【预测模型】基于蝙蝠算法改进的BP神经网络预测数据matlab源码
1 简介
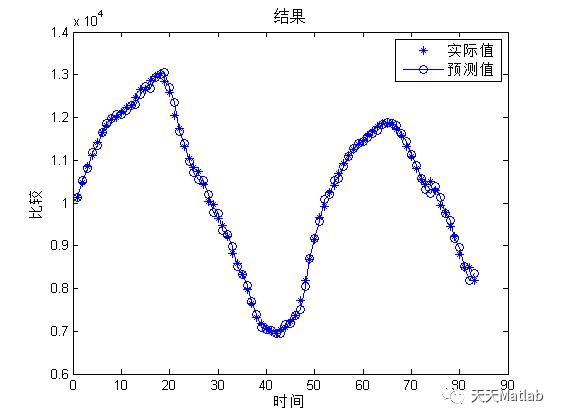
为了提高短期电力负荷预测结果的准确性,该文提出了蝙蝠算法优化BP神经网络的方法.该方法利用蝙蝠算法对BP神经网络参数进行优化,并用优化后的参数建立短期电力负荷预测模型.最后,将搜集到的某地区历史负荷数据输入模型,通过仿真结果分析,表明该方法具有一定的可行性和有效性
1.1 蝙蝠算法
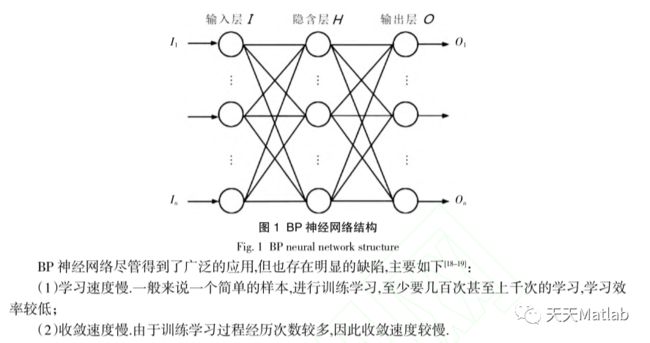
1.2 BP神经网络
2 部分代码
%% Cost or Objective function
function [nbest,fbest,NumEval]=ffa_mincon(u0,Lb,Ub,para,inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn) % para=[20 500 0.5 0.2 1];
% Check input parameters (otherwise set as default values)
if nargin<5, para=[20 50 0.25 0.20 1]; end
if nargin<4, Ub=[]; end
if nargin<3, Lb=[]; end
if nargin<2,
disp('Usuage: FA_mincon(@cost,u0,Lb,Ub,para)');
end
% n=number of fireflies
% MaxGeneration=number of pseudo time steps
% ------------------------------------------------
% alpha=0.25; % Randomness 0--1 (highly random)
% betamn=0.20; % minimum value of beta
% gamma=1; % Absorption coefficient
% ------------------------------------------------
n=para(1);
MaxGeneration=para(2); %MaxGeneration
alpha=para(3);
betamin=para(4);
gamma=para(5);
NumEval=n*MaxGeneration;
% Check if the upper bound & lower bound are the same size
if length(Lb) ~=length(Ub),
disp('Simple bounds/limits are improper!');
return
end
% Calcualte dimension
d=length(u0); %
% Initial values of an array
zn=ones(n,1)*10^100;
% ------------------------------------------------
% generating the initial locations of n fireflies
[ns,Lightn]=init_ffa(n,d,Lb,Ub,u0); %
% Iterations or pseudo time marching
for k=1:MaxGeneration, %%%%% start iterations
% This line of reducing alpha is optional
alpha=alpha_new(alpha,MaxGeneration);
% Evaluate new solutions (for all n fireflies)
for i=1:n,
zn(i)=fun(ns(i,:),inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn);
Lightn(i)=zn(i);
end
% Display the shape of the objective function
% Ranking fireflies by their light intensity/objectives
[Lightn,Index]=sort(zn);
ns_tmp=ns;
for i=1:n,
ns(i,:)=ns_tmp(Index(i),:);
end
%% Find the current best
nso=ns;
Lighto=Lightn;
nbest=ns(1,:);
Lightbest=Lightn(1);
% For output only
fbest=Lightbest;
% Move all fireflies to the better locations
[ns]=ffa_move(n,d,ns,Lightn,nso,Lighto,nbest,Lightbest,alpha,betamin,gamma,Lb,Ub);
end %%%%% end of iterations
% The initial locations of n fireflies
function [ns,Lightn]=init_ffa(n,d,Lb,Ub,u0)
% if there are bounds/limits,
if length(Lb)>0,
for i=1:n,
ns(i,:)=Lb+(Ub-Lb).*rand(1,d);
end
else
% generate solutions around the random guess
for i=1:n,
ns(i,:)=u0+randn(1,d);
end
end
% initial value before function evaluations
Lightn=ones(n,1)*10^100;
% Move all fireflies toward brighter ones
function [ns]=ffa_move(n,d,ns,Lightn,nso,Lighto,nbest,Lightbest,alpha,betamin,gamma,Lb,Ub)
% Scaling of the system
scale=abs(Ub-Lb);
% Updating fireflies
for i=1:n
% The attractiveness parameter beta=exp(-gamma*r)
for j=1:n,
r=sqrt(sum((ns(i,:)-ns(j,:)).^2)); %
% Update moves
if Lightn(i)>Lighto(j), % Brighter and more attractive
beta0=1; beta=(beta0-betamin)*exp(-gamma*r.^2)+betamin;
tmpf=alpha.*(rand(1,d)-0.5).*scale;
ns(i,:)=ns(i,:).*(1-beta)+nso(j,:).*beta+tmpf;
[ns]=findlimits(n,ns,Lb,Ub);
end
end % end for j
end % end for i
% convergence can occur. So use with care.
function alpha=alpha_new(alpha,NGen) %
% alpha_n=alpha_0(1-delta)^NGen=0.005
% alpha_0=0.9
delta=1-(10^(-4)/0.9)^(1/NGen);
alpha=(1-delta)*alpha;
function [ns]=findlimits(n,ns,Lb,Ub)
for i=1:n,
% Apply the lower bound
ns_tmp=ns(i,:);
I=ns_tmpUb;
ns_tmp(J)=Ub(J);
% Update this new move
ns(i,:)=ns_tmp;
end
3 仿真结果
4 参考文献
[1]姚珊. (2019). 基于蝙蝠算法的神经网络预测模型的研究及应用. (Doctoral dissertation, 辽宁科技大学).