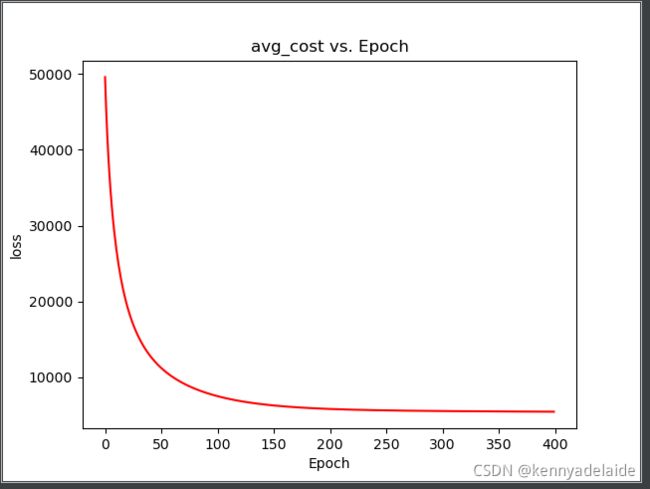
接着上一篇文章实现svd系列的biasSVD算法
上图的公式需要手动推写一遍加深印象,总体难度不大,适合在此基础之上做出相应的修改, 下一篇将继续实现svd系列的svd++ 算法,该算法增加和时间因素。采用分桶原理实现。
import numpy as np
from numpy import *
import ray
import socket
import pandas as pd
import os
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn import preprocessing
from collections import Counter
import time
import progressbar
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.seterr(divide='ignore', invalid='ignore')
'''
this is a function to come true svd model named svd++ algorithm. and using ray freamwork.
name: kenny adelaide
email: [email protected]
time: 2021/11/17
'''
# ray.init(address='192.168.0.219:6379', _redis_password="5241590000000000")
'''
=================================================common function area==============================================================
'''
def onloaddata():
'''
onload data to memory.
Returns:matirx, userno and videono
'''
dictionary = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
path = os.path.join(dictionary, 'data/00000005.csv')
o_data = pd.read_csv(path)
userno = o_data['userid'].max() + 1
videono = o_data['videoid'].max() + 1
return [o_data, userno, videono]
def build_score_matrix_R(data, userno, videono):
'''
this is common function for all algorithm-model.
via original data to build the true score matrix.
Args:
data:
userno: 用户编号最大
videono:视频编号最大
Returns: score matrix
'''
matrix = [[None] * videono] * userno
matrix = np.array(matrix)
# matrix = np.zeros((videono, userno))
for index, row in data.iterrows():
matrix[int(row['userid']), int(row['videoid'])] = float(row['score'])
return matrix
def L2Norm(a, vector):
result = list(np.dot(vector, vector) * a)[0][0]
return result
'''
===============================================bias svd=================================================================
'''
def init_P_Q_B_matrix_bias(user_disms=[3, 3], item_disms=[3, 3], init_method='quadrature'):
'''
this is a function to create two matrix for sgd training.
we via quadrature distribution function.
Args:
user_disms: user matrix shape.
item_disms: item matrix shape
init_method: generating matrix approach.
Returns: return four matrix, B matrix as the bias matrix. P,Q is the lower dismisional matrix to fit original score-matrix.
'''
if str(init_method) == str('quadrature'):
P = random.randn(user_disms[0], user_disms[1])
Q = random.randn(item_disms[1], item_disms[0])
B_i = random.randn(user_disms[0], 1)
B_j = random.randn(item_disms[0], 1)
return [P, Q, B_i, B_j]
return
def cal_mean_rating_bias(y_matirx):
'''
calculate the mean score as the parameter uf u.
Returns: return a float number-type.
'''
shape = y_matirx.shape
rows, cols = np.nonzero(y_matirx != None)
u = np.sum(y_matirx[rows, cols]) / (shape[0] * shape[1])
return u
def gradient_bias(u, a, B_i, B_j, y_matrix, P, Q):
'''
via min(f(x)) to calculate the gradient about four parameters, named pi,qj,bi,bj.
Returns:
'''
rows, cols = np.nonzero(y_matrix != None)
R = np.sum(P[rows] * Q.T[cols], axis=1)
error = list((y_matrix[rows, cols] - np.array(R)) - B_i[rows, 0] - B_j[cols, 0] - u)
error = np.array([i for i in error]).reshape(len(rows), 1)
gradient_p_i = -2 * error * Q[:, cols].T + 2 * a * P[rows, :]
gradient_q_j = -2 * error * P[rows, :] + 2 * a * Q[:, cols].T
gradient_b_i = -2 * error + 2 * a * B_i[rows]
gradient_b_j = -2 * error + 2 * a * B_j[cols]
return [error, gradient_p_i, gradient_q_j, gradient_b_i, gradient_b_j]
def bias_svd():
'''
in order to think about some low rating-defined factors, named bias.
eg: some item defined unrelated to user about rating may reduce
the user's rating. detail defined as user-bias and item bias.
Returns: cost, and iters count.
'''
[o_data, userno, videono] = onloaddata()
learning_rate = 0.01
iters = 400
a = 0.5
cost_arr = []
count = 0
[P, Q, B_i, B_j] = init_P_Q_B_matrix_bias(user_disms=[userno, 2], item_disms=[videono, 2], init_method='quadrature')
y_matirx = build_score_matrix_R(o_data, userno, videono)
if not isinstance(P, np.ndarray):
P = np.array(P).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(Q, np.ndarray):
Q = np.array(Q).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(y_matirx, np.ndarray):
y_matirx = np.array(y_matirx).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(y_matirx, np.ndarray):
B_i = np.array(B_i).around(decimals=4)
if not isinstance(y_matirx, np.ndarray):
B_j = np.array(B_j).around(decimals=4)
u = cal_mean_rating_bias(y_matirx)
# to fetch the position(index) about score matrix element.
rows, cols = np.nonzero(y_matirx != None)
bar = progressbar
for i in bar.progressbar(range(iters)):
[error, gradient_p_i, gradient_q_j, gradient_b_i, gradient_b_j] = gradient_bias(u, a, B_i, B_j, y_matirx, P, Q)
# for index in range(len(rows)):
# error = errors[index]
P[rows, :] -= learning_rate * gradient_p_i
Q[:, cols] -= learning_rate * gradient_q_j.T
B_i[rows] -= learning_rate * gradient_b_i
B_j[cols] -= learning_rate * gradient_b_j
cost = np.sum(np.square(error))
cost_arr.append(cost)
count += 1
if cost <= 0.001:
break
print(np.dot(P, Q))
return cost_arr, count