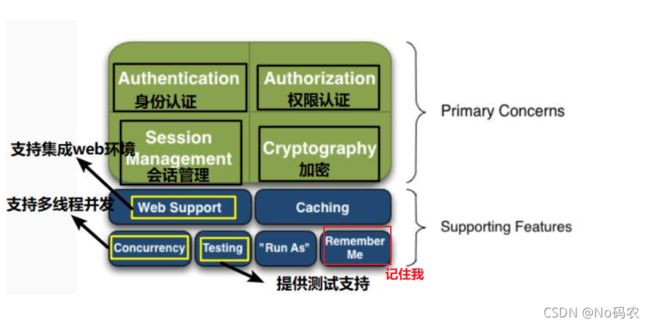
- Shiro可以完成,认证,授权,加密,会话管理,Web集成,缓存等。
- 下载地址: http://shiro.apache.org/
1.2、shiro能干嘛
- Authentication:身份认证、登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份;
- Authorization:授权,即权限验证,验证某个已认证的用户是否拥有某个权限,即判断用户能否进行什么操作,如:验证某个用户是否拥有某个角色,或者细粒度的验证某个用户对某个资源是否具有某个权限!
- Session Manager:会话管理,即用户登录后就是第一次会话, 在没有退出之前,它的所有信息都在会话中;会话可以是普通的avaSE环境,也可以是Web环境;
- Cryptography:加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库中,而不是明文存储;
- Web Support: Web支持,可以非常容易的集成到Web环境;
- Caching:缓存,比如用户登录后,其用户信息,拥有的角色、权限不必每次去查,这样可以提高效率
- Concurrency: Shiro支持多线程应用的并发验证,即,如在一个线程中开启另一个线程,能把权限自动的传播过去.
- Testing:提供测试支持;
- Run As:允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问;
- Remember Me:记住我,这个是非常常见的功能,即一次登录后,下次再来的话不用登录了;
1.3、shiro架构(外部)
- 从外部来看Shiro,即从应用程序角度来观察如何使用shiro完成工作:
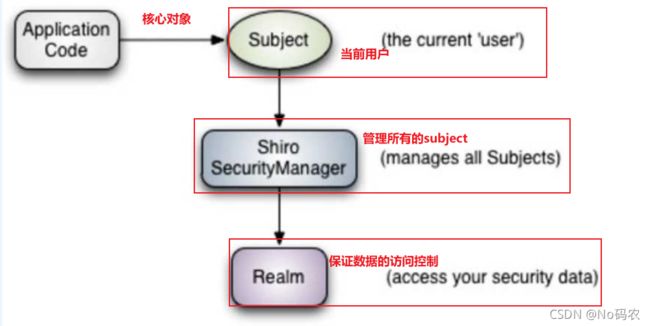
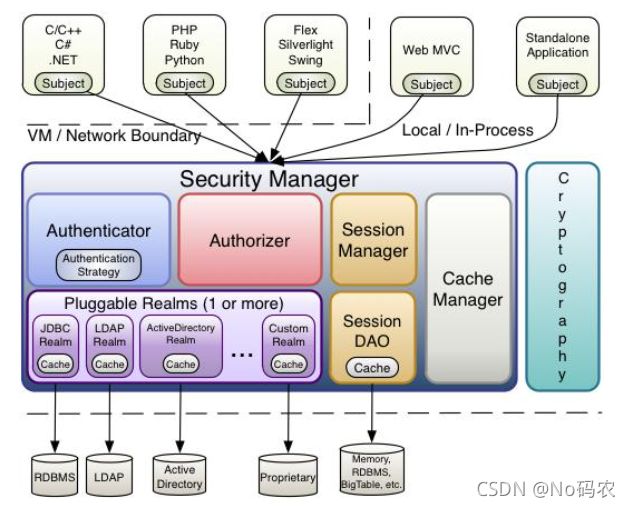
- subject:应用代码直接交互的对象是Subject, 也就是说Shiro的对外API核心就是Subject, Subject代表 了当前的用户,这个用户不一定是一个具体的人,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是Subject,如网络爬虫,机器人等,与Subject的所有交互都会委托给,SecurityManager; Subject其实是一个门面, SecurityManageer 才是实际的执行者。
- SecurityManager:安全管理器,即所有与安全有关的操作都会与SercurityManager交互,并且它管理着所有的Subject,可以看出它是Shiro的核心,它负责与Shiro的其他组件进行交互,它相当于SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet的角色。
- Realm: Shiro从Realm获取安全数据(如用户,角色,权限), 就是说SecurityManager 要验证用户身份,那么它需要从Realm获取相应的用户进行比较,来确定用户的身份是否合法;也需要从Realm得到用户相应的角色、权限,进行验证用户的操作是否能够进行,可以把Realm看成DataSource。
1.4、shiro结构(内部)
- Subject:任何可以与应用交互的用户;
- Security Manager:相当于SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet; 是Shiro的心脏,所有具体的交互都通过;
- Security Manager进行控制,它管理者所有的Subject,且负责进行认证,授权,会话,及缓存的管理;
- Authenticator:负责Subject认证,是一个扩 展点,可以自定义实现;可以使用认证策略(AuthenticationStrategy),即什么情况下算用户认证通过了;
- Authorizer:授权器,即访问控制器,用来决定主体是否有权限进行相应的操作;即控制着用户能访问应用中的那些功能;
- Realm:可以有一个或者多个的realm,可以认为是安全实体数据源,即用于获取安全实体的,可以用JDBC实现,也可以是内存实现等等,由用户提供;所以一般在应用中都需要实现自己的realm;
- SessionManager:管理Session生命周期的组件,而Shiro并不仅仅可以用在Web环境, 也可以用在普通的JavaSE环境中;
- CacheManager:缓存控制器,来管理如用户,角色,权限等缓存的;因为这些数据基本.上很少改变,放到缓存中后可以提高访问的性能;
- Cryptography:密码模块, Shiro 提高了一些常见的加密组件用于密码加密, 解密等;
2、HelloWord
2.1、快速开始
-
官方quickstart
-
创建一个springboot快速开始工程,删掉不必要的东西。
-
根据官方文档,我们来导入Shiro的依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId> <artifactId>shiro-coreartifactId> <version>1.8.0version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4jgroupId> <artifactId>jcl-over-slf4jartifactId> <version>1.7.21version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4jgroupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12artifactId> <version>1.7.21version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4jgroupId> <artifactId>log4jartifactId> <version>1.2.17version> dependency> -
导入官方quickstart工程的日志配置文件和shiro.ini。
log4j.properties:log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m %n # General Apache libraries log4j.logger.org.apache=WARN # Spring log4j.logger.org.springframework=WARN # Default Shiro logging log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro=INFO # Disable verbose logging log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.util.ThreadContext=WARN log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCache=WARNshiro.ini:
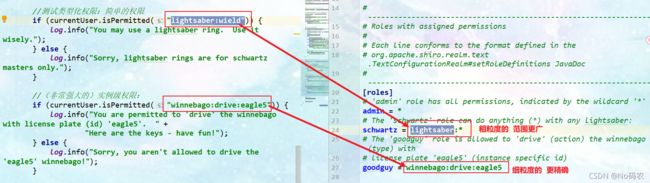
[users] # user 'root' with password 'secret' and the 'admin' role root = secret, admin # user 'guest' with the password 'guest' and the 'guest' role guest = guest, guest # user 'presidentskroob' with password '12345' ("That's the same combination on # my luggage!!!" ;)), and role 'president' presidentskroob = 12345, president # user 'darkhelmet' with password 'ludicrousspeed' and roles 'darklord' and 'schwartz' darkhelmet = ludicrousspeed, darklord, schwartz # user 'lonestarr' with password 'vespa' and roles 'goodguy' and 'schwartz' lonestarr = vespa, goodguy, schwartz # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Roles with assigned permissions # # Each line conforms to the format defined in the # org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setRoleDefinitions JavaDoc # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- [roles] # 'admin' role has all permissions, indicated by the wildcard '*' admin = * # The 'schwartz' role can do anything (*) with any lightsaber: schwartz = lightsaber:* # The 'goodguy' role is allowed to 'drive' (action) the winnebago (type) with # license plate 'eagle5' (instance specific id) goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5 -
导入官方quickstart工程的 Quickstart.java。
package com.pj.securityandshiro.quickstart; import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils; import org.apache.shiro.authc.*; import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory; import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager; import org.apache.shiro.session.Session; import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject; import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; /** * 演示如何使用Shiro API的简单快速入门应用程序。 */ public class Quickstart { //定义日志类用于输出 private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Quickstart.class); public static void main(String[] args) { //创建具有配置的Shiro SecurityManager的最简单方法 //领域(realm)、用户(users)、角色(roles)和权限(permissions)将使用简单的INI配置,我们将通过使用一个可以接收.ini文件,使用类路径根目录下的shiro.ini文件(文件和url:前缀分别从文件和url加载),返回SecurityManager实例: Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini"); SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance(); //设置可作为JVM单例对象访问。 SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 获取当前正在执行的用户(三大对象之一),与以上代码无关,可直接获取 Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 得到shiro中的session,使用会话做一些事情(不需要web或EJB容器!!!) Session session = currentUser.getSession(); //给session中设置值 session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue"); //获取session的值 String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey"); if (value.equals("aValue")) { log.info("Subject==>session中的==>aValue ! [" + value + "]"); } // 让我们登录当前用户,以便检查角色和权限: if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) { //判断我们当前的用户是否被认证 //Token 令牌 。这里是随机设置的验证,没有经过配置文件 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa"); //设置记住我 token.setRememberMe(true); try { currentUser.login(token);//执行了登陆操作 会根据Realm中的对象比较 } catch (UnknownAccountException uae) { //用户不存在,抛出这个异常 log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal()); } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) { //密码错误,抛出这个异常 log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!"); } catch (LockedAccountException lae) { //用户被锁定了,抛出这个异常 log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " + "Please contact your administrator to unlock it."); } // ... catch 这里有更多的例外情况(可能是特定于您的应用程序的自定义例外情况),AuthenticationException包括了上面的异常 catch (AuthenticationException ae) { //unexpected condition? error? } } //打印其标识主体(在本例中为用户名)获取当前的用户 log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully."); //测试角色 当前角色是否有schwartz这个权限 if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) { log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!"); } else { log.info("Hello, mere mortal."); } //测试类型化权限:简单的权限 if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) { log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely."); } else { log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only."); } //(非常强大的)实例级权限: if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) { log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " + "Here are the keys - have fun!"); } else { log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!"); } //全部完成-注销! currentUser.logout(); //结束 System.exit(0); } } -
总结:主要方法及其作用。
// 获取当前正在执行的用户(三大对象之一),与以上代码无关,可直接获取 Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 得到shiro中的session,使用会话做一些事情(不需要web或EJB容器!!!) Session session = currentUser.getSession(); //判断我们当前的用户是否被认证 currentUser.isAuthenticated(); //执行了登陆操作 会根据Realm中的对象比较 currentUser.login(token); //获取当前的用户 currentUser.getPrincipal(); //测试角色 当前角色是否是有schwartz这个权限标识的 currentUser.hasRole("schwartz"); //当前角色是否有lightsaber:wield这个权限 currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield"); //注销! currentUser.logout();
3、整合 SpringBoot
- 官方整合springboot案例
3.1、准备基本环境
- 导入spring和shiro的整合依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId> <artifactId>shiro-springartifactId> <version>1.4.0version> dependency> - 编写两个配置类。
ShiroConfig:配置拦截规则、安全管理器工厂、安全数据等。
UserRealm:配置认证、受权。/** * shiro配置类 */ @Configuration public class ShiroConfig { //shiroFilterFactoryBean:配置拦截规则 @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("defaultWebSecurityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //设置安全管理器 bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager); return bean; } //DefaultWebSecurityManager 安全管理器工厂 //@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm 会从容器中找到进行注入 @Bean(name = "defaultWebSecurityManager") public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm){ DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); //关联UserRealm defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(userRealm); return defaultWebSecurityManager; } //创建一个realm对象(安全管理器工厂的依赖) @Bean(name = "userRealm") public UserRealm getUserRealm(){ return new UserRealm(); } }/** * Shiro从Realm获取安全数据(如用户,角色,权限), * 就是说SecurityManager 要验证用户身份, * 那么它需要从Realm获取相应的用户进行比较, * 来确定用户的身份是否合法; * 也需要从Realm得到用户相应的角色、权限,进行验证用户的操作是否能够进行, * 可以把Realm看成DataSource。 */ //自定义 UserRealm public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm { //授权:就是访问控制,控制某个用户在应用程序中是否有权限做某件事 //每次需要经过权限判断时,都要经过这个方法 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("执行了===》授权doGetAuthorizationInfo"); return null; } //验证:验证对象是否存在 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行了===》验证doGetAuthorizationInfo"); return null; } } - 编写测试页面。update.html、add.html、index.html页面,用于测试。
index.html:
update.html:DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>首页h1> <hr/> <a th:href="@{/shiro/add/}">adda> | <a th:href="@{/shiro/add/}">updatea> body> html>
add.html:DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>updateh1> body> html>DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>addh1> body> html> - 测试各个页面跳转(还未设置权限验证等功能,都能跳转)。
3.2、增加验证请求
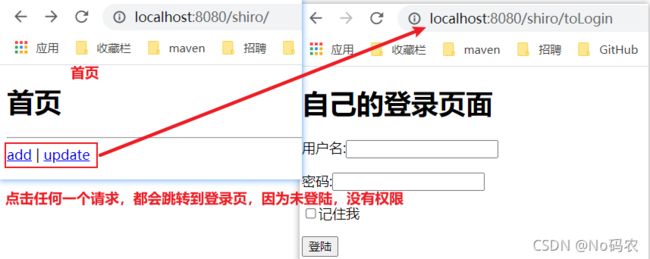
-
需求:上述基本环境,是谁都可以访问的,我们使用 shiro 增加上认证的功能,使其没登录前,无法访问,如果认证失败,跳往登陆界面。
-
编写一个login.html页面。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>logintitle> head> <body> <h1>自己的登录页面h1> <p th:text="${msg}" style="color: red;">p> <div th:if="${param.error}" style="color: red;"> 用户名或密码错误! div> <div th:if="${param.logout}" style="color: darkgreen;"> 注销成功! div> <form th:action="@{/shiro/login}" method="post"> <p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username">p> <p>密码:<input type="password" name="password">p> <p><input type="checkbox" name="remember">记住我p> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> form> body> html> -
编写 ShiroConfig 配置类的 getShiroFilterFactoryBean()方法中添加代码。
//shiroFilterFactoryBean:配置拦截规则 @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("defaultWebSecurityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //设置安全管理器 bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager); //以下为:新增代码 /* 添加shiro的内置过滤器 设置拦截的规则如下: anon:无需认证就可以访问 authc:必须认证才能访问 user:必须拥有记住我的功能才能访问 perms:拥有对某个资源的权限才能访问 role:拥有某个角色权限才能访问 */ Map<String ,String > filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); //设置请求;/shrio/add、/shrio/update 必须认证登陆后才能访问 filterMap.put("/shiro/user/add", "authc"); filterMap.put("/shiro/user/update", "authc"); //设置请求:/shrio/user/* 下的所有请求,必须认证登陆后才能访问 //filterMap.put("/shrio/user/*", "authc"); bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap); //认证失败后,去往登录页面,设置登陆页请求 bean.setLoginUrl("/shiro/toLogin"); return bean; }
3.3、增加登陆功能
1、使用内存数据模拟用户
- 在controller中编写登陆请求。
@PostMapping("/login") public String login(String username, String password, Map<String,Object> map){ //获取当前的用户 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //将传递的数据封装成 Token 令牌 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password); try { //登陆请求,shiro自己定义的 subject.login(token); return "/shiro/index"; } catch (UnknownAccountException uae) { //用户不存在,抛出这个异常 map.put("msg", "用户名不存在"); return "/shiro/login"; } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) { //密码错误,抛出这个异常 map.put("msg", "密码错误"); return "/shiro/login"; } } - 在自定义 UserRealm类中的 doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) 验证方法添加代码。
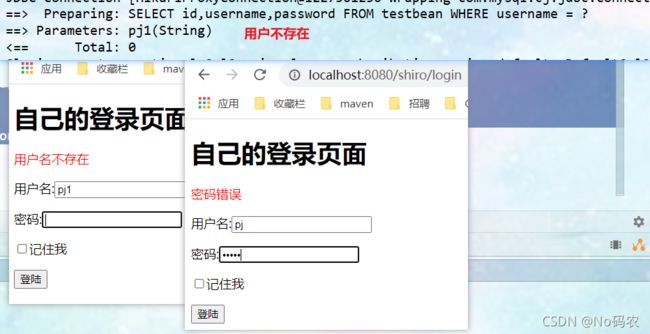
//验证:验证对象是否存在 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行了===》验证doGetAuthorizationInfo"); //模拟可以登陆的数据 String username = "root"; String password = "123"; //强转成 UsernamePasswordToken 对象 该对象可直接获取需要登陆的用户名和密码 UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken)authenticationToken; //如果登陆的用户名不等于 root 返回null 就会抛出UnknownAccountException用户不存在异常 if (!(token.getUsername().equals(username))){ return null; } //AuthenticationInfo 接口 需要创建一个实现类SimpleAccount对象 //密码的验证 shiro做,不需要们验证 /* 使用给定的主体和凭据为指定领域构造SimpleAccount实例。 主体-帐户的"主要"标识属性,例如,用户ID或用户名。 凭据-验证帐户身份的凭据(密码) 领域名称-访问此帐户数据的领域的名称 */ return new SimpleAccount("", password, ""); } - 测试。使用不存在的用户名登陆和存在的用户但密码错误的数据进行测试,会提示对应的错误信息。

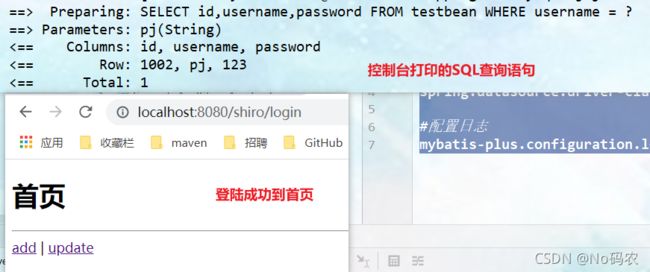
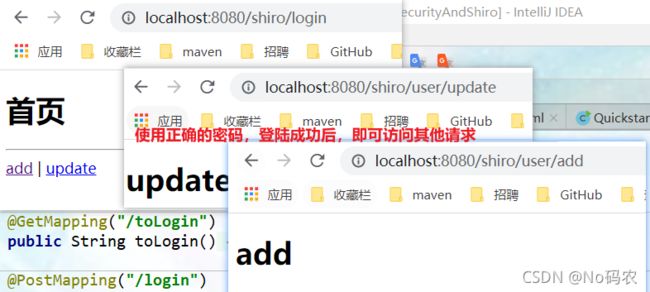
- 使用正确的用户名和密码访问(root 123),登陆成功后,即可访问各种请求。
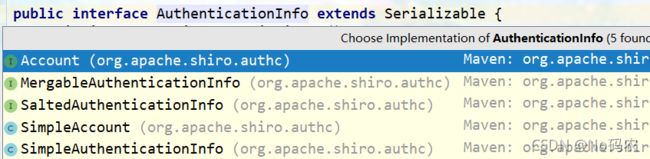
- 扩展:AuthenticationInfo接口的实现类。
2、使用数据库中数据进行的验证
我使用的是mybatis-plus。
-
导入mybati-plus的依赖和数据库驱动依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>com.baomidougroupId> <artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId> <version>3.0.5version> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysqlgroupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId> <artifactId>lombokartifactId> dependency> -
编写application.properties配置文件,配置数据源。
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #打印mybatis日志 mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl -
编写 mapper、service、pojo层。
- mapper层
TestbeanMapper:@Mapper public interface TestbeanMapper extends BaseMapper<Testbean> { } - service层
//接口类 public interface TestbeanService extends IService<Testbean> { } //实现层 @Service public class TestbeanServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<TestbeanMapper, Testbean> implements TestbeanService{ } - pojo层
Testbean:@Data public class Testbean { private Long id; private String username; private String password; }
- mapper层
-
编写自定义 UserRealm类中的 doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) 验证方法修改代码。
//验证:就是访问控制,控制某个用户在应用程序中是否有权限做某件事 //每次需要经过权限判断时,都要经过这个方法 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行了===》验证doGetAuthorizationInfo"); //使用数据库中的数据进行验证 //强转成 UsernamePasswordToken 对象 该对象可直接获取需要登陆的用户名和密码 UsernamePasswordToken token = (UsernamePasswordToken)authenticationToken; QueryWrapper<Testbean> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.eq("username", token.getUsername()); Testbean testbean = testbeanService.getOne(queryWrapper); //如果数据库中没有该用户名就会返回null 就会抛出UnknownAccountException用户不存在异常 if (testbean == null){ return null; } //AuthenticationInfo 接口 需要创建一个实现类 simpleAccount对象 //密码的验证 shiro做,不需要们验证 /* 使用给定的主体和凭据为指定领域构造SimpleAccount实例。 主体-帐户的"主要"标识属性,例如,用户ID或用户名。 凭据-验证帐户身份的凭据(密码) 领域名称-访问此帐户数据的领域的名称 */ return new SimpleAccount("", testbean.getPassword(), ""); }
3.4、请求、用户增加访问权限
1、给请求增加访问权限
- 编写 ShiroConfig配置类下的 getShiroFilterFactoryBean()方法,增加如下代码。
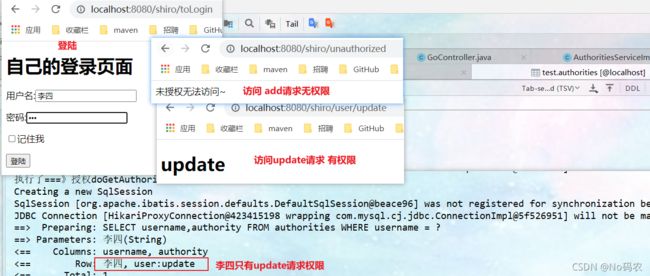
//访问 "/shiro/user/add请求 ,必须拥有 user:add权限才可以访问 filterMap.put("/shiro/user/add", "perms[user:add]"); - 测试访问,前提需要先登陆,在访问/shiro/user/add请求。
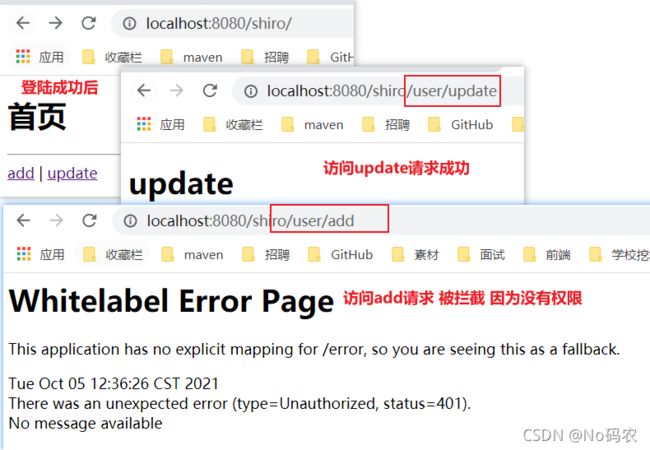
- 添加未授权时跳转的页面,不能给用户展示默认的。需要在ShiroConfig配置类下的 getShiroFilterFactoryBean()方法,增加如下代码。
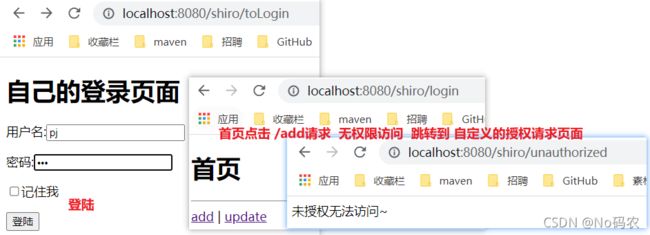
//设置未有权限时跳转的请求 bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/shiro/unauthorized"); - 在controller中处理这个请求。
@GetMapping("/unauthorized") @ResponseBody public String unauthorized(){ return "未授权无法访问~"; } - 测试没有权限的访问add请求。
2、给用户添加能够访问的权限
-
编写 自定义的UserRealm类下 doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) 的授权方法,代码如下。
//授权:就是访问控制,控制某个用户在应用程序中是否有权限做某件事 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("执行了===》授权doGetAuthorizationInfo"); //给用户授权类 SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); //给所有用户授权,不管那个用户,涉及权限认证都会经过,写死了就是每个用户都有user:add权限, // 一般需要从数据库中去查找对应的权限 info.addStringPermission("user:add"); return info; } -
创建对应的pojo、mapper、service层。
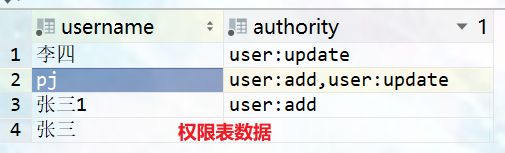
pojo:@Data public class Authorities { private String username; private String authority; }mapper:
@Mapper public interface AuthoritiesMapper extends BaseMapper<Authorities> { }service:
//接口 public interface AuthoritiesService extends IService<Authorities> { } //实现层 @Service public class AuthoritiesServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<AuthoritiesMapper, Authorities> implements AuthoritiesService { } -
增加update请求的需要的权限。修改ShiroConfig配置类下的 getShiroFilterFactoryBean()方法,增加如下代码。
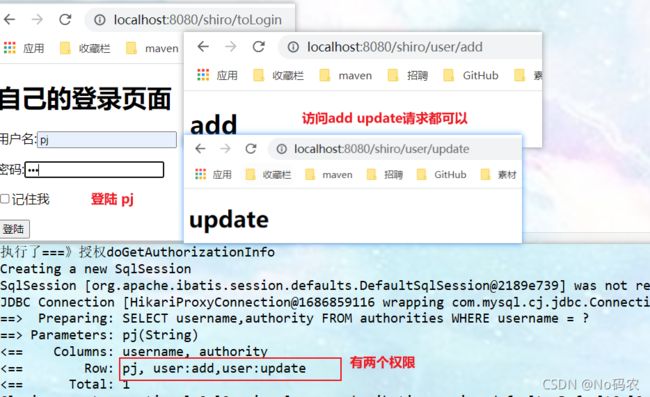
//访问 "/user/update ,必须拥有 user:update权限才可以访问 filterMap.put("/shiro/user/update", "perms[user:update]"); -
在进行授权时,通过用户名查找对应的权限,再给当前对象授于他该有的权限。这就涉及到用户的数据如何进入授权的方法,可在验证的时候将用户数据存储进去(shiro帮我们做的),需要修改 自定义 UserRealm类下的doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken)认证方法。
/* 使用给定的主体和凭据为指定领域构造SimpleAccount实例。 主体-帐户的"主要"标识属性,例如,用户ID或用户名。 凭据-验证帐户身份的凭据(密码) 领域名称-访问此帐户数据的领域的名称 */ //验证密码时,带上用户的数据,shiro会帮我们存储到Subject(当前用户)对象中, //进行授权时,可以获取到这个对象 return new SimpleAccount(testbean, testbean.getPassword(), ""); -
修改自定义 UserRealm类下的 doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) 授权方法,获取当当前用户,从数据库中查找对应权限。
@Autowired private TestbeanService testbeanService; @Autowired private AuthoritiesService authoritiesService; //授权:就是访问控制,控制某个用户在应用程序中是否有权限做某件事 每次需要经过权限判断时,都要经过这个方法 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("执行了===》授权doGetAuthorizationInfo"); //给用户授权类 SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); //获取当前的用户 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //获取用户的信息 Testbean testbean = (Testbean) subject.getPrincipal(); //创建条件查询 QueryWrapper<Authorities> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.eq("username", testbean.getUsername()); //通过用户名查找对应的权限 Authorities authorities = authoritiesService.getOne(queryWrapper); //通过,分割字符串,就得到用户拥有的各个权限 String[] authoritie = authorities.getAuthority().split(","); //判断是否有权限,没有权限就直接跳过 if (authoritie !=null && authoritie.length>0){ //循环遍历所有权限 for (String s : authoritie) { //添加对应权限 info.addStringPermission(s); } } return info; } -
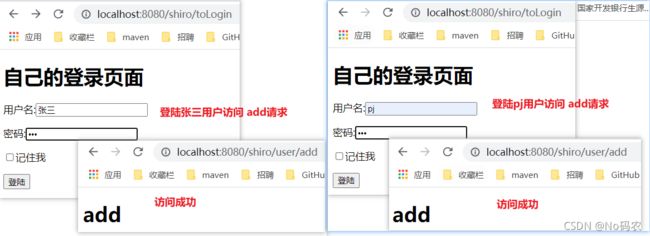
测试不同用户,访问add、update请求。
3.5、thymeleaf和shiro的整合
-
导入thymeleaf和shiro的整合依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.theborakompanionigroupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-shiroartifactId> <version>2.0.0version> dependency> -
在 Shiro的配置类中添加一个方法,创建一个ShiroDialect 对象放容器中。
//thymeleaf和shiro的整合 所需要的类 @Bean public ShiroDialect getShiroDialect(){ return new ShiroDialect(); } -
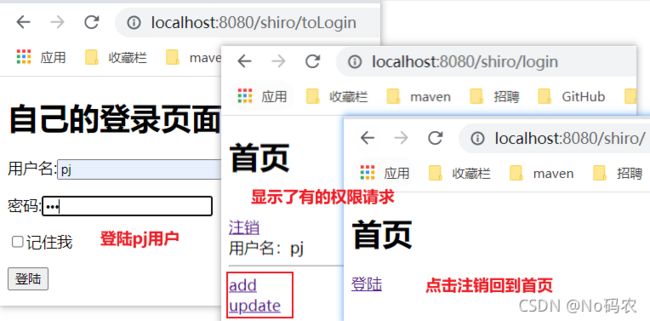
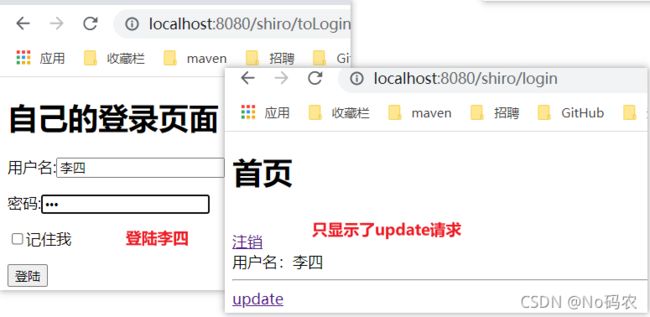
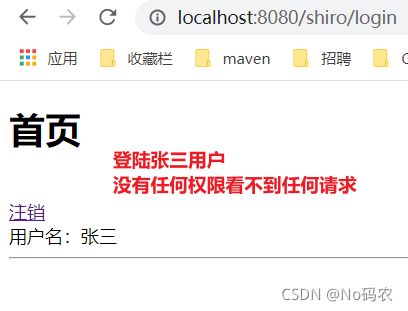
编写前端首页。根据不同的权限显示不同的请求(记得引入命令空间)、显示用户名等。
DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:shiro="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Titletitle> head> <body> <h1>首页h1> <div shiro:guest> <p><a th:href="@{/shiro/toLogin}">登陆a>p> div> <br/> <div shiro:user> <a th:href="@{/shiro/logout}">注销a> <br/> 用户名:<span shiro:principal property="username"/>span> <br/> div> <hr/> <div shiro:hasPermission="user:add"> <a th:href="@{/shiro/user/add}">adda> div> <div shiro:hasPermission="user:update"> <a th:href="@{/shiro/user/update}">updatea> div> body> html> -
处理注销请求,编写controller。
@GetMapping("/logout") public String logout(){ //获取当前用户 Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); //注销 currentUser.logout(); return "redirect:/shiro/"; }
四、代码汇总链接。
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1z7c6zCv4RmLtGk0ciws8jA 提取码: p48a
注意:如有问题可以评论区发言,多谢指教。