文章目录
-
-
- 1.常用损失函数
- 2.自定义损失函数
-
- 3.实战1:Focal Loss实现自定义损失函数(以minist数据集构建图像分类算法)
1.常用损失函数
tf.keras.losses
列举常用的,如下:

BinaryCrossentropy和binary_crossentropy有什么区别?
前者是类的实现形式,后者是函数的实现形式
这两者并没有本质的区别
使用损失函数时,首先要确定到底是分类还是回归问题?一定要对应
每个损失函数是如何实现的一定要清楚
交叉熵损失函数-多分类

import tensorflow as tf
cce = tf.keras.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy()
loss = cce(
[[1.,0.,0.],[0.,1.,0.],[0.,0.,1.]],
[[.9,.05,.05],[.05,.89,.06],[.05,.01,.94]])
print('Loss:',loss.numpy())
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1.,0.,0.],[0.,1.,0.],[0.,0.,1.]])
b = np.array([[.9,.05,.05],[.05,.89,.06],[.05,.01,.94]])
np.average(-np.sum(a * np.log(b),axis=1))
2.自定义损失函数
mse

Focal loss损失函数

多分类的Focal loss函数:
gamma 用来减小易分类样本的权重,使得模型训练时更加专注于难分类的样本
α 用来计算每个类别的概率-权重-二分类变成多分类时,α会失效
class SparseFocalLoss(tf.keras.losses.Loss):
def __init__(self,gamma=2.0,alpha=0.25,class_num=10):
self.gamma = gamma
self.alpha = alpha
self.class_num = class_num
super(SparseFocalLoss,self).__init__()
def call(self,y_true,y_pred):
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(y_pred,axis=-1)
epsilon = tf.keras.backend.epsilon()
y_pred = tf.clip_by_value(y_pred,epsilon,1.0)
y_true = tf.one_hot(y_true,depth=self.class_num)
y_true = tf.cast(y_true,tf.float32)
loss = -y_true * tf.math.pow(1 - y_pred,self.gamma) * tf.math.log(y_pred)
loss = tf.math.reduce_sum(loss,axis=1)
return loss
def focal_loss(gamma=2.0,alpha=0.25):
def focal_loss_fixed(y_true,y_pred):
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(y_pred,axis=-1)
epsilon = tf.keras.backend.epsilon()
y_pred = tf.clip_by_value(y_pred,epsilon,1.0)
y_true = tf.cast(y_true,tf.float32)
loss = -y_true * tf.math.pow(1-y_pred,gamma) * tf.math.log(y_pred)
loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss,axis=1)
return loss
return focal_loss_fixed
3.实战1:Focal Loss实现自定义损失函数(以minist数据集构建图像分类算法)

子类模型
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras import Model
import numpy as np
print(tf.__version__)
print(np.__version__)
mnist = np.load("mnist.npz")
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test =
mnist['x_train'],mnist['y_train'],mnist['x_test'],mnist['y_test']
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(
nrows=2,
ncols=5,
sharex=True,
sharey=True, )
ax = ax.flatten()
for i in range(10):
img = x_train[y_train == i][0].reshape(28, 28)
ax[i].imshow(img, cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
ax[0].set_xticks([])
ax[0].set_yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
x_train = x_train[..., tf.newaxis]
x_test = x_test[..., tf.newaxis]
y_train = tf.one_hot(y_train,depth=10)
y_test = tf.one_hot(y_test,depth=10)
train_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train)).shuffle(10000).batch(32)
test_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)).batch(32)
class MyModel(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(MyModel,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = Conv2D(32,3,activation='relu')
self.flatten = Flatten()
self.d1 = Dense(128,activation='relu')
self.d2 = Dense(10,activation='softmax')
def call(self,x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.d1(x)
return self.d2(x)
class FocalLoss(tf.keras.losses.Loss):
def __init__(self,gamma=2.0,alpha=0.25):
self.gamma = gamma
self.alpha = alpha
super(FocalLoss, self).__init__()
def call(self,y_true,y_pred):
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(y_pred,axis=-1)
epsilon = tf.keras.backend.epsilon()
y_pred = tf.clip_by_value(y_pred, epsilon, 1.0)
y_true = tf.cast(y_true,tf.float32)
loss = - y_true * tf.math.pow(1 - y_pred, self.gamma) * tf.math.log(y_pred)
loss = tf.math.reduce_sum(loss,axis=1)
return loss
def FocalLoss(gamma=2.0,alpha=0.25):
def focal_loss_fixed(y_true, y_pred):
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(y_pred,axis=-1)
epsilon = tf.keras.backend.epsilon()
y_pred = tf.clip_by_value(y_pred, epsilon, 1.0)
y_true = tf.cast(y_true,tf.float32)
loss = - y_true * tf.math.pow(1 - y_pred, gamma) * tf.math.log(y_pred)
loss = tf.math.reduce_sum(loss,axis=1)
return loss
return focal_loss_fixed
model = MyModel()
loss_object = FocalLoss(gamma=2.0,alpha=0.25)
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
train_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='train_loss')
train_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.CategoricalAccuracy(name='train_accuracy')
test_loss = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='test_loss')
test_accuracy = tf.keras.metrics.CategoricalAccuracy(name='test_accuracy')
@tf.function
def train_step(images, labels):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
predictions = model(images)
loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))
train_loss(loss)
train_accuracy(labels, predictions)
@tf.function
def test_step(images, labels):
predictions = model(images)
t_loss = loss_object(labels, predictions)
test_loss(t_loss)
test_accuracy(labels, predictions)
EPOCHS = 5
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
train_loss.reset_states()
train_accuracy.reset_states()
test_loss.reset_states()
test_accuracy.reset_states()
for images, labels in train_ds:
train_step(images, labels)
for test_images, test_labels in test_ds:
test_step(test_images, test_labels)
template = 'Epoch {}, Loss: {}, Accuracy: {}, Test Loss: {}, Test Accuracy: {}'
print(template.format(epoch + 1,
train_loss.result(),
train_accuracy.result() * 100,
test_loss.result(),
test_accuracy.result() * 100))


函数模型
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten, Conv2D
from tensorflow.keras import Model
import numpy as np
print(tf.__version__)
print(np.__version__)
mnist = np.load("mnist.npz")
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = mnist['x_train'],mnist['y_train'],mnist['x_test'],mnist['y_test']
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0
y_train = np.int32(y_train)
y_test = np.int32(y_test)
x_train = x_train[..., tf.newaxis]
x_test = x_test[..., tf.newaxis]
y_train = tf.one_hot(y_train,depth=10)
y_test = tf.one_hot(y_test,depth=10)
train_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train)).shuffle(10000).batch(32)
test_ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)).shuffle(100).batch(32)
def MyModel():
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(28,28,1), name='digits')
x = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, 3, activation='relu')(inputs)
x = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu')(x)
outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10,activation='softmax', name='predictions')(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
return model
class FocalLoss(tf.keras.losses.Loss):
def __init__(self,gamma=2.0,alpha=0.25):
self.gamma = gamma
self.alpha = alpha
super(FocalLoss, self).__init__()
def call(self,y_true,y_pred):
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(y_pred,axis=-1)
epsilon = tf.keras.backend.epsilon()
y_pred = tf.clip_by_value(y_pred, epsilon, 1.0)
y_true = tf.cast(y_true,tf.float32)
loss = - y_true * tf.math.pow(1 - y_pred, self.gamma) * tf.math.log(y_pred)
loss = tf.math.reduce_sum(loss,axis=1)
return loss
model = MyModel()
model.compile(optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001),
loss = FocalLoss(gamma=2.0,alpha=0.25),
metrics = [tf.keras.metrics.CategoricalAccuracy()]
)
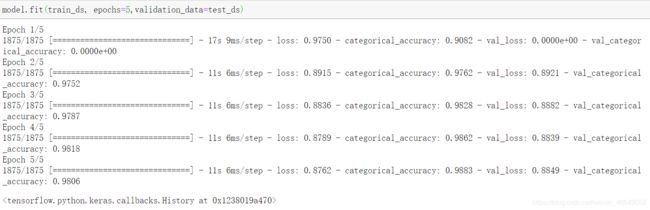
model.fit(train_ds, epochs=5,validation_data=test_ds)