本篇文章意在通过某个功能逐步熟悉 hudi 整体架构上的实现,不会讨论算法的实现细节
hudi 新人,有问题欢迎指正
spark : version, 3.1.2
hudi : branch, master
Time: 2022/02/06 第一版
目的:通过改变数据布局的方式,减少 data scan 的数据量。
举个简单的栗子:
- 一张 text 表,包含 id,name 两个字段
有两个数据文件 a.parquet 和 b.parquet
- a.parquet 数据 2,zs、1,ls、4,wu, 3,ts
- b.parquet 数据 1,ls、2,zs、4,wu 5,ts
- 这时候我们需要对 id = 2 做过滤数量统计,需要扫描 a.parquet 和 b.parquet 两个文件
对数据进行排序并进行 Min/Max 索引记录后
- a.parquet 数据 1,ls、1,ls、2,zs、2,zs Min-id:1 | Max-id:2
- b.parquet 数据 3,ts、4,wu、4,wu、5,ts Min-id:3 | Max-id:5
- 这时候我们需要对 id = 2 做过滤数量统计,只需要扫描 a.parquet 一个文件
查询阶段
入口类,DefaultSource,createRelation方法 创建 Relation
type 条件:
- hoodie.datasource.query.type 为 read_optimized 时,hoodie.table.type 为 cow 或者 mor
- hoodie.datasource.query.type 为 snapshot 时,hoodie.table.type 为 cow
满足上面的条件后,会创建 HadoopFsRelation。其中,需要创建 HoodieFileIndex 并初始化,在初始化 HoodieFileIndex 的时候,会调用 refresh0() 构建需要查询的 fileSice,如果是分区表,依然会读取 list 所有分区目录下的文件路径以及相关信息,缓存在 cachedAllInputFileSlices
private def refresh0(): Unit = {
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
// 加载所有分区的 file
val partitionFiles = loadPartitionPathFiles()
val allFiles = partitionFiles.values.reduceOption(_ ++ _)
.getOrElse(Array.empty[FileStatus])
metaClient.reloadActiveTimeline()
val activeInstants = metaClient.getActiveTimeline.getCommitsTimeline.filterCompletedInstants
val latestInstant = activeInstants.lastInstant()
fileSystemView = new HoodieTableFileSystemView(metaClient, activeInstants, allFiles)
val queryInstant = if (specifiedQueryInstant.isDefined) {
specifiedQueryInstant
} else if (latestInstant.isPresent) {
Some(latestInstant.get.getTimestamp)
} else {
None
}
(tableType, queryType) match {
case (MERGE_ON_READ, QUERY_TYPE_SNAPSHOT_OPT_VAL) =>
// Fetch and store latest base and log files, and their sizes
// 所有的 FileSlices 会存储在这
cachedAllInputFileSlices = partitionFiles.map(p => {
val latestSlices = if (latestInstant.isPresent) {
fileSystemView.getLatestMergedFileSlicesBeforeOrOn(p._1.partitionPath, queryInstant.get)
.iterator().asScala.toSeq
} else {
Seq()
}
(p._1, latestSlices)
})
cachedFileSize = cachedAllInputFileSlices.values.flatten.map(fileSlice => {
if (fileSlice.getBaseFile.isPresent) {
fileSlice.getBaseFile.get().getFileLen + fileSlice.getLogFiles.iterator().asScala.map(_.getFileSize).sum
} else {
fileSlice.getLogFiles.iterator().asScala.map(_.getFileSize).sum
}
}).sum
case (_, _) =>
// Fetch and store latest base files and its sizes
cachedAllInputFileSlices = partitionFiles.map(p => {
val fileSlices = specifiedQueryInstant
.map(instant =>
fileSystemView.getLatestFileSlicesBeforeOrOn(p._1.partitionPath, instant, true))
.getOrElse(fileSystemView.getLatestFileSlices(p._1.partitionPath))
.iterator().asScala.toSeq
(p._1, fileSlices)
})
cachedFileSize = cachedAllInputFileSlices.values.flatten.map(fileSliceSize).sum
}HoodieFileIndex 继承 org.apache.spark.sql.execution.datasources.FileIndex 实现 listFiles 接口,用来读取 zIndex 索引以及达到分区过滤的效果。HoodieFileIndex 作为 HadoopFsRelation 的 location 的实现作为 data input 的数据
HoodieFileIndex 的 listFiles 实现
lookupCandidateFilesInZIndex 会使用 ZIndex 找到需要读取的文件
// 代码片段
override def listFiles(partitionFilters: Seq[Expression],
dataFilters: Seq[Expression]): Seq[PartitionDirectory] = {
// Look up candidate files names in the Z-index, if all of the following conditions are true
// - Data-skipping is enabled
// - Z-index is present
// - List of predicates (filters) is present
val candidateFilesNamesOpt: Option[Set[String]] =
lookupCandidateFilesInZIndex(dataFilters) match {
case Success(opt) => opt
case Failure(e) =>
if (e.isInstanceOf[AnalysisException]) {
logDebug("Failed to relay provided data filters to Z-index lookup", e)
} else {
logError("Failed to lookup candidate files in Z-index", e)
}
Option.empty
}
...
}先看 .zindex 索引的文件数据 /.zindex/20220202225600359/part-00000-3b9cdcd9-28ed-4cef-8f97-2bb6097b1445-c000.snappy.parquet(这里的例子是按 name,id 进行 zorder 排序),可以看出,每一行数据对应一个数据文件,并且记录了每个数据文件列 name 和列 id 的最大最小值,以实现数据过滤。
(注:数据是测试数据,可能不符合过滤逻辑,因为每一个数据文件只有一行数据,并且没有达到 compact 的条件)
{"file": "859ccf12-253f-40d5-ba0b-a831e48e4f16-0_0-45-468_20220202155755496.parquet", "name_minValue": "cql", "name_maxValue": "wlq", "name_num_nulls": 0, "id_minValue": 1, "id_maxValue": 9, "id_num_nulls": 0}
{"file": "9f3054c8-5f57-45c8-8bdf-400707edd2d3-0_0-26-29_20220202223215267.parquet", "name_minValue": "cql", "name_maxValue": "wlq_update", "name_num_nulls": 0, "id_minValue": 1, "id_maxValue": 1, "id_num_nulls": 0}
{"file": "9c76a87b-8263-41c5-a830-08698b27ec0f-0_0-49-440_20220202160249241.parquet", "name_minValue": "cql", "name_maxValue": "cql", "name_num_nulls": 0, "id_minValue": 1, "id_maxValue": 1, "id_num_nulls": 0}lookupCandidateFilesInZIndex 实现
private def lookupCandidateFilesInZIndex(queryFilters: Seq[Expression]): Try[Option[Set[String]]] = Try {
// .zindex 路径,在 tableName/.hoodie/.zindex
val indexPath = metaClient.getZindexPath
val fs = metaClient.getFs
if (!enableDataSkipping() || !fs.exists(new Path(indexPath)) || queryFilters.isEmpty) {
// scalastyle:off return
return Success(Option.empty)
// scalastyle:on return
}
// Collect all index tables present in `.zindex` folder
val candidateIndexTables =
fs.listStatus(new Path(indexPath))
.filter(_.isDirectory)
.map(_.getPath.getName)
.filter(f => completedCommits.contains(f))
.sortBy(x => x)
if (candidateIndexTables.isEmpty) {
// scalastyle:off return
return Success(Option.empty)
// scalastyle:on return
}
val dataFrameOpt = try {
Some(spark.read.load(new Path(indexPath, candidateIndexTables.last).toString))
} catch {
case t: Throwable =>
logError("Failed to read Z-index; skipping", t)
None
}
dataFrameOpt.map(df => {
val indexSchema = df.schema
// 通过索引文件的 schema 和下推的 querySchame 构建出过滤表达式
val indexFilter =
queryFilters.map(createZIndexLookupFilter(_, indexSchema))
.reduce(And)
logInfo(s"Index filter condition: $indexFilter")
df.persist()
// 获取所有的 file
val allIndexedFileNames =
df.select("file")
.collect()
.map(_.getString(0))
.toSet
// 过滤出满足条件的的 file
val prunedCandidateFileNames =
df.where(new Column(indexFilter))
.select("file")
.collect()
.map(_.getString(0))
.toSet
df.unpersist()
// NOTE: Z-index isn't guaranteed to have complete set of statistics for every
// base-file: since it's bound to clustering, which could occur asynchronously
// at arbitrary point in time, and is not likely to touching all of the base files.
//
// To close that gap, we manually compute the difference b/w all indexed (Z-index)
// files and all outstanding base-files, and make sure that all base files not
// represented w/in Z-index are included in the output of this method
// 不是所有的历史文件,或者分区使用 zOrder 索引,所以下推得到的 file 不一定是所有的查询结果,比如有历史文件 a.parquet,这时候新加了 zorder 优化,没有刷历史,新增数据文件 b.parquet 和 c.parquet,这时候 zindex 索引只有 b.parquet 的信息,没有 a.parquet,如果直接使用会导致数据都是。所以,假设 zindex 命中了 b.parquet,只需要排除 c.parquet 就可以了,使用上面 cachedAllInputFileSlices - c.parquet,查询的就是 a.parquet + b.parquet 文件,过滤掉 c.parqeut
val notIndexedFileNames =
lookupFileNamesMissingFromIndex(allIndexedFileNames)
prunedCandidateFileNames ++ notIndexedFileNames
})
}生成阶段
// 每次 write 完执行
hoodie.clustering.inline = 'true'
hoodie.clustering.inline.max.commits = '1'
hoodie.layout.optimize.strategy = 'z-order'
hoodie.layout.optimize.enable = 'true'
hoodie.clustering.plan.strategy.sort.columns = 'name,id'类 AbstractHoodieWriteClient 在 commitStats 释放 lock 后,会 runTableServicesInline 执行相关的 compact 等操作,包括 zindex 的生成流程。流程主要分成两个步骤,首先是排序,然后再根据 replace 生成 zindex file
注意:上面的排序并不会发生在 spark 任务的核心流程中(而且可以异步执行),不会影响下次的 spark data write 的 commit 提交
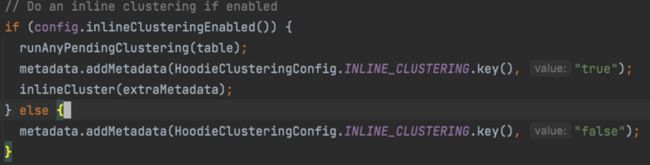
runTableServicesInline 方法中,判断 inline_cluster 是否开启
重点关注 inlineCluster 方法,最终使用子类 SparkRDDWriteClient 实现的 cluster
@Override
public HoodieWriteMetadata> cluster(String clusteringInstant, boolean shouldComplete) {
HoodieSparkTable table = HoodieSparkTable.create(config, context, config.isMetadataTableEnabled());
preWrite(clusteringInstant, WriteOperationType.CLUSTER, table.getMetaClient());
HoodieTimeline pendingClusteringTimeline = table.getActiveTimeline().filterPendingReplaceTimeline();
HoodieInstant inflightInstant = HoodieTimeline.getReplaceCommitInflightInstant(clusteringInstant);
if (pendingClusteringTimeline.containsInstant(inflightInstant)) {
rollbackInflightClustering(inflightInstant, table);
table.getMetaClient().reloadActiveTimeline();
}
clusteringTimer = metrics.getClusteringCtx();
LOG.info("Starting clustering at " + clusteringInstant);
// 根据需要构建 Partitioner 对数据进行排序,然后返回元数据
HoodieWriteMetadata> clusteringMetadata = table.cluster(context, clusteringInstant);
JavaRDD statuses = clusteringMetadata.getWriteStatuses();
// TODO : Where is shouldComplete used ?
if (shouldComplete && clusteringMetadata.getCommitMetadata().isPresent()) {
// 生成 zindex
completeTableService(TableServiceType.CLUSTER, clusteringMetadata.getCommitMetadata().get(), statuses, table, clusteringInstant);
}
return clusteringMetadata;
} 排序阶段
table.cluster 最终会创建 SparkExecuteClusteringCommitActionExecutor 执行相关操作
@Override
public HoodieWriteMetadata> execute() {
HoodieInstant instant = HoodieTimeline.getReplaceCommitRequestedInstant(instantTime);
// Mark instant as clustering inflight
table.getActiveTimeline().transitionReplaceRequestedToInflight(instant, Option.empty());
table.getMetaClient().reloadActiveTimeline();
final Schema schema = HoodieAvroUtils.addMetadataFields(new Schema.Parser().parse(config.getSchema()));
// 使用功能 SparkSortAndSizeExecutionStrategy 进行排序优化,performClustering
HoodieWriteMetadata> writeMetadata = ((ClusteringExecutionStrategy>, JavaRDD, JavaRDD>)
ReflectionUtils.loadClass(config.getClusteringExecutionStrategyClass(),
new Class[] {HoodieTable.class, HoodieEngineContext.class, HoodieWriteConfig.class}, table, context, config))
.performClustering(clusteringPlan, schema, instantTime);
JavaRDD writeStatusRDD = writeMetadata.getWriteStatuses();
JavaRDD statuses = updateIndex(writeStatusRDD, writeMetadata);
writeMetadata.setWriteStats(statuses.map(WriteStatus::getStat).collect());
writeMetadata.setPartitionToReplaceFileIds(getPartitionToReplacedFileIds(writeMetadata));
commitOnAutoCommit(writeMetadata);
if (!writeMetadata.getCommitMetadata().isPresent()) {
HoodieCommitMetadata commitMetadata = CommitUtils.buildMetadata(writeMetadata.getWriteStats().get(), writeMetadata.getPartitionToReplaceFileIds(),
extraMetadata, operationType, getSchemaToStoreInCommit(), getCommitActionType());
writeMetadata.setCommitMetadata(Option.of(commitMetadata));
}
return writeMetadata;
} SparkSortAndSizeExecutionStrategy 的 performClusteringWithRecordsRDD 实现
@Override
public JavaRDD performClusteringWithRecordsRDD(final JavaRDD> inputRecords, final int numOutputGroups,
final String instantTime, final Map strategyParams, final Schema schema,
final List fileGroupIdList, final boolean preserveHoodieMetadata) {
LOG.info("Starting clustering for a group, parallelism:" + numOutputGroups + " commit:" + instantTime);
Properties props = getWriteConfig().getProps();
props.put(HoodieWriteConfig.BULKINSERT_PARALLELISM_VALUE.key(), String.valueOf(numOutputGroups));
// We are calling another action executor - disable auto commit. Strategy is only expected to write data in new files.
props.put(HoodieWriteConfig.AUTO_COMMIT_ENABLE.key(), Boolean.FALSE.toString());
props.put(HoodieStorageConfig.PARQUET_MAX_FILE_SIZE.key(), String.valueOf(getWriteConfig().getClusteringTargetFileMaxBytes()));
HoodieWriteConfig newConfig = HoodieWriteConfig.newBuilder().withProps(props).build();
// 这里关注 getPartitioner 方法,如果开启 hoodie.layout.optimize.enable,就会返回 RDDSpatialCurveOptimizationSortPartitioner,最终调用分区器的 repartitionRecords
return (JavaRDD) SparkBulkInsertHelper.newInstance().bulkInsert(inputRecords, instantTime, getHoodieTable(), newConfig,
false, getPartitioner(strategyParams, schema), true, numOutputGroups, new CreateHandleFactory(preserveHoodieMetadata));
} RDDSpatialCurveOptimizationSortPartitioner 的 repartitionRecords 内会根据 hoodie.layout.optimize.curve.build.method 调用 OrderingIndexHelper 的 createOptimizedDataFrameByXXX 方法
public static Dataset createOptimizedDataFrameByMapValue(Dataset df, List sortCols, int fileNum, String sortMode) {
Map columnsMap = Arrays.stream(df.schema().fields()).collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e.name(), e -> e));
int fieldNum = df.schema().fields().length;
List checkCols = sortCols.stream().filter(f -> columnsMap.containsKey(f)).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (sortCols.size() != checkCols.size()) {
return df;
}
// only one col to sort, no need to use z-order
if (sortCols.size() == 1) {
return df.repartitionByRange(fieldNum, org.apache.spark.sql.functions.col(sortCols.get(0)));
}
Map fieldMap = sortCols
.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> Arrays.asList(df.schema().fields()).indexOf(columnsMap.get(e)), e -> columnsMap.get(e)));
// do optimize
// 可以看出目前支持两种排序曲线,z 和 hilbert
JavaRDD sortedRDD = null;
switch (HoodieClusteringConfig.BuildLayoutOptimizationStrategy.fromValue(sortMode)) {
case ZORDER:
sortedRDD = createZCurveSortedRDD(df.toJavaRDD(), fieldMap, fieldNum, fileNum);
break;
case HILBERT:
sortedRDD = createHilbertSortedRDD(df.toJavaRDD(), fieldMap, fieldNum, fileNum);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("new only support z-order/hilbert optimize but find: %s", sortMode));
}
// create new StructType
List newFields = new ArrayList<>();
newFields.addAll(Arrays.asList(df.schema().fields()));
newFields.add(new StructField("Index", BinaryType$.MODULE$, true, Metadata.empty()));
// create new DataFrame
return df.sparkSession().createDataFrame(sortedRDD, StructType$.MODULE$.apply(newFields)).drop("Index");
}
生成 Index 阶段
回到 SparkRDDWriteClient 的 cluster 方法,最终调用 completeTableService 执行 commit 操作
private void completeClustering(HoodieReplaceCommitMetadata metadata, JavaRDD writeStatuses,
HoodieTable>, JavaRDD, JavaRDD> table,
String clusteringCommitTime) {
List writeStats = metadata.getPartitionToWriteStats().entrySet().stream().flatMap(e ->
e.getValue().stream()).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (writeStats.stream().mapToLong(s -> s.getTotalWriteErrors()).sum() > 0) {
throw new HoodieClusteringException("Clustering failed to write to files:"
+ writeStats.stream().filter(s -> s.getTotalWriteErrors() > 0L).map(s -> s.getFileId()).collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
}
try {
HoodieInstant clusteringInstant = new HoodieInstant(HoodieInstant.State.INFLIGHT, HoodieTimeline.REPLACE_COMMIT_ACTION, clusteringCommitTime);
this.txnManager.beginTransaction(Option.of(clusteringInstant), Option.empty());
finalizeWrite(table, clusteringCommitTime, writeStats);
writeTableMetadataForTableServices(table, metadata,clusteringInstant);
// Update outstanding metadata indexes
if (config.isLayoutOptimizationEnabled()
&& !config.getClusteringSortColumns().isEmpty()) {
// 更新元数据索引
table.updateMetadataIndexes(context, writeStats, clusteringCommitTime);
}
LOG.info("Committing Clustering " + clusteringCommitTime + ". Finished with result " + metadata);
table.getActiveTimeline().transitionReplaceInflightToComplete(
HoodieTimeline.getReplaceCommitInflightInstant(clusteringCommitTime),
Option.of(metadata.toJsonString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new HoodieClusteringException("unable to transition clustering inflight to complete: " + clusteringCommitTime, e);
} finally {
this.txnManager.endTransaction();
}
WriteMarkersFactory.get(config.getMarkersType(), table, clusteringCommitTime)
.quietDeleteMarkerDir(context, config.getMarkersDeleteParallelism());
if (clusteringTimer != null) {
long durationInMs = metrics.getDurationInMs(clusteringTimer.stop());
try {
metrics.updateCommitMetrics(HoodieActiveTimeline.parseDateFromInstantTime(clusteringCommitTime).getTime(),
durationInMs, metadata, HoodieActiveTimeline.REPLACE_COMMIT_ACTION);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new HoodieCommitException("Commit time is not of valid format. Failed to commit compaction "
+ config.getBasePath() + " at time " + clusteringCommitTime, e);
}
}
LOG.info("Clustering successfully on commit " + clusteringCommitTime);
} HoodieSparkCopyOnWriteTable 的 updateZIndex 方法
private void updateZIndex(
@Nonnull HoodieEngineContext context,
@Nonnull List updatedFilesStats,
@Nonnull String instantTime
) throws Exception {
String sortColsList = config.getClusteringSortColumns();
String basePath = metaClient.getBasePath();
String indexPath = metaClient.getZindexPath();
// 获取所有的 commit 和 replaceCommit 的 instant 时间
List completedCommits =
metaClient.getCommitsTimeline()
.filterCompletedInstants()
.getInstants()
.map(HoodieInstant::getTimestamp)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 获取新写入数据文件的路径
List touchedFiles =
updatedFilesStats.stream()
.map(s -> new Path(basePath, s.getPath()).toString())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
if (touchedFiles.isEmpty() || StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(sortColsList) || StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(indexPath)) {
return;
}
LOG.info(String.format("Updating Z-index table (%s)", indexPath));
List sortCols = Arrays.stream(sortColsList.split(","))
.map(String::trim)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
HoodieSparkEngineContext sparkEngineContext = (HoodieSparkEngineContext)context;
// Fetch table schema to appropriately construct Z-index schema
Schema tableWriteSchema =
HoodieAvroUtils.createHoodieWriteSchema(
new TableSchemaResolver(metaClient).getTableAvroSchemaWithoutMetadataFields()
);
// 更新索引文件
ZOrderingIndexHelper.updateZIndexFor(
sparkEngineContext.getSqlContext().sparkSession(),
AvroConversionUtils.convertAvroSchemaToStructType(tableWriteSchema),
touchedFiles,
sortCols,
indexPath,
instantTime,
completedCommits
);
LOG.info(String.format("Successfully updated Z-index at instant (%s)", instantTime));
} ZOrderingIndexHelper.updateZIndexFor
public static void updateZIndexFor(
@Nonnull SparkSession sparkSession,
@Nonnull StructType sourceTableSchema,
@Nonnull List sourceBaseFiles,
@Nonnull List zorderedCols,
@Nonnull String zindexFolderPath,
@Nonnull String commitTime,
@Nonnull List completedCommits
) {
FileSystem fs = FSUtils.getFs(zindexFolderPath, sparkSession.sparkContext().hadoopConfiguration());
// Compose new Z-index table for the given source base files
// 读取新写入数据文件的 metadata 信息,用来构建索引
Dataset newZIndexDf =
buildZIndexTableFor(
sparkSession,
sourceBaseFiles,
zorderedCols.stream()
.map(col -> sourceTableSchema.fields()[sourceTableSchema.fieldIndex(col)])
.collect(Collectors.toList())
);
try {
//
// Z-Index has the following folder structure:
//
// .hoodie/
// ├── .zindex/
// │ ├── /
// │ │ ├── .parquet
// │ │ └── ...
//
// If index is currently empty (no persisted tables), we simply create one
// using clustering operation's commit instance as it's name
Path newIndexTablePath = new Path(zindexFolderPath, commitTime);
// 如果 .zindex 原本没有,首次写入,则直接覆盖写入,否则合并历史追加
if (!fs.exists(new Path(zindexFolderPath))) {
newZIndexDf.repartition(1)
.write()
.format("parquet")
.mode("overwrite")
.save(newIndexTablePath.toString());
return;
}
// Filter in all index tables (w/in {@code .zindex} folder)
// 获取 .zindex 目录下所有 instant 文件夹
List allIndexTables =
Arrays.stream(
fs.listStatus(new Path(zindexFolderPath))
)
.filter(FileStatus::isDirectory)
.map(f -> f.getPath().getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// Compile list of valid index tables that were produced as part
// of previously successfully committed iterations
List validIndexTables =
allIndexTables.stream()
.filter(completedCommits::contains)
.sorted()
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List tablesToCleanup =
allIndexTables.stream()
.filter(f -> !completedCommits.contains(f))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
Dataset finalZIndexDf;
// Before writing out new version of the Z-index table we need to merge it
// with the most recent one that were successfully persisted previously
if (validIndexTables.isEmpty()) {
finalZIndexDf = newZIndexDf;
} else {
// NOTE: That Parquet schema might deviate from the original table schema (for ex,
// by upcasting "short" to "integer" types, etc), and hence we need to re-adjust it
// prior to merging, since merging might fail otherwise due to schemas incompatibility
finalZIndexDf =
tryMergeMostRecentIndexTableInto(
sparkSession,
newZIndexDf,
// Load current most recent Z-index table
sparkSession.read().load(
new Path(zindexFolderPath, validIndexTables.get(validIndexTables.size() - 1)).toString()
)
);
// Clean up all index tables (after creation of the new index)
tablesToCleanup.addAll(validIndexTables);
}
// Persist new Z-index table
finalZIndexDf
.repartition(1)
.write()
.format("parquet")
.save(newIndexTablePath.toString());
// Clean up residual Z-index tables that have might have been dangling since
// previous iterations (due to intermittent failures during previous clean up)
tablesToCleanup.forEach(f -> {
try {
fs.delete(new Path(zindexFolderPath, f), true);
} catch (IOException ie) {
// NOTE: Exception is deliberately swallowed to not affect overall clustering operation,
// since failing Z-index table will be attempted to be cleaned up upon subsequent
// clustering iteration
LOG.warn(String.format("Failed to cleanup residual Z-index table: %s", f), ie);
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.error("Failed to build new Z-index table", e);
throw new HoodieException("Failed to build new Z-index table", e);
}
}
总结
读取:
- 查询类型为优化读取时,cow 和 mor 都能使用 zorder 索引优化,查询类型为快照时,只有 cow 可以
- scan 的文件 = 所有文件 - 使用了 zindex 的数据却没有命中的文件
写入:
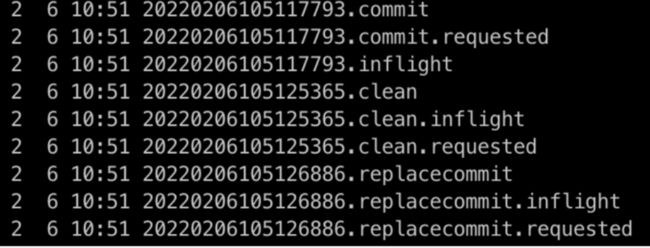
- 不影响任务主流程的写入,数据写完 commit 后生成上图 20220206105117793.commit,其它消费端正常查询
- 后续的排序,索引生成,可以在每次 write 完同步执行,或者起个 scheduler 任务异步后台执行,本次测试 inline 每次 write 结束后 cluster,最终生成 20220206105126886.replacecommit instant
相关
iceberg 本身元数据就有统计每个文件列的 Min/Max,所以实现上只需要对数据进行重排序,近期有相关的 pr Spark: Spark3 ZOrder Rewrite Strategy。依然是需要手动触发的 Action,新增 Zorder 的排序策略,具体细节会专门写一篇来说明,主要也是熟悉 iceberg 架构和 hudi 架构上的区别