iOS 底层探索: 学习大纲 OC篇
前言
- 这篇主要内容是分析消息转发机制
objc_msgSend。之前分析了cache_t的流程,只是探讨了Cache writers,这篇就来分析cache_fill之前的objc_msgSend,并引入方法本质的探索。
准备工作
- 复习:iOS 底层探索:方法缓存(cache_t)的分析
一 、了解runtime
在分析objc_msgSend 之前,必须了解一下runtime的定义和基本内容。
-
- runtime的官方文档:Objective-C Runtime Programming Guide
-
- runtime版本信息
Runtime有两个版本 ⼀个Legacy版本(早期版本) ,⼀个Modern版本(现⾏版本)
- 早期版本对应的编程接⼝:Objective-C 1.0
- 现⾏版本对应的编程接⼝:Objective-C 2.0
- 早期版本⽤于Objective-C 1.0, 32位的Mac OS X的平台上
- 现⾏版本:iPhone程序和Mac OS X v10.5 及以后的系统中的 64 位程序
-
- runtime 介绍:
将源代码转换为可执行的程序,通常要经过三个步骤:
编译、链接、运行。不同的编译语言,在这三个步骤中所进行的操作又有些不同。
编译时顾名思义就是正在编译的时候 . 那啥叫编译呢?就是编译器帮你把源代码翻译成机器能识别的代码 . 主要是对语言进行最基本的检查报错,即词法分析、语法分析等,是一个静态的阶段
运⾏时就是代码跑起来了.被装载到内存中去了 .
Objective-C 语言把一些决定性的工作从编译阶段、链接阶段推迟到运行时阶段的机制,使得 Objective-C 变得更加灵活。而实现 Objective-C 语言
运行时机制的一切基础就是Runtime。
Runtime实际上是一个库,这个库使我们可以在程序运行时动态的创建对象、检查对象,修改类和对象的方法。
-
4 .runtime 在oc中编译层和底层的关系图:
注:其中的compiler就是编译器LLVM, runtime system libarary 就是底层库。
-
- runtime 常用使用方式:
通过OC代码,例如 :
[person doSometing]通过NSObject方法,例如:
isKindOfClass通过Runtime API,例如:
class_getInstanceSize
二 、方法本质的探索
-
- 利用
clang查看方法编译之后的代码:
- 利用
clang使用步骤: isa与类关联的原理 有提过。
// - (void)sayHello;
// - (void)sayNB;
// + (void)sayCool;
/* @end */
// @implementation LGPerson
static void _I_LGPerson_sayNB(LGPerson * self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_pw_vld75tl93j1cx5xjwrjd80f00000gn_T_main_350155_mi_1);
}
static void _C_LGPerson_sayCool(Class self, SEL _cmd) {
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_pw_vld75tl93j1cx5xjwrjd80f00000gn_T_main_ebda0d_mi_2);
}
// @end
//main.m中方法的调用
LGPerson *person = [LGPerson alloc];
[person sayNB];
[person sayHello];
[LGPerson sayCool];
//clang编译后的底层实现
LGPerson *person = ((LGPerson *(*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)objc_getClass("LGPerson"), sel_registerName("alloc"));
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)person, sel_registerName("sayNB"));
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)person, sel_registerName("sayHello"));
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)objc_getClass("LGPerson"), sel_registerName("sayCool"));
可以看出:不论是类方法还是对象方法,被编译后都是执行objc_msgSend;所以方法的本质就是objc_msgSend消息发送;
结论:Objective-C 方法调用在编译时都会转化为对 C 函数objc_msgSend的调用。objc_msgSend(receiver,selector)是[receiver selector] 对应的C 函数。
注:
- 1、直接调用
objc_msgSend,需要导入头文件#import,其中包含了#include- 2、需要将target --> Build Setting -->搜索msg -- 将enable strict checking of obc_msgSend calls由YES 改为NO,将严厉的检查机制关掉,否则objc_msgSend的参数会报错
3.拓展:子类调用父类的对象方法(objc_msgSend 和 objc_msgSendSuper)
注:解析objc_msgSendSuper
OBJC_EXPORT id _Nullable
objc_msgSendSuper(struct objc_super * _Nonnull super, SEL _Nonnull op, ...)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0, 2.0);
#endif
/// Specifies the superclass of an instance. 指定实例的父类。
struct objc_super {
/// Specifies an instance of a class. 指定类的实例。
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull id receiver;
/// Specifies the particular superclass of the instance to message. 指定message实例的特定父类。
#if !defined(__cplusplus) && !__OBJC2__
/* For compatibility with old objc-runtime.h header */
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull Class class;
#else
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull Class super_class;
#endif
/* super_class is the first class to search */
};
#endif
-
objc_msgSendSuper方法中有两个参数(结构体,sel),其结构体类型是objc_super定义的结构体对象,且需要指定receiver和super_class两个属性
4 : 提出疑问:为什么LGPerson类中没有sayHello 方法 ,却还是能找到父类LGTeacher的sayHello的呢?是怎么找到的呢?是如何执行的呢? 带着疑问我们开始了objc_msgSend的快速查找原理的探索。
二 、探索objc_msgSend 快速查找流程
老办法查看源码:在objc4-781源码中,搜索objc_msgSend,由于我们日常开发的都是架构是arm64,所以需要在arm64.s后缀的文件中查找objc_msgSend源码实现,打开一看全是汇编,瞬间懵逼。arm64汇编指令集如图:
在源码进行注释:
/*
---- 消息发送 -- 汇编入口--objc_msgSend主要是拿到接收者的isa信息
*/
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
/*
---- 无窗口
*/
UNWIND _objc_msgSend, NoFrame
/*
---- p0 和空#0对比,即判断接收者是否存在,其中p0是objc_msgSend的第一个参数-消息接收者receiver
*/
cmp p0, #0 // nil check and tagged pointer check
//---- le小于 --支持taggedpointer(小对象类型)的流程
#if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
b.le LNilOrTagged // (MSB tagged pointer looks negative)
#else
//---- p0 等于 0 时,直接返回 空
b.eq LReturnZero
#endif
//---- p0即receiver 肯定存在的流程
//---- 根据对象拿出isa ,即从x0寄存器指向的地址 取出 isa,存入 p13寄存器
ldr p13, [x0] // p13 = isa
//---- 在64位架构下通过 p16 = isa(p13) & ISA_MASK,拿出shiftcls信息,得到class信息
GetClassFromIsa_p16 p13 // p16 = class
LGetIsaDone:
// calls imp or objc_msgSend_uncached
//---- 如果有isa,走到CacheLookup 即缓存查找流程,也就是所谓的sel-imp快速查找流程
CacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSend
#if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
LNilOrTagged:
//---- 等于空,返回空
b.eq LReturnZero // nil check
// tagged
adrp x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes@PAGE
add x10, x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes@PAGEOFF
ubfx x11, x0, #60, #4
ldr x16, [x10, x11, LSL #3]
adrp x10, _OBJC_CLASS_$___NSUnrecognizedTaggedPointer@PAGE
add x10, x10, _OBJC_CLASS_$___NSUnrecognizedTaggedPointer@PAGEOFF
cmp x10, x16
b.ne LGetIsaDone
// ext tagged
adrp x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_ext_classes@PAGE
add x10, x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_ext_classes@PAGEOFF
ubfx x11, x0, #52, #8
ldr x16, [x10, x11, LSL #3]
b LGetIsaDone
// SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
#endif
-
- 我们想在平时写oc的方法的时候假如需要传参,是不是也需要对参数进行判断,提高健壮性。当然在汇编中也是一样,我们在使用
objc_msgSend(receiver,selector);也需要判断传入receiver和selector;
- 我们想在平时写oc的方法的时候假如需要传参,是不是也需要对参数进行判断,提高健壮性。当然在汇编中也是一样,我们在使用
-
- 我们需要明确我们我们的目的:找到cache中缓存的方法。
弄清这两点之后,我们再去慢慢解读源代码objc_msgSend。
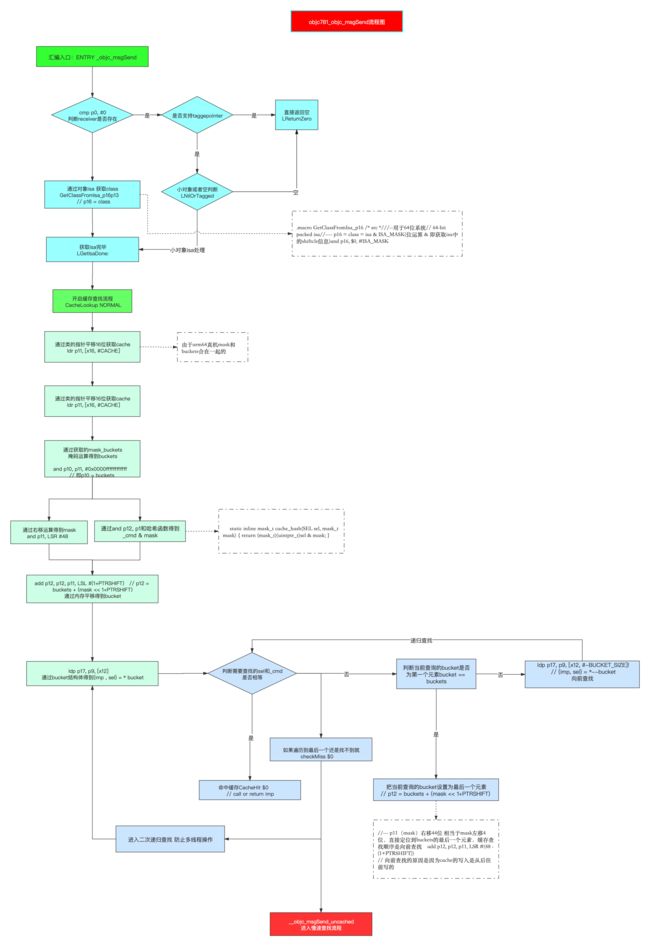
流程解析:
【步骤1】:判断objc_msgSend方法的第一个参数receiver是否为空:
- 如果支持tagged pointer,跳转至LNilOrTagged;
- 如果小对象为空,则直接返回空,即LReturnZero
【步骤2】:receiver不为空,从receiver中取出isa,通过GetClassFromIsa_p16中,arm64架构下通过isa & ISA_MASK 获取shiftcls位域的类信息,执行 CacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSend
注:
ldr p13, [x0] // p13 = isa
GetClassFromIsa_p16 p13 // p16 = class这两句的意思就是将isa 赋值给13号寄存器,通过13号寄存器中的isa,找到类信息,然后将类信息赋值给16号寄存器。
GetClassFromIsa_p16源码如下:
.macro GetClassFromIsa_p16 /* src */
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
// Indexed isa
//---- 将isa的值存入p16寄存器
mov p16, $0 // optimistically set dst = src
tbz p16, #ISA_INDEX_IS_NPI_BIT, 1f // done if not non-pointer isa -- 判断是否是 nonapointer isa
// isa in p16 is indexed
//---- 将_objc_indexed_classes所在的页的基址 读入x10寄存器
adrp x10, _objc_indexed_classes@PAGE
//---- x10 = x10 + _objc_indexed_classes(page中的偏移量) --x10基址 根据 偏移量 进行 内存偏移
add x10, x10, _objc_indexed_classes@PAGEOFF
//---- 从p16的第ISA_INDEX_SHIFT位开始,提取 ISA_INDEX_BITS 位 到 p16寄存器,剩余的高位用0补充
ubfx p16, p16, #ISA_INDEX_SHIFT, #ISA_INDEX_BITS // extract index
ldr p16, [x10, p16, UXTP #PTRSHIFT] // load class from array
1:
//--用于64位系统
#elif __LP64__
// 64-bit packed isa
//---- p16 = class = isa & ISA_MASK(位运算 & 即获取isa中的shiftcls信息)
and p16, $0, #ISA_MASK
#else
// 32-bit raw isa ---- 用于32位系统
mov p16, $0
#endif
.endmacro
【步骤3】 :缓存方法的查找
CacheLookup 缓存查找汇编源码
.macro CacheLookup
// GETIMP:
// The cache-miss is just returning NULL (setting x0 to 0)
//
// NORMAL and LOOKUP:
// - x0 contains the receiver
// - x1 contains the selector
// - x16 contains the isa
// - other registers are set as per calling conventions
//
LLookupStart$1:
/****------------------step1---------------------****/
//---- p1 = SEL, p16 = isa --- #define CACHE (2 * __SIZEOF_POINTER__),其中 __SIZEOF_POINTER__表示pointer的大小 ,即 2*8 = 16
//---- p11 = mask|buckets -- 从x16(即isa)中平移16字节,取出cache 存入p11寄存器 -- isa距离cache 正好16字节:isa(8字节)-superClass(8字节)-cache(mask高16位 + buckets低48位)
ldr p11, [x16, #CACHE]
/****------------------step2---------------------****/
//---- 64位真机
#if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16
//--- p11(cache) & 0x0000ffffffffffff ,mask高16位抹零,得到buckets 存入p10寄存器-- 即去掉mask,留下buckets
and p10, p11, #0x0000ffffffffffff // p10 = buckets
//--- p11(cache)右移48位,得到mask(即p11 存储mask),mask & p1(msgSend的第二个参数 cmd-sel) ,得到sel-imp的下标index(即搜索下标) 存入p12(cache insert写入时的哈希下标计算是 通过 sel & mask,读取时也需要通过这种方式)
and p12, p1, p11, LSR #48 // x12 = _cmd & mask
//--- 非64位真机
#elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4
and p10, p11, #~0xf // p10 = buckets
and p11, p11, #0xf // p11 = maskShift
mov p12, #0xffff
lsr p11, p12, p11 // p11 = mask = 0xffff >> p11
and p12, p1, p11 // x12 = _cmd & mask
#else
#error Unsupported cache mask storage for ARM64.
#endif
/****------------------step3---------------------****/
//--- p12是下标 p10是buckets数组首地址,下标 * 1<<4(即16) 得到实际内存的偏移量,通过buckets的首地址偏移,获取bucket存入p12寄存器
//--- LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT)-- 实际含义就是得到一个bucket占用的内存大小 -- 相当于mask = occupied -1-- _cmd & mask -- 取余数
add p12, p10, p12, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT)
// p12 = buckets + ((_cmd & mask) << (1+PTRSHIFT)) -- PTRSHIFT是3
//--- 从x12(即p12)中取出 bucket 分别将imp和sel 存入 p17(存储imp) 和 p9(存储sel)
ldp p17, p9, [x12] // {imp, sel} = *bucket
/****------------------step4---------------------****/
//--- 比较 sel 与 p1(传入的参数cmd)
1: cmp p9, p1 // if (bucket->sel != _cmd)
//--- 如果不相等,即没有找到,请跳转至 2f
b.ne 2f // scan more
//--- 如果相等 即执行cacheHit ,直接返回imp
CacheHit $0 // call or return imp
/****------------------step5 和 step6---------------------****/
2: // not hit: p12 = not-hit bucket
//--- 如果一直都找不到, 因为是normal ,跳转至__objc_msgSend_uncached
CheckMiss $0 // miss if bucket->sel == 0
//--- 判断p12(下标对应的bucket) 是否 等于 p10(buckets数组第一个元素,),如果等于,则跳转至第3步
cmp p12, p10 // wrap if bucket == buckets
//--- 定位到最后一个元素(即第一个bucket)
b.eq 3f
//--- 从x12(即p12 buckets首地址)- 实际需要平移的内存大小BUCKET_SIZE,得到得到第二个bucket元素,imp-sel分别存入p17-p9,即向前查找
ldp p17, p9, [x12, #-BUCKET_SIZE]! // {imp, sel} = *--bucket
//--- 跳转至第1步,继续对比 sel 与 cmd
b 1b // loop
3: // wrap: p12 = first bucket, w11 = mask
#if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16
//--- 人为设置到最后一个元素
//--- p11(mask)右移44位 相当于mask左移4位,直接定位到buckets的最后一个元素,缓存查找顺序是向前查找
add p12, p12, p11, LSR #(48 - (1+PTRSHIFT))
// p12 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT)
#elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4
add p12, p12, p11, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT)
// p12 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT)
#else
#error Unsupported cache mask storage for ARM64.
#endif
/****------------------step6---------------------****/
// Clone scanning loop to miss instead of hang when cache is corrupt.
// The slow path may detect any corruption and halt later.
//--- 再查找一遍缓存()
//--- 拿到x12(即p12)bucket中的 imp-sel 分别存入 p17-p9
ldp p17, p9, [x12] // {imp, sel} = *bucket
//--- 比较 sel 与 p1(传入的参数cmd)
1: cmp p9, p1 // if (bucket->sel != _cmd)
//--- 如果不相等,即走到第二步
b.ne 2f // scan more
//--- 如果相等 即命中,直接返回imp
CacheHit $0 // call or return imp
2: // not hit: p12 = not-hit bucket
//--- 如果一直找不到,则CheckMiss
CheckMiss $0 // miss if bucket->sel == 0
//--- 判断p12(下标对应的bucket) 是否 等于 p10(buckets数组第一个元素)-- 表示前面已经没有了,但是还是没有找到
cmp p12, p10 // wrap if bucket == buckets
b.eq 3f //如果等于,跳转至第3步
//--- 从x12(即p12 buckets首地址)- 实际需要平移的内存大小BUCKET_SIZE,得到得到第二个bucket元素,imp-sel分别存入p17-p9,即向前查找
ldp p17, p9, [x12, #-BUCKET_SIZE]! // {imp, sel} = *--bucket
//--- 跳转至第1步,继续对比 sel 与 cmd
b 1b // loop
LLookupEnd$1:
LLookupRecover$1:
3: // double wrap
//--- 跳转至JumpMiss 因为是normal ,跳转至__objc_msgSend_uncached
JumpMiss $0
.endmacro
//以下是最后跳转的汇编函数
.macro CacheHit
.if $0 == NORMAL
TailCallCachedImp x17, x12, x1, x16 // authenticate and call imp
.elseif $0 == GETIMP
mov p0, p17
cbz p0, 9f // don't ptrauth a nil imp
AuthAndResignAsIMP x0, x12, x1, x16 // authenticate imp and re-sign as IMP
9: ret // return IMP
.elseif $0 == LOOKUP
// No nil check for ptrauth: the caller would crash anyway when they
// jump to a nil IMP. We don't care if that jump also fails ptrauth.
AuthAndResignAsIMP x17, x12, x1, x16 // authenticate imp and re-sign as IMP
ret // return imp via x17
.else
.abort oops
.endif
.endmacro
.macro CheckMiss
// miss if bucket->sel == 0
.if $0 == GETIMP
//--- 如果为GETIMP ,则跳转至 LGetImpMiss
cbz p9, LGetImpMiss
.elseif $0 == NORMAL
//--- 如果为NORMAL ,则跳转至 __objc_msgSend_uncached
cbz p9, __objc_msgSend_uncached
.elseif $0 == LOOKUP
//--- 如果为LOOKUP ,则跳转至 __objc_msgLookup_uncached
cbz p9, __objc_msgLookup_uncached
.else
.abort oops
.endif
.endmacro
.macro JumpMiss
.if $0 == GETIMP
b LGetImpMiss
.elseif $0 == NORMAL
b __objc_msgSend_uncached
.elseif $0 == LOOKUP
b __objc_msgLookup_uncached
.else
.abort oops
.endif
.endmacro
以上内容分为以下几步
- step1:通过
cache首地址平移16字节(因为在objc_class中,首地址距离cache正好16字节,即isa占8字节,superClass占8字节),获取cahce,cache中高16位存mask,低48位存buckets,ldr p11, [x16, #CACHE],将p11赋值cahce;- CACHE 这是一个宏;
step2 :从cache中分别取出buckets和mask,并由mask根据哈希算法计算出哈希下标
通过
cache和掩码(即0x0000ffffffffffff)的&运算,将高16位mask抹零,得到buckets指针地址,即p10 = buckets将
cache右移48位,得到mask,即p11 = mask将
objc_msgSend的参数p1(即第二个参数_cmd)& msak,通过哈希算法,得到需要查找存储sel-imp的bucket下标index,即p12 = index = _cmd & mask,为什么通过这种方式呢?因为在存储sel-imp时,也是通过同样哈希算法计算哈希下标进行存储,所以读取也需要通过同样的方式读取,如下
mask_t m = capacity - 1;
mask_t begin = cache_hash(sel, m);
mask_t i = begin;
static inline mask_t cache_hash(SEL sel, mask_t mask)
{
return (mask_t)(uintptr_t)sel & mask;
}
-
step3 :根据所得的
哈希下标index和buckets首地址,取出哈希下标对应的bucket其中
PTRSHIFT等于3,左移1+3位(即2^4 = 16字节)的目的是计算出一个bucket实际占用的大小,结构体bucket_t中sel占8字节,imp占8字节根据计算的哈希下标
index 乘以单个bucket占用的内存大小,得到buckets首地址在实际内存中的偏移量通过
首地址 + 实际偏移量,获取哈希下标index对应的bucket
step4 :根据获取的
bucket,取出其中的sel存入p17,即p17 = sel,取出imp存入p9,即p9 = imp-
step5 :第一次递归循环
比较获取的
bucket中sel与objc_msgSend的第二个参数的_cmd(即p1)是否相等如果相等,则执行缓存命中
CacheHit,返回imp-
如果不相等,有以下两种情况
如果一直都找不到,直接跳转至
CheckMiss,因为$0是normal,会跳转至__objc_msgSend_uncached,进入慢速查找流程如果
根据index获取的bucket等于buckets的第一个元素,则人为的将当前bucket设置为buckets的最后一个元素(通过buckets首地址+mask右移44位(等同于左移4位)直接定位到bucker的最后一个元素),然后继续向前查找,进行递归循环
step6 :第二次递归循环:重复step5的操作,与step5中
唯一区别是,如果当前的bucket等于 buckets的第一个元素,则直接跳转至JumpMiss,此时的$0是normal,也是直接跳转至__objc_msgSend_uncached,即进入慢速查找流程
三 、总结
- objc_msgSend 用汇编写的原因:
- 1.因为c语言中不可能通过写一个函数来保留未知的参数,并且跳转到一个任意的函数指针。c语言没有满足这件事的必要特性;
-
- objc_msgSend调用频繁,必须足够快,在 Objective-C Runtime 中调用频率较高的函数好多都用汇编写的。
- objc_msgSend流程图