Tensorflow模型保存与预测
目录
1. Estimator形式
1.1 模型导出
A. 用到了tf.feature_column接口
B. 没用到tf.feature_column接口,需要自己定义feature_spec
1.2 模型检查
1.3 模型预测
A. 使用CLI指令
B. python加载模型预测
2. Keras Model 训练
1.1 模型导出
1.2 模型预测
A. 使用CLI指令
B. python加载模型预测
版本:tensorflow 1.14
保存形式:svaedModel
1. Estimator形式
模型保存后,预测数据以example格式输入
1.1 模型导出
A. 用到了tf.feature_column接口
# feature_columns
feature_columns = [
tf.feature_column.numeric_column('dense_features', (10,)),
...
]
serving_feature_spec = tf.feature_column.make_parse_example_spec(feature_columns)
serving_input_receiver_fn = tf.estimator.export.build_parsing_serving_input_receiver_fn(serving_feature_spec)
model_estimator.export_saved_model(export_dir_base=save_model_dir,
serving_input_receiver_fn=serving_input_receiver_fn)- 第4行 make_parse_example_spec() 会根据创建的feature column列表,构建出解析tf.Example所需要的信息,比如:
{
'feature_1': VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.int64),
'feature_2': VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.int64),
'dense_features': FixedLenFeature(shape=(10,), dtype=tf.float32, default_value=None)
}- 第5行 build_parsing_serving_input_receiver_fn函数 注册接收key为examples的string tensor作为input,依据feature_spec解析后给到模型,源码如下:
- 本质是:将来模型的输入是一个example形式的序列化string,对其按照feature_spec解析成一个个字段,形成features
def build_parsing_serving_input_receiver_fn(feature_spec, default_batch_size=None):
def serving_input_receiver_fn():
"""An input_fn that expects a serialized tf.Example."""
serialized_tf_example = array_ops.placeholder(dtype=dtypes.string,
shape=[default_batch_size],
name='input_example_tensor')
receiver_tensors = {'examples': serialized_tf_example}
features = parsing_ops.parse_example(serialized_tf_example, feature_spec)
return ServingInputReceiver(features, receiver_tensors)
return serving_input_receiver_fnB. 没用到tf.feature_column接口,需要自己定义feature_spec
feature_spec = {
'feature_1': tf.io.VarLenFeature(tf.int64),
'feature_2': tf.io.VarLenFeature(tf.int64),
'abc': tf.io.FixedLenFeature([1], tf.int64, default_value=[0]),
...
'dense_features': tf.io.FixedLenFeature(shape=(10,), dtype=tf.float32, default_value=[0] * 10)
}- 可以自己重写build函数(其实本质和原来的一样...)
def my_build_serving_input_receiver_fn(cols_description):
def serving_input_receiver_fn():
serialized_tf_example = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.string, shape=None,
name='input_example_tensor')
# key (e.g. 'examples') should be same with the inputKey when you
# buid the request for prediction
receiver_tensors = {'input_examples': serialized_tf_example}
features = tf.parse_example(serialized_tf_example, cols_description)
return tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver(features, receiver_tensors)
return serving_input_receiver_fn最后进行导出
serving_input_receiver_fn = my_build_serving_input_receiver_fn(feature_spec)
model_estimator.export_saved_model(export_dir_base=save_model_dir,
serving_input_receiver_fn=serving_input_receiver_fn)导出的模型目录结构如下
/export/model
└── 1784256271
├── saved_model.pb
└── variables
├── variables.data-00000-of-00002
├── variables.data-00001-of-00002
└── variables.index1.2 模型检查
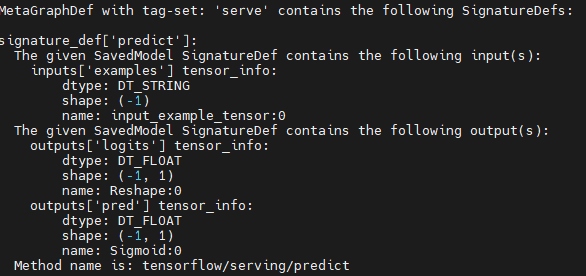
命令行 使用CLI指令 检查保存的模型
saved_model_cli show --all --dir ./model_path1.3 模型预测
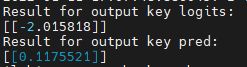
A. 使用CLI指令
saved_model_cli run --dir ${model_path} \
--tag_set serve \
--signature_def="predict" \
--input_examples='examples=[{"feature_1":[0], "feature_2":[1], "dense_features":[0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.5, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 0.2, 5.0, 0.0]}]'结果:
B. python加载模型预测
需要包装成tf.Example序列化成string后喂入
# 将pandas df包装成tf.example
def predict_example(df):
examples = []
colNames = df.columns
dtypes = df.dtypes
for row in df.iterrows():
features = collections.OrderedDict()
for i in range(len(colNames)):
dtype = dtypes[i]
colName = colNames[i]
value = row[1][colName]
if dtype == "int":
features[colName] = tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])) # 注意,要包装成list
elif dtype == 'float':
features[colName] = tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[value]))
else:
features[colName] = tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=value)) # 本来就是List,不用包装了
tf_features = tf.train.Features(feature=features)
tf_example = tf.train.Example(features=tf_features)
tf_example = tf_example.SerializeToString()
examples.append(tf_example)
return examples
# dataframe case
data = [{
"feature_1: 0, "feature_2": 1, "dense_features": [0.0]*10
}]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# 构建预测器和预测样本
predict_fn = tf.contrib.predictor.from_saved_model(model_path, signature_def_key="predict")
examples = predict_example(df)
predictions = predict_fn({"examples": examples})
print(predictions)2. Keras Model 训练
1.1 模型导出
定义好模型预测的输入输出节点
save_path = "./keras_model/1"
builder = tf.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder(save_path)
with tf.get_default_graph().as_default():
# define signature which specify input and out nodes
tensor_info_output = tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(model.output)
prediction_signature = (tf.saved_model.signature_def_utils.build_signature_def(
inputs={f"input_{x}": tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(item) for x, item in enumerate(model.input)},
outputs={"pred": tensor_info_output},
method_name=tf.saved_model.signature_constants.PREDICT_METHOD_NAME))
# add graph and variables
builder.add_meta_graph_and_variables(
# tags:SERVING,TRAINING,EVAL,GPU,TPU
sess=tf.compat.v1.keras.backend.get_session(),
tags=[tf.saved_model.tag_constants.SERVING],
signature_def_map={'predict': prediction_signature},
)
builder.save()1.2 模型预测
A. 使用CLI指令
saved_model_cli run --dir ${keras_path} \
--tag_set serve \
--signature_def="predict" \
--input_exprs 'input_0=[[0]];input_1=[[0]];input_3=[[0.0]*10]'B. python加载模型预测
以字典的形式直接喂入,每个输入值都要用list包起来
predict_fn = tf.contrib.predictor.from_saved_model(model_path, signature_def_key="predict")
predictions = predict_fn({"input_0": [[0]],
"input_1": [[0]],
"input_3": [[0.0]*10],
})