react源码解析9.diff算法
视频讲解(高效学习):进入学习
往期目录:
在render阶段更新Fiber节点时,我们会调用reconcileChildFibers对比current Fiber和jsx对象构建workInProgress Fiber,这里current Fiber是指当前dom对应的fiber树,jsx是class组件render方法或者函数组件的返回值。
在reconcileChildFibers中会根据newChild的类型来进入单节点的diff或者多节点diff
//ReactChildFiber.old.js
function reconcileChildFibers(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
newChild: any,
): Fiber | null {
const isObject = typeof newChild === 'object' && newChild !== null;
if (isObject) {
switch (newChild.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
//单一节点diff
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleElement(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes,
),
);
}
}
//...
if (isArray(newChild)) {
//多节点diff
return reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChild,
lanes,
);
}
// 删除节点
return deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, currentFirstChild);
}diff过程的主要流程如下图:
![]()
我们知道对比两颗树的复杂度本身是O(n3),对我们的应用来说这个是不能承受的量级,react为了降低复杂度,提出了三个前提:
- 只对同级比较,跨层级的dom不会进行复用
- 不同类型节点生成的dom树不同,此时会直接销毁老节点及子孙节点,并新建节点
可以通过key来对元素diff的过程提供复用的线索,例如:
const a = ( <>0
1
); const b = ( <>1
0
);
如果a和b里的元素都没有key,因为节点的更新前后文本节点不同,导致他们都不能复用,所以会销毁之前的节点,并新建节点,但是现在有key了,b中的节点会在老的a中寻找key相同的节点尝试复用,最后发现只是交换位置就可以完成更新,具体对比过程后面会讲到。
单节点diff
单点diff有如下几种情况:
- key和type相同表示可以复用节点
- key不同直接标记删除节点,然后新建节点
- key相同type不同,标记删除该节点和兄弟节点,然后新创建节点
function reconcileSingleElement(
returnFiber: Fiber,
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,
element: ReactElement
): Fiber {
const key = element.key;
let child = currentFirstChild;
//child节点不为null执行对比
while (child !== null) {
// 1.比较key
if (child.key === key) {
// 2.比较type
switch (child.tag) {
//...
default: {
if (child.elementType === element.type) {
// type相同则可以复用 返回复用的节点
return existing;
}
// type不同跳出
break;
}
}
//key相同,type不同则把fiber及和兄弟fiber标记删除
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, child);
break;
} else {
//key不同直接标记删除该节点
deleteChild(returnFiber, child);
}
child = child.sibling;
}
//新建新Fiber
}多节点diff
多节点diff比较复杂,我们分三种情况进行讨论,其中a表示更新前的节点,b表示更新后的节点
属性变化
const a = ( <>0
1
); const b = ( <>0
1
);
type变化
const a = ( <>0
1
); const b = ( <>01
);
新增节点
const a = ( <>0
1
); const b = ( <>0
1
2
);
节点删除
const a = ( <>0
1
2
); const b = ( <>0
1
);
节点位置变化
const a = ( <>0
1
); const b = ( <>1
0
);
在源码中多节点diff有三个for循环遍历(并不意味着所有更新都有经历三个遍历,进入循环体有条件,也有条件跳出循环),第一个遍历处理节点的更新(包括props更新和type更新和删除),第二个遍历处理其他的情况(节点新增),其原因在于在大多数的应用中,节点更新的频率更加频繁,第三个处理位节点置改变
第一次遍历
因为老的节点存在于current Fiber中,所以它是个链表结构,还记得Fiber双缓存结构嘛,节点通过child、return、sibling连接,而newChildren存在于jsx当中,所以遍历对比的时候,首先让newChildren[i]`与`oldFiber对比,然后让i++、nextOldFiber = oldFiber.sibling。在第一轮遍历中,会处理三种情况,其中第1,2两种情况会结束第一次循环- key不同,第一次循环结束
- newChildren或者oldFiber遍历完,第一次循环结束
- key同type不同,标记oldFiber为DELETION
- key相同type相同则可以复用
newChildren遍历完,oldFiber没遍历完,在第一次遍历完成之后将oldFiber中没遍历完的节点标记为DELETION,即删除的DELETION Tag
第二个遍历
第二个遍历考虑三种情况newChildren和oldFiber都遍历完:多节点diff过程结束
newChildren没遍历完,oldFiber遍历完,将剩下的newChildren的节点标记为Placement,即插入的Tag
- newChildren和oldFiber没遍历完,则进入节点移动的逻辑
第三个遍历
主要逻辑在placeChild函数中,例如更新前节点顺序是ABCD,更新后是ACDBnewChild中第一个位置的A和oldFiber第一个位置的A,key相同可复用,lastPlacedIndex=0
- newChild中第二个位置的C和oldFiber第二个位置的B,key不同跳出第一次循环,将oldFiber中的BCD保存在map中
- newChild中第二个位置的C在oldFiber中的index=2 > lastPlacedIndex=0不需要移动,lastPlacedIndex=2
- newChild中第三个位置的D在oldFiber中的index=3 > lastPlacedIndex=2不需要移动,lastPlacedIndex=3
- newChild中第四个位置的B在oldFiber中的index=1 < lastPlacedIndex=3,移动到最后
看图更直观
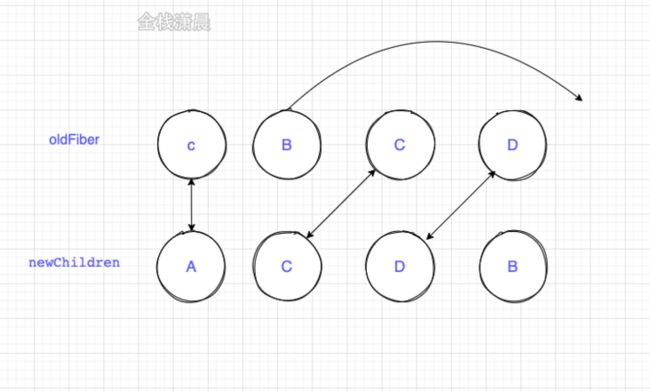
例如更新前节点顺序是ABCD,更新后是DABC
newChild中第一个位置的D和oldFiber第一个位置的A,key不相同不可复用,将oldFiber中的ABCD保存在map中,lastPlacedIndex=0
- newChild中第一个位置的D在oldFiber中的index=3 > lastPlacedIndex=0不需要移动,lastPlacedIndex=3
- newChild中第二个位置的A在oldFiber中的index=0 < lastPlacedIndex=3,移动到最后
- newChild中第三个位置的B在oldFiber中的index=1 < lastPlacedIndex=3,移动到最后
- newChild中第四个位置的C在oldFiber中的index=2 < lastPlacedIndex=3,移动到最后
看图更直观
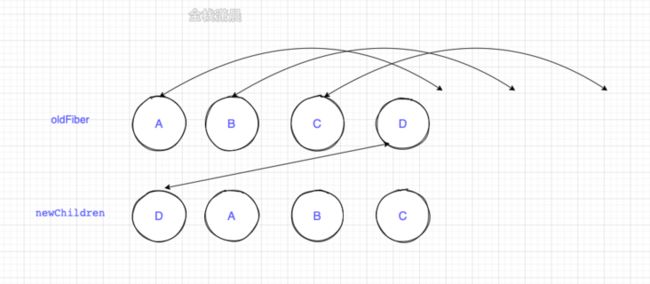
代码如下:
//ReactChildFiber.old.js
function placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIndex) {
newFiber.index = newIndex;
if (!shouldTrackSideEffects) {
return lastPlacedIndex;
}
var current = newFiber.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
var oldIndex = current.index;
if (oldIndex < lastPlacedIndex) {
//oldIndex小于lastPlacedIndex的位置 则将节点插入到最后
newFiber.flags = Placement;
return lastPlacedIndex;
} else {
return oldIndex;//不需要移动 lastPlacedIndex = oldIndex;
}
} else {
//新增插入
newFiber.flags = Placement;
return lastPlacedIndex;
}
}//ReactChildFiber.old.js
function reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber: Fiber,//父fiber节点
currentFirstChild: Fiber | null,//childs中第一个节点
newChildren: Array<*>,//新节点数组 也就是jsx数组
lanes: Lanes,//lane相关 第12章介绍
): Fiber | null {
let resultingFirstChild: Fiber | null = null;//diff之后返回的第一个节点
let previousNewFiber: Fiber | null = null;//新节点中上次对比过的节点
let oldFiber = currentFirstChild;//正在对比的oldFiber
let lastPlacedIndex = 0;//上次可复用的节点位置 或者oldFiber的位置
let newIdx = 0;//新节点中对比到了的位置
let nextOldFiber = null;//正在对比的oldFiber
for (; oldFiber !== null && newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {//第一次遍历
if (oldFiber.index > newIdx) {//nextOldFiber赋值
nextOldFiber = oldFiber;
oldFiber = null;
} else {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
const newFiber = updateSlot(//更新节点,如果key不同则newFiber=null
returnFiber,
oldFiber,
newChildren[newIdx],
lanes,
);
if (newFiber === null) {
if (oldFiber === null) {
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
break;//跳出第一次遍历
}
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {//检查shouldTrackSideEffects
if (oldFiber && newFiber.alternate === null) {
deleteChild(returnFiber, oldFiber);
}
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);//标记节点插入
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
if (newIdx === newChildren.length) {
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, oldFiber);//将oldFiber中没遍历完的节点标记为DELETION
return resultingFirstChild;
}
if (oldFiber === null) {
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {//第2次遍历
const newFiber = createChild(returnFiber, newChildren[newIdx], lanes);
if (newFiber === null) {
continue;
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);//插入新增节点
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}
// 将剩下的oldFiber加入map中
const existingChildren = mapRemainingChildren(returnFiber, oldFiber);
for (; newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {//第三次循环 处理节点移动
const newFiber = updateFromMap(
existingChildren,
returnFiber,
newIdx,
newChildren[newIdx],
lanes,
);
if (newFiber !== null) {
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
if (newFiber.alternate !== null) {
existingChildren.delete(//删除找到的节点
newFiber.key === null ? newIdx : newFiber.key,
);
}
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);//标记为插入的逻辑
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
}
}
if (shouldTrackSideEffects) {
//删除existingChildren中剩下的节点
existingChildren.forEach(child => deleteChild(returnFiber, child));
}
return resultingFirstChild;
}