C++实现疫情感染扩散模型
题目如下:
我们对疫情的感染过程进行以下数学建模:
- 将人简化为质点;
- 人在活动区域内随机行走,行走规则为:每个人只能向上、下、左、右四个方向行走,向四个方向行走的概率相等,行走速度V为1米/时间步,在活动区域边界处,向离开活动区域方向行走的概率降为0,向其他三个方向行走的概率不变;
- 感染半径R为2米;
- 未接种疫苗时,感染概率P(只要在感染半径内)为0.6;
- 感染时间T为10个时间步;
- 致死概率D(被感染者在感染时间内每个时间步都有可能致死)为0.001,致死后移除出活动区域;
- 非致死,即治愈,被治愈者不再被感染;
活动区域为200米*200米的正方形,被划分为1米*1米的网格点。初始化时,每个人随机出现在活动区域内的网格点上,并且所有人除致死外均不离开活动区域,随机选择一个人,其初始状态为被感染(即零号感染者)。
请模拟出上述传播过程。
题解:
首先,定义Person类:
class Person
{
public:
//公共参数
int activeRadius = 200; //活动区域
int V = 1; //行走速度
int R = 2; //感染半径
double P = 0.6; //感染概率
int T = 10; //感染时间
double D = 0.001; //致死概率
//个人参数
int positionX; //X方向位置
int positionY; //Y方向位置
bool isInfected = false; //是否被感染
bool isDead = false; //是否死亡
bool isCured = false;
int infectedTimeRemain; //当前剩余感染时间
//成员函数
Person(int infected); //构造函数
void Move(); //移动
vector JudgeState(int X, int Y); //判断当前移动状态
void Infected(); //执行感染操作
void Dead(); //执行死亡操作
void getString();
}; 首先,使用随机数初始化当前Person的位置,并在所有人中随机初始化一个感染者:
Person::Person(int infected)
{
//初始化位置
positionX = rand() % (activeRadius + 1);
positionY = rand() % (activeRadius + 1);
//初始化感染状态
isInfected = infected == 0 ? false:true;
}第二步,模拟Person的移动,在移动前,首先需要根据其位置坐标判断其可以执行的移动方式,这里使用了枚举的方式,将当前状态下可以执行的移动方式保存下来:
vector Person::JudgeState(int X, int Y)
{
//1为向左,2为向上,3为向右,4为向下
vector ans;
if (X == 0)
{
if (Y == 0)
{
ans.push_back(2);
ans.push_back(3);
return ans;
}
else if (Y == activeRadius)
{
ans.push_back(3);
ans.push_back(4);
return ans;
}
else
{
ans.push_back(2);
ans.push_back(3);
ans.push_back(4);
return ans;
}
}
else if (X == activeRadius)
{
if (Y == 0)
{
ans.push_back(1);
ans.push_back(2);
return ans;
}
else if (Y == activeRadius)
{
ans.push_back(1);
ans.push_back(4);
return ans;
}
else
{
ans.push_back(1);
ans.push_back(2);
ans.push_back(4);
return ans;
}
}
else
{
if (Y == 0)
{
ans.push_back(1);
ans.push_back(2);
ans.push_back(3);
return ans;
}
else if (Y == activeRadius)
{
ans.push_back(1);
ans.push_back(3);
ans.push_back(4);
return ans;
}
else
{
ans.push_back(1);
ans.push_back(2);
ans.push_back(3);
ans.push_back(4);
return ans;
}
}
} 接下来,定义移动操作,这里采用了随机的方式,首先获取当前状态下可以进行的移动方式数组,随机从该数组中获取一个移动操作:
void Person::Move()
{
vector state = JudgeState(positionX, positionY);
//初始化随机种子
int r = rand() % state.size();
int direction = state[r];
//1为向左,2为向上,3为向右,4为向下
if (direction == 1)
{
positionX -= 1;
}
if (direction == 2)
{
positionY += 1;
}
if (direction == 3)
{
positionX += 1;
}
if (direction == 4)
{
positionY -= 1;
}
} 感染操作定义如下(P为感染概率)这里使用rand()生成一个整数,并取其最后一位,+1使得其范围变为[1,10],若此时得到的数字≤ P*10,则处于概率范围内,故被感染:
void Person::Infected()
{
int r = rand() % 10 + 1;
if (r <= P * 10)
{
isInfected = true;
infectedTimeRemain = T;
}
}死亡操作定义如下(概率为1/1000):
void Person::Dead()
{
int r = rand() % 1000 + 1;
if (r == 1)
{
//执行死亡
isDead = true;
}
}到这里,Person类就实现完了,接下来是主函数的实现:
首先是一个工具函数,用于计算两点之间的欧氏距离:
double Distance(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
int ans = sqrt(pow(x2 - x1, 2) + pow(y2 - y1, 2));
return ans;
}主函数中包含了题目中所提到的人物移动及感染过程,其实现如下:
int main()
{
//活动人数
int personNum = 10000;
//时间步
int timeStep = 20;
//初始化所有Person
cout << "initializing......\n";
vector personList;
//随机选择一个人物作为零号感染者
srand(time(0));
int r = rand() % personNum;
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < personNum; i++)
{
int infected = 0;
if (i == r)
{
infected = 1;
}
Person* p = new Person(infected);
personList.push_back(p);
}
cout << "moving......\n";
//移动,当前迭代timeStep个时间步
for (int i = 0; i < timeStep; i++)
{
for (Person* p : personList)
{
//若当前人物已死,则不再参与
if (p->isDead) { continue; }
//如果当前已经感染
if (p->isInfected)
{
//若当前剩余感染时间为0,则已治愈
if (p->infectedTimeRemain == 0)
{
p->isInfected = false;
p->isCured = true;
}
else
{
//否则,当前感染时间-1,并尝试死亡操作
p->infectedTimeRemain -= 1;
p->Dead();
}
}
//如果当前未感染
else
{
//若当前已治愈,则不会再感染
if (p->isCured) { continue; }
//判断当前感染半径内是否存在感染者
for (Person* temp : personList)
{
//如果感染半径内存在感染者,则尝试感染操作
if (temp->isInfected == true && Distance(p->positionX, p->positionY, temp->positionX, temp->positionY) <= p->R)
{
//尝试感染操作
p->Infected();
}
}
}
//移动
p->Move();
}
int infected = 0;
int dead = 0;
int cure = 0;
for (Person* p : personList)
{
if (p->isDead)
{
dead += 1;
continue;
}
if (p->isInfected)
{
infected += 1;
continue;
}
if (p->isCured)
{
cure += 1;
}
}
cout << "第" << i + 1<< "轮:";
cout << "死亡:" << dead << "人 ";
cout << "目前仍感染:" << infected << "人 ";
cout << "治愈:" << cure << "人\n";
}
for (Person* p : personList)
{
delete(p);
}
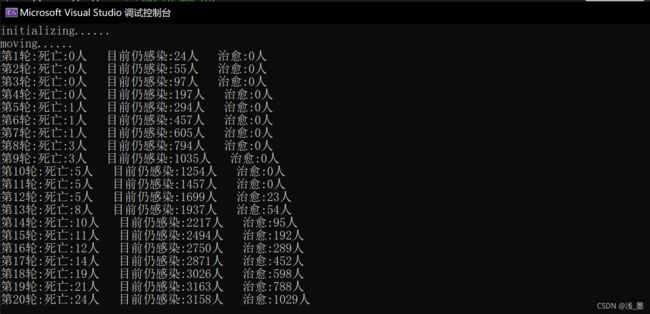
} 最后,当人数为10000,执行20个时间步时,执行结果如下: