io模型合集及NIO详解
三大IO模型
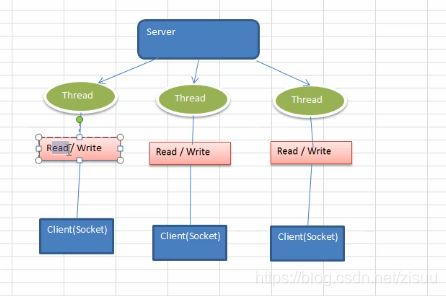
BIO模型
每一个请求开一个线程,缺点:
- 这种方式势必会造成线程开销
- 当请求没有结果的时候,会造成阻塞
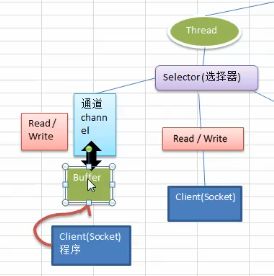
NIO模型
一个线程处理多个请求,即客户端发送的请求会发送到多路复用器上,多路复用器轮询到连接又I/O请求就进行处理

从上面这幅图可以看出,一个线程维护一个选择器,一个选择器轮询多个请求,只要有请求带着事件到来,就去处理----即netty这个框架是一个事件驱动的框架NIO框架
AIO模型
NIO三大组件
NIO三大组件的关系:
三大组件:selector,channel,buffer
一个Select对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个channel
程序切换到那个channel是由事件决定的
Selector会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换
Buffer是一个内存块,底层是一个数据
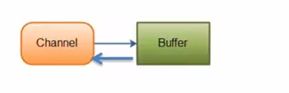
数据的读取写入是通过Buffer.在传统Bio中要么是输入流,要么是输出流,不能是双向,但是NIO的Buffer是可以读也可以写,需要通过flip方法进行切换
channel是双向的
在传统的BIO模型中,如果一个请求没有携带数据或者返回数据,可能会造成线程阻塞,但是在NIO模型中,数据被缓冲在Buffer里,客户端只能从Buffer中读取数据及发送数据,如果缓冲区中没有数据,服务器的Select就不会区处理这个通道,而是处理其他Buffer区中有数据的通道
Nio与Bio的比较
组件一 Buffer
简单demo
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个Buffer,可以存放5个Int类型数据
IntBuffer intBuffer=IntBuffer.allocate(5);
for(int i=0;i<intBuffer.capacity();i++){
//放数据
intBuffer.put(i*2);
}
//将buffer转换,读写切换(!!!!!)
intBuffer.flip();
while(intBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
}
}
常用Buffer子类

常用方法
buffer类的常用方法总结
组件二 通道channel
基本介绍
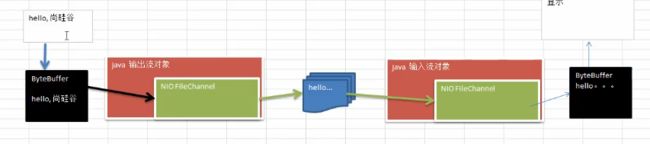
案例一:本地文件写数据
其实FileChannel是对输出流的一个包装
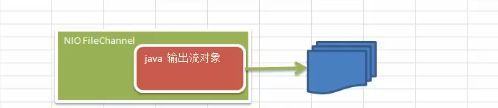
代码实列:’
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String str="hello world";
//创建一个输出流
FileOutputStream stream=new FileOutputStream("D://Aimg//test/5.txt");
//这个fileChanel真是类型是FileChannelImpl
FileChannel channel=stream.getChannel();
//创建一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//放str入byteBuffer
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
//读写反装
byteBuffer.flip();
//将缓冲区数据写入通道
channel.write(byteBuffer);
stream.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//文件
File file=new File("D://Aimg//test/5.txt");
FileInputStream inputStream=new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel channel=inputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate((int)file.length());
//将通道数据读入到buffer中,注意,write方法是从缓冲区读取数据到通道
channel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
}
上述两个案列的示意图:
案例三:一个Buffer完成文件的读写
流程:

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//文件
File file=new File("D://Aimg//test/5.txt");
FileInputStream inputStream=new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel readChannel=inputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D://Aimg//test/6.txt");
FileChannel writeChannel=outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(true){
//每次读的时候要记得清空缓存
buffer.clear();
int read= readChannel.read(buffer);
if(read!=-1){
//读写反装
buffer.flip();
writeChannel.write(buffer);
}else break;
}
}
案例四:channel的transferFrom拷贝文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//文件
File file=new File("D://Aimg//12.jpg");
FileInputStream inputStream=new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel readChannel=inputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D://Aimg//13.jpg");
FileChannel writeChannel=outputStream.getChannel();
writeChannel.transferFrom(readChannel,0,readChannel.size());
}
组件三 Selector选择器
常用方法

一个channel通道对应了一个selectKey,每次有事件发生时,selector会根据获取的selectKeys数组来遍历channel
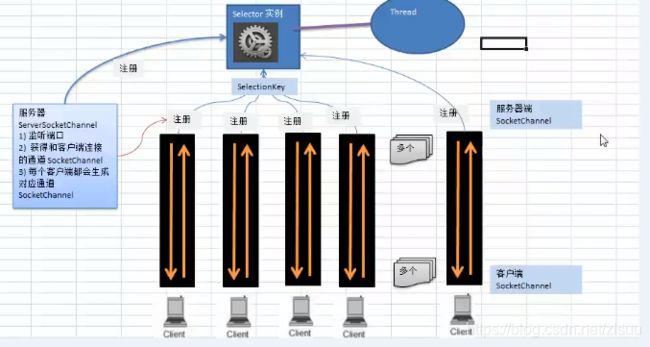
Selector关系图及解析:
当客户端连接时,会通过ServerSocketChannel
,得到SocketChannel将socketChannel注册到Selector上,并且返回一个
selectorKey,该SelectorKey会和Selector关联selector进行监听select方法,返回有事件发生的通道个数
进一步得到各个SelectKey
再通过SelectKey,反向获取channel
最后通过channel完成对应的事件
NIO快速入门
在学习nio入门前,请先学习前一篇文章,理清nio三大组件的关系
图解关系:
当客户端连接时,会通过ServerSocketChannel
,得到SocketChannel将socketChannel注册到Selector上,并且返回一个
selectorKey,该SelectorKey会和Selector关联selector进行监听select方法,返回有事件发生的通道个数
进一步得到各个SelectKey
再通过SelectKey,反向获取channel
最后通过channel完成对应的事件
服务端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建serverSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//创建selector对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//绑定端口6666,在服务器端监听
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
//设置非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//把ServerSocketChannel注册到Selector
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//循环等待客户端请求
while (true) {
if (selector.select(1000) == 0) {
System.out.println("服务器等待了1秒,无连接");
continue;
}
//获取selectorKey集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
//遍历集合
for (SelectionKey key : selectionKeys) {
//反向获取到channel,根据不同事件做出处理
if (key.isAcceptable()) {//如果是连接请求
//给该客户端生成一个socketChannel
SocketChannel channel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
//将当前的channel注册到selector上
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if (key.isReadable()) {//读的请求
//获取到该channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//获取buffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
channel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println("from 客户端" + new String(byteBuffer.array()));
}
//最后移出
selectionKeys.remove(key);
}
}
}
客户端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel=SocketChannel.open();
//非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//提供服务端的ip和端口
InetSocketAddress address=new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",6666);
//连接服务器
if(!socketChannel.connect(address)){
while(!socketChannel.finishConnect()){
System.out.println("因为连接需要事件,可以做其他的事情");
}
}else {
//连接成功了
String str="hello world";
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
//将数据写入channel
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
}
}