sklearn笔记30手写代码实现线性回归
完整代码 sklearn代码22 3-手写代码实现线性回归
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
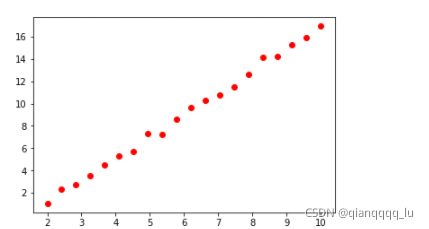
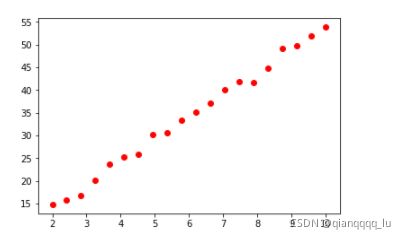
X = np.linspace(2,10,20).reshape(-1,1)
# f(x) = wx +b
y = np.random.randint(1,6,size = 1)*X + np.random.randint(-5,5,size =1)
# 噪声,加盐
y += np.random.randn(20,1)*0.5
plt.scatter(X,y,color = 'red')
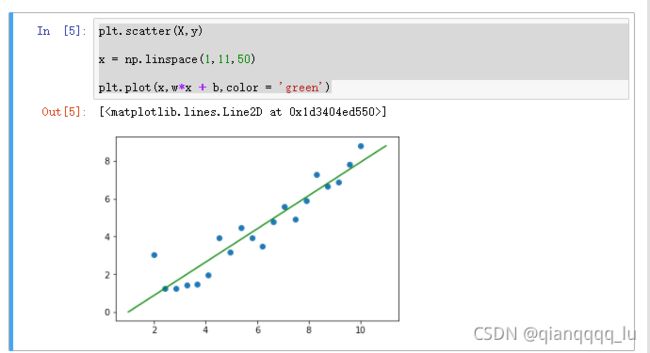
对数据进行拟合,让线尽量经过点的中间位置

使用线性回归去计算
lr = LinearRegression()
lr.fit(X,y)
w = lr.coef_[0,0]
b = lr.intercept_[0]
print(w,b)
plt.scatter(X,y)
x = np.linspace(1,11,50)
plt.plot(x,w*x + b,color = 'green')
# 使用梯度下降解决一元一次的线性问题:w,b
class LinearModel(object):
def __init__(self):
self.w = np.random.randn(1)[0]
self.b = np.random.randn(1)[0]
# 数学建模:将数据X和目标值关系用数学公式来表达
def model(self,x): # model模型 f(x) = wx + b
return self.w*x + b
def loss(self,x,y): #最小二乘法
cost = (y - self.model(x))**2
# 偏导数,求解两个未知数:w,b
gradient_w = 2*(y-self.model(x))*(-x)
gradient_b = 2*(y-self.model(x))*(-1)
return cost,gradient_w,gradient_b
# 梯度下降
def gradient_descent(self,gradient_w,gradient_b,learning_rate=0.1):
# 更新w,b
self.w -= gradient_w*learning_rate
self.b -= gradient_b*learning_rate
# 训练fit
def fit(self,X,y):
count = 0 # 算法执行优化了3000次,退出 代表着算法执行的最大次数
tol = 0.0001
last_w = self.w + 0.1
last_b = self.b + 0.1
length = len(X)
while True:
if count > 3000: # 执行的次数到了
break
# 求解的斜率和截距的精确度达到要求
if (abs(last_w - self.w) < tol) and (abs(last_b - self.b) < tol):
break
cost = 0
gradient_w = 0
gradient_b = 0
for i in range(length):
cost_,gradient_w_,gradient_b_ = self.loss(X[i,0],y[i,0])
cost += cost_/length
gradient_w += gradient_w_/length
gradient_b += gradient_b_/length
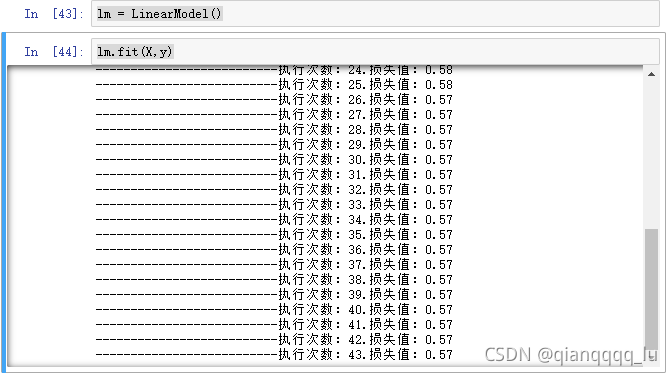
print('--------------------------执行次数:%d.损失值:%0.2f'%(count,cost))
last_w = self.w
last_b = self.b
# 更新截距和斜率
self.gradient_descent(gradient_w,gradient_b,0.002)
count += 1
def result(self):
return self.w,self.b
lm = LinearModel()
lm.fit(X,y)
lm.result()
# sklearn中的LinerRegression
print(w,b)
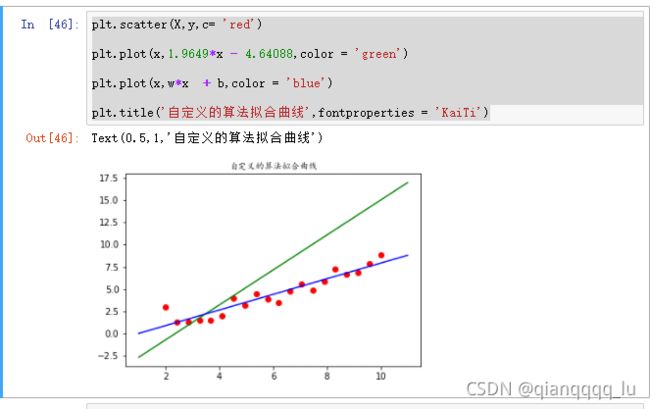
plt.scatter(X,y,c= 'red')
plt.plot(x,1.9649*x - 4.64088,color = 'green')
plt.plot(x,w*x + b,color = 'blue')
plt.title('自定义的算法拟合曲线',fontproperties = 'KaiTi')