作者:CHAITANYA SINGH
来源:https://www.koofun.com//pro/kfpostsdetail?kfpostsid=18
当我们需要根据一个条件执行一组语句时,我们需要使用控制流语句。例如,如果一个数字大于零,那么我们想要打印“正数”,但是如果它小于零,那么我们要打印“负数”。在这种情况下,程序中有两个print语句,但根据对输入值的条件比较结果,每次只执行一个print语句。我们将看到如何使用控制语句在java程序中编写这种类型的条件。
下面我们将学习如何根据需求在java程序中使用四种类型的控制语句。在本教程中,我们将介绍以下条件语句:if语句、嵌套if语句、if-else语句、if-else-if语句
1)if语句
if语句包含一个条件,后面是语句或一组语句,如下所示:
if(condition){
Statement(s);
}
这些语句只有在给定条件判断为true(真)时才会执行。如果条件为false(假),则if语句正文中的语句将被完全忽略。
if语句示例
public class IfStatementExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
int num=70;
if( num < 100){
/* This println statement will only execute,
* if the above condition is true
*/
System.out.println("number is less than 100");
}
}
}
输出:
number is less than 100
2)Java中的嵌套if语句
当一个if语句嵌套在另一个if语句中时,这个if语句就被称为嵌套if语句.
嵌套if的结构如下所示:
if(condition_1) {
Statement1(s);
if(condition_2) {
Statement2(s);
}
}
如果condition_1(条件1)为true(真),则Statement1语句将会执行。执行完了Statement1语句后,程序走到下一个语句if(condition_2),如果condition_2(条件2)的值为true(真),则Statement2语句就会执行,反之,程序会跳过Statement2(s)语句,继续执行后面的语句。由此可见,只有在condition_1和condition_2都为true(真)的情况下,语句Statement2才会执行。
嵌套if语句示例
public class NestedIfExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
intnum=70;
if(num < 100){
System.out.println("number is less than 100");
if(num > 50){
System.out.println("number is greater than 50");
}
}
}
}
输出:
number is less than 100
number is greater than 50
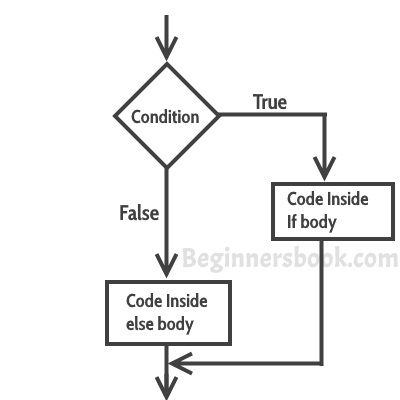
3)Java中的if-else语句
if-else语句结构看上去是这样的:
if(condition) {
Statement(s);
}
else{
Statement(s);
}
如果if后面的condition(条件)为true(真),则“if”后面的大括号{ }中的语句将执行,如果if后面的condition(条件)为false(假),则“else”后面的大括号{ }中的语句将执行。
if-else语句示例
public class IfElseExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
int num=120;
if( num < 50){
System.out.println("num is less than 50");
}
else{
System.out.println("num is greater than or equal 50");
}
}
}
输出:
num is greater than or equal 50
4)if-else-if 语句
当我们需要检查多个条件时,使用if-else-if语句。在上面的声明语句中,我们只有一个“if”和一个“else”,但是我们可以有多个“else if”,也就是梯状的if语句,如下所示
if(condition_1) {
/*if condition_1 is true execute this*/
statement(s);
}
else if(condition_2) {
/* execute this if condition_1 is not met and
* condition_2 is met
*/
statement(s);
}
else if(condition_3) {
/* execute this if condition_1 & condition_2 are
* not met and condition_3 is met
*/
statement(s);
}
.
.
.
else {
/* if none of the condition is true
* then these statements gets executed
*/
statement(s);
}
注:这里需要注意的最重要一点是,在“if-else-if”语句中,一旦一个“else if”后面的条件满足了,这个条件版块里面的语句集就会被执行,其余“else if”条件版块里面的语句就都会被忽略。如果所有的else if后面的条件都不满足,则执行最后面的“other”版块中的语句。
if-else-if实例
public class IfElseIfExample {
public static void main(String args[]){
int num=1234;
if(num <100&& num>=1) {
System.out.println("Its a two digit number");
}
else if(num <1000&& num>=100) {
System.out.println("Its a three digit number");
}
else if(num <10000&& num>=1000) {
System.out.println("Its a four digit number");
}
else if(num <100000&& num>=10000) {
System.out.println("Its a five digit number");
}
else{
System.out.println("number is not between 1 & 99999");
}
}
}
输出:
Its a four digit number