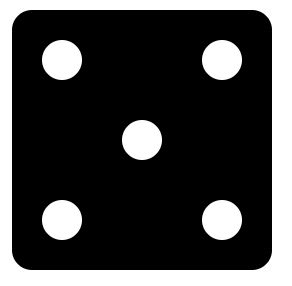
1. flex实现骰子5点布局(答案不唯一)
简单的思路:
1.flex布局横向排列,flex-flow:wrap 可以折行
2.通过给第一个点设置右边距把第二个点顶到最右侧
3.通过给中间点设置左右边距居中
4.给第4个点设置右边距把第5个点顶到右边
5.容器设置align-content:space-between; 上下位置调整
效果图:
2. 说下js中继承
//方式一 构造函数继承
//缺点:只实现部分继承,原型中的属性和方法没有继承过来
//优点:在初始化子类时,可以给父类构造传递参数
function Parent(name){
this.name=name;
}
//Parent.prototype.say = function(){
// console.log("hello");
//}
function Child(name){
Parent.call(this,name);
}
var a = new Child("zsl");
console.log(a.name); //zsl
//方式二 原型链继承
//缺点 1. 是改变对象的引用属性,其他对象也跟着一起改变;
//缺点 2. 是在创建子类的实例中不能向父类构造传递参数;
function Parent(){
this.name="zhang";
this.arr=[1,2,3];
}
function Child(age){
this.age = age;
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
var a = new Child(18);
var b = new Child(18);
a.arr.push(4);
console.log(a.arr); //[1,2,3,4]
console.log(b.arr); //[1,2,3,4]
//方式三 组合继承
//优点:避免了原型链继承和构造函数继承的缺点
//缺点:创建对象时会执行2次父类的构造方法
function Parent(){
this.name="zhang";
this.arr=[1,2,3];
}
function Child(age){
Parent.call(this);
this.age = age;
}
Child.prototype = new Parent();
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
var a = new Child(18);
var b = new Child(18);
a.arr.push(4);
console.log(a.arr); //[1,2,3]
console.log(b.arr); //[1,2,3,4]
//方式四 寄生组合式继承(最优方式)
//优点:避免了实例化对象,执行2次父类构造
function object(o){
function F(){}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
function extend(child,parent){
var copyObj = object(parent.prototype);
copyObj.constructor = child;
child.prototype = copyObj;
}
function Parent(){
this.name="zhang";
this.arr=[1,2,3];
}
function Child(age){
Parent.call(this);
this.age = age;
}
extend(Child,Parent);
3. 以下代码运行的结果是输出()
var a=b=1;
(function(){
var a=b=2;
})();
console.log(a,b);
// 解析
// 赋值是从右到左,所以var a=b=2;相当于 b=2;var a=b;
// b没有var在非严格模式默认是全局变量,a有var修饰是局部变量
// console是在全局环境中,只能访问到全局变量,所以结果是a=1 b=2
4. 运行的结果在控制台输出什么?
if([] instanceof Object){
console.log(typeof null);
}else{
console.log(typeof undefined);
}
// 输出 object
javascript的数据类型有:
string 、number 、boolean、object、undefined (null也是object类型)
这里注意:
typeof undefined --> undefined
typeof null --> object
5. 以下程序输出什么?
function say(word){
let word = "hello";
console.log(word);
}
say("hi lili");
//报错 Uncaught SyntaxError: Identifier 'word' has already been declared
6.请选择正确的输出()
for(var i=0;i<5;i++){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(i);
},0);
}
// 5 5 5 5 5
//分析这个问题前我们先看下这段代码
//正常输入 0 1 2 3 4
for(var i=0;i<5;i++){
(function(i){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(i);
},0);
})(i);
}
for(let i=0;i<5;i++){
setTimeout(function(){
console.log(i);
},0);
}
你会发现虽然setTimeout在前面立即执行,但输入的结果仍然是:22 11
那么为什么会先输出22呢?
因为定时器都会被放在一个队列的数据结构中(先进先出)
只有上下文的可执行代码都执行完毕了,才会执行队列中的定时器。
这样我们就知道了,上面for循环中,先循环完5次后(这时i已经为5),才会执行定时器的代码。所以输出5个5。
7. 怎样快速去判断一个数据类型
我们熟悉的有2中方法:typeof和instanceof
这俩种方法不够快速,因为你需要不断试,才能最终确定什么类型。下面这种方法最快速:
Object.prototype.toString.call()
比如:
let o = {name:"zhang"};
let arr = [1,2,3];
let type1 = Object.prototype.toString.call(o);
let type2 = Object.prototype.toString.call(arr);
console.log(type1);
console.log(type2);
//[Object Object]
//[Object Array]
8. Vue 双向绑定原理
参考:https://juejin.im/entry/5923973da22b9d005893805a
9. 问输出结果是啥
123 instanceof Number //false
new Number(123) instanceof Number //true
Number(123) instanceof Number //false
//instanceof 只能判断对象、数组等的对象类型,不能判断基本数据类型
10. js实现二分法查找,并说出时间复杂度
//二分查找数组必须有序
function search(key,arr){
let start=0, end=arr.length-1;
while(start<=end){
let mid = (start+end)/2;
if(keyarr[mid]){
start = mid+1;
}else{
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
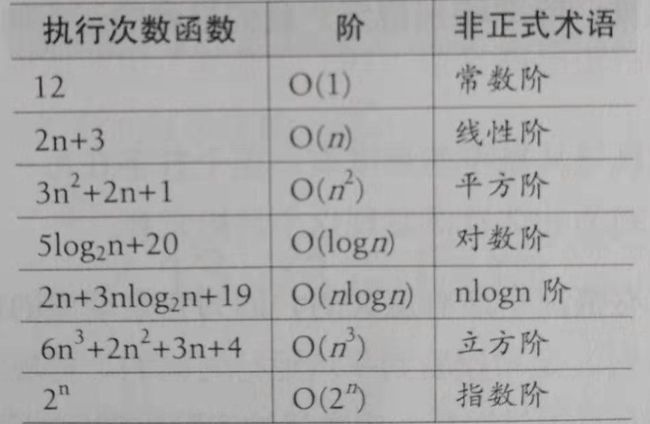
这里说下时间复杂度和空间复杂度的概念和算法:
时间复杂度:方法运行时占用的时间
空间复杂度:方法运行时占用的内存
常用的时间复杂度记法为大O记法:T(n) = O( f(n) )
f(n) 是一个函数,表示随着问题规模n的增大,执行时间的增长率。
O(n):
比如求1到n之间数的和:
let sum=0;
for(let i=1;i<=n;i++){
sum+=i;
}
显然循环内语句执行了n了,也就说这个方法的运行次数和问题规模n成正比,n大运行时间长,n小运行时间短。所以这个方法的时间复杂度为O(n)。
O(1)
那么还有一种算法,求1到n之间数的和:
1+2+3+...(n-2)+(n-1)+n
//收尾相加
n/2(n+1)
这种方法也问题规模n没有关系,无论n是多少,只需要执行n/2(n+1)这一句代码就能得出结果,所以这个算法问题规模没有关系的,我们都就说他的时间复杂度为O(1)。
O(n²)
for(let i=0;i到这里需要说下推导大O阶的定律:
- 用常数1取代运行时间中所有的加法常数
- 在修改后的运行次数函数中,只保留最高阶项
- 如果最高阶项存在且不是1,则去除与这个项目相乘的常数
到这里我们出一个考察题,看看掌握的怎么样:
for(let i=0;i里面for循环一次执行次数的顺序是:
n+(n-1)+(n-2)+....+2+1
也就是n/2(n+1),取高阶为n²/2,去除相乘的常数后就是n²,
所以这个方法的时间复杂度也是O(n²)
那接下来我们回过头看看二分法查找的时间复杂度:
其实主要看while循环的次数,比如数组长度n,一次后是n/2,while执行2次后剩的遍历区间长度就是n/2²,假设x次后找到,就是n/2ˣ >=1 ,即令 n/2ˣ =1,x= log₂n,所以二分法的时间复杂度是O(logn)。
11. 输出的顺序
setTimeout(
function(){
console.log("11");
}
);
console.log("22");
Promise.resolve().then(function(){
console.log("33");
});
// 22 33 11
注意:
Promise.resolve()返回一个Promise新的实例,这个方法中的参数有4中类型:thenable,promise对象,不具有then方法的对象或者不是对象,空参数。
立即resolve的promise对象是在本轮事件结束时执行,而setTimeout是在下一轮事件开始时执行
12. 深拷贝浅拷贝的区别,并分别用js实现
let obj = {
name:"zhang",
age:18,
score:[88,80,90]
}
浅拷贝:拷贝上面obj对象,会重新生成一个一样对象,但是浅拷贝只能拷贝表层数据,不能拷贝对象的属性是对象或数组的。也就是说新对象的score属性,指向的还是原来对象score属性数组的地址。所以修改浅拷贝的对象可能会影响原来的对象。
深拷贝:完全的复制一份,生成的新对象和原来的对象互不影响。
//浅拷贝
function shallowCopy(obj){
let c = {};
for(let i in obj){
c[i] = obj[i];
}
return c;
}
//深拷贝(递归调用)
function deepCopy(obj,c){
let c = c || {};
for(let i in obj){
if(typeof obj[i] ==="object "){
c[i] = (obj[i]===Array)?[]:{};
deepCopy(obj[i],c[i]);
}else{
c[i] = obj[i];
}
}
return c;
}
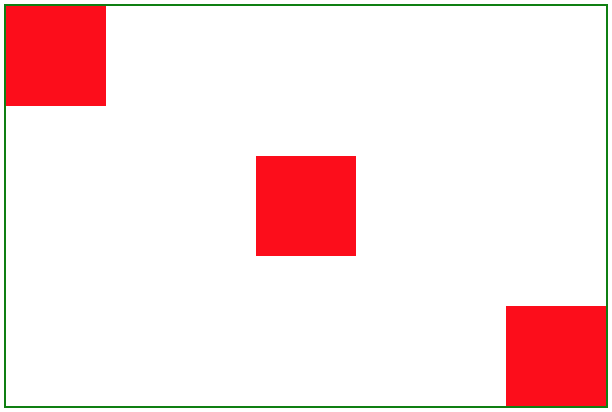
13. flex实现下面的布局
14. 获取页面元素宽高和位置
var node = document.getElementById("div");
//只能获取行内样式的宽高,并且无论标准还是ie盒模型,只取height属性的值
var h = node.style.height;
//只使用于ie浏览器
var h = node.currentStyle.height;
//都使用 但也是只取height值
var h = window.getComputedStyle(node).height;
// content+padding
var h = node.clientHeight;
// content + padding +border
var h = node.offsetHeight;
// content + padding + border
var h = node.getBoundingClientRect().height;
//获取位置就用
node.getBoundingClientRect().left
node.getBoundingClientRect().top
node.getBoundingClientRect().bottom
node.getBoundingClientRect().right
//注意:这些值是从boder开始算起的
15. 下面代码输出什么(原型链知识)
Function.prototype.a = 'a';
Object.prototype.b = 'b';
function Person(){};
var p = new Person();
console.log('p.a: '+ p.a); // p.a: undefined
console.log('p.b: '+ p.b); // p.b: b
//Object.prototype.aa = "aa";
Function.prototype.aa = "bb";
function fn() {}
console.log("zhang=" + fn.aa); //bb
Object.prototype.aa = "aa";
//Function.prototype.aa = "bb";
function fn() {}
console.log("zhang=" + fn.aa); //aa
Object.prototype.aa = "aa";
Function.prototype.aa = "bb";
function fn() {}
console.log("zhang=" + fn.aa); //bb
16. 什么是闭包,手写一个闭包,说其作用
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2009/08/learning_javascript_closures.html
闭包是指有权访问另一个函数作用域中的变量的函数。
function closure(){
var temp = 'zhang';
function inner(){
console.log(temp);
}
return inner;
}
作用:可以实现在函数外部访问函数内部变量
17.Dom0级事件和Dom2级事件的区别,以及Dom事件和IE事件的区别
Dom0级事件有俩种绑定方式:
点我
或者
var div = document.getElementById("div");
div.onclick = function(){
//处理
}
//删除事件
div.onclick =null;
Dom2级事件的绑定方式:
div.addEventListener('click',function(){
//处理
},false);
//删除事件
//匿名函数的方式无效
div.removeEventListener('click',function(){
//处理
},false);
//这种方式有效
div.removeEventListener('click',handler,false);
var handler = function(){
//处理事件
}
Dom0和Dom2最主要区别:给一个元素注册同一类的多个Dom0级事件,会覆盖前面的事件,只有最后注册的有效。而同样注册多个Dom2级事件会都有效,并按注册顺序执行。
Dom0和Dom2可以同时注册到一个元素,执行顺序按注册顺序。
Dom事件和IE事件的区别:Dom事件流的顺序是先捕获再冒泡,而IE事件只有冒泡,没有捕获。
注册事件的方式也不同:
// 注意事件类型onclick不是click
div.attachEvent('onclick',function(){
//处理事件
});
//解除事件绑定
div.detachEvent('onclick',function(){
});
注意:IE事件和Dom2级事件一样,可以给一个元素注册多个同类型的事件,但是Dom2执行顺序是按注册顺序,而IE的执行顺序和注册顺序相反。
div.attachEvent('onclick',function(){
console.log("ie事件1");
});
div.attachEvent('onclick',function(){
console.log("ie事件2");
});
//ie事件2
//ie事件1
注意:Dom事件执行的作用域是其所属元素的作用域,而IE事件执行的作用域是全局作用域。
div.addEventListener('click',function(){
//这里this是div所属作用域环境
},false);
div.attachEvent('onclick',function(){
//这里this是全局作用域,即window环境
console.log(this==window); //true
});
18. Vue父子组件和兄弟组件之间通信
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000020053344?from=groupmessage&isappinstalled=0
19.html自上向下加载遇到
普通script加载流程:
-
document解析 - 遇到
script标签,停document解析 - 请求
a.js - 执行
a.js中的脚本 - 继续解析
document
给script标签加上defer 或 async属性后,script标签不会阻塞document的解析,这时所有带defer 或 async的script标签都会并行下载。
defer
- 不阻止解析 document, 并行下载 a.js, b.js
- 下载完 a.js, b.js 不会立即执行,仍继续解析 document
- 按页面的出现顺序,同步脚本都执行完,DomContentLoaded事件前,按顺序执行a.js b.js
async
- 不阻止解析 document, 并行下载 a.js, b.js
- 下载完后立即执行,两者执行顺序不一定,执行时间不一定,可能在DomContentLoaded前,也可能在其后
20.@import 和 link引入外部样式有什么区别?
首先,样式有三种方式:行内样式、内联样式、外联样式
他们的权重是:行内样式>内联样式>外联样式
-
@import是放在//显示红色22.下面代码输出什么
try{ console.log(1); setTimeout(()=>{ console.log(2); throw new Error(3); },0); }catch(e){ console.log(e); } // 1 2 // Uncaught error 3try catch是同步代码,同步代码执行完毕输出1。然后执行异步代码,输出2,然后抛出异常,由于try catch已经执行完,所以不能捕获到异常。
23.求俩个数组的交集
//ES6 写法 时间复杂度O(n²) function insertSection(arr1, arr2) { var a = new Set(arr1); var b = new Set(arr2); return Array.from(a).filter(x => b.has(x)); }如果时间复杂度为O(n),怎么写?
注意:我们解决这类问题的一个思路是,将时间复杂多为On的n次方,拆为n个复杂度为O(n)的算法,再让这些算法串行执行。//时间复杂度 O(n) function insertSection(arr1,arr2){ //去重 var a = new Set(arr1); var b = new Set(arr2); //合并 var c = [...a,...b]; //排序 这里是一个O(n) var d = c.sort(); var e = []; var temp; for(let i=0;i24."abc efg".replace(),输入表达式,使得到的结果为"efg abc"
先来了解下String.prototype.replace(参数1,参数2)这个api
str.replace( regexp|substr, newSubStr|function )
这题我们用正则在解,所以先了解正则的几个预定义模式:
^ 表示开头 $表示结尾 ()表示一组
\w : 匹配任意的字母、数字和下划线,相当于[A-Za-z0-9_]
\s : 匹配空格(包括换行符、制表符、空格符等,相当于[ \t\r\n\v\f]
$n : 匹配成功的第n组内容,n是从1开始的自然数。var reg = /(\w+)\s(\w+)/; "abc efg".replace(reg,'$2 $1'); //efg abc25. for、for...of、for...in、forEach、map、filter、every、some、reduce
var arr = [3,5,8];- for 对数组遍历,可以使用
return break continue结束或进行下一次循环; - forEach是数组的方法,遍历数组中的每一项数据,接受一个对每一项数据的回调函数,但是内部不能用
return break continue不起作用;
arr.forEach(function(item,index){ console.log(item); }); // 3 5 8- for...in 遍历数组的索引,对象的属性
for(let i in arr){ console.log(arr[i]); //遍历数组索引 } //3 5 8 var obj = {name:'zhang',age:18}; for(let i in obj){ console.log(obj[i]); //遍历对象属性 } //zhang 18有一点需要注意,用for...in遍历时,原型链上的所有属性都会被遍历,比如:
Array.prototype.other = [10,11]; for(let i in arr){ console.log(arr[i]); } //3 5 8 [10,11] Object.prototype.a = { sex: "man" }; var b = { name: "zhang", age: 18 }; for (let i in b) { console.log(b[i]); } //zhang 18 {sex:'man'}那么我不想遍历原型链上的属性,怎么办呢?
hasOwnProperty:只有实例的属性可以遍历,原型上的属性不能遍历到。Array.prototype.other = [10,11]; for(let i in arr){ if(arr.hasOwnProperty(i)){ console.log(arr[i]); } } //3 5 8- for...of ES6提出的,可以遍历Array、String、Map、Set、arguments、dom集合,但是不能遍历对象。
//遍历数组 for(let i of arr){ console.log(i); } //3 5 8 //遍历字符串 var str = "zhang"; for (let i of str) { console.log(i); } //z h a n g //遍历Map //遍历Set //遍历Dom集合 //遍历arguments- map 根据传入的函数,返回新的数组,原数组不变
var b = arr.map(x=>{ return x*2; }); console.log(b); //[6,10,16]- filter根据传入的函数,筛选出符合规则的值,组成新数组,原数组不变
var arr = [3,5,8,10]; var b = arr.filter(x=>{ return x>5; }); console.log(b); //[8,10]- every是数组的方法,结果为boolean类型,每一项都满足函数,返回true,只要有一项不满足,就返回false
var arr =[3,5,8]; var result = arr.every(x=>{ return x>2; }); //true var result = arr.every(x=>{ return x>5; }); //false- some和every恰恰相反,数组中有一项满足函数规则,就返回true,否则返回false
var arr = [3,5,8]; var result = arr.some(x=>{ return x>5; }); //true var result = arr.some(x=>{ return x>12; }); //false- reduce为数组中的每一项,执行你提供的函数计算,最后返回一个结果值。
arr.reduce(参数一,参数二);
参数一:为自定义函数reducer,他接受4个参数,分别为sum(累加器)、item(当前值)、index(当前索引)、arr(原数组);
参数二:为累加器sum的初始值;
var arr = [3,5,8]; var b = arr.reduce(function(sum,item){ return sum+item; },0); //初始值为0 console.log(b); //16 var b = arr.reduce(function(sum,item){ return sum+item; },2); //初始值为2 console.log(b); //1826:for...in、Object.keys()、Object.getOwnPropertyNames()的区别
var parent = Object.create(Object.prototype, { a: { value: 1, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true } }); var child = Object.create(parent, { b: { value: 2, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true }, c: { value: 3, writable: true, enumerable: false, configurable: true } });child继承parent,child有俩个属性,b和c,不是可枚举的,c不可枚举的。
现在我们用遍历的方式打印child的属性://for in 遍历的是自身和原型的可枚举属性 for(let i in child){ console.log(i); } // b a for(let i in child){ if(child.hasOwnProperty(i)){ console.log(i); } } //b //object.keys() 相当于for...in + hasOwnProperty()形式 console.log(Object.keys(child)); //获取自身可枚举属性,不包括原型 //b //打印出自己的属性,无论是否可枚举 console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(child)); //b c27.说下防抖和截流,以及怎样实现
防抖:在n秒后执行回调函数,如果在n秒内再触发事件,重新计算时间。
function dance(fn,delay){ var timeId; return function (){ clearTimeout(timeId); timeId = setTimeout(fn,delay); } } function callback(){ console.log("网络请求中……"); } var preventDance = dance(callback,500); var btn = document.getElementById("btn"); btn.onclick = preventDance;截流:顾名思义就是限流的意思,在规定的时间内只能执行一次回调函数
28.target 和 currentTarget的区别
var a = document.getElementById('A'); a.addEventListener('click',function(e){ console.log(e.target); console.log(e.currentTarget); },false);- 点击
A时输出的是A元素A元素 - 点击
B时输出的是B元素A元素
所以最终的结论是:target是点击哪个元素,就代表谁。而currentTarget是事件绑定的对象
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ee83be05468229.父元素宽高固定200px,里面是宽高未知的图片,怎样使图片水平垂直居中

.parent{ position:relative; width:200px; height:200px; border:1px solid red; }/* 方式一 flex */ .parent{ position:relative; width:200px; height:200px; border:1px solid red; display:flex; justify-content:center; align-items:center; }/* 方式二 position + transform */ .child{ position:absolute; left:50%; top:50%; transform:translate(-50%,-50%); }/* 方式三:table-cell */ .parent{ position:relative; width:200px; height:200px; border:1px solid red; display:table-cell; text-align:center; vertical-align:middle; }/* 方式四 */ /* 注意:position:absolute 和 float:left都会隐式将元素的display转化 为display:inline-block */ .child{ position:absolute; left:0; top:0; bottom:0; right:0; margin:auto; }/* 方式五 grid */ .parent { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid red; position: relative; display: grid; } .child { justify-self: center; align-self: center; }30.响应式布局中,子元素的宽度是父元素宽度的80%,怎样使子元素的宽高比是2:1 (css实现)
.parent{ width:100%; border:1px solid red; } /* 方法一 */ .child{ width:80vw; height:40vw; } /* 方式二 */ .child{ width:80%; height:0; padding-bottom:40%; } /* padding 在使用百分比时,相对的是父元素的宽度 */31.上下高度固定,中间自适应
/* 方式一: 上下固定,中间超出内容滚动 */ .wrapper>div{ position:absolute; } .top{ top:0; height:100px; width:100%; } .center{ top:100px; bottom:100px; width:100%; overflow:auto; } .bottom{ bottom:0; height:100px; width:100%; }/* 方式二: grid 上下固定,中间超出部分会将footer挤出屏幕外 */ html,body{ width:100%; heigth:100%; } .wrapper{ display:grid; height:100%; grid-template-rows:100px auto 100px; }/* 方式三:flex */ .wrapper{ display:flex; flex-direction:column; } .top{ height:100px; flex:0 0 auto; } .center{ flex:1 1 auto; } .bottom{ height:100px; flex: 0 0 auto; }/* 方式四:table */ html,body{ width:100%; height:100%; } .wrapper{ height:100%; display:table: } .wrapper > div{ display:table-row; } .top, .bottom{ height:100px; } /*table-row 中必须有内容,否则不显示*/32.输出结果是什么?
var x = 1; var kit = { x: 2, buf: { x: 3, fac() { return this.x; }, til: () => { return this.x; } } }; var foo = kit.buf.fac; console.log(foo()); console.log(kit.buf.fac()); console.log(kit.buf.til()); //1 3 1注意:这道题主要考察this指向问题,箭头函数是绑定外侧this,也就是指向window的,还有setTimeout和setInterval里面的this也是指向外层window。
var x = 5; setTimeout(function() { var x = 3; console.log(this.x); }, 1000); // 533. 输出结果是什么,为什么
var k =10; function fac(){ k =10; return; function k(){} } fac(); console.log(k); // 1此题主要理解函数的变量提升,执行fac时相当于这样:
function fac(){ var k = function (){} k =10; return; }所以k改变的是局部变量,所以打印出来当然还是1。
34.各种小算法
add(2)(3) //5
function add(num){ var sum = num; return function (x){ sum +=x; return sum; } }add(2)(3)(4)(5)(6) //20
function add(num){ var sum=num,index=1; var temp = function (x){ index++; sum += x; if(index==5){ return sum; }else{ return temp; } } return temp; }add(2)(3)返回add()函数,只有不传参数时返回值,比如add(2)(3)() //输出5
function add(num){ var sum; if(arguments.length==0){ return 0; }else{ sum =num; } var temp = function (x){ if(arguments.length==0){ return sum; }else{ sum += x; return temp; } } return temp; }27、说下BFC
18. call() apply() bind()区别
https://wangdoc.com/javascript/oop/this.html
vue 无限循环列表,要加一个key
computed 和 watch区别
- for 对数组遍历,可以使用