欢迎访问我的GitHub
这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos
关于《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》系列
《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》是欣宸在Java领域的系列原创,旨在通过项目实战与大家一起学习和掌握Spring Cloud Gateway,更好的为实际项目服务
本篇概览
作为《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》的开篇,本文的主要内容如下:
- 基础知识简介
- 确认环境涉及到的工具和服务的版本
- 启动nacos,作为后续实战的注册中心和配置中心
- 创建maven父工程,为后续实战的代码和依赖库版本做好管理
- 创建名为common的子工程,存放共用的常量和数据结构
- 创建名为provider-hello的web应用,用于gateway路由的目标
- 运行一个简单的demo,完成spring-cloud-gateway的初体验
关于Spring Cloud Gateway
- 这是一个基于Spring技术栈构建的API网关,涉及到:Spring5、Spring Boot 2、Reactor等,目标是为项目提供简单高效的API路由,以及强大的扩展能力:安全、监控、弹性计算等
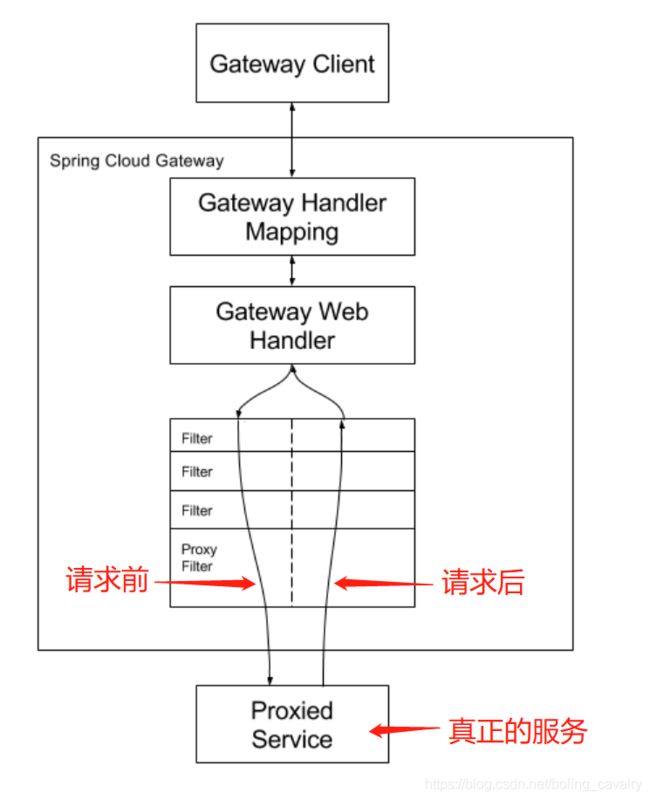
- 官方架构图如下,可见请求到来后,由Handler Mapping决定请求对应的真实目标,然后交给Web Handler,由一系列过滤器(filter)执行链式处理,从红色箭头和注释可以发现,请求前后都有过滤器在运行:
版本信息
- 《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》系列涉及的软件和库版本信息如下:
- 本篇实战涉及到的主要版本情况如下:
- JDK:1.8.0_291
- IDEA:2021.1.3 (Ultimate Edition)
- maven:3.8.1
- 操作系统:win10 64位
- springboot:2.4.2
- spring-cloud:2020.0.1
- spring-cloud-alibaba:2021.1
- 更详细的版本匹配关系请参考:https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba/wiki/版本说明
经典配置中的核心概念
- 先通过一个典型的简化版配置来了解几个核心概念,假设Spring Cloud Gateway应用正在运行,监听8080端口,一旦有远程请求来到8080端口,下面的配置就会生效了,三个核心概念,以及每个配置的作用,请参考中文注释:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
# 核心概念1:路由,一个路由代表一个处理逻辑,
# 该逻辑里面包含三个元素:匹配条件(是否该此路由处理)、真实处理地址、过滤器
routes:
# id要确保唯一性
- id: add_request_header_route
# 真实处理地址,请求一旦确定是当前路由处理,就会转发到这个地址去
uri: https://example.org
# 核心概念2:谓语或者断言,作用是判断请求是否由当前路由处理
predicates:
# 这是断言的一种,检查请求的Cookie中mycookie的值是否等于mycookievalue
- Cookie=mycookie,mycookievalue
# 核心概念3:过滤器,请求前和请求后都可以有过滤器处理请求响应数据
filters:
# 这个过滤器的作用是在请求header中添加一个键值对,值等于"aaabbbccc"
- AddRequestHeader=X-Request-Red, aaabbbccc
- 上述配置信息中的predicates是简化版配置,和完整配置对比效果如下,简单的说就是把一行拆成了三项:name、args.name、args.regexp
- 理论知识点到为止,咱们还是尽快动手吧
启动nacos-2.0.3
-
整个《pring Cloud Gateway实战》系列,我们会涉及到多个服务,这就不可避免的会用到注册中心和配置中心,这里我选择了nacos,它可以很好地承担注册中心和配置中心的角色,接下来介绍如何部署和启动nacos
-
下载nacos,地址是:https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases/download/2.0.3/nacos-server-2.0.3.zip
-
解压后进入nacos\bin目录,执行以下命令启动nacos:
startup.cmd -m standalone
- 如果您的电脑是mac或者linux,请执行以下命令启动nacos:
sh startup.sh -m standalone
-
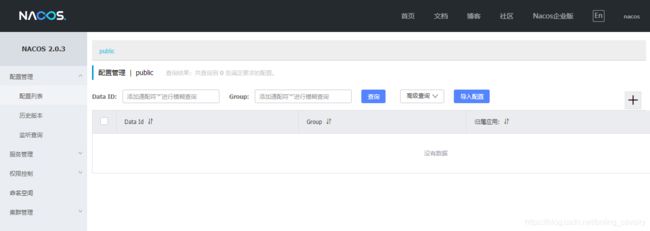
浏览器登录nacos,地址是http://localhost:8848/nacos,账号和密码都是nacos
-
登录成功后显示如下:
源码下载
- 本篇实战中的完整源码可在GitHub下载到,地址和链接信息如下表所示(https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos):
| 名称 | 链接 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 项目主页 | https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos | 该项目在GitHub上的主页 |
| git仓库地址(https) | https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos.git | 该项目源码的仓库地址,https协议 |
| git仓库地址(ssh) | [email protected]:zq2599/blog_demos.git | 该项目源码的仓库地址,ssh协议 |
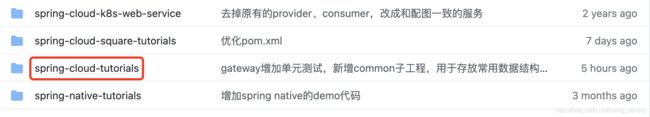
- 这个git项目中有多个文件夹,本篇的源码在spring-cloud-tutorials文件夹下,如下图红框所示:
《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》系列的父工程
- 新建名为spring-cloud-tutorials的maven工程,这就是《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》系列所有源码的父工程就,pom.xml内容如下,可见这里将springboot、spring-cloud、spring-cloud-alibaba库的版本号都已经确定,今后子工程就无需关注依赖库的版本号了:
4.0.0
hello-gateway
provider-hello
common
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.4.2
com.bolingcavalry
spring-cloud-tutorials
1.0-SNAPSHOT
8
8
1.8
2020.0.1
2021.1
pom
Demo project for Spring Cloud
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-dependencies
${spring-cloud.version}
pom
import
com.alibaba.cloud
spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies
${spring-cloud-alibaba.version}
pom
import
com.squareup.okhttp3
okhttp
3.14.9
compile
ch.qos.logback
logback-classic
1.1.7
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.16.16
创建名为common的子工程,存放共用的常量和数据结构
-
现在创建名为common的子工程,整个《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》系列涉及的常量和数据结构都放在这个子工程中,方便其他工程使用
-
新增常量Constants.java:
package com.bolingcavalry.common;
public interface Constants {
String HELLO_PREFIX = "Hello World";
}
创建web应用,作为服务提供方
-
现在创建名为provider-hello的web应用,这是个极其普通的web应用,提供几个http接口服务,咱们在尝试Spring Cloud Gateway的基本功能时,都会将请求路由到provider-hello上来
-
provider-hello是个普通的springboot应用,会在nacos进行注册,其pom.xml内容如下:
spring-cloud-tutorials
com.bolingcavalry
1.0-SNAPSHOT
4.0.0
provider-hello
jar
com.bolingcavalry
common
${project.version}
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
com.alibaba.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config
com.alibaba.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
com.bolingcavalry.provider.ProviderApplication
repackage
- 工程的配置文件application.yml如下,web端口是8082,还有一处要注意的是nacos服务地址:
server:
#服务端口
port: 8082
spring:
application:
name: provider-hello
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
# nacos服务地址
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
- 启动类ProviderApplication.java
package com.bolingcavalry.provider;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProviderApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 普通的Controller类Hello.java,对外提供一个http服务:
package com.bolingcavalry.provider.controller;
import com.bolingcavalry.common.Constants;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class Hello {
private String dateStr(){
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss").format(new Date());
}
/**
* 返回字符串类型
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/str")
public String helloStr() {
return Constants.HELLO_PREFIX + ", " + dateStr();
}
}
- 新增测试类HelloTest.java,用于检查应用的服务是否正常:
package com.bolingcavalry.provider.controller;
import com.bolingcavalry.common.Constants;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.containsString;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.print;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@Slf4j
class HelloTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
@Test
void hello() throws Exception {
String responseString = mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/hello/str").accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string(containsString(Constants.HELLO_PREFIX)))
.andDo(print())
.andReturn()
.getResponse()
.getContentAsString();
log.info("response in junit test :\n" + responseString);
}
}
- 执行单元测试(此时nacos是否启动无所谓,只是不启动的话控制台会有一些错误信息,但是没有影响),如下,测试通过表示服务是正常的:
开发一个简单的demo,完成spring-cloud-gateway的初体验
-
前面做了那么多准备,接下来咱们会投入到Spring Cloud Gateway的开发中,先写个简单的demo快速体验一下
-
新增名为hello-gateway的子工程,pom.xml如下,重点是依赖了spring-cloud-starter-gateway库,还有一处要重点小心的:测试库用的是reactor-test和spring-boot-starter-test,这和之前的单元测试很不一样,用的是webflux:
spring-cloud-tutorials
com.bolingcavalry
1.0-SNAPSHOT
4.0.0
hello-gateway
com.bolingcavalry
common
${project.version}
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-gateway
io.projectreactor
reactor-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
- 下面是重点,Spring Cloud Gateway的配置文件application.yml:
server:
#服务端口
port: 8081
spring:
application:
name: hello-gateway
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: path_route
# 匹配成功后,会被转发到8082端口,至于端口后面的path,会直接使用原始请求的
# 例如http://127.0.0.1:8081/hello/str,会被转发到http://127.0.0.1:8082/hello/str
uri: http://127.0.0.1:8082
predicates:
# 根据请求路径中带有"/hello/",就算匹配成功
- Path=/hello/**
- 如果要转发到其他域名下,需要创建配置类解决跨域问题:
package com.bolingcavalry.hellogateway.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.reactive.CorsWebFilter;
import org.springframework.web.cors.reactive.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource;
import org.springframework.web.util.pattern.PathPatternParser;
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig {
@Bean
public CorsWebFilter corsFilter() {
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
config.addAllowedMethod("*");
config.addAllowedOrigin("*");
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource(new PathPatternParser());
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
return new CorsWebFilter(source);
}
}
- 启动类:
package com.bolingcavalry.hellogateway;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloGatewayApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloGatewayApplication.class,args);
}
}
- 最后是单元测试类,请注意,由于Spring Cloud Gateway使用了webflux技术栈,因此不能用常见的MockMvc来模拟请求,几个注解也值得注意,另外也要注意WebTestClient的expectStatus、expectBody等API的用法:
package com.bolingcavalry.hellogateway;
import com.bolingcavalry.common.Constants;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.reactive.AutoConfigureWebTestClient;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import org.springframework.test.web.reactive.server.WebTestClient;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
@SpringBootTest
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@AutoConfigureWebTestClient
public class HelloTest {
@Autowired
private WebTestClient webClient;
@Test
void testHelloPredicates() {
webClient.get()
.uri("/hello/str")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.exchange()
// 验证状态
.expectStatus().isOk()
// 验证结果,注意结果是字符串格式
.expectBody(String.class).consumeWith(result -> assertTrue(result.getResponseBody().contains(Constants.HELLO_PREFIX)));
}
}
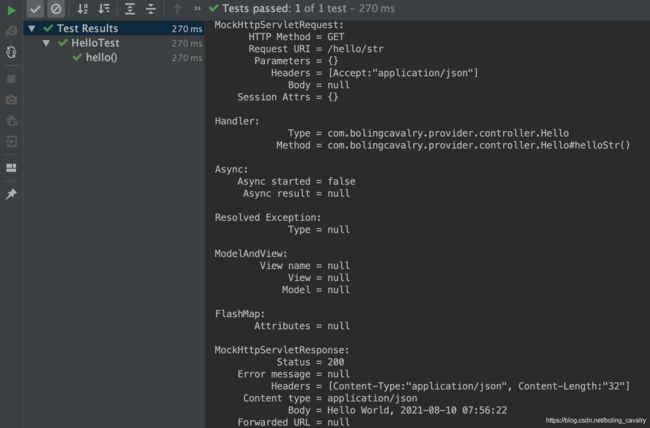
- 请确保provider-hello应用已经启动,再运行上面创建的HelloTest.java,得到结果如下,测试通过,证明hello-gateway的功能符合预期,成功的将请求转发到provider-hello应用,并且成功收到响应:
- 至此,《Spring Cloud Gateway实战》系列的准备工作已经完成,而且开发了一个简单的应用体验最基本的Spring Cloud Gateway功能,接下来的文章,咱们一起实战更多基本功能。
你不孤单,欣宸原创一路相伴
- Java系列
- Spring系列
- Docker系列
- kubernetes系列
- 数据库+中间件系列
- DevOps系列
欢迎关注公众号:程序员欣宸
微信搜索「程序员欣宸」,我是欣宸,期待与您一同畅游Java世界...
https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos