接着上一篇《netty alloc 初始化过程》 初始化完成后,调用directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) 方法获取 ByteBuf 对象,再此过程中会
1、优先从缓存中获取,如果获取不到。
2、从PoolArena 中根据分配规格获取已经拆分好了的 "子page"
3、如果仍然获取不到,那么从已经创建的 chunk 中划分一块内存
4、如果没有创建过那么创建chunk ,并且划分一块内存
5、init ByteBuf 后返回。
那这些步骤 netty 具体是怎么实现的呢。我们一块来看源码
directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) 方法
PooledByteBuf allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, int reqCapacity, int maxCapacity) {
//拿到一个 PooledByteBuf 对象
PooledByteBuf buf = newByteBuf(maxCapacity);
//内存分配
allocate(cache, buf, reqCapacity);
return buf;
}
@Override
protected PooledByteBuf newByteBuf(int maxCapacity) {
if (HAS_UNSAFE) {
//从对象池中取出一个 PooledByteBuf 复用
return PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf.newInstance(maxCapacity);
} else {
return PooledDirectByteBuf.newInstance(maxCapacity);
}
}
可以看到首先获取了一个 PooledByteBuf 对象通过 newByteBuf 方法,这里用了对象池存存储了,前边分析过netty 对象池原理,此处只是为了减少PooledByteBuf 对象的创建。
一、然后调用了一个非常重要的方法 allocate
1、对入参内存size标准化normCapacity(类似HashMap计算容量的算法)
2、从缓存上进行内存获取
4、如果没成功,就做实际的内存分配
缓存命中流程:
1、找到对应 size 的 memoryRegionCache
2、从 queue 中弹出一个 entry 给 ByteBuf 初始化
3、将弹出的 entry 仍到对象池 Recycler 进行复用,
private void allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf buf, final int reqCapacity) {
//对入参reqCapacity 申请内存大小 size 标准化,如果不是 2 的整数倍将转化成 2 的整数倍
final int normCapacity = normalizeCapacity(reqCapacity);
if (isTinyOrSmall(normCapacity)) { // capacity < pageSize
int tableIdx;
PoolSubpage[] table;
boolean tiny = isTiny(normCapacity);
if (tiny) { // < 512
//试着从缓存中获取
if (cache.allocateTiny(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
//
tableIdx = tinyIdx(normCapacity);
table = tinySubpagePools;
} else {
//试着从缓存中获取
if (cache.allocateSmall(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
tableIdx = smallIdx(normCapacity);
table = smallSubpagePools;
}
//找到 PoolArena.tinySubpagePools 或 PoolArena.smallSubpagePools
//中缓存的未分配完成的 subpage,因为 PoolChunk.allocateSubpage() 拆分 page 的时候,将没有分配完成的 subpage
//存放到了 PoolArena.tinySubpagePools 或 PoolArena.smallSubpagePools 数组的相应规格的节点链中了
final PoolSubpage head = table[tableIdx];
/**
* Synchronize on the head. This is needed as {@link PoolChunk#allocateSubpage(int)} and
* {@link PoolChunk#free(long)} may modify the doubly linked list as well.
*/
synchronized (head) {
final PoolSubpage s = head.next;
//此处从 PoolArena 中已经切分好的 "子page" 中分配
if (s != head) {
assert s.doNotDestroy && s.elemSize == normCapacity;
long handle = s.allocate();
assert handle >= 0;
s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, null, handle, reqCapacity);
incTinySmallAllocation(tiny);
return;
}
}
synchronized (this) {
//直接分配内存
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
}
incTinySmallAllocation(tiny);
return;
}
//chunkSize 16M
if (normCapacity <= chunkSize) {
//通过缓存分配
if (cache.allocateNormal(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
// was able to allocate out of the cache so move on
return;
}
//如果缓存分配不到
synchronized (this) {
//page 级别的内存分配,要么分配 N 个page,不会分配单个page的某一个部分的空间
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
++allocationsNormal;
}
} else {
//大于16m 的内存
// Huge allocations are never served via the cache so just call allocateHuge
allocateHuge(buf, reqCapacity);
}
}
这里有两个小方法比较有意思,netty 已经给出了注释还算有良心哈哈
subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize - 1);
// capacity < pageSize
boolean isTinyOrSmall(int normCapacity) {
return (normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) == 0;
}
// normCapacity < 512
static boolean isTiny(int normCapacity) {
return (normCapacity & 0xFFFFFE00) == 0;
}
要讲清楚这个必须举例子, pageSize 默认 8k 也就是 8192
subpageOverflowMask = ~(8192-1) = 二进制 "10000000000000"
因为 normCapacity 是规格化后的数字二的倍数所以二进制每一位都是1.
normCapacity = 1111...111 。& 运算,必须两个数都是1,运算结果才是1.
10000000000000 & 1111...111 。 所以如果 111...111 小于10000000000000 运算结果才能为0。等价于capacity < pageSize。高明吧? 哈哈 。另一个 isTiny 方法也是一样的。
1、先看一下缓存命中的代码,以 tiny 规格缓缓存为例
cache.allocateTiny(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)
boolean allocateTiny(PoolArena area, PooledByteBuf buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
return allocate(cacheForTiny(area, normCapacity), buf, reqCapacity);
}
查找到 size 对应的 MemoryRegionCache
因为tiny规格的 MemoryRegionCache 数组中存放顺序为 tinySubPageHeapCaches[1] =16B tinySubPageHeapCaches[2] = 32B ... 496B。所以可以根据 size/16拿到数组的 index,继而从数组中获取对应的 MemoryRegionCache
private MemoryRegionCache cacheForTiny(PoolArena area, int normCapacity) {
//将 normCapacity 除以 16
//取数组中的第几个 index . 因为不同的数组中的容量不一样,容量是 index * 16 = normCapacity
int idx = PoolArena.tinyIdx(normCapacity); //normCapacity >>> 4
//是否为堆外内存
if (area.isDirect()) {
return cache(tinySubPageDirectCaches, idx);
}
return cache(tinySubPageHeapCaches, idx);
}
然后调用 MemoryRegionCache 的 allocate 方法
1、从缓存队列中弹出 一个 Entry
2、用 entry 携带的信息创建 ByteBuf
3、将 entry 用对象池回收,避免重复创建 entry 对象
public final boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf buf, int reqCapacity) {
//从缓存中弹出一个 Entry
Entry entry = queue.poll();
if (entry == null) {
return false;
}
initBuf(entry.chunk, entry.nioBuffer, entry.handle, buf, reqCapacity);
//因为 entry poll 出来之后,方法返回之后,就没有地方引用到了,所以可能会被 Gc .
//为了复用 Entry 所以用对象池 Recycler 存储, 后续 ByteBuf buf 释放的时候
//可以从对象池中 get 出来 Entry,然后将 Entry 的 chunk 和 handle 指向被回收的 ByteBuf buf 。避免创建 Entry
entry.recycle();
// allocations is not thread-safe which is fine as this is only called from the same thread all time.
++ allocations;
return true;
}
//Entry 的 recycle 方法
void recycle() {
//表示 Entry 不指向任何一块内存
chunk = null;
nioBuffer = null;
handle = -1;
recyclerHandle.recycle(this);
}
initBuf 方法后边在分析
2、没有命中缓存,然后优先在 PoolArena 中已经切分好的 "子page" 中分配。
首先拿到 PoolArena 中的 PoolSubpage
PoolSubpage[1] = 16b PoolSubpage[2] = 32b .... PoolSubpage[31] = 512B
,所以定位方法是 tableIdx=normCapacity >>> 4,继而拿到 PoolSubpage 对象
注意:s != head 说明 PoolSubpage 链表非空,可以分配对象
//找到 PoolArena.tinySubpagePools 或 PoolArena.smallSubpagePools
//中缓存的未分配完成的 subpage,因为 PoolChunk.allocateSubpage() 拆分 page 的时候,将没有分配完成的 subpage
//存放到了 PoolArena.tinySubpagePools 或 PoolArena.smallSubpagePools 数组的相应规格的节点链中了
final PoolSubpage head = table[tableIdx];//tableIdx=normCapacity >>> 4
synchronized (head) {
final PoolSubpage s = head.next;
if (s != head) {
assert s.doNotDestroy && s.elemSize == normCapacity;
//此处从 PoolArena 中已经切分好的 "子page" 中分配
long handle = s.allocate();
assert handle >= 0;
s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, null, handle, reqCapacity);
incTinySmallAllocation(tiny);
return;
}
}
long handle = s.allocate(); 方法和 s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, null, handle, reqCapacity); 涉及到 "子page" 的内存分配后边讲。
3、如果 PoolArena 中不存在已经切分好的 "子page" ,那么直接从chunk 中分配内存
synchronized (this) {
//直接分配内存
allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
}
allocateNormal 方法的执行步骤:
1、尝试在现有的 Chunk 上进行分配
根据内存使用率,优先级为q050 q025 q000 qInit q075。依次尝试进行分配内存
2、否则创建 Chunk 进行分配
3、初始化 PooledByteBuf
// Method must be called inside synchronized(this) { ... } block
private void allocateNormal(PooledByteBuf buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
//尝试在现有的 Chunk 上进行分批
if (q050.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q025.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) ||
q000.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || qInit.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) ||
q075.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
return;
}
// Add a new chunk.
//创建一个 16M 的连续内存 封装成 PoolChunk,此块连续的内存可能是 byte[] 或 java.nio.ByteBuffer
PoolChunk c = newChunk(pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize);
//创建一个连续的内存之后,将 PooledByteBuf 和 byte[] 或 java.nio.ByteBuffer 关联
//关联方法: 用标记位 handle 和 偏移位
boolean success = c.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
assert success;
//根据内存使用情况,添加到 ChunkList 队列
qInit.add(c);
}
3.1、尝试在现有的 Chunk 上进行分配,看一下 PoolChunkList.allocate 方法。
1、从 head 节点进行遍历
2、尝试从每个 PoolChunk 中分配内存
3、如果分配成功,并且 PoolChunk 的内存使用率大于所在的 PoolChunkList 定义的最大上限,那么将PoolChunk 流转到更大规格的内存使用率的 PoolChunkList 中。
boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
if (normCapacity > maxCapacity) {
// Either this PoolChunkList is empty or the requested capacity is larger then the capacity which can
// be handled by the PoolChunks that are contained in this PoolChunkList.
return false;
}
//从 head 节点进行遍历
for (PoolChunk cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next) {
//尝试从 Chunk cur 进行分配
if (cur.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) {
//试着根据内存使用率,流转到其他 ChunkList
if (cur.usage() >= maxUsage) {
//在当前PoolChunkList删除PoolChunk节点
remove(cur);
// //PoolChunk 流转到更大规格的内存使用率的 PoolChunkList 中
nextList.add(cur);
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
4、如果现有的 Chunk (PoolChunkList) 中没有分配成功、那么创建Chunk,并且在 Chunk 上分配内存
创建一个 16M 的连续内存, chunkSize = 16777216,封装成 PoolChunk,此块连续的内存可能是 byte[] 或 java.nio.ByteBuffer
PoolChunk c = newChunk(pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize);
初始化 PoolChunk
根据 pageSize 和 maxOrder ,生成映射完全二叉树的内存分配规则数组
PoolChunk(PoolArena arena, T memory, int pageSize, int maxOrder, int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int offset) {
unpooled = false;
this.arena = arena;
//byte[] 或 java.nio.DirectByteBuffer (java.nio.ByteBuffer)
this.memory = memory;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
this.pageShifts = pageShifts;
//完全二叉树树的最大高度
this.maxOrder = maxOrder;
this.chunkSize = chunkSize;
//偏移量默认为 0
this.offset = offset;
unusable = (byte) (maxOrder + 1);
log2ChunkSize = log2(chunkSize);
subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize - 1);
freeBytes = chunkSize;
assert maxOrder < 30 : "maxOrder should be < 30, but is: " + maxOrder;
maxSubpageAllocs = 1 << maxOrder;
//生成节点数组,memoryMap
// Generate the memory map.
memoryMap = new byte[maxSubpageAllocs << 1];
depthMap = new byte[memoryMap.length];
int memoryMapIndex = 1;
//通过节点的所在层级,推断表示那一段的连续空间是否被分配
//层级遍历
for (int d = 0; d <= maxOrder; ++ d) { // move down the tree one level at a time
int depth = 1 << d;
for (int p = 0; p < depth; ++ p) {
//memoryMapIndex 表示第几个节点,(byte) d 表示在第几层
// in each level traverse left to right and set value to the depth of subtree
memoryMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d;
depthMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d;
memoryMapIndex ++;
}
}
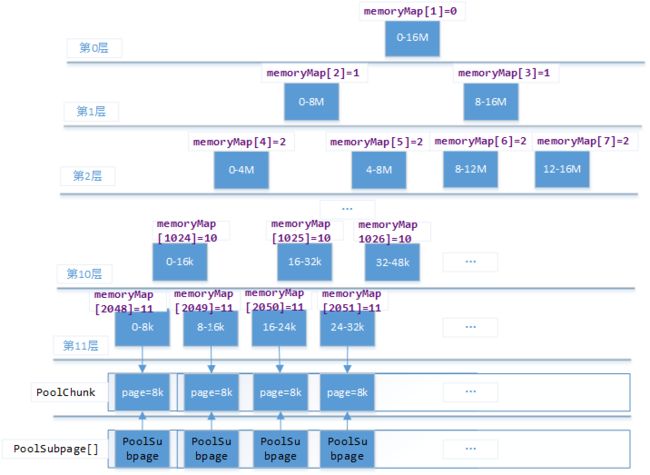
为了说清楚这个数据结构,提供下图
为啥要定义一个分配规则的完全二叉树呢?
因为这种数据结构,在查询对应大小的内存块时效率比较高,当分配完成一个节点将父节点的层级加一就可以了,如果层级等于12那么当前子树的内存已经全部分配完成了。具体如何使用的请看 PoolChunk.allocate()
5、非常重要的方法 PoolChunk.allocate()
主要功能: 在 Chunk 上分配内存,将 PooledByteBuf 和 byte[] 或 java.nio.ByteBuffer 关联,关联方法: 用标记位 handle 和 偏移位。
1、allocateRun 分配一整个 page 8k
2、allocateSubpage 分配不足 8k 的内存
3、initBuf 初始化 PooledByteBuf
boolean success = c.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity);
boolean allocate(PooledByteBuf buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) {
final long handle;
if ((normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0) { // >= pageSize
//分配几个 page. Run 英文代表一段, handle 为数组 index.可以定位一个节点
handle = allocateRun(normCapacity);
} else {
handle = allocateSubpage(normCapacity);
}
if (handle < 0) {
return false;
}
ByteBuffer nioBuffer = cachedNioBuffers != null ? cachedNioBuffers.pollLast() : null;
initBuf(buf, nioBuffer, handle, reqCapacity);
return true;
}
(normCapacity & subpageOverflowMask) != 0 这段代码上边已经讲过了,就是判断 normCapacity 是否大于 pageSize
5.1、allocateRun 分配一整个 page 8k,个人感觉这里是 netty 中最难的地方。
1、定位所在层级
2、在 d 层进行分配
3、修改Chunk的内存使用率
private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) {
//d 代表第几层,从第几次分配
int d = maxOrder - (log2(normCapacity) - pageShifts);
//在 d 层进行分配
int id = allocateNode(d);
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
//修改内存使用率
freeBytes -= runLength(id);
return id;
}
要想说明白
int d = maxOrder - (log2(normCapacity) - pageShifts);
必须举个例子:
//d 代表第几层,从第几次分配
//normCapacity 占用1个page 二进制为 10000000000000 log2(normCapacity) = 13
//normCapacity 占用2个page 二进制为 100000000000000 log2(normCapacity) = 14
//normCapacity 占用4个page 二进制为 1000000000000000 log2(normCapacity) = 15
//normCapacity 占用8个page 二进制为 10000000000000000 log2(normCapacity) = 16
//pageSize 二进制为 10000000000000 log2(pageSize) = 13 = pageShifts
//log2(normCapacity) - log2(pageSize) = log2(占用了多少个 page)
//因为占用n个page, 是在倒数 log2(占用了n个page) 层
//所以用最大层级数 maxOrder 减去 log2(占用了多少个 page) 就等于该 normCapacity 所在层级
5.1.1、找到所在层级后,调用 allocateNode() 方法进行对d层进行分配
1、对层级做简单的校验,如果第一个节点所在层级大于入参,检验失败
2、从第1层开始遍历完全二叉树,找到d层没有被分配的 memoryMap 的 index (二叉树的 d 层级没有被分配节点的 index)
3、将已经使用的节点打标(默认12代表子树全部分配完成)
4、所有父节点层级加1
5、将找到的memoryMap[] 数组的 index 返回,(用于定位 byte[] 或 ByteBuffer 中的一段区域)
private int allocateNode(int d) {
//id 是二叉树节点,在 memoryMap数组中的 index
int id = 1;
// 使 initial = 1000 或 initial=1000...
int initial = - (1 << d); // has last d bits = 0 and rest all = 1
byte val = value(id);
//如果 memoryMap 数组中第一个节点,所在层级大于入参所在层级,那么错误退出
if (val > d) { // unusable
return -1;
}
//0 & 0 = 0 0 & 1 = 0 1 & 0 = 0 1 & 1 =1
//从第1层开始遍历,找到d层没有被分配的 memoryMap 的 index (二叉树的 d 层级没有被分配节点的 index)
/**
* 过程:
* 一颗子树分配完之后 , 通过 updateParentsAlloc 将所有分配完的节点打标后,
* 再次遍历到子树的根节点后,位移一位就是将原来的id*2。跳过了对这颗子树的遍历,直接查找下一颗子树
*/
while (val < d || (id & initial) == 0) { // id & initial == 1 << d for all ids at depth d, for < d it is 0
//获取子节点(下一个层级),的 memoryMap 数组的 index
id <<= 1;
val = value(id);
if (val > d) {
//0 ^ 0 = 0 0 ^ 1 = 1 1 ^ 0 = 1 1 ^ 1 = 0
//兄弟节点
id ^= 1;
val = value(id);
}
}
byte value = value(id);
assert value == d && (id & initial) == 1 << d : String.format("val = %d, id & initial = %d, d = %d",
value, id & initial, d);
//给节点打上标记,使用 unusable = (maxOrder + 1);
setValue(id, unusable); // mark as unusable
//逐层向上标记为已经使用了
updateParentsAlloc(id);
return id;
}
(1)、 将每个父节点的层级加1
private void updateParentsAlloc(int id) {
//直到遍历到最顶层
while (id > 1) {
//父节点id
int parentId = id >>> 1;
//本节点层级
byte val1 = value(id);
//兄弟节点层级
byte val2 = value(id ^ 1);
//兄弟节点层级大于本节点层级说明父节点的内存还没有分配完成
//此处在兄弟中找到一个最小的层级赋给父节点层级
byte val = val1 < val2 ? val1 : val2;
setValue(parentId, val);
id = parentId;
}
}
(2)、 修改Chunk的内存使用率
还记得吗? 在初始化 PoolChunk 时创建两个相同的数组 depthMap 和 memoryMap,都用于映射一颗完全二叉树,但是 memoryMap 是根据分配内存情况动态变化的,而 depthMap 始终不变的。memoryMap 用于表示内存的分配情况,depthMap 主要获取节点代表的内存大小。
根据运算符优先级
1 << log2ChunkSize - depth(id) = 1 << (log2ChunkSize - depth(id))
2的( 树的总层级减去节点所在层级)次方,等于节点所代表的内存容量
freeBytes -= runLength(id);
private int runLength(int id) {
// represents the size in #bytes supported by node 'id' in the tree
return 1 << log2ChunkSize - depth(id);
}
5.2、allocateSubpage 方法负责分配不足 8k 的内存
1、在 PoolArena 中找到对应规格"子page" 的 head 节点
2、调用 allocateNode 方法划分一页 8k,并且返回划分页所在的index
3、修改内存使用率
4、根据页所在的 index 找到 PoolSubpage(拆分 page 的工具,每个page都对应一个PoolSubpage)
5、初始化 PoolSubpage
6、重置 PoolSubpage
7、PoolSubpage.allocate() 划分一个"子page"
private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) {
// Obtain the head of the PoolSubPage pool that is owned by the PoolArena and synchronize on it.
// This is need as we may add it back and so alter the linked-list structure.
//通过 arena.tinySubpagePools 或 arena.smallSubpagePools 数组找到 normCapacity 规格的头节点
PoolSubpage head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity);
//maxOrder 最大层级
int d = maxOrder; // subpages are only be allocated from pages i.e., leaves
synchronized (head) {
//因为最大层级是叶子节点也就是 page,所以找到未分配的 page 的 id
int id = allocateNode(d);
if (id < 0) {
return id;
}
final PoolSubpage[] subpages = this.subpages;
//pageSize 8k
final int pageSize = this.pageSize;
//修改空闲内存数量
freeBytes -= pageSize;
//计算 subpage 位于 PoolChunk.subpages 中的第几个位置
int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id);
PoolSubpage subpage = subpages[subpageIdx];
//初始化 PoolSubpage 并且添加到 PoolArena 中的
//private final PoolSubpage[] tinySubpagePools;
//private final PoolSubpage[] smallSubpagePools;
if (subpage == null) {
//初始化的 PoolSubpage 加入到 arena.tinySubpagePools 或 arena.smallSubpagePools 数组值的链表中
subpage = new PoolSubpage(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity);
subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage;
} else {
//init() 方法加入到 arena.tinySubpagePools 或 arena.smallSubpagePools 数组值的链表中
subpage.init(head, normCapacity);
}
//从 subpage 工具中,取出一个子page
return subpage.allocate();
}
}
5.2.1、在 PoolArena 中找到对应规格"子page" 的 head 节点
"子page" 有两种规格:
1、Tiny
按照内存大小顺序为:
PoolSubpage[1] = 16b PoolSubpage[2] = 32b .... PoolSubpage[31] = 512B
可以看出 index = elemSize/16
2、Small
按照内存大小顺序为:
PoolSubpage[0] = 512 PoolSubpage[1] = 1k PoolSubpage[2] = 2k PoolSubpage[3] = 4k....
可以发现规律:
可以得出:除了第0个位置其他都可以用index = log2(elemSize>>10)。
PoolSubpage findSubpagePoolHead(int elemSize) {
int tableIdx;
PoolSubpage[] table;
if (isTiny(elemSize)) { // < 512
tableIdx = elemSize >>> 4;
table = tinySubpagePools;
} else {
tableIdx = 0;
elemSize >>>= 10;
while (elemSize != 0) {
elemSize >>>= 1;
//累计有多少个 2 的倍数 类似 log2
tableIdx ++;
}
table = smallSubpagePools;
}
return table[tableIdx];
}
5.2.2、根据页所在的 index 找到 PoolSubpage(拆分 page 的工具,每个page都对应一个PoolSubpage)
maxSubpageAllocs 是完全二叉树的最大层级的第一个位置的index值。二进制为:100000000000 十进制 2048
memoryMap[] 和 PoolSubpage[] 的关系
memoryMap[2048] 对应 PoolSubpage[0]
memoryMap[2049] 对应 PoolSubpage[1]
^ 位运算,不同为1,相同为0
所以 memoryMapIdx ^ maxSubpageAllocs = PoolSubpage[] 的 index
maxSubpageAllocs = 1 << maxOrder;
private int subpageIdx(int memoryMapIdx) {
return memoryMapIdx ^ maxSubpageAllocs; // remove highest set bit, to get offset
}
5.2.3、初始化或重置 PoolSubpage
初始化:
1、计算 memoryMap[index] 的内存偏移量
2、创建记录 page 中 "子page" 的使用情况的数组 bitmap
PoolSubpage(PoolSubpage head, PoolChunk chunk, int memoryMapIdx, int runOffset, int pageSize, int elemSize) {
this.chunk = chunk;
this.memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx;
this.runOffset = runOffset;
this.pageSize = pageSize;
bitmap = new long[pageSize >>> 10]; // pageSize / 16 / 64
init(head, elemSize);
}
(1)、 计算 memoryMap[index] 代表的内存偏移量
1、 id ^ 1 << depth(id) : 计算 id(数组index) 所在层级的第几个位置
可以理解成 memoryMap 的 index 左位移所在层级数,得到的结果就是所在层级从左数第几个位置
2、计算节点所代表的内存容量 runLength 方法上文讲过。
private int runOffset(int id) {
// represents the 0-based offset in #bytes from start of the byte-array chunk
//计算 id(数组index) 所在层级的第几个位置
int shift = id ^ 1 << depth(id);
return shift * runLength(id);
}
(2)、创建记录 page 中 "子page" 的使用情况的数组 bitmap
因为每个"子page" 的最小为 16b,所以一个page最多可以拆分成page/16个"子page"
注意:数组类型为 long 二进制为 64 位。意味着数组中的一个long值可以表示64个 "子page" ,所以 bitmap 数组的最大值 page/16/64 = pageSize >>> 10
bitmap = new long[pageSize >>> 10]; // pageSize / 16 / 64
5.2.4、重置 PoolSubpage
1、计算将 page 划分多少份
2、将情况的数组 bitmap,每一位重置为0 (未使用)
3、PoolSubpage加入到 arena.tinySubpagePools 或arena.smallSubpagePools 数组值的链表中
// 该page切分后每一段的大小
void init(PoolSubpage head, int elemSize) {
doNotDestroy = true;
this.elemSize = elemSize;
if (elemSize != 0) {
//需要将 page 划分多少份
maxNumElems = numAvail = pageSize / elemSize;
nextAvail = 0;
//64 是一个 long 的总字节数。所以一个 long 可以表示 64 个 subpage, 因为 maxNumElems >>> 6 = maxNumElems/64
bitmapLength = maxNumElems >>> 6;
// 这是因为如果其小于64,前面一步的位移操作结果为0,但其还是需要一个long来记录
if ((maxNumElems & 63) != 0) {
bitmapLength ++;
}
//记录 page 中 subpage 的使用情况,0 为没有被分配
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapLength; i ++) {
bitmap[i] = 0;
}
}
//将自己加入到 arena.tinySubpagePools 或 arena.smallSubpagePools 数组值的链表中
addToPool(head);
}
private void addToPool(PoolSubpage head) {
assert prev == null && next == null;
prev = head;
next = head.next;
next.prev = this;
head.next = this;
}
5.2.5、PoolSubpage.allocate() 划分一个"子page"
1、找到一个未被使用的 子page 的位置
2、将子page 标记为已使用
3、如果 PoolSubpage 中所有 子page 都被使用了,那么从 arena.tinySubpagePools 或 arena.smallSubpagePools 数组值的链表中移除节点。
4、返回handle
long allocate() {
if (elemSize == 0) {
return toHandle(0);
}
if (numAvail == 0 || !doNotDestroy) {
return -1;
}
//找到一个未被使用的 子page,没有被分配的分段位置
final int bitmapIdx = getNextAvail();
//q 为bitmapIdx/64, bitmap数组中 index
int q = bitmapIdx >>> 6;
//从低位截取6位控制 r<64,如果在64之内那么 r = bitmapIdx
int r = bitmapIdx & 63;
//断言bitmap[q]位置的long型值的二进制形式可以表示第r位
assert (bitmap[q] >>> r & 1) == 0;
//将对应位置q设置为1;
bitmap[q] |= 1L << r;
//当 PoolSubpage 中所有的 子page 都被使用了
if (-- numAvail == 0) {
//从 arena.tinySubpagePools 或 arena.smallSubpagePools 数组值的链表中移除节点
removeFromPool();
}
//将 bitmapIdx 和 memoryMapIdx 拼接
//为了使 handle 可以表达,Chunk 二叉树的叶子节点的(page 索引位置),和 page 中,子page的位置
return toHandle(bitmapIdx);
}
假设需要分配大小为128的内存,这时page会拆分成64个内存段,需要1个long类型的数字描述这64个内存段的状态,所以bitmap数组只会用到第一个元素。
(1)、找到一个未被使用的 子page 的位置
1、获取PoolSubpage 记录的空闲位置,当 ByteBuf.release() 时候会填充此值,如果获取不到。
2、从0开始遍历 bitmap[i] 找到没有被分配的 long 类型值
3、从第一位开始遍历 64 位long类型二进制的每一位,判断该位置是否被分配了,如果没有被分配
4、校验该位置所代表的 "子page" 数量不能超过上限
private int getNextAvail() {
//PoolSubpage 记录的空闲位置,当 ByteBuf.release() 时候会填充此值
int nextAvail = this.nextAvail;
if (nextAvail >= 0) {
this.nextAvail = -1;
return nextAvail;
}
//如果没有被释放的空闲位置
return findNextAvail();
}
private int findNextAvail() {
final long[] bitmap = this.bitmap;
final int bitmapLength = this.bitmapLength;
for (int i = 0; i < bitmapLength; i ++) {
long bits = bitmap[i];
//~111111....1111111 = 0
//如果此 long 类型的二进制位没有被分配完成
if (~bits != 0) {
//按照 64 位 long 进行查找没有被分配完成的位置
return findNextAvail0(i, bits);
}
}
return -1;
}
private int findNextAvail0(int i, long bits) {
//该 PoolSubpage 的 "子page" 数量
final int maxNumElems = this.maxNumElems;
//bitmap 数组,第 0 到 i-1 个 index 能代表的 "子page" 数量
final int baseVal = i << 6;
for (int j = 0; j < 64; j ++) {
//判断 bits 的最后一位是否被分配了 (0为没有被分配)
if ((bits & 1) == 0) {
//因为 baseVal 是 2 的倍数所以 baseVal | j = baseVal + j
int val = baseVal | j;
//校验如果 "子page" 数量不能超过上限
if (val < maxNumElems) {
return val;
} else {
break;
}
}
//向前找一位
bits >>>= 1;
}
return -1;
}
(2)、返回handle
PoolSubpage.allocate() 方法的返回的 handle 和 PoolChunk.allocateRun 返回的 handle 不一样,后者返回是单纯的 memoryMap [] 数组的 index。
而前者
高32位是 bitmap[] 的 index。低32位才是 memoryMap [] 数组的 index
private long toHandle(int bitmapIdx) {
return 0x4000000000000000L | (long) bitmapIdx << 32 | memoryMapIdx;
}
5.3、initBuf 初始化 PooledByteBuf
1、根据 handle 获取,page 在 memoryMap [] 中的index, 和 "子page" 在bitmap[] 中的index.
2、根据完整的页初始化 PooledByteBuf
3、根据 "子page" 初始化 PooledByteBuf
void initBuf(PooledByteBuf buf, ByteBuffer nioBuffer, long handle, int reqCapacity) {
int memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx(handle);
int bitmapIdx = bitmapIdx(handle);
if (bitmapIdx == 0) {
//断言节点是否被使用了
byte val = value(memoryMapIdx);
assert val == unusable : String.valueOf(val);
buf.init(this, nioBuffer, handle, runOffset(memoryMapIdx) + offset,
reqCapacity, runLength(memoryMapIdx), arena.parent.threadCache());
} else {
//用 子page 初始化 Buf
initBufWithSubpage(buf, nioBuffer, handle, bitmapIdx, reqCapacity);
}
}
(1)、据完整的页初始化 PooledByteBuf
runOffset 和 runLength 方法之前讲过
前者:计算 memoryMap[index] 代表的内存偏移量
后者计算:计算 memoryMap[index ]节点所代表的内存容量
private void init0(PoolChunk chunk, ByteBuffer nioBuffer,
long handle, int offset, int length, int maxLength, PoolThreadCache cache) {
//通过 memory 和 offset、length 确定一块 ByteBuf 的内存
assert handle >= 0;
assert chunk != null;
this.chunk = chunk;
memory = chunk.memory;
tmpNioBuf = nioBuffer;
allocator = chunk.arena.parent;
this.cache = cache;
this.handle = handle;
//offset 是 PooledByteBuf 所在 memory 的从第0个byte开始的偏移量
this.offset = offset;
//用户分配请求 的长度
this.length = length;
//规格化后的实际在 memory 中占用的长度
this.maxLength = maxLength;
}
(2)根据 Subpage "子page" 初始化 PooledByteBuf
1、根据 handle 拿到 PoolSubpage
2、计算Offset:
page 的内存偏移量 + 子page的内存偏移量 +基础offset(默认0)
private void initBufWithSubpage(PooledByteBuf buf, ByteBuffer nioBuffer,
long handle, int bitmapIdx, int reqCapacity) {
assert bitmapIdx != 0;
int memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx(handle);
PoolSubpage subpage = subpages[subpageIdx(memoryMapIdx)];
assert subpage.doNotDestroy;
assert reqCapacity <= subpage.elemSize;
//用 page 的偏移量 + 子page的偏移量,初始化 buf
buf.init(
this, nioBuffer, handle,
runOffset(memoryMapIdx) + (bitmapIdx & 0x3FFFFFFF) * subpage.elemSize + offset,
reqCapacity, subpage.elemSize, arena.parent.threadCache());
}
到此为止 PooledByteBuf 就已经分配完成了
下边给个彩蛋
二、PooledByteBuf 的使用分析
既然已经初始化了 PooledByteBuf ,并且将
protected T memory;
protected int offset;
protected int length;
赋值了,那么如何使用呢??
(1)、分析一下 AbstractByteBuf.writeBytes() 方法
1、经过简单的校验后调用了子类的setBytes方法
2、然后记录 writerIndex 写指针的位置
@Override
public ByteBuf writeBytes(byte[] src, int srcIndex, int length) {
//校验缓冲区 最大长度是否满足,否则抛出异常,如果写入的 length 大于数组容量则扩容
ensureWritable(length);
setBytes(writerIndex, src, srcIndex, length);
//写索引累计
writerIndex += length;
return this;
}
(2)、这以 PooledDirectByteBuf 为例
T memory (此处T 为 java.nio.ByteBuffer )
1、获取在 memory 中写入的偏移量 index = offset + index
2、根据 memory 创建 ByteBuffer ,其实内存都指向同一个区域,只是各种指针不同而已。
3、设置java.nio.ByteBuffer 的指针
//入参index为已经写入的byte累加的
@Override
public ByteBuf setBytes(int index, byte[] src, int srcIndex, int length) {
//边界检查
checkSrcIndex(index, length, srcIndex, src.length);
_internalNioBuffer(index, length, false).put(src, srcIndex, length);
return this;
}
final ByteBuffer _internalNioBuffer(int index, int length, boolean duplicate) {
index = idx(index);
ByteBuffer buffer = duplicate ? newInternalNioBuffer(memory) : internalNioBuffer();
buffer.limit(index + length).position(index);
return buffer;
}
protected final int idx(int index) {
return offset + index;
}
关于 java.nio.ByteBuffer 的操作不是本文的重点详情请看,
https://blog.csdn.net/mrliuzhao/article/details/89453082
关于内存回收 buffer.release(); 方法后文讲解