异常检测第二篇:一分类SVM(OneClassSVM)
大家好,我是菜菜卷。
在上篇中,我们简要介绍了使用孤立森林(isolate forest)来进行无监督异常检测,在今天的内容中,我们将使用ocsvm(One Class SVM)来进行半监督异常检测,我们一起开始吧!~
关于数据集的介绍和数据读入方向可以参考第一篇的详细介绍:异常检测之孤立森林(isolate forest)
什么是SVM(支持向量机)
熟悉机器学习的同学肯定对svm已经了如指掌了,下面我们就简要的说一下,SVM的目的就是使用一条“线”将两类或者多类的数据分隔开来,使其每一侧的数据都是同一类别的,在简单的线性可分的二维平面中(如下图所示),我们可以很容易的找到一条线将两个类别的点区分开,
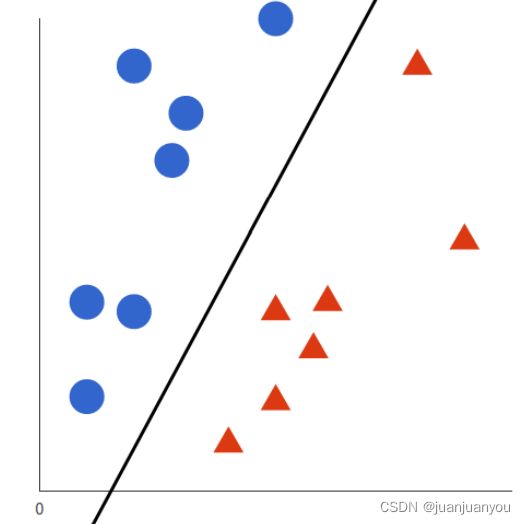
但是现实生活中的数据往往是多维和复杂的(线性不可分的),所以我们要找的往往是一个多维向量空间中的一个超平面,使得两类点尽可能的被划分在超平面的两侧。感兴趣的同学可以更详细的去了解一下SVM。
而我们今天使用的ocsvm也是svm最基础的一个应用,其基本原理如下:其输入的数据只需要有正常数据及其标签即可,在训练过程中,ocsvm会学习正常观测值的决策边界(svm中划分正负样本的超平面),同时考虑一些离群值,如果奇异值(模型未见过的新数据点)落在决策边界内,则模型将其认为是正常的,反之认为其是异常的。
ocsvm要实现的目标是:使用正常数据对模型进行训练,然后尝试在新数据中找出异常,因此ocsvm是一种半监督的异常检测方法。
所用数据集
数据集获取地址:KDDcup99
前往以上的地址,下载kddcup.data.gz即可。
该数据集是由若干正常和异常的数据分类,有41和特征和1个标签构成,因为后面我们只想对网页攻击方向的数据进行分析,所以要强调一下,第三个特征是表示异常的方向(即是哪种方面的异常,比如http还是其他)
项目所用环境
numpy 1.15.3
pandas 0.23.4
scikit-learn 0.19.1
matplotlib 2.2.2
大家可以使用pip或者conda自行安装项目环境,为保证顺利无bug复现结果,建议使用所示版本的包。
项目实战
1、包的导入
首先我们先导入实验所需的第三方包:
import time
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.svm import OneClassSVM
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
其中time可以用来记录时间和程序运行时间;numpy可以高效做矩阵运算,在数据处理中有广泛的运用;pandas可以快速方便的读入和处理数据的格式;sklearn是一个非常丰富的机器学习库,内部集成了基本的机器学习方法、数据集处理方法、模型衡量指标等功能。
2、使用pandas读入和处理数据
像上篇孤立森林中的处理一样,我们使用如下代码读入数据并过滤出只和http相关的数据(具体解读见第一篇博客的内容):
data_path = r'dataset/kddcup.data.corrected'
columns = [str(i) for i in range(1, 42)]
columns.append('label')
df = pd.read_csv(data_path, sep=',', names=columns, index_col=None)
df = df[df['3'] == 'http']
df = df.drop('3', axis=1)
columns.remove('3')
3、划分数据集
首先我们要获得用来训练模型的训练集x_train(只包含正常数据):
normal = df[df['label'] == 'normal.']
因为我们是半监督的任务,所以也需要正常数据和异常数据混合组成的数据集(如下所示):
novelties = df[df['label'] != 'normal.']
novelties_normal = normal[: 4045]
novelties = pd.concat([novelties, novelties_normal])
我们首先通过df[df['label'] != 'normal.']获得所有的异常数据,然后再取正常数据的前4045个并与异常数据混合在一起,从而得到了同时包含异常数据和正常数据的数据集,下面我们使用print(novelties.shape来看一下novelties的数据量,其shape为(8090, 41),所以其有一半的正常数据和一半的异常数据构成(之前正常数据之所以取4045也是因为只有4045个异常数据)。
类似于孤立森林中处理object的属性一样,我们使用以下代码处理新构成的novelties和normal中的object属性:
for col in normal.columns:
if normal[col].dtype == 'object':
encoded = LabelEncoder()
encoded.fit(normal[col])
normal[col] = encoded.transform(normal[col])
for col in novelties.columns:
if novelties[col].dtype == 'object':
encoded = LabelEncoder()
encoded.fit(novelties[col])
novelties[col] = encoded.transform(novelties[col])
下面我们进行train,val和test数据集的划分:
# shuffle
for _ in range(5):
normal = normal.iloc[np.random.permutation(len(normal))]
df2 = normal[: 150000]
df_validate = normal[150000: 200000]
x_train, x_test = train_test_split(df2, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
x_val = df_validate
print('the shapes of x_train, x_test and x_val are {}, {} and {}'.format(x_train.shape, x_test.shape, x_val.shape))
根据打印出的内容我们看到:
the shapes of x_train, x_test and x_val are (120000, 41), (30000, 41) and (50000, 41)
训练集,测试集和验证集分别由12w,3w和5w个数据组成。
4、OCSVM模型的构建和训练
我们使用如下代码来建立ocsvm模型,并用正常的数据集normal对其进行训练:
# create OneClassSVM
ocsvm = OneClassSVM(kernel='rbf', gamma=5e-5, random_state=42, nu=0.1)
print("---------------------start training-------------------")
start_time = time.time()
ocsvm.fit(x_train)
print('the training costs {}s'.format(time.time() - start_time))
print("---------------------end training-------------------")
因为ocsvm训练需要的时间较久(10min左右),在训练的过程中大家可以做点其他事情放松一下,训练完成后,其结果会如下所示:
---------------------start training-------------------
the training costs 454.88993668556213s
---------------------end training-------------------
然后我们使用以下代码来计算模型在test数据集上的准确率:
preds = ocsvm.predict(x_test)
score = 0
for idx in range(x_test.shape[0]):
if preds[idx] == 1:
score += 1
accuracy = score / x_test.shape[0]
print('Accuracy:{:.2%}'.format(accuracy))
其结果如下所示:
Accuracy:89.46%
从最终结果可以看出,我们的训练花费了454s的时间,最后准确率有89.46%,因为我们在创建模型的时候,使用参数nu=0.1指定了数据中大致有10%的异常数据,因此我们的模型在干净数据上的表现已经非常好了。
5、泛化性能测试(正常+异常数据)
上面我们已经测试了模型在正常数据上的acc已经非常好了,现在我们要测试一下,如果加入异常数据的话,其效果是不是也同样好,我们使用以下代码来完成测试:
preds = ocsvm.predict(novelties)
matches = novelties['label'] == 4
auc = roc_auc_score(preds, matches)
print('AUC:{:.2%}'.format(auc))
其结果如下所示:
AUC:94.50%
可见训练好的ocsvm在未见过的异常数据中也有相当的高的精度。OneClassSVM的实战到此也介绍的差不多了,其完整代码如下:
import time
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.svm import OneClassSVM
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
if __name__ == '__main__':
data_path = r'dataset/kddcup.data.corrected'
columns = [str(i) for i in range(1, 42)]
columns.append('label')
df = pd.read_csv(data_path, sep=',', names=columns, index_col=None)
# print(df.shape)
df = df[df['3'] == 'http']
df = df.drop('3', axis=1)
columns.remove('3')
novelties = df[df['label'] != 'normal.']
normal = df[df['label'] == 'normal.']
novelties_normal = normal[: 4045]
novelties = pd.concat([novelties, novelties_normal])
# print(novelties.shape)
# print(normal.shape)
for col in normal.columns:
if normal[col].dtype == 'object':
encoded = LabelEncoder()
encoded.fit(normal[col])
normal[col] = encoded.transform(normal[col])
for col in novelties.columns:
if novelties[col].dtype == 'object':
encoded = LabelEncoder()
encoded.fit(novelties[col])
novelties[col] = encoded.transform(novelties[col])
# shuffle
for _ in range(5):
normal = normal.iloc[np.random.permutation(len(normal))]
df2 = normal[: 150000]
df_validate = normal[150000: 200000]
x_train, x_test = train_test_split(df2, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
x_val = df_validate
print('the shapes of x_train, x_test and x_val are {}, {} and {}'.format(x_train.shape, x_test.shape, x_val.shape))
# create OneClassSVM
ocsvm = OneClassSVM(kernel='rbf', gamma=5e-5, random_state=42, nu=0.1)
print("---------------------start training-------------------")
start_time = time.time()
ocsvm.fit(x_train)
print('the training costs {}s'.format(time.time() - start_time))
print("---------------------end training-------------------")
preds = ocsvm.predict(x_test)
score = 0
for idx in range(x_test.shape[0]):
if preds[idx] == 1:
score += 1
accuracy = score / x_test.shape[0]
print('Accuracy:{:.2%}'.format(accuracy))
preds = ocsvm.predict(novelties)
matches = novelties['label'] == 4
auc = roc_auc_score(preds, matches)
print('AUC:{:.2%}'.format(auc))
我是菜菜卷,我们下篇再见!!