斐波那契数列
剑指offer 10-i 斐波那契数列
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
int a = 0;
int b = 1;
int sum;
for(int i=0; i剑指offer 10-ii 青蛙跳台
class Solution {
/* 动态规划 空间复杂度为n
*/
public int numWays(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1;
// dp[n].length = n+1
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i=2; i<=n ; i++){
// 思路:当跳到台阶i时,无非来自台阶 i-1 或者 i-2,故将两种情况相加
dp[i] = (dp[i-1] + dp[i-2])%1000000007;
}
return dp[n];
}
/*动态规划 空间复杂度为1
符合Fb[i] = Fb[i-1] + Fb[i-2]
的斐波那契数列
*/
public int numWays2(int n){
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
int sum;
for(int i=0; i搜索算法
剑指offer 04 二维数组中的查找
[ [1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]]
设一个flag在右上角,flag = 15,后比较target,若小于target,则向下,若大于则向左。
时间复杂度 O(M+N)O(M+N) :其中,NN 和 MM 分别为矩阵行数和列数,此算法最多循环 M+NM+N 次。
空间复杂度 O(1)O(1) : i, j 指针使用常数大小额外空间。
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
// 先解决 [] 和 [[],[],[]] 的问题
if(matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) return false;
int i = 0;
int j = matrix[0].length - 1;
while(i < matrix.length && j >=0){
if(matrix[i][j] == target) return true;
else if(matrix[i][j] < target) i++;
else j--;
}
return false;
}
}
剑指offer 11旋转数组的最小数字
二分法:当数组呈半单调性时,通过二分法来收窄搜索范围
class Solution {
public int minArray(int[] numbers) {
int right = numbers.length -1;
int left = 0;
// "/" 除是向下除
// 注意while 判别条件
while(left < right){
int mid = (right + left)/2;
if(numbers[mid] < numbers[right]) right = mid;
else if(numbers[mid] > numbers[right]) left = mid + 1;
else right = right - 1;
}
return numbers[right];
}
}
剑指offer 56-i数组中数字出现的次数
本题主要考察异或运算和二进制等运算符
“<<”
a = 0001; a = a << 1 则 a = 0010
"^"
^异或运算符顾名思义,异就是不同,其运算规则为
1 ^ 0 = 1 , 1 ^ 1 = 0 , 0 ^ 1 = 1 , 0 ^ 0 = 0
故4 ^ 4 ^ 5 ^ 5 ^ 8 = 8
"&"
1 & 1=1 , 1 & 0=0 , 0 & 1=0 , 0 & 0=0
class Solution {
public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) {
if(nums == null) return new int[0];
int number = 0;
int a = 1;
// 数组的异或运算
for(int x: nums){
number ^= x;
}
//找出二进制中第一位不同
// 1&1=1 , 1&0=0 , 0&1=0 , 0&0=0
while((number & a) == 0){
a <<= 1;
}
int n = 0, m = 0;
//通过第一位的不同来分出两个部分
for(int i:nums){
// != 0 与 ==1 不等价:2 & 2 => 0010 & 0010 => 0010 => 2 !=0
if((a & i) != 0) n ^= i;
else m ^= i;
}
return new int[]{n,m};
}
}
全排列
剑指offer 38字符串的排列
输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。
你可以以任意顺序返回这个字符串数组,但里面不能有重复元素。
输入:s = "abc"
输出:["abc","acb","bac","bca","cab","cba"]
图析:
class Solution {
public String[] permutation(String s) {
Set set = new HashSet<>();
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
dfs(0,c,set);
// HashSet 的大小用.size()表示
String[] res = new String[set.size()];
int i = 0;
for(String str:set){
res[i++] = str;
}
return res;
}
public void dfs(int index, char[] c, Set set){
if(index == c.length-1){
// String.valueOf(): char[] => String
set.add(String.valueOf(c));
// 退出dfs
return;
}
// 核心是 i=index 和dfs(index+1,...)来保证进一步的全遍历
for(int i=index; i 动态规划
Leetcode 337打家劫舍iii
剑指offer 42连续子数组最大的和
示例:
输出: 6
解释: 连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6。
思路:sum为当前和的变量,当sum小于0时,sum清零,加后续元素
每次求和后,res记录当前遇见的最大和。故最终只需遍历一遍
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i剑指offer 51数组中的逆序对
示例:输入: [7,5,6,4] 输出: 5 解释:["7,5", "7,6", "7,4", "5,4", "6,4"]
思路: 利用归并排序,将数组利用递归拆分成只含有一个元素的数组,然后比大小进行合并,在合并过程中,如果后数组某元素nums[j]小于前数组某元素nums[i],则count 加nums[i]之后的长度
class Solution {
public int reversePairs(int[] nums) {
int res = mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.length-1);
return res;
}
public int mergeSort(int[] nums, int l, int r){
if(l >= r) return 0;
// “>> 1” <=> "/2" 位运算的效率大于普通运算
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
//递归方法,最底层完成后,再完成上一层
int count = mergeSort(nums, l, mid) + mergeSort(nums, mid+1, r);
int[] temp = new int[r-l+1];
int i = l;
int j = mid+1;
int k = 0;
while(i <= mid && j <= r){
// 等于的时候不算逆序列
count += nums[i] > nums[j] ? (mid - i + 1) : 0;
// 一定记着要 <=, 等于的情况下先放左边
temp[k++] = nums[i] <= nums[j] ? nums[i++] : nums[j++];
}
while(i <= mid){
temp[k++] = nums[i++];
}
while(j <= r){
temp[k++] = nums[j++];
}
// 将temp放到nums中相应的位置,为之后上一层nums[]还要比较
System.arraycopy(temp, 0, nums, l, r-l+1);
return count;
}
}
剑指offer 15二进制中1的个数
示例:
输入:1011
输出:3
解释:输入的二进制串 1011 中,共有三位为 '1'
思路: 采用n & n-1的思路,例如:8的二进制是1000, 7的二进制是0111, 对1000和0111做并运算,得出0000, 故只做了一次并运算就返回,count为1。
一次并运算可消除一个1。
public class Solution {
// you need to treat n as an unsigned value
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n != 0){
n &= n-1;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
剑指offer 16数值的整数次方
示例:
输入:x = 2.10000, n = 3
输出:9.26100
思路:
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
double res = 1;
// long 型保证不会溢出
long b = n;
if(b < 0){
x = 1/x;
b = -b;
}
while(b != 0){
if(b % 2 != 0) res *= x;
b >>= 1;
x *= x;
}
return res;
}
}
剑指offer 05替换空格
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
String res = s.replace(" ","%20");
return res;
}
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(char c: s.toCharArray()){
//注意是 c == ' ', 不是 c == " "
if(c == ' ') res.append("%20");
else res.append(c);
}
return res.toString();
}
}
剑指offer 21调整数组顺序使奇数在前偶数在后
思路:双指针,前后夹击
class Solution {
public int[] exchange(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length <= 1) return nums;
int l = 0;
int r = nums.length - 1;
while(l < r){
// 记得加入条件l剑指offer 39数组中出现次数超过一半的元素
示例:
输入: [1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 5, 4, 2]
输出: 2
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 1) return nums[0];
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
int len = nums.length/2;
// 遍历nums,元素的value非1即+1
for(int i:nums){
map.put(i,map.getOrDefault(i,0)+1);
if(map.get(i) > len) return i;
}
return 0;
}
// 排序后,一个元素次数超过一半,那么中间的肯定为这个元素
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 1) return nums[0];
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length/2];
}
}
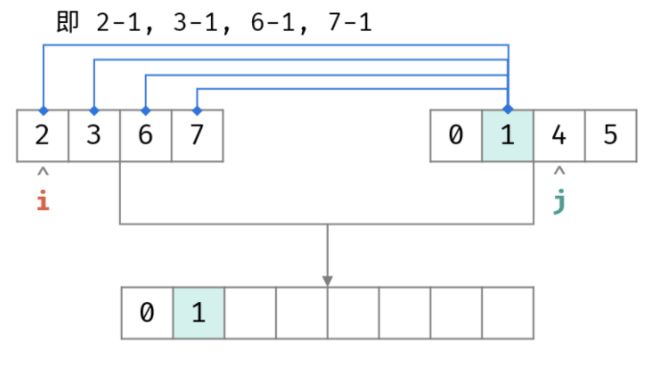
剑指offer 03数组中重复的数字
示例:
数组内所有元素都小于其长度。长度为N的数组,其元素范围在0 ~ N-1
输入:
[2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5, 3]
输出:2 或 3
解析:方法二中:
- 若不存在
nums[index] == index, 将会在index位置上把所有元素交换一遍,直至碰到相同元素。如下所示:
[图片上传中...(image.png-3465a5-1619170008947-0)]
[2,3,1,2,5,3] <= swap 2 and 1
[1,3,2,2,5,3] <= swap 1 and 3
[3,1,2,2,5,3] <= swap 3 and 2
[2,1,2,3,5,3] <= nums[0] == nums[2]
nums[0] == nums[nums[0]]
- 若存在,总会出现
nums[0] == nums[nums[0]],例如:
数组 :[0, 1, 2, 3, (2), 5, 3]
index: 0, 1, 2, 3, (4), 5, 6
class Solution {
// 方法一:暴力法
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0; i 剑指offer 14-i剪绳子
示例:
输入: 10
输出: 36
解释: 10 = 3 + 3 + 4, 3 × 3 × 4 = 36
class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
// 思路: 每段相等且值为3时,乘积最大
// 当最后一段为1是,借用前面的一段凑成 2×2 > 3×1
if(n < 3) return 1;
if(n == 3) return 2;
if(n > 3){
int res1 = n / 3;
int res2 = n % 3;
if(res2 == 0) return (int)Math.pow(3, res1);
if(res2 == 1) return (int)Math.pow(3, res1-1) * 4;
if(res2 == 2) return (int)Math.pow(3, res1) * res2;
}
return -1;
}
}
剑指offer 14-ii剪绳子
import java.math.BigInteger;
class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
// 思路: 每段相等且值为3时,乘积最大
// 当最后一段为1是,借用前面的一段凑成 2×2 > 3×1
if(n < 3) return 1;
if(n == 3) return 2;
BigInteger res = new BigInteger("3");
BigInteger ans = new BigInteger("1");
if(n > 3){
int res1 = n / 3;
int res2 = n % 3;
if(res2 == 0) {
ans = res.pow(res1);
}
if(res2 == 1) {
ans = res.pow(res1-1);
ans = ans.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(4));
}
if(res2 == 2){
ans = res.pow(res1);
ans = ans.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(2));
}
}
// 取余
ans = ans.remainder(BigInteger.valueOf(1000000007));
return ans.intValue();
}
// 思路:每一遍都 ×3 取余直到 n == 4
public int cuttingRope(int n){
if(n < 3) return 1;
if(n == 3) return 2;
long res = 1;
while(n > 4){
res = res * 3 % 1000000007;
n -= 3;
}
return (int)(res * n % 1000000007);
}
}