在《Kubernetes 的自动伸缩你用对了吗?》
一文中详细说明了如何使用 Kubernetes 的自动伸缩。在 Kubernetes 中弹性伸缩主要有三种:HPA、VPA、CA。本文不再详细说明,有兴趣的可以看那篇文章。这里主要来说下 Pod 水平缩放 HPA。
随着 Kubernetes v1.23 的发布,HPA 的 API 来到了稳定版 autoscaling/v2:
- 基于自定义指标的伸缩
- 基于多项指标的伸缩
- 可配置的伸缩行为
从最初的 v1 版本 HPA 只支持 CPU、内存利用率的伸缩,到后来的自定义指标、聚合层 API 的支持,到了 v1.18 版本又加入了配置伸缩行为的支持,HPA 也越来越好用、可靠。
依靠 CPU 或者内存指标的扩容并非使用所有系统,看起来也没那么可靠。对大部分的 web 后端系统来说,基于 RPS(每秒请求数)的弹性伸缩来处理突发的流量则会更加靠谱。
Prometheus 也是当下流行开源监控系统,通过 Prometheus 可以获取到系统的实时流量负载指标,今天我们就来尝试下基于 Prometheus 的自定义指标进行弹性伸缩。
注:目前 HPA 的缩容0 (scale to 0),则需要在 feature gate 打开 alpha 版本的 HPAScaleToZero 以及配置一个对象或者外部指标。即使是打开了,从 0 到 1 的扩容需要调度、IP 分配、镜像拉取等过程,存在一定的开销。如果降低这部分开销,这里先卖个关子,后续的文章进行补充。
文章中使用的所有代码都可以从这里下载。
整体架构
HPA 要获取 Prometheus 的指标数据,这里引入 Prometheus Adapter 组件。Prometheus Adapter 实现了 resource metrics、custom metrics 和 external metrics APIs API,支持 autoscaling/v2 的 HPA。
获取到指标数据后,根据预定义的规则对工作负载的示例数进行调整。
环境搭建
K3s
我们使用最新 1.23 版本的 K3s 作为 Kubernetes 环境。
export INSTALL_K3S_VERSION=v1.23.1+k3s2
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -s - --write-kubeconfig-mode 644 --write-kubeconfig ~/.kube/config示例应用
我们准备一个简单的 web 应用,可以记录请求次数并通过 /metrics 端点输出 Prometheus 格式的指标 http_requests_total。
func main() {
metrics := prometheus.NewCounterVec(
prometheus.CounterOpts{
Name: "http_requests_total",
Help: "Number of total http requests",
},
[]string{"status"},
)
prometheus.MustRegister(metrics)
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
path := r.URL.Path
statusCode := 200
switch path {
case "/metrics":
promhttp.Handler().ServeHTTP(w, r)
default:
w.WriteHeader(statusCode)
w.Write([]byte("Hello World!"))
}
metrics.WithLabelValues(strconv.Itoa(statusCode)).Inc()
})
http.ListenAndServe(":3000", nil)
}将应用部署到集群:
kubectl apply -f kubernetes/sample-httpserver-deployment.yamlPrometheus
使用 Helm 安装 Prometheus,先添加 prometheus 的 chart 仓库:
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts这里的测试只需要用到 prometheus-server,安装时禁用其他组件。同时为了演示效果的实效性,将指标的拉取间隔设置为 10s。
# install prometheus with some components disabled
# set scrape interval to 10s
helm install prometheus prometheus-community/prometheus -n default --set alertmanager.enabled=false,pushgateway.enabled=false,nodeExporter.enabled=false,kubeStateMetrics.enabled=false,server.global.scrape_interval=10s通过端口转发,可以在浏览器中访问 web 页面。
# port forward
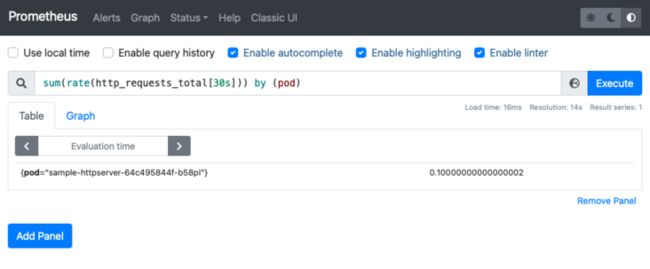
kubectl port-forward svc/prometheus-server 9090:80 -n prometheus这里查询 Pod 的 RPS 使用 sum(rate(http_requests_total[30s])) by (pod) 语句查询:
Prometheus Adapter
同样使用 Helm 安装 Produmetheus Adapter,这里要进行额外的配置。
helm install prometheus-adapter prometheus-community/prometheus-adapter -n default -f kubernetes/values-adapter.yaml除了要配置 Prometheus server 的访问方式外,还要配置自定义指标的计算规则,告诉 adapter 如何从 Prometheus 获取指标并计算出我们需要的指标:
rules:
default: false
custom:
- seriesQuery: '{__name__=~"^http_requests.*_total$",container!="POD",namespace!="",pod!=""}'
resources:
overrides:
namespace: { resource: "namespace" }
pod: { resource: "pod" }
name:
matches: "(.*)_total"
as: "${1}_qps"
metricsQuery: sum(rate(<<.Series>>{<<.LabelMatchers>>}[30s])) by (<<.GroupBy>>)可以参考详细的 Adapter 配置。
待 promethues-adapter pod 成功运行后,可以执行 custom.metrics.k8s.io 请求:
kubectl get --raw '/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/default/pods/*/http_requests_qps' | jq .
{
"kind": "MetricValueList",
"apiVersion": "custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1",
"metadata": {
"selfLink": "/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/default/pods/%2A/http_requests_qps"
},
"items": [
{
"describedObject": {
"kind": "Pod",
"namespace": "default",
"name": "sample-httpserver-64c495844f-b58pl",
"apiVersion": "/v1"
},
"metricName": "http_requests_qps",
"timestamp": "2022-01-18T03:32:51Z",
"value": "100m",
"selector": null
}
]
}注意:这里的 value: 100m,值的后缀“m” 标识 milli-requests per seconds,所以这里的 100m 的意思是 0.1/s 每秒0.1 个请求。
HPA
最后就是 HPA 的配置了:
- 最小最大的副本数分别设置 1、10
- 为了测试效果的实效性,设置扩缩容的行为
behavior - 指定指标
http_requests_qps、类型Pods以及目标值50000m:表示平均每个 pod 的 RPS50。比如以 300 的 RPS 访问,副本数就是 300/50=6 。
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
metadata:
name: sample-httpserver
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: sample-httpserver
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 10
behavior:
scaleDown:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 30
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 100
periodSeconds: 15
scaleUp:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 0
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 100
periodSeconds: 15
metrics:
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: http_requests_qps
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 50000m测试
测试工具选用 vegeta,因为其可以指定 RPS。
先为应用创建 NodePort service:
kubectl expose deploy sample-httpserver --name sample-httpserver-host --type NodePort --target-port 3000
kubectl get svc sample-httpserver-host
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
sample-httpserver-host NodePort 10.43.66.206 3000:31617/TCP 12h 分别使用 240、120、40 的 RPS 发起请求:
# 240
echo "GET http://192.168.1.92:31617" | vegeta attack -duration 60s -connections 10 -rate 240 | vegeta report
# 120
echo "GET http://192.168.1.92:31617" | vegeta attack -duration 60s -connections 10 -rate 120 | vegeta report
# 40
echo "GET http://192.168.1.92:31617" | vegeta attack -duration 60s -connections 10 -rate 40 | vegeta report从 Prometheus 的 web 界面上观察请求量与示例数的变化:
kubectl describe hpa sample-httpserver
Warning: autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavailable in v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler
Name: sample-httpserver
Namespace: default
Labels:
Annotations:
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 17 Jan 2022 23:18:46 +0800
Reference: Deployment/sample-httpserver
Metrics: ( current / target )
"http_requests_qps" on pods: 100m / 50
Min replicas: 1
Max replicas: 10
Behavior:
Scale Up:
Stabilization Window: 0 seconds
Select Policy: Max
Policies:
- Type: Percent Value: 100 Period: 15 seconds
Scale Down:
Stabilization Window: 30 seconds
Select Policy: Max
Policies:
- Type: Percent Value: 100 Period: 15 seconds
Deployment pods: 1 current / 1 desired
Conditions:
Type Status Reason Message
---- ------ ------ -------
AbleToScale True ReadyForNewScale recommended size matches current size
ScalingActive True ValidMetricFound the HPA was able to successfully calculate a replica count from pods metric http_requests_qps
ScalingLimited False DesiredWithinRange the desired count is within the acceptable range
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal SuccessfulRescale 25m horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 6; reason: pods metric http_requests_qps above target
Normal SuccessfulRescale 19m horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 4; reason: All metrics below target
Normal SuccessfulRescale 12m (x2 over 9h) horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 4; reason: pods metric http_requests_qps above target
Normal SuccessfulRescale 11m horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 5; reason: pods metric http_requests_qps above target
Normal SuccessfulRescale 9m40s (x2 over 12m) horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 2; reason: pods metric http_requests_qps above target
Normal SuccessfulRescale 9m24s (x4 over 10h) horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 3; reason: pods metric http_requests_qps above target
Normal SuccessfulRescale 7m54s (x3 over 9h) horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 2; reason: All metrics below target
Normal SuccessfulRescale 7m39s (x4 over 9h) horizontal-pod-autoscaler New size: 1; reason: All metrics below target 总结
基于自定义指标比如每秒请求量进行应用的水平扩容相比 CPU/内存 作为依据更加靠谱,适用于大部分的 web 系统。在突发流量时可以进行快速扩容,通过对伸缩行为的控制,可以减少副本数的抖动。Promeheus 作为流行应用的监控系统,在 Adapter 和 Aggregate API 的支持下,可以作为伸缩的指标。
目前 HPA 的 scale to 0 还在 alpha 的阶段,还需要关注副本从 0 到 N 的实效性。如果最小副本数大于0 ,对某些服务来说又会占用资源。接下来,我们会为尝试解决 0 到 N 的性能,以及资源占用的问题。
文章统一发布在公众号
云原生指北