Neptune Android11 resources.arsc不支持压缩问题解决
前言
最近维护Neptune框架的时候,发现插件在升级compileSdkVersion、targetSdkVersion到30之后,会出现插件无法安装的问题。这里记录下相关的内容。
问题原因
这里先放下根本原因:Android R+不在允许app压缩resource.asrc。
出问题的代码
这里简单描述下一些前置的背景知识:
- 插件也是一个独立的apk
- Neptune框架的插件是可以访问宿主资源的
- 插件安装到宿主需要校验包名和版本号等信息
以下的代码,就是主动获取插件Apk的一些基本信息,包括包名、版本号等。
PackageManager pm = context.getPackageManager();
PackageInfo pkgInfo = pm.getPackageArchiveInfo(apkFilePath, PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES);
这个代码在compileSdkVersion、targetSdkVersion为30以下的时候,并不会有任何的问题。
Debug结果
这里放下当插件的compileSdkVersion、targetSdkVersion升级到30后出现的崩溃信息:
Targeting R+ (version 30 and above) requires the resources.arsc of installed APKs to be stored uncompressed and aligned on a 4-byte boundary.
相关代码请见:
- frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/pm/parsing/ParsingPackageUtils.java
相关源码:
private ParseResult<ParsingPackage> parseBaseApk(ParseInput input, File apkFile,
String codePath, AssetManager assets, int flags) {
final String apkPath = apkFile.getAbsolutePath();
...忽略了大部分的代码...
final ParsingPackage pkg = result.getResult();
// 抛出异常的地方
if (assets.containsAllocatedTable()) {
final ParseResult<?> deferResult = input.deferError(
"Targeting R+ (version " + Build.VERSION_CODES.R + " and above) requires"
+ " the resources.arsc of installed APKs to be stored uncompressed"
+ " and aligned on a 4-byte boundary",
DeferredError.RESOURCES_ARSC_COMPRESSED);
if (deferResult.isError()) {
return input.error(INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_RESOURCES_ARSC_COMPRESSED,
deferResult.getErrorMessage());
}
}
}
官方文档
详见:Compressed resource files
Apps that target Android 11 (API level 30) or higher can’t be installed if they contain a compressed resources.arsc file or if this file is not aligned on a 4-byte boundary. This file cannot by memory-mapped by the system if either of these conditions is present. Resources tables that cannot be memory-mapped must be read into a buffer in RAM resulting in unnecessary memory pressure on the system and greatly increased device RAM usage.
如果以 Android 11(API 级别 30)或更高版本为目标平台的应用包含压缩的 resources.arsc 文件或者如果此文件未按 4 字节边界对齐,应用将无法安装。如果存在其中任意一种情况,系统将无法对此文件进行内存映射。无法进行内存映射的资源表必须读入 RAM 中的缓冲区,从而给系统造成不必要的内存压力,并大大增加设备的 RAM 使用量。
验证
zipalign 是一种归档对齐工具,可对 Android 应用 (APK) 文件提供重要的优化。
找一个无法安装的插件验证下:
➜ 30.0.2 ./zipalign -c -v 4 ~/Desktop/com.qiyi.xxx.apk
5078317 res/xml/filepaths.xml (OK - compressed)
5078776 res/xml/network_security_config.xml (OK - compressed)
5079095 res/xml/network_security_config_release.xml (OK - compressed)
5079286 resources.arsc (OK - compressed) # 被压缩了
Verification succesful
- 最后一行:
resources.arsc (OK - compressed)。
看起来是官方限制死了。当Android工程的compileSdkVersion、targetSdkVersion升级到30,强制要求resources.arsc不能被压缩。
解决方案
关于资源编译相关的部分,可以先从booster分析-App资源压缩了解下基本原理。
- 官方文档:AAPT2 (Android Asset Packaging Tool) 工具的使用文档
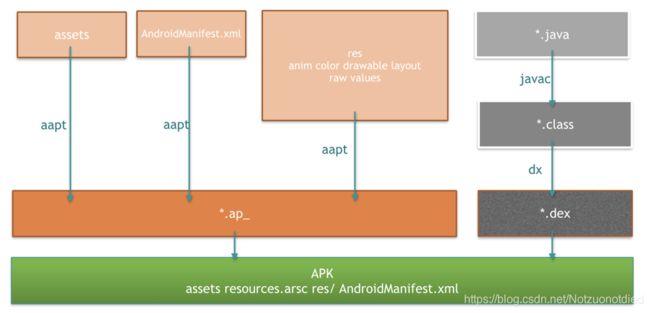
流程分析
图片源于:booster分析-App资源压缩
插件框架的Gradle插件主要是用于上述*.ap_生成后,对资源文件进行修改、删除、添加的操作,以便固定资源id和剔除不必要的资源。
代码分析
核心代码:com.qiyi.plugin.hooker.TaskHookerManager#reWriteArscFile
private void reWriteArscFile(ProcessAndroidResources par, ApkVariant variant) {
// 删除多余的资源
ZipUtil.with(apFile).deleteAll(filteredResources + updatedResources)
// 将有变动的资源重新使用aapt add回去
addUpdatedResources(aaptPath, resourcesDir, apFile, updatedResources)
}
/**
* 重新更新资源 - 通过验证,使用该命令添加的资源默认会被压缩
*
* $ aapt add resources.ap_ file1 file2
*/
def addUpdatedResources(String aaptPath, File resourcesDir,
File apFile, Collection<String> updatedResources) {
project.exec {
executable aaptPath
workingDir resourcesDir
args 'add', apFile.path
args updatedResources
standardOutput = System.out
errorOutput = System.err
}
}
- 从验证的结果来看,
aapt add resources.ap_ file1 file2默认会压缩。
修复方案
从AAPT的文档中,没有发现add的命令支持不压缩的方案,我们只能手动的通过Java的Zip API将resources.arsc以存档的形式补充回去。其他的资源还是老样子添加即可。
- 修复方案:将压缩的方式改为文档存储的形式。
ZipEntry
Class ZipEntry文档
STORED:未压缩条目的压缩方法。DEFLATED:压缩条目的压缩方法。
代码实现
这里就不放代码了,具体实现可以参见:
- Android资源混淆工具(知名库):
- shwenzhang/AndResGuard:com.tencent.mm.util.FileOperation#zipFile
- 或者这个:
- Java 实现文件【夹】压缩
- Zip压缩zipOut.setMethod(ZipOutputStream.STORED);如何处理
- ╮(╯▽╰)╭代码全靠抄……
附录
- Android Gradle plugin release notes
- iBotPeaches/Apktool
- 行为变更:以 Android 11 为目标平台的应用
- shwenzhang/AndResGuard:targetSdkVersion 设置成30,在R系统上无法安装
- Android R+不在允许app压缩resource.asrc。
- [core] Stop to compress resources.asrc when targeting R+(version 30 a…
- resources.arsc压缩会影响性能吗?
- Java appending files into a zip
- Is app-release.apk zipaligned apk?
APK瘦身
- APK瘦身记,如何实现高达53%的压缩效果
- 美团:Android App包瘦身优化实践
- 抖音:抖音包大小优化:资源优化