HandlerThread 相信大家都比较熟悉了,从名字上看是一个带有Handler消息循环机制的一个线程,比一般的线程多了消息循环的机制,可以说是Handler+Thread的结合,从源码上看也是如此的设计,一般情况下如果需要子线程和主线程之间相互交互,可以用HandlerThread来设计,这比单纯的Thread要方便,而且更容易管理,因为大家都知道Thread的生命周期在一些情况下是不可控制的,比如直接new Thread().start(),这种方式在项目中是不推荐使用的,实际上Android的源码中也有很多地方用到了HandlerThread,下面我将分析一下HandlerThread以及涉及到的一些其他相关的问题。
HandlerThread的源码简单分析
int mPriority;
int mTid = -1;
Looper mLooper;
private @Nullable Handler mHandler;
public HandlerThread(String name) {
super(name);
mPriority = Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_DEFAULT;
}
首先字段有优先级,可以看到HandlerThread里面的优先级是默认的,当然了,你也可以修改,调用有二个参数的构造函数就可以了,在构造函数里面有个String类型,代表HandlerThread名字的,这个一般情况下可以取线程的名称。
/**
* Call back method that can be explicitly overridden if needed to execute some
* setup before Looper loops.
*/
protected void onLooperPrepared() {
}
@Override
public void run() {
mTid = Process.myTid();
Looper.prepare();
synchronized (this) {
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
notifyAll();
}
Process.setThreadPriority(mPriority);
onLooperPrepared();
Looper.loop();
mTid = -1;
}
这里面有一个方法onLooperPrepared(),在实际中,我们可以重写这个方法做一些初始化的操作,这个run()是重点,可以看到Looper进行了初始化并且开始循环接收消息了,并且唤醒了当前所有等待的线程,由于run方法是在start之后才会启动的,因此在用HandlertThread的时候,在初始化了实例之后就必须调用start方法开启消息循环了。
public Looper getLooper() {
if (!isAlive()) {
return null;
}
// If the thread has been started, wait until the looper has been created.
synchronized (this) {
while (isAlive() && mLooper == null) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
return mLooper;
}
这个方法是获取当前的looper,可以看到如果没有获取的时候就一直等待直到获取,而前面也提到了获取到了就唤醒了所有的线程,看来这是线程的等待-唤醒机制应用。
public Handler getThreadHandler() {
if (mHandler == null) {
mHandler = new Handler(getLooper());
}
return mHandler;
}
这个是获取HandlerThread绑定的Looper线程的Handler
public boolean quit() {
Looper looper = getLooper();
if (looper != null) {
looper.quit();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean quitSafely() {
Looper looper = getLooper();
if (looper != null) {
looper.quitSafely();
return true;
}
return false;
}
可以看到这两个方法去退出线程的Looper循环,那么这两个方法有什么区别呢,实际上都是调用了MessageQueue的quit()方法,源码如下:
void quit(boolean safe) {
if (!mQuitAllowed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Main thread not allowed to quit.");
}
synchronized (this) {
if (mQuitting) {
return;
}
mQuitting = true;
if (safe) {
removeAllFutureMessagesLocked();
} else {
removeAllMessagesLocked();
}
// We can assume mPtr != 0 because mQuitting was previously false.
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
}
可以看到: 当我们调用quit方法的时候,实际上执行了MessageQueue中的removeAllMessagesLocked方法,该方法的作用是把MessageQueue消息池中所有的消息全部清空,无论是延迟消息(延迟消息是指通过sendMessageDelayed或通过postDelayed等方法发送的需要延迟执行的消息,只要不是立即执行的消息都是延迟消息)还是非延迟消息。
而quitSafely方法时,实际上执行了MessageQueue中的removeAllFutureMessagesLocked方法,通过名字就可以看出,该方法只会清空MessageQueue消息池中所有的延迟消息,并将消息池中所有的非延迟消息派发出去让Handler去处理,quitSafely相比于quit方法安全之处在于清空消息之前会派发所有的非延迟消息,一句话,就是清除未来需要执行的消息。
这两个方法有一个共同的特点就是:Looper不再接收新的消息了,消息循环就此结束,此时通过Handler发送的消息也不会在放入消息杜队列了,因为消息队列已经退出了。 应用这2个方法的时候需要注意的是:quit方法从API 1就开始存在了,比较早,而quitSafely直到API 18才添加进来.
到此源码分析结束,下面看一个实际的简单的例子:
private static class UserHandlerThread extends HandlerThread implements Handler.Callback {
private Handler mHandler;
public UserHandlerThread(String name) {
super(name);
start();
mHandler = new Handler(getLooper(), this);
}
@Override
protected void onLooperPrepared() {
super.onLooperPrepared();
}
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what==0x123){
Log.d("[app]","收到消息了");
}
return false;
}
public Handler getHandler() {
return mHandler;
}
}
private UserHandlerThread handlerThread;
handlerThread = new UserHandlerThread("handlerThread");
handlerThread.getHandler().sendEmptyMessage(0x123);
OK,大家都知道结果了吧,一般情况下,在OnDestroy方法中需要退出循环,比如下面代码:
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
if (handlerThread != null) {
handlerThread.getHandler().removeCallbacksAndMessages(null);
handlerThread.quit();
handlerThread = null;
}
}
//Looper.getMainLooper().quit();
大家先忽略注释的那句代码, 好了,下面分析3个涉及到相关的问题:
● 既然子线程可以退出消息循环队列,那么UI线程,也就是主线程是否也一样可以在onDestroy方法退出消息循环呢,就是取消刚才代码的注释.
先说答案:不能退出主线程的消息队列,不然会抛出Main thread not allowed to quit.错误,是不是很熟悉,没错,上面的代码中已经贴出来了,为什么呢,MessageQueue有一个字段:mQuitAllowed
// True if the message queue can be quit.
private final boolean mQuitAllowed;
这个字段代表:是否可以退出消息队列的意思,那么主线程的这个字段是什么呢,是false,就是不能退出当前消息的消息队列的意思,来看主线程的消息初始化代码:Looper.prepareMainLooper();
public static void prepareMainLooper() {
prepare(false);
synchronized (Looper.class) {
if (sMainLooper != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared.");
}
sMainLooper = myLooper();
}
}
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {
mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);
mThread = Thread.currentThread();
}
可以看到prepare参数中,主线程传入的是false,而在Looper的构造函数里面被赋值了,也就是主线程的是false,所以这就决定了主线程是不能退出消息队列,那为什么子线程就可以退出消息队列呢,因为子线程传入的是true,代码如下:
Looper.prepare();
public static void prepare() {
prepare(true);
}
看到没,子线程传入的是true,这说明子线程是可以退出消息队列的, 实际上真正退出主线程的消息队列是FrameWork层做的事情,下面的第三个问题会提到。
● Handler里面发出去的消息,究竟是在哪个线程执行的呢?
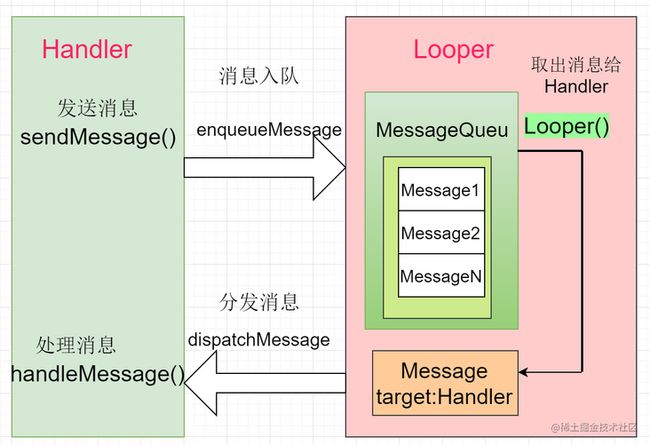
本文并不打算长篇分析Handler的源码,只简单讨论跟Handler线程相关的问题,实际上,对于Handler,如果能理解下面的图,然后再自己去分析源码,我想理解会更深
我们知道,handler的构造函数中有一个参数,就是设置当前Looper的,代码如下:
/**
* Use the provided {@link Looper} instead of the default one.
*
* @param looper The looper, must not be null.
*/
public Handler(Looper looper) {
this(looper, null, false);
}
public Handler(Looper looper, Callback callback, boolean async) {
mLooper = looper;
mQueue = looper.mQueue;
mCallback = callback;
mAsynchronous = async;
}
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
可以看到传入的Looper最终会被赋值到mLooper字段,如果没有调用这个构造函数,那么mLooper由当前线程获取,而消息队列MessageQueue是由Looper得到的,换句话说:Handler的消息在哪个Looper循环,那意味着所有的消息将会被哪个Looper的消息队列所存储和处理,而一个线程只能绑定一个Looper,因此一个Handler只能绑定一个Looper,也就意味着,Handler绑定了哪个线程的Looper,那么所有的消息都会在哪个线程执行,这跟上面的图是一致的,当然了有同学说我在Handler里面开线程就另外说了,但Handler操作的本身一定是在对应的Looper所在的线程的,就是如果Handler绑定了主线程的Looper,那么所有的消息都会在主线程处理,如果绑定的是子线程,那么所有的消息都会在子线程处理。
●在Android一个应用程序"退出"的真正含义是什么呢?
对于这个问题,有同学可能说我杀掉进程,应用程序挂了,也就相当于退出了。实际上这个说法是不正确的,因为这里的杀掉进程,不仅仅是程序本身,而且连程序的内存空间也一并被处理,我们前面说了,子线程可以退出消息队列,意味着子线程就再也无法接收到任何消息了,这就是子线程的退出含义,实际上,主线程也是一样的,只是这个过程对我们开发者不可见而已,在主线程中,如果退出了消息队列,那么意味着主线程也无法接收到任何消息,下面是代码,在ActivityThread.java里面:
public final void scheduleExit() {
sendMessage(H.EXIT_APPLICATION, null);
}
case EXIT_APPLICATION:
if (mInitialApplication != null) {
mInitialApplication.onTerminate();
}
Looper.myLooper().quit();
break;
看到这里,我想熟悉IPC过程的同学应该都知道了,没错,scheduleExit()不是本地进程调用的,而是由服务端进程ActivityAManagerService服务进行调用的,这也是我为什么说退出主线程是由FrameWork调用的原因,在AMS里面有2处地方调用了退出的代码,分别是绑定本地进程和内存回收工作的时候调用的,下面是代码(在ActivityManagerService.Java里面):
在APP本地进程绑定到AMS进程的时候调用
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
// Find the application record that is being attached... either via
// the pid if we are running in multiple processes, or just pull the
// next app record if we are emulating process with anonymous threads.
ProcessRecord app;
if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) {
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
}
} else {
app = null;
}
if (app == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "No pending application record for pid " + pid
+ " (IApplicationThread " + thread + "); dropping process");
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_DROP_PROCESS, pid);
if (pid > 0 && pid != MY_PID) {
Process.killProcessQuiet(pid);
//TODO: killProcessGroup(app.info.uid, pid);
} else {
try {
//这里也调用了
thread.scheduleExit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore exceptions.
}
}
return false;
}
//省略一些非必要代码
}
//i清理内存的时候调用
final void trimApplications() {
synchronized (this) {
int i;
// First remove any unused application processes whose package
// has been removed.
for (i=mRemovedProcesses.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
final ProcessRecord app = mRemovedProcesses.get(i);
if (app.activities.size() == 0
&& app.curReceiver == null && app.services.size() == 0) {
Slog.i(
TAG, "Exiting empty application process "
+ app.toShortString() + " ("
+ (app.thread != null ? app.thread.asBinder() : null)
+ ")\n");
if (app.pid > 0 && app.pid != MY_PID) {
//杀进程
app.kill("empty", false);
} else {
try {
//这里调用了退出主线程消息队列代码
app.thread.scheduleExit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore exceptions.
}
}
cleanUpApplicationRecordLocked(app, false, true, -1, false /*replacingPid*/);
mRemovedProcesses.remove(i);
if (app.persistent) {
addAppLocked(app.info, false, null /* ABI override */);
}
}
}
// Now update the oom adj for all processes.
updateOomAdjLocked();
}
}
看到了吧,在首次App绑定进程的时候,如果发生app==null这个错误的时候就调用了退出主线程消息队列,另一个就是在清理内存的时候调用,这两个过程对我们开发者不可见,我们了解就好,在源码面前,并没有什么是神奇的地方。
感谢大家阅读,如果有什么错误的地方,请欢迎指出,谢谢。
相关视频推荐:
【安卓面试合集】5-FrameWork源码之handler源码解析(一)-01
【安卓面试合集】6-FrameWork源码之handler源码解析(一)-02
本文转自 https://juejin.cn/post/6844903526468943886,如有侵权,请联系删除。