【AcWing】蓝桥杯C++ AB组辅导课
蓝桥杯 C++ AB 组辅导课
- 教学计划与递归
-
- 如何准备蓝桥杯比赛
- 做题的套路
- 第一讲 递归与递推
-
- 递归实现指数型枚举
- 递归实现排列型枚举
- 递归实现组合型枚举
- AcWing116.飞行员兄弟
- 第二讲 二分与前缀和
-
- AcWing789.数的范围
- AcWing790.数的三次方根
- AcWing795.前缀和
- AcWing796.子矩阵的和
- AcWing1221.四平方和
- AcWing1230.K倍区间
- 第四讲 枚举、模拟与排序
-
- AcWing1210.连号区间数
- AcWing1236.递增三元组
- AcWing1245.特别数的和
- AcWing1204.错误票据
- AcWing466.回文日期
- AcWing1219.移动距离
- AcWing1229.日期问题
- AcWing1231.航班时间
- AcWing1241.外卖店优先级
- 第六讲 双指针、BFS与图论
-
- AcWing1238.日志统计
- AcWing1101.献给阿尔吉侬的花束
- AcWing1113.红与黑
- AcWing1224.交换瓶子
- AcWing1096.地牢大师
- AcWing1233.全球变暖
- AcWing1207.大臣的旅费
- 第十一届蓝桥杯省赛第一场C++A/B组真题
-
- AcWing2065.整除序列
- AcWing2066.解码
- AcWing2067.走方格
- AcWing2068.整数拼接
教学计划与递归
如何准备蓝桥杯比赛
-
要有一定刷题量
若想在省赛中取得较好成绩,建议做200题左右。
若想在国赛中取得较好成绩,建议做300题左右。
本课程约讲解100题左右。 -
要重视调试
有思路得前提下,若调试不过,不要立马问别人。要自己努力解决问题。 -
要重视考试。
感受真实氛围,检验学习成果。 -
比赛时比的并不是去发明或者去创造某一个思路,比赛比的是熟练度。
做题的套路
-
算法题特点:
1、与数学、物理等学科相比,算法题的模型相对较少。
2、思维量高
3、编写编程能力 。要用理论去指导实践。数学题想出来就能做出来,但是算法题能想出来不一定能实现出来。 -
做题过程
1、看题目描述
2、分析,抽象出来它考什么模型。分析出题人是想问什么。
3、回忆之前学过的算法或做过的题目能不能解决这个问题。若不能,再去回溯。解决方案是平时多去积累一些题目,多去刷一些题目。只有平时积累的多了,考试的时候才能学以致用。 -
如何判断一个算法能不能用?
1、首先看正确性
2、再看时间是否超限制。
C++ 评测机一秒约运行一亿次。若算法的的时间复杂度超过108,则可能会超时。

做题时,先看数据范围,排除不能使用的算法。找到题目数据范围区间之内的算法。这样做题思路会更明确。
数据范围可以带给我们非常多的信息。 -
学算法一定要落实到代码上
-
若输入输出 范围 小于 105 推荐用 cin / cout 否则用 scanf / printf 输入时间会快一倍左右。
第一讲 递归与递推
- 递归是什么?递归就是自己调用自己。
递归计算斐波那契数列
#include- 如何分析判断 递归执行顺序
所有递归都可以转化为一颗递归搜索树

- 记忆几个比较常用的数据
21 = 2
22 = 4
23 = 8
24 = 16
25 = 32
26 = 64
27 = 128
28 = 256
29 = 512
210 = 1024
215 = 32768
216 = 65536
220 约等于106
263 约等于 108
递归实现指数型枚举
#include变形 :如何输出所有方案?
#include递归实现排列型枚举
#include递归实现组合型枚举
#includeAcWing116.飞行员兄弟
第二讲 二分与前缀和
AcWing789.数的范围
#include AcWing790.数的三次方根
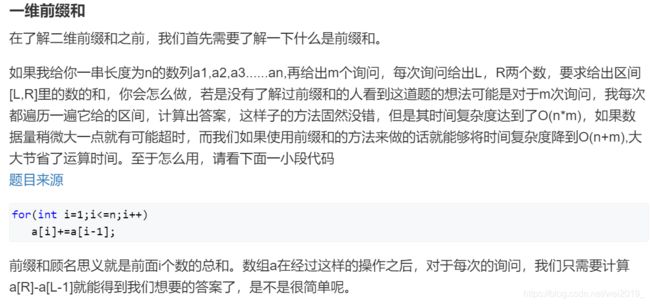
#include AcWing795.前缀和
#include AcWing796.子矩阵的和
#include #include AcWing1221.四平方和
#includeAcWing1230.K倍区间
#include 第四讲 枚举、模拟与排序
AcWing1210.连号区间数
#include AcWing1236.递增三元组
#include //暴力做法 通过了6/12 个数据
#include AcWing1245.特别数的和
// int -> string
string get(int x)
{
string res;
int t = x % 10;
x /= 10;
res += t;
return res
}
// string -> int
int uget(string s)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i ++)
res = res * 10 + s[i] - '0';
return res;
}
#include AcWing1204.错误票据
#include AcWing466.回文日期
//求四位回文数的程序
#include #include AcWing1219.移动距离
#include AcWing1229.日期问题
#include #include AcWing1231.航班时间
#include AcWing1241.外卖店优先级
#include 第六讲 双指针、BFS与图论
AcWing1238.日志统计
#include AcWing1101.献给阿尔吉侬的花束
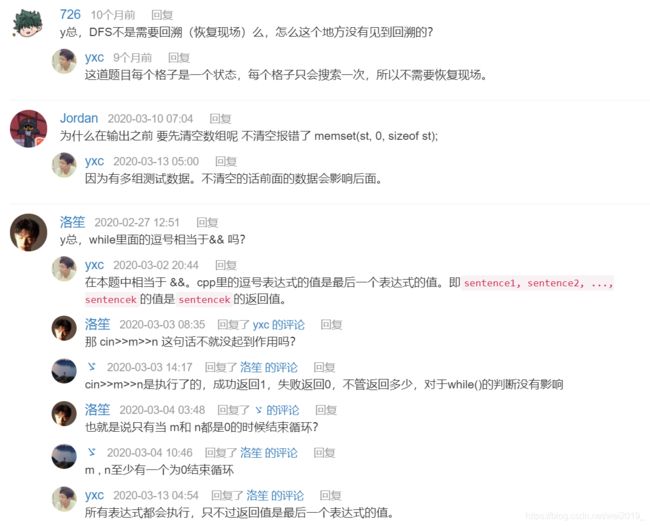
BFS可以找到最少步数因为BFS是按层搜索的
逻辑性的问题要一遍一遍的重复才可以记住

#include q;
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
int tt = 0;
int hh = 0;
dist[start.x][start.y] = 0; //**
// q.push(start);
q[0] = start;
st[start.x][start.y] = 1;
while (hh <= tt)
{
// auto t = q.front();
// q.pop();
PII t = q[hh ++ ];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
{
int x = t.x + dx[i], y = t.y + dy[i];
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m || g[x][y] == '#' || st[x][y]) continue; // 出界
dist[x][y] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1;
if (end == make_pair(x, y)) return dist[x][y];
// q.push({x, y});
q[++ tt] = {
x, y};
st[x][y] = true;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T -- )
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%s", g[i]);
PII start, end;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++ )
if (g[i][j] == 'S') start = {
i, j};
else if (g[i][j] == 'E') end = {
i, j};
int distance = bfs(start, end);
if (distance == -1) puts("oop!"); // 最后是有返回值的
else printf("%d\n", distance);
}
return 0;
}
#include q;
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
int tt = 0;
int hh = 0;
dist[start.x][start.y] = 0;
// q.push(start);
q[0] = start;
while (hh <= tt)
{
// auto t = q.front();
// q.pop();
PII t = q[hh ++ ];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
{
int x = t.x + dx[i], y = t.y + dy[i];
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m || g[x][y] == '#' || dist[x][y] != -1) continue; // 出界
dist[x][y] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1;
if (end == make_pair(x, y)) return dist[x][y];
// q.push({x, y});
q[++ tt] = {
x, y};
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T -- )
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%s", g[i]);
PII start, end;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++ )
if (g[i][j] == 'S') start = {
i, j};
else if (g[i][j] == 'E') end = {
i, j};
int distance = bfs(start, end);
if (distance == -1) puts("oop!"); // 最后是有返回值的
else printf("%d\n", distance);
}
return 0;
}
AcWing1113.红与黑
#include q;
// q.push({sx, sy});
memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
int tt = 0; int hh = 0;
q[0] = {
sx, sy};
st[sx][sy] = true;
// g[sx][sy] = '#';
int res = 0;
//q.size()
while (hh <= tt)
{
// auto t = q.front();
auto t = q[hh ++];
// q.pop();
res ++ ;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
int x = t.x + dx[i], y = t.y + dy[i];
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m || st[x][y] || g[x][y] != '.') continue;
// q.push({x, y});
q[++tt] = {
x, y};
// g[x][y] = '#';
st[x][y] = true;
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
while(cin >> m >> n, n || m)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cin >> g[i];
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j ++)
if (g[i][j] == '@')
{
x = i;
y = j;
}
cout << bfs(x, y) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
AcWing1224.交换瓶子
#include AcWing1096.地牢大师
#include AcWing1233.全球变暖
//while头入队标记 for尾出队统计
#include AcWing1207.大臣的旅费
//用vector存储图
#include 第十一届蓝桥杯省赛第一场C++A/B组真题
AcWing2065.整除序列
#includeAcWing2066.解码
#include AcWing2067.走方格

注意题干要求,如果行号和列数都是偶数,不能走入这一格中。
不能走的地方不走就可以了 全局变量的整型数组默认赋值为0 所以跳过就行
#include AcWing2068.整数拼接
#include