参考W3C Spring教程
8. AOP
Spring 框架的一个关键组件是面向方面的编程(AOP)框架。面向方面的编程需要把程序逻辑分解成不同的部分称为所谓的关注点。跨一个应用程序的多个点的功能被称为横切关注点,这些横切关注点在概念上独立于应用程序的业务逻辑。有各种各样的常见的很好的方面的例子,如日志记录、审计、声明式事务、安全性和缓存等。
在 OOP 中,关键单元模块度是类,而在 AOP 中单元模块度是方面。依赖注入帮助你对应用程序对象相互解耦, AOP 可以帮助你从它们所影响的对象中对横切关注点解耦。AOP 是像编程语言的触发物,如 Perl,.NET,Java 或者其他。
Spring AOP 模块提供拦截器来拦截一个应用程序,例如,当执行一个方法时,你可以在方法执行之前或之后添加额外的功能。-
AOP术语
1)连接点(Joinpoint)
程序执行的某个特定位置:如类开始初始化前、类初始化后、类某个方法调用前、调用后、方法抛出异常后。一个类或一段程序代码拥有一些具有边界性质的特定点,这些点中的特定点就称为“连接点”。Spring仅支持方法的连接点,即仅能在方法调用前、方法调用后、方法抛出异常时以及方法调用前后这些程序执行点织入增强。连接点由两个信息确定:第一是用方法表示的程序执行点;第二是用相对点表示的方位。2)切点(Pointcut)
每个程序类都拥有多个连接点,如一个拥有两个方法的类,这两个方法都是连接点,即连接点是程序类中客观存在的事物。AOP通过“切点”定位特定的连接点。连接点相当于数据库中的记录,而切点相当于查询条件。切点和连接点不是一对一的关系,一个切点可以匹配多个连接点。在Spring中,切点通过org.springframework.aop.Pointcut接口进行描述,它使用类和方法作为连接点的查询条件,Spring AOP的规则解析引擎负责切点所设定的查询条件,找到对应的连接点。其实确切地说,不能称之为查询连接点,因为连接点是方法执行前、执行后等包括方位信息的具体程序执行点,而切点只定位到某个方法上,所以如果希望定位到具体连接点上,还需要提供方位信息。3)增强(Advice)
增强是织入到目标类连接点上的一段程序代码,在Spring中,增强除用于描述一段程序代码外,还拥有另一个和连接点相关的信息,这便是执行点的方位。结合执行点方位信息和切点信息,我们就可以找到特定的连接点。4)目标对象(Target)
增强逻辑的织入目标类。如果没有AOP,目标业务类需要自己实现所有逻辑,而在AOP的帮助下,目标业务类只实现那些非横切逻辑的程序逻辑,而性能监视和事务管理等这些横切逻辑则可以使用AOP动态织入到特定的连接点上。5)引介(Introduction)
引介是一种特殊的增强,它为类添加一些属性和方法。这样,即使一个业务类原本没有实现某个接口,通过AOP的引介功能,我们可以动态地为该业务类添加接口的实现逻辑,让业务类成为这个接口的实现类。6)织入(Weaving)
织入是将增强添加对目标类具体连接点上的过程。AOP像一台织布机,将目标类、增强或引介通过AOP这台织布机天衣无缝地编织到一起。根据不同的实现技术,AOP有三种织入的方式:
a、编译期织入,这要求使用特殊的Java编译器。
b、类装载期织入,这要求使用特殊的类装载器。
c、动态代理织入,在运行期为目标类添加增强生成子类的方式。
Spring采用动态代理织入,而AspectJ采用编译期织入和类装载期织入。7)代理(Proxy)
一个类被AOP织入增强后,就产出了一个结果类,它是融合了原类和增强逻辑的代理类。根据不同的代理方式,代理类既可能是和原类具有相同接口的类,也可能就是原类的子类,所以我们可以采用调用原类相同的方式调用代理类。8)切面(Aspect)
切面由切点和增强(引介)组成,它既包括了横切逻辑的定义,也包括了连接点的定义,Spring AOP就是负责实施切面的框架,它将切面所定义的横切逻辑织入到切面所指定的连接点中。 -
通知的类型
8.1 基于AOP的XML架构
- 需要使用以下 AspectJ 库文件
aspectjrt.jar
aspectjweaver.jar
aspectj.jar
aopalliance.jar
8.2 基于AOP的@AspectJ
- 同样需要使用以下 AspectJ 库文件
aspectjrt.jar
aspectjweaver.jar
aspectj.jar
aopalliance.jar - @AspectJ 作为通过 Java 5 注释注释的普通的 Java 类,它指的是声明 aspects 的一种风格。通过在你的基于架构的 XML 配置文件中包含以下元素,@AspectJ 支持是可用的。
- 声明一个 aspect
package org.xyz;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect
public class AspectModule {
}
- 声明一个Pointcut
一个切入点有助于确定使用不同建议执行的感兴趣的连接点(即方法)。在处理基于配置的 XML 架构时,切入点的声明有两个部分:
1)一个切入点表达式决定了我们感兴趣的哪个方法会真正被执行。
2)一个切入点标签包含一个名称和任意数量的参数。方法的真正内容是不相干的,并且实际上它应该是空的。
下面的示例中定义了一个名为 ‘businessService’ 的切入点,该切入点将与 com.xyz.myapp.service 包下的类中可用的每一个方法相匹配:
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Pointcut("execution(* com.xyz.myapp.service.*.*(..))") // expression
private void businessService() {} // signature
下面的示例中定义了一个名为 ‘getname’ 的切入点,该切入点将与 com.tutorialspoint 包下的 Student 类中的 getName() 方法相匹配:
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Pointcut("execution(* com.tutorialspoint.Student.getName(..))")
private void getname() {}
- 声明一个Advice(增强)
可以使用 @{ADVICE-NAME} 注释声明五个建议中的任意一个。假设已经定义了一个切入点标签方法 businessService():
@Before("businessService()")
public void doBeforeTask(){
...
}
@After("businessService()")
public void doAfterTask(){
...
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "businessService()", returning="retVal")
public void doAfterReturnningTask(Object retVal){
// you can intercept retVal here.
...
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "businessService()", throwing="ex")
public void doAfterThrowingTask(Exception ex){
// you can intercept thrown exception here.
...
}
@Around("businessService()")
public void doAroundTask(){
...
}
- 一个示例
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
@Aspect
public class Logging {
/** Following is the definition for a pointcut to select
* all the methods available. So advice will be called
* for all the methods.
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.tutorialspoint.*.*(..))")
private void selectAll(){}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* before a selected method execution.
*/
@Before("selectAll()")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("Going to setup student profile.");
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* after a selected method execution.
*/
@After("selectAll()")
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("Student profile has been setup.");
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* when any method returns.
*/
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "selectAll()", returning="retVal")
public void afterReturningAdvice(Object retVal){
System.out.println("Returning:" + retVal.toString() );
}
/**
* This is the method which I would like to execute
* if there is an exception raised by any method.
*/
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "selectAll()", throwing = "ex")
public void AfterThrowingAdvice(IllegalArgumentException ex){
System.out.println("There has been an exception: " + ex.toString());
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
System.out.println("Age : " + age );
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
System.out.println("Name : " + name );
return name;
}
public void printThrowException(){
System.out.println("Exception raised");
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
student.getName();
student.getAge();
student.printThrowException();
}
}
Going to setup student profile.
Name : Zara
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:Zara
Going to setup student profile.
Age : 11
Student profile has been setup.
Returning:11
Going to setup student profile.
Exception raised
Student profile has been setup.
There has been an exception: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
.....
other exception content
9. JDBC框架
在使用普通的 JDBC 数据库时,就会很麻烦的写不必要的代码来处理异常,打开和关闭数据库连接等。但 Spring JDBC 框架负责所有的低层细节,从开始打开连接,准备和执行 SQL 语句,处理异常,处理事务,到最后关闭连接。
所以当从数据库中获取数据时,你所做的是定义连接参数,指定要执行的 SQL 语句,每次迭代完成所需的工作。
Spring JDBC 提供几种方法和数据库中相应的不同的类与接口。我将给出使用 JdbcTemplate 类框架的经典和最受欢迎的方法。这是管理所有数据库通信和异常处理的核心框架类。JdbcTemplate 类
JdbcTemplate 类执行 SQL 查询、更新语句和存储过程调用,执行迭代结果集和提取返回参数值。它也捕获 JDBC 异常并转换它们到 org.springframework.dao 包中定义的通用类、更多的信息、异常层次结构。
JdbcTemplate 类的实例是线程安全配置的。所以你可以配置 JdbcTemplate 的单个实例,然后将这个共享的引用安全地注入到多个 DAOs 中。
使用 JdbcTemplate 类时常见的做法是在你的 Spring 配置文件中配置数据源,然后共享数据源 bean 依赖注入到 DAO 类中,并在数据源的设值函数中创建了 JdbcTemplate。配置数据源
我们在数据库 TEST 中创建一个数据库表 Student。假设你正在使用 MySQL 数据库,如果你使用其他数据库,那么你可以改变你的 DDL 和相应的 SQL 查询。
CREATE TABLE Student(
ID INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
现在,我们需要提供一个数据源到 JdbcTemplate 中,所以它可以配置本身来获得数据库访问。你可以在 XML 文件中配置数据源,其中一段代码如下所示:
数据访问对象(DAO)
DAO 代表常用的数据库交互的数据访问对象。DAOs 提供一种方法来读取数据并将数据写入到数据库中,它们应该通过一个接口显示此功能,应用程序的其余部分将访问它们。
在 Spring 中,数据访问对象(DAO)支持很容易用统一的方法使用数据访问技术,如 JDBC、Hibernate、JPA 或者 JDO。执行 SQL 语句
我们看看如何使用 SQL 和 jdbcTemplate 对象在数据库表中执行 CRUD(创建、读取、更新和删除)操作。
查询一个整数类型:
String SQL = "select count(*) from Student";
int rowCount = jdbcTemplateObject.queryForInt( SQL );
查询并返回一个对象:
String SQL = "select * from Student where id = ?";
Student student = jdbcTemplateObject.queryForObject(SQL,
new Object[]{10}, new StudentMapper());
public class StudentMapper implements RowMapper {
public Student mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Student student = new Student();
student.setID(rs.getInt("id"));
student.setName(rs.getString("name"));
student.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
return student;
}
}
- 执行 DDL 语句
你可以使用 jdbcTemplate 中的 execute(..) 方法来执行任何 SQL 语句或 DDL 语句。下面是一个使用 CREATE 语句创建一个表的示例:
String SQL = "CREATE TABLE Student( " +
"ID INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, " +
"NAME VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, " +
"AGE INT NOT NULL, " +
"PRIMARY KEY (ID));"
jdbcTemplateObject.execute( SQL );
9.1 JDBC示例
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public interface StudentDAO {
/**
* This is the method to be used to initialize
* database resources ie. connection.
*/
public void setDataSource(DataSource ds);
/**
* This is the method to be used to create
* a record in the Student table.
*/
public void create(String name, Integer age);
/**
* This is the method to be used to list down
* a record from the Student table corresponding
* to a passed student id.
*/
public Student getStudent(Integer id);
/**
* This is the method to be used to list down
* all the records from the Student table.
*/
public List listStudents();
/**
* This is the method to be used to delete
* a record from the Student table corresponding
* to a passed student id.
*/
public void delete(Integer id);
/**
* This is the method to be used to update
* a record into the Student table.
*/
public void update(Integer id, Integer age);
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
private Integer id;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
public class StudentMapper implements RowMapper {
public Student mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
student.setName(rs.getString("name"));
student.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
return student;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class StudentJDBCTemplate implements StudentDAO {
private DataSource dataSource;
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateObject;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.jdbcTemplateObject = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
public void create(String name, Integer age) {
String SQL = "insert into Student (name, age) values (?, ?)";
jdbcTemplateObject.update( SQL, name, age);
System.out.println("Created Record Name = " + name + " Age = " + age);
return;
}
public Student getStudent(Integer id) {
String SQL = "select * from Student where id = ?";
Student student = jdbcTemplateObject.queryForObject(SQL,
new Object[]{id}, new StudentMapper());
return student;
}
public List listStudents() {
String SQL = "select * from Student";
List students = jdbcTemplateObject.query(SQL,
new StudentMapper());
return students;
}
public void delete(Integer id){
String SQL = "delete from Student where id = ?";
jdbcTemplateObject.update(SQL, id);
System.out.println("Deleted Record with ID = " + id );
return;
}
public void update(Integer id, Integer age){
String SQL = "update Student set age = ? where id = ?";
jdbcTemplateObject.update(SQL, age, id);
System.out.println("Updated Record with ID = " + id );
return;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.tutorialspoint.StudentJDBCTemplate;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
StudentJDBCTemplate studentJDBCTemplate =
(StudentJDBCTemplate)context.getBean("studentJDBCTemplate");
System.out.println("------Records Creation--------" );
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Zara", 11);
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Nuha", 2);
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Ayan", 15);
System.out.println("------Listing Multiple Records--------" );
List students = studentJDBCTemplate.listStudents();
for (Student record : students) {
System.out.print("ID : " + record.getId() );
System.out.print(", Name : " + record.getName() );
System.out.println(", Age : " + record.getAge());
}
System.out.println("----Updating Record with ID = 2 -----" );
studentJDBCTemplate.update(2, 20);
System.out.println("----Listing Record with ID = 2 -----" );
Student student = studentJDBCTemplate.getStudent(2);
System.out.print("ID : " + student.getId() );
System.out.print(", Name : " + student.getName() );
System.out.println(", Age : " + student.getAge());
}
}
------Records Creation--------
Created Record Name = Zara Age = 11
Created Record Name = Nuha Age = 2
Created Record Name = Ayan Age = 15
------Listing Multiple Records--------
ID : 1, Name : Zara, Age : 11
ID : 2, Name : Nuha, Age : 2
ID : 3, Name : Ayan, Age : 15
----Updating Record with ID = 2 -----
Updated Record with ID = 2
----Listing Record with ID = 2 -----
ID : 2, Name : Nuha, Age : 20
9.2 SQL存储过程
- SimpleJdbcCall 类可以被用于调用一个包含 IN 和 OUT 参数的存储过程。
- 创建表
CREATE TABLE Student(
ID INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
- 创建存储过程
DELIMITER $$
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `TEST`.`getRecord` $$
CREATE PROCEDURE `TEST`.`getRecord` (
IN in_id INTEGER,
OUT out_name VARCHAR(20),
OUT out_age INTEGER)
BEGIN
SELECT name, age
INTO out_name, out_age
FROM Student where id = in_id;
END $$
DELIMITER ;
- 程序示例如下
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public interface StudentDAO {
/**
* This is the method to be used to initialize
* database resources ie. connection.
*/
public void setDataSource(DataSource ds);
/**
* This is the method to be used to create
* a record in the Student table.
*/
public void create(String name, Integer age);
/**
* This is the method to be used to list down
* a record from the Student table corresponding
* to a passed student id.
*/
public Student getStudent(Integer id);
/**
* This is the method to be used to list down
* all the records from the Student table.
*/
public List listStudents();
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private String name;
private Integer id;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
public class StudentMapper implements RowMapper {
public Student mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
student.setName(rs.getString("name"));
student.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
return student;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.simple.SimpleJdbcCall;
public class StudentJDBCTemplate implements StudentDAO {
private DataSource dataSource;
private SimpleJdbcCall jdbcCall;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.jdbcCall = new SimpleJdbcCall(dataSource).
withProcedureName("getRecord");
}
public void create(String name, Integer age) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateObject = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
String SQL = "insert into Student (name, age) values (?, ?)";
jdbcTemplateObject.update( SQL, name, age);
System.out.println("Created Record Name = " + name + " Age = " + age);
return;
}
public Student getStudent(Integer id) {
SqlParameterSource in = new MapSqlParameterSource().
addValue("in_id", id);
Map out = jdbcCall.execute(in);
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(id);
student.setName((String) out.get("out_name"));
student.setAge((Integer) out.get("out_age"));
return student;
}
public List listStudents() {
String SQL = "select * from Student";
List students = jdbcTemplateObject.query(SQL,
new StudentMapper());
return students;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.tutorialspoint.StudentJDBCTemplate;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
StudentJDBCTemplate studentJDBCTemplate =
(StudentJDBCTemplate)context.getBean("studentJDBCTemplate");
System.out.println("------Records Creation--------" );
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Zara", 11);
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Nuha", 2);
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Ayan", 15);
System.out.println("------Listing Multiple Records--------" );
List students = studentJDBCTemplate.listStudents();
for (Student record : students) {
System.out.print("ID : " + record.getId() );
System.out.print(", Name : " + record.getName() );
System.out.println(", Age : " + record.getAge());
}
System.out.println("----Listing Record with ID = 2 -----" );
Student student = studentJDBCTemplate.getStudent(2);
System.out.print("ID : " + student.getId() );
System.out.print(", Name : " + student.getName() );
System.out.println(", Age : " + student.getAge());
}
}
------Records Creation--------
Created Record Name = Zara Age = 11
Created Record Name = Nuha Age = 2
Created Record Name = Ayan Age = 15
------Listing Multiple Records--------
ID : 1, Name : Zara, Age : 11
ID : 2, Name : Nuha, Age : 2
ID : 3, Name : Ayan, Age : 15
----Listing Record with ID = 2 -----
ID : 2, Name : Nuha, Age : 2
10. 事务管理
事务管理
一个数据库事务是一个被视为单一的工作单元的操作序列。这些操作应该要么完整地执行,要么完全不执行。事务管理是一个重要组成部分,RDBMS 面向企业应用程序,以确保数据完整性和一致性。事务的概念可以描述为具有以下四个关键属性说成是 ACID:
1)原子性:事务应该当作一个单独单元的操作,这意味着整个序列操作要么是成功,要么是失败的。
2)一致性:这表示数据库的引用完整性的一致性,表中唯一的主键等。
3)隔离性:可能同时处理很多有相同的数据集的事务,每个事务应该与其他事务隔离,以防止数据损坏。
4)持久性:一个事务一旦完成全部操作后,这个事务的结果必须是永久性的,不能因系统故障而从数据库中删除。
一个真正的 RDBMS 数据库系统将为每个事务保证所有的四个属性。使用 SQL 发布到数据库中的事务的简单视图如下:
1)使用 begin transaction 命令开始事务。
2)使用 SQL 查询语句执行各种删除、更新或插入操作。
3)如果所有的操作都成功,则执行提交操作,否则回滚所有操作。
Spring 框架在不同的底层事务管理 APIs 的顶部提供了一个抽象层。Spring 的事务支持旨在通过添加事务能力到 POJOs 来提供给 EJB 事务一个选择方案。Spring 支持编程式和声明式事务管理。EJBs 需要一个应用程序服务器,但 Spring 事务管理可以在不需要应用程序服务器的情况下实现。局部事物 vs. 全局事务
局部事务是特定于一个单一的事务资源,如一个 JDBC 连接,而全局事务可以跨多个事务资源事务,如在一个分布式系统中的事务。
局部事务管理在一个集中的计算环境中是有用的,该计算环境中应用程序组件和资源位于一个单位点,而事务管理只涉及到一个运行在一个单一机器中的本地数据管理器。局部事务更容易实现。
全局事务管理需要在分布式计算环境中,所有的资源都分布在多个系统中。在这种情况下事务管理需要同时在局部和全局范围内进行。分布式或全局事务跨多个系统执行,它的执行需要全局事务管理系统和所有相关系统的局部数据管理人员之间的协调。-
编程式 vs. 声明式
Spring 支持两种类型的事务管理:
1)编程式事务管理 :这意味着你在编程的帮助管理事务。这给了你极大的灵活性,但却很难维护。
2)声明式事务管理 :这意味着你从业务代码中分离事务管理。你仅仅使用注释或 XML 配置来管理事务。
声明式事务管理比编程式事务管理更可取,尽管它不如编程式事务管理灵活,但它允许你通过代码控制事务。但作为一种横切关注点,声明式事务管理可以使用 AOP 方法进行模块化。Spring 支持使用 Spring AOP 框架的声明式事务管理。
- Spring 事务抽象
Spring 事务抽象的关键是由 org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager 接口定义,如下所示:
public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition);
throws TransactionException;
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
}
TransactionDefinition 是在 Spring 中事务支持的核心接口
public interface TransactionDefinition {
int getPropagationBehavior();
int getIsolationLevel();
String getName();
int getTimeout();
boolean isReadOnly();
}
TransactionStatus 接口为事务代码提供了一个简单的方法来控制事务的执行和查询事务状态。
public interface TransactionStatus extends SavepointManager {
boolean isNewTransaction();
boolean hasSavepoint();
void setRollbackOnly();
boolean isRollbackOnly();
boolean isCompleted();
}
10.1 编程式事务管理
- 建立两张表
CREATE TABLE Student(
ID INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
NAME VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
CREATE TABLE Marks(
SID INT NOT NULL,
MARKS INT NOT NULL,
YEAR INT NOT NULL
);
- 让我们直接使用 PlatformTransactionManager 来实现编程式方法从而实现事务。要开始一个新事务,你需要有一个带有适当的 transaction 属性的 TransactionDefinition 的实例。这个例子中,我们使用默认的 transaction 属性简单的创建了 DefaultTransactionDefinition 的一个实例。
当 TransactionDefinition 创建后,你可以通过调用 getTransaction() 方法来开始你的事务,该方法会返回 TransactionStatus 的一个实例。 TransactionStatus 对象帮助追踪当前的事务状态,并且最终,如果一切运行顺利,你可以使用 PlatformTransactionManager 的 commit() 方法来提交这个事务,否则的话,你可以使用 rollback() 方法来回滚整个操作。
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
public interface StudentDAO {
/**
* This is the method to be used to initialize
* database resources ie. connection.
*/
public void setDataSource(DataSource ds);
/**
* This is the method to be used to create
* a record in the Student and Marks tables.
*/
public void create(String name, Integer age, Integer marks, Integer year);
/**
* This is the method to be used to list down
* all the records from the Student and Marks tables.
*/
public List listStudents();
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class StudentMarks {
private Integer age;
private String name;
private Integer id;
private Integer marks;
private Integer year;
private Integer sid;
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setMarks(Integer marks) {
this.marks = marks;
}
public Integer getMarks() {
return marks;
}
public void setYear(Integer year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Integer getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setSid(Integer sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public Integer getSid() {
return sid;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
public class StudentMarksMapper implements RowMapper {
public StudentMarks mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
StudentMarks studentMarks = new StudentMarks();
studentMarks.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
studentMarks.setName(rs.getString("name"));
studentMarks.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
studentMarks.setSid(rs.getInt("sid"));
studentMarks.setMarks(rs.getInt("marks"));
studentMarks.setYear(rs.getInt("year"));
return studentMarks;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionStatus;
import org.springframework.transaction.support.DefaultTransactionDefinition;
public class StudentJDBCTemplate implements StudentDAO {
private DataSource dataSource;
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateObject;
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.jdbcTemplateObject = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
public void setTransactionManager(
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
}
public void create(String name, Integer age, Integer marks, Integer year){
TransactionDefinition def = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(def);
try {
String SQL1 = "insert into Student (name, age) values (?, ?)";
jdbcTemplateObject.update( SQL1, name, age);
// Get the latest student id to be used in Marks table
String SQL2 = "select max(id) from Student";
int sid = jdbcTemplateObject.queryForInt( SQL2 );
String SQL3 = "insert into Marks(sid, marks, year) " +
"values (?, ?, ?)";
jdbcTemplateObject.update( SQL3, sid, marks, year);
System.out.println("Created Name = " + name + ", Age = " + age);
transactionManager.commit(status);
} catch (DataAccessException e) {
System.out.println("Error in creating record, rolling back");
transactionManager.rollback(status);
throw e;
}
return;
}
public List listStudents() {
String SQL = "select * from Student, Marks where Student.id=Marks.sid";
List studentMarks = jdbcTemplateObject.query(SQL,
new StudentMarksMapper());
return studentMarks;
}
}
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.tutorialspoint.StudentJDBCTemplate;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
StudentJDBCTemplate studentJDBCTemplate =
(StudentJDBCTemplate)context.getBean("studentJDBCTemplate");
System.out.println("------Records creation--------" );
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Zara", 11, 99, 2010);
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Nuha", 20, 97, 2010);
studentJDBCTemplate.create("Ayan", 25, 100, 2011);
System.out.println("------Listing all the records--------" );
List studentMarks = studentJDBCTemplate.listStudents();
for (StudentMarks record : studentMarks) {
System.out.print("ID : " + record.getId() );
System.out.print(", Name : " + record.getName() );
System.out.print(", Marks : " + record.getMarks());
System.out.print(", Year : " + record.getYear());
System.out.println(", Age : " + record.getAge());
}
}
}
------Records creation--------
Created Name = Zara, Age = 11
Created Name = Nuha, Age = 20
Created Name = Ayan, Age = 25
------Listing all the records--------
ID : 1, Name : Zara, Marks : 99, Year : 2010, Age : 11
ID : 2, Name : Nuha, Marks : 97, Year : 2010, Age : 20
ID : 3, Name : Ayan, Marks : 100, Year : 2011, Age : 25
10.2 声明式事务管理
*声明式事务管理方法允许你在配置的帮助下而不是源代码硬编程来管理事务。这意味着你可以将事务管理从事务代码中隔离出来。你可以只使用注释或基于配置的 XML 来管理事务。 bean 配置会指定事务型方法。下面是与声明式事务相关的步骤:
1)我们使用标签,它创建一个事务处理的建议,同时,我们定义一个匹配所有方法的切入点,我们希望这些方法是事务型的并且会引用事务型的建议。
2)如果在事务型配置中包含了一个方法的名称,那么创建的建议在调用方法之前就会在事务中开始进行。
3)目标方法会在 try / catch 块中执行。
4)如果方法正常结束,AOP 建议会成功的提交事务,否则它执行回滚操作。
package com.tutorialspoint;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class StudentJDBCTemplate implements StudentDAO{
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateObject;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.jdbcTemplateObject = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
public void create(String name, Integer age, Integer marks, Integer year){
try {
String SQL1 = "insert into Student (name, age) values (?, ?)";
jdbcTemplateObject.update( SQL1, name, age);
// Get the latest student id to be used in Marks table
String SQL2 = "select max(id) from Student";
int sid = jdbcTemplateObject.queryForInt( SQL2 );
String SQL3 = "insert into Marks(sid, marks, year) " +
"values (?, ?, ?)";
jdbcTemplateObject.update( SQL3, sid, marks, year);
System.out.println("Created Name = " + name + ", Age = " + age);
// to simulate the exception.
throw new RuntimeException("simulate Error condition") ;
} catch (DataAccessException e) {
System.out.println("Error in creating record, rolling back");
throw e;
}
}
public List listStudents() {
String SQL = "select * from Student, Marks where Student.id=Marks.sid";
List studentMarks=jdbcTemplateObject.query(SQL,
new StudentMarksMapper());
return studentMarks;
}
}
11. Web MVC框架
MVC 框架提供了模型-视图-控制的体系结构和可以用来开发灵活、松散耦合的 web 应用程序的组件。MVC 模式导致了应用程序的不同方面(输入逻辑、业务逻辑和 UI 逻辑)的分离,同时提供了在这些元素之间的松散耦合。
1)模型封装了应用程序数据,并且通常它们由 POJO 组成。
2)视图主要用于呈现模型数据,并且通常它生成客户端的浏览器可以解释的 HTML 输出。
3)控制器主要用于处理用户请求,并且构建合适的模型并将其传递到视图呈现。-
DispatcherServlet
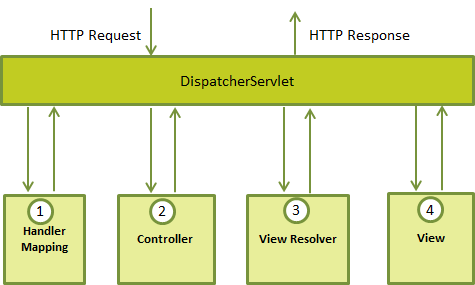
Spring Web 模型-视图-控制(MVC)框架是围绕 DispatcherServlet 设计的,DispatcherServlet 用来处理所有的 HTTP 请求和响应。Spring Web MVC DispatcherServlet 的请求处理的工作流程如下图所示:
下面是对应于 DispatcherServlet 传入 HTTP 请求的事件序列:
1)收到一个 HTTP 请求后,DispatcherServlet 根据 HandlerMapping 来选择并且调用适当的控制器。
2) 控制器接受请求,并基于使用的 GET 或 POST 方法来调用适当的 service 方法。Service 方法将设置基于定义的业务逻辑的模型数据,并返回视图名称到 DispatcherServlet 中。
3) DispatcherServlet 会从 ViewResolver 获取帮助,为请求检取定义视图。
4) 一旦确定视图,DispatcherServlet 将把模型数据传递给视图,最后呈现在浏览器中。
上面所提到的所有组件,即 HandlerMapping、Controller 和 ViewResolver 是 WebApplicationContext 的一部分,而 WebApplicationContext 是带有一些对 web 应用程序必要的额外特性的 ApplicationContext 的扩展。 需求配置
你需要映射你想让 DispatcherServlet 处理的请求,通过使用在 web.xml 文件中的一个 URL 映射。
以下是关于 HelloWeb-servlet.xml 文件的一些要点:
1)[servlet-name]-servlet.xml 文件将用于创建 bean 定义,重新定义在全局范围内具有相同名称的任何已定义的 bean。
2) 标签将用于激活 Spring MVC 注释扫描功能,该功能允许使用注释,如 @Controller 和 @RequestMapping 等等。
3)InternalResourceViewResolver 将使用定义的规则来解决视图名称。按照上述定义的规则,一个名称为 hello 的逻辑视图将发送给位于 /WEB-INF/jsp/hello.jsp 中实现的视图。
HelloWeb
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1
HelloWeb
*.jsp
- 定义控制器
DispatcherServlet 发送请求到控制器中执行特定的功能。@Controller 注释表明一个特定类是一个控制器的作用。@RequestMapping 注释用于映射 URL 到整个类或一个特定的处理方法。
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController{
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String printHello(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello Spring MVC Framework!");
return "hello";
}
}
@Controller 注释定义该类作为一个 Spring MVC 控制器。在这里,第一次使用的 @RequestMapping 表明在该控制器中处理的所有方法都是相对于 /hello 路径的。下一个注释 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET) 用于声明 printHello() 方法作为控制器的默认 service 方法来处理 HTTP GET 请求。你可以在相同的 URL 中定义其他方法来处理任何 POST 请求。
你可以用另一种形式来编写上面的控制器,你可以在 @RequestMapping 中添加额外的属性,如下所示:
@Controller
public class HelloController{
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String printHello(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello Spring MVC Framework!");
return "hello";
}
}
值属性表明 URL 映射到哪个处理方法,方法属性定义了 service 方法来处理 HTTP GET 请求。关于上面定义的控制器,这里有以下几个要注意的要点:
1)你将在一个 service 方法中定义需要的业务逻辑。你可以根据每次需求在这个方法中调用其他方法。
2)基于定义的业务逻辑,你将在这个方法中创建一个模型。你可以设置不同的模型属性,这些属性将被视图访问并显示最终的结果。这个示例创建了一个带有属性 “message” 的模型。
3)一个定义的 service 方法可以返回一个包含视图名称的字符串用于呈现该模型。这个示例返回 “hello” 作为逻辑视图的名称。
- 创建JSP视图
对于不同的表示技术,Spring MVC 支持许多类型的视图。这些包括 JSP、HTML、PDF、Excel 工作表、XML、Velocity 模板、XSLT、JSON、Atom 和 RSS 提要、JasperReports 等等。但我们最常使用利用 JSTL 编写的 JSP 模板。所以让我们在 /WEB-INF/hello/hello.jsp 中编写一个简单的 hello 视图:
Hello Spring MVC
${message}
其中,${message} 是我们在控制器内部设置的属性。你可以在你的视图中有多个属性显示。
11.1 Hello World例子
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class HelloController{
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String printHello(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("message", "Hello Spring MVC Framework!");
return "hello";
}
}
- web.xml
Spring MVC Application
HelloWeb
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1
HelloWeb
/
- HelloWeb-servlet.xml
- hello.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" %>
Hello World
${message}
需要的库文件
需要将这些文件拖拽到 WebContent/WEB-INF/lib 文件夹中。
commons-logging-x.y.z.jar
org.springframework.asm-x.y.z.jar
org.springframework.beans-x.y.z.jar
org.springframework.context-x.y.z.jar
org.springframework.core-x.y.z.jar
org.springframework.expression-x.y.z.jar
org.springframework.web.servlet-x.y.z.jar
org.springframework.web-x.y.z.jar
spring-web.jar测试
一旦你完成了创建源代码和配置文件后,导出你的应用程序。右键单击你的应用程序,并且使用 Export > WAR File 选项,在 Tomcat 的 webapps 文件夹中保存你的 HelloWeb.war 文件。
现在启动你的 Tomcat 服务器,并且确保你能够使用标准的浏览器访问 webapps 文件夹中的其他 web 页面。现在尝试访问该 URL http://localhost:8080/HelloWeb/hello。如果你的 Spring Web 应用程序一切都正常,你应该看到下面的结果: