ElasticSearch基础-ES存储查询原理、倒排索引、脚本操作ES、分词器、ES JavaAPI
基础篇
1 初识ElasticSearch
先来认识一下ES的作用
应用案例:
1、课程管理服务将数据写到MySQL数据库
2、使用Logstash将MySQL数据库中的数据写到ES的索引库。
3、用户在前端搜索课程信息,请求到搜索服务。
4、搜索服务请求ES搜索课程信息。
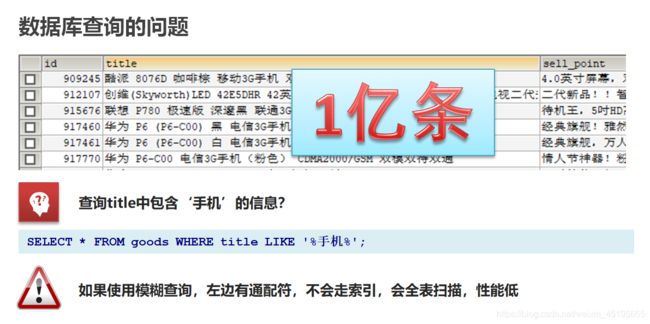
1.1 基于数据库查询的问题
索引:就是数据的一个定位关系,用于快速查找相应的数据
1,在插入数据后添加索引
2,数据的维护会增强索引的维护工作量
3,索引不适合太多,查找索引本身也需要时间
4,索引本身也占存储空间
5,针对哪些列建索引:搜索时常作为查询条件的
1.2 倒排索引
倒排索引:将文档进行分词,形成词条和id的对应关系即为反向索引。
以唐诗为例,所处包含“前”的诗句
正向索引:由《静夜思》–>窗前明月光—>“前”字
反向索引:“前”字–>窗前明月光–>《静夜思》
反向索引的实现就是对诗句进行分词,分成单个的词,由词推据,即为反向索引
1.3 ES存储和查询的原理
index(索引):相当于mysql的库
映射:相当于mysql 的表结构
document(文档):相当于mysql的表中的数据
数据库查询存在的问题:
- 性能低:使用模糊查询,左边有通配符,不会走索引,会全表扫描,性能低
- 功能弱:如果以”华为手机“作为条件,查询不出来数据
1.4 ES概念详解
•ElasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器
•是一个分布式、高扩展、高实时的搜索与数据分析引擎
•基于RESTful web接口
•Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,并作为Apache许可条款下的开放源码发布,是一种流行的企业级搜索引擎
•官网:https://www.elastic.co/
应用场景
•搜索:海量数据的查询
•日志数据分析
•实时数据分析
* Lucene是apache软件基金会4 jakarta项目组的一个子项目,是一个开放源代码的全文检索引擎工具包,但它不是一个完整的全文检索引擎,而是一个全文检索引擎的架构,提供了完整的查询引擎和索引引擎,部分文本分析引擎(英文与德文两种西方语言)。Lucene的目的是为软件开发人员提供一个简单易用的工具包,以方便的在目标系统中实现全文检索的功能,或者是以此为基础建立起完整的全文检索引擎。Lucene是一套用于全文检索和搜寻的开源程式库,由Apache软件基金会支持和提供。Lucene提供了一个简单却强大的应用程式接口,能够做全文索引和搜寻
ElasticSearch和Mysql的区别
•MySQL有事务性,而ElasticSearch没有事务性,所以你删了的数据是无法恢复的。
•ElasticSearch没有物理外键这个特性,如果你的数据强一致性要求比较高,还是建议慎用
ElasticSearch和MySql分工不同,MySQL负责存储数据,ElasticSearch负责搜索数据。
2 安装ElasticSearch
2.1 ES安装
参见ElasticSearch安装:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45195665/article/details/110347173
进入ES目录启动:
cd /opt/elasticsearch-7.4.0/bin
nohup ./elasticsearch &
注:
nohup 保证在退出SSH客户端后程序能一直执行
& 表示后台执行
查看elastic是否启动
ps -ef|grep elastic
http://192.168.52.128:9200/
注:本人使用的是自己安装es虚拟机,固定IP为 192.168.52.128 虚拟机为centos7的64位系统。
服务其它相关操作命令: kibana服务同
1.查找ES进程
ps -ef | grep elastic
2.杀掉ES进程
kill -9 2382(进程号)
3.重启ES
sh elasticsearch -d
可以使用jps命令查看运行的进程,看看服务是否启动。
2.2 ES辅助工具安装
参见ElasticSearch辅助工具安装:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45195665/article/details/110347173
进入目录后台启动kibana
cd /opt/kibana-7.4.0-linux-x86_64/bin
nohup ./kibana --allow-root &
访问kibana: http://192.168.52.128:5601/
补充:
因为kibana是使用node.js写的,所以进程在node中。但是查找到的node进程不一定就是kibana的,所以还需要根据端口进一步确认,直接查看5601端口的占用情况,确定下进程ID,然后在查看下node进程的ID,如果一致,就可以确定该node进程就是kiban的进程了.
netstat -tunlp|grep 5601 查看端口占用情况
ps aux | grep node 查看node进程
3 ElasticSearch核心概念
索引(index)
ElasticSearch存储数据的地方,可以理解成关系型数据库中的数据库概念。
映射(mapping)
mapping定义了每个字段的类型、字段所使用的分词器等。相当于关系型数据库中的表结构。
文档(document)
Elasticsearch中的最小数据单元,常以json格式显示。一个document相当于关系型数据库中的一行数据。
倒排索引
一个倒排索引由文档中所有不重复词的列表构成,对于其中每个词,对应一个包含它的文档id列表。
类型(type)
一种type就像一类表。如用户表、角色表等。在Elasticsearch7.X默认type为_doc
\- ES 5.x中一个index可以有多种type。
\- ES 6.x中一个index只能有一种type。
\- ES 7.x以后,将逐步移除type这个概念,现在的操作已经不再使用,默认_doc
4 脚本操作ES
4.1 RESTful风格介绍
1.REST(Representational State Transfer),表述性状态转移,是一组架构约束条件和原则。满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序或设计就是RESTful。就是一种定义接口的规范。
2.基于HTTP。
3.使用XML格式定义或JSON格式定义。
4.每一个URI代表1种资源。
5.客户端使用GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 4个表示操作方式的动词对服务端资源进行操作:
GET:用来获取资源
POST:用来新建资源(也可以用于更新资源)
PUT:用来更新资源
DELETE:用来删除资源
4.2 操作索引
打开PostMan测试工具,使用restful风格的请求来进行相应的操作:
PUT
http://192.168.52.128:9200/索引名称
查询
GET http://192.168.52.128:9200/索引名称 # 查询单个索引信息
GET http://192.168.52.128:9200/索引名称1,索引名称2... # 查询多个索引信息
GET http://192.168.52.128:9200/_all # 查询所有索引信息
•删除索引
DELETE http://192.168.52.128:9200/索引名称
•关闭、打开索引
POST http://192.168.52.128:9200/索引名称/_close
索引关闭后可以查看索引数据,但不能再往索引里添加数据
POST http://192.168.52.128:9200/索引名称/_open
4.3 ES数据类型
- 简单数据类型
- 字符串
聚合:相当于mysql 中的sum(求和)
text:会分词,不支持聚合
keyword:不会分词,将全部内容作为一个词条,支持聚合
-
数值:long、integer、short、byte、double、float、half_float、scaled_float
-
布尔:boolean
-
二进制:binary
-
范围类型
integer_range, float_range, long_range, double_range, date_range
- 日期:date
- 复杂数据类型
•数组:[ ] Nested: nested (for arrays of JSON objects 数组类型的JSON对象)
•对象:{ } Object: object(for single JSON objects 单个JSON对象)
范围类型的应用案例:
# 映射定义
PUT example
PUT example/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"expectedAttendees":{
"type": "integer_range"
},
"time": {
"type": "date_range",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
# 数据新增
PUT example/112313213?refresh
{
"expectedAttendees": {
"gte": 10,
"lte": 20
},
"time": {
"gte": "2019-12-01 12:00:00",
"lte": "2019-12-02 17:00:00"
}
}
# 查询数据
GET example/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"expectedAttendees": {
"value": 12
}
}
}
}
4.4 操作映射
使用kibana来进行操作演示:http://192.168.52.128:5601/
进入操作界面:
#创建索引
PUT person
#查询索引
GET person
#添加映射 此时是根据己有的索引创建映射 :前提是person必须已经创建,否则提示索引不存在
PUT /person/_mapping
{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
}
}
}
#创建索引并添加映射
#创建索引并添加映射 不能重复操作:提示索引己存在
PUT /person1
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
},
"address":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
#查询person1索引库的映射结构
GET person1/_mapping
添加字段
#添加字段
PUT /person1/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text"
},
"age": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
注意:映射 一旦创建,可以新增字段,不能去除己有字段,只能删除索引后重建
4.5 操作文档
•添加文档,指定id
POST /person1/_doc/2
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"address":"北京"
}
GET /person1/_doc/1
•添加文档,不指定id
#添加文档,不指定id 会自动分配一个唯的ID
POST /person1/_doc/
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"address":"北京"
}
#查询所有文档
GET /person1/_search
#删除指定id文档
DELETE /person1/_doc/1
5 分词器
5.1分词器-介绍
分词器(Analyzer):将一段文本,按照一定逻辑,分析成多个词语的一种工具
如:华为手机 — > 华为、手、手机
ElasticSearch 内置分词器
•Standard Analyzer - 默认分词器,按词切分,小写处理
•Simple Analyzer - 按照非字母切分(符号被过滤), 小写处理
•Stop Analyzer - 小写处理,停用词过滤(the,a,is)
•Whitespace Analyzer - 按照空格切分,不转小写
•Keyword Analyzer - 不分词,直接将输入当作输出
•Patter Analyzer - 正则表达式,默认\W+(非字符分割)
•Language - 提供了30多种常见语言的分词器
IK分词器介绍:
•IKAnalyzer是一个开源的,基于java语言开发的轻量级的中文分词工具包
•是一个基于Maven构建的项目
•具有60万字/秒的高速处理能力
•支持用户词典扩展定义
•下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/archive/v7.4.0.zip
5.2 ik分词器安装
参见 ik分词器安装:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45195665/article/details/110347321
5.3 ik分词器使用
IK分词器有两种分词模式:ik_max_word和ik_smart模式。
1、ik_max_word
会将文本做最细粒度的拆分,比如会将“乒乓球明年总冠军”拆分为“乒乓球、乒乓、球、明年、总冠军、冠军。
#方式一ik_max_word
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"
}
ik_max_word分词器执行如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "乒乓球",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "乒乓",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "球",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "明年",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "总冠军",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "冠军",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 5
}
]
}
2、ik_smart
会做最粗粒度的拆分,比如会将“乒乓球明年总冠军”拆分为乒乓球、明年、总冠军。
#方式二ik_smart
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"
}
ik_smart分词器执行如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "乒乓球",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "明年",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "总冠军",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
}
]
}
由此可见 使用ik_smart可以将文本"text": "乒乓球明年总冠军"分成了【乒乓球】【明年】【总冠军】
这样看的话,这样的分词效果达到了我们的要求。
小结:
ik_max_word:细粒度的分词
应用:在插入ES文档时,一般建议采用细粒度的分词,可以更容易被搜索到
ik_smart:粗粒度的分词
应用:对搜索的关键字进行分词时,建议采用粗粒度的分词,这样搜索的精确度更高
5.4 使用IK分词器-查询文档
•词条查询:term
词条查询不会分析查询条件,只有当词条和查询字符串完全匹配时才匹配搜索
•全文查询:match
全文查询会分析查询条件,先将查询条件进行分词,然后查询,求并集
1.创建索引,添加映射,并指定分词器为ik分词器
PUT person2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"address": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
2.添加文档
POST /person2/_doc/1
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"address":"北京海淀区"
}
POST /person2/_doc/2
{
"name":"李四",
"age":18,
"address":"北京朝阳区"
}
POST /person2/_doc/3
{
"name":"王五",
"age":18,
"address":"北京昌平区"
}
3.查询映射
GET person2
4.查看分词效果
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "北京海淀"
}
5.词条查询:term
查询person2中匹配到"北京"两字的词条:term 查询不会对查询条件进行分词,而作为一个整体来进行匹配
GET /person2/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"address": {
"value": "北京昌平"
}
}
}
}
6.全文查询:match
全文查询会分析查询条件,先将查询条件进行分词,然后查询,求并集
GET /person2/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address":"北京昌平"
}
}
}
6 ElasticSearch JavaApi
6.1 SpringBoot整合ES
①搭建SpringBoot工程
②引入ElasticSearch相关坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-clientartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.clientgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-clientartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearchgroupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearchartifactId>
<version>7.4.0version>
dependency>
③测试
ElasticSearchConfig
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="elasticsearch")
public class ElasticSearchConfig {
private String host;
private int port;
public String getHost() {
return host;
}
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
public int getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient client(){
return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost(host,port,"http")
));
}
}
ElasticsearchDay01ApplicationTests
注意:使用@Autowired注入RestHighLevelClient 如果报红线,则是因为配置类所在的包和测试类所在的包,包名不一致造成的,并不影响运行
@SpringBootTest
class ElasticsearchDay01ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
RestHighLevelClient client;
/**
* 测试
*/
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(client);
}
}
6.2 创建索引
1.添加索引
/**
* 添加索引
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void addIndex() throws IOException {
//1.使用client获取操作索引对象
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
//2.具体操作获取返回值
//2.1 设置索引名称
CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest=new CreateIndexRequest("lichee");
CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = indices.create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3.根据返回值判断结果
System.out.println(createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged());
}
2.添加索引,并添加映射
/**
* 添加索引,并添加映射
*/
@Test
public void addIndexAndMapping() throws IOException {
//1.使用client获取操作索引对象
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
//2.具体操作获取返回值
//2.具体操作,获取返回值
CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest("test");
//2.1 设置mappings
String mapping = "{\n" +
" \"properties\" : {\n" +
" \"address\" : {\n" +
" \"type\" : \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\" : \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"age\" : {\n" +
" \"type\" : \"long\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\" : {\n" +
" \"type\" : \"keyword\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }";
createIndexRequest.mapping(mapping,XContentType.JSON);
CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = indices.create(createIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//3.根据返回值判断结果
System.out.println(createIndexResponse.isAcknowledged());
}
RequestOptions说明:
RequestOptions:ES6.7.0增加了RequestOptions选项。可以通过它对请求进行更多自定义的配置,且不影响正常的Elasticsearch请求。RequestOptions.DEFAULT表示默认的基本配置。
例如:
private static final RequestOptions COMMON_OPTIONS;
static {
RequestOptions.Builder builder = RequestOptions.DEFAULT.toBuilder();
// 默认缓存限制为100MB,此处修改为30MB。
builder.setHttpAsyncResponseConsumerFactory(
new HttpAsyncResponseConsumerFactory
.HeapBufferedResponseConsumerFactory(30 * 1024 * 1024));
COMMON_OPTIONS = builder.build();
}
//创建索引时引用上面构建的RequestOptions对象即可
CreateIndexResponse response = indicesClient.create(createRequest, COMMON_OPTIONS);
6.3 查询、删除、判断索引
查询索引
/**
* 查询索引
*/
@Test
public void queryIndex() throws IOException {
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
GetIndexRequest getRequest=new GetIndexRequest("test");
GetIndexResponse response = indices.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
Map<String, MappingMetaData> mappings = response.getMappings();
//iter 提示foreach
for (String key : mappings.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key+"==="+mappings.get(key).getSourceAsMap());
}
}
删除索引
/**
* 删除索引
*/
@Test
public void deleteIndex() throws IOException {
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
DeleteIndexRequest deleteRequest=new DeleteIndexRequest("lichee");
AcknowledgedResponse delete = indices.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(delete.isAcknowledged());
}
索引是否存在
/**
* 索引是否存在
*/
@Test
public void existIndex() throws IOException {
IndicesClient indices = client.indices();
GetIndexRequest getIndexRequest=new GetIndexRequest("lichee");
boolean exists = indices.exists(getIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(exists);
}
6.4 添加文档
1.添加文档,使用map作为数据
@Test
public void addDoc1() throws IOException {
Map<String, Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","张三");
map.put("age","18");
map.put("address","北京二环");
IndexRequest request=new IndexRequest("test").id("1").source(map);
IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getId());
}
2.添加文档,使用对象作为数据
@Test
public void addDoc2() throws IOException {
Person person=new Person();
person.setId("2");
person.setName("李四");
person.setAge(20);
person.setAddress("北京三环");
String data = JSON.toJSONString(person);
IndexRequest request=new IndexRequest("test").id(person.getId()).source(data,XContentType.JSON);
IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getId());
}
6.5 修改、查询、删除文档
1.修改文档:添加文档时,如果id存在则修改,id不存在则添加
/**
* 修改文档:添加文档时,如果id存在则修改,id不存在则添加
*/
@Test
public void UpdateDoc() throws IOException {
Person person=new Person();
person.setId("2");
person.setName("李四");
person.setAge(20);
person.setAddress("北京三环车王");
String data = JSON.toJSONString(person);
IndexRequest request=new IndexRequest("test").id(person.getId()).source(data,XContentType.JSON);
IndexResponse response = client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getId());
}
2.根据id查询文档
/**
* 根据id查询文档
*/
@Test
public void getDoc() throws IOException {
//设置查询的索引、文档
GetRequest indexRequest=new GetRequest("test","2");
GetResponse response = client.get(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getSourceAsString());
}
3.根据id删除文档
/**
* 根据id删除文档
*/
@Test
public void delDoc() throws IOException {
//设置要删除的索引、文档
DeleteRequest deleteRequest=new DeleteRequest("test","1");
DeleteResponse response = client.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.getId());
}