模板模式
简介
参考文档:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template_method_pattern
通常叫模板方法模式定义一个算法的骨架,并允许子类为一个或者多个步骤提供实现。
能够使得子类可以在不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法的某些步骤。
属于行为性设计模式
通用的类图
public abstract class AbstractClass {
protected void step1() {
System.out.println("AbstractClass:step1");
}
protected void step2() {
System.out.println("AbstractClass:step2");
}
protected void step3() {
System.out.println("AbstractClass:step3");
}
// 声明为final方法,避免子类覆写
public final void templateMehthod() {
this.step1();
this.step2();
this.step3();
}
}
需要注意公共方法,流程方法一般都是final修饰的,避免被子类重写
生活中的场景
这种固定的步骤
-
把大象放进冰箱
- 打开门
- 大象放进冰箱
- 关闭们
炒菜
固定的流程放在最顶部,具体实现类来实现细节
案例
案例代码来自https://github.com/iluwatar/java-design-patterns
一个小偷偷东西一般分成几个步骤:
- 寻找目标
- 迷惑目标
- 下手
所以我们先定义一个小偷
public class HalflingThief {
private StealingMethod method;
public HalflingThief(StealingMethod method) {
this.method = method;
}
public void steal() {
method.steal();
}
public void changeMethod(StealingMethod method) {
this.method = method;
}
}
因为小偷偷东西都是几个固定步骤,所以我们使用模板方法,但是下手的过程有多种方式,所以开放钩子steal方法
public abstract class StealingMethod {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StealingMethod.class);
protected abstract String pickTarget();
protected abstract void confuseTarget(String target);
protected abstract void stealTheItem(String target);
public void steal() {
String target = pickTarget();
LOGGER.info("The target has been chosen as {}.", target);
confuseTarget(target);
stealTheItem(target);
}
}
撞击然后开溜
public class HitAndRunMethod extends StealingMethod {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HitAndRunMethod.class);
@Override
protected String pickTarget() {
return "old goblin woman";
}
@Override
protected void confuseTarget(String target) {
LOGGER.info("Approach the {} from behind.", target);
}
@Override
protected void stealTheItem(String target) {
LOGGER.info("Grab the handbag and run away fast!");
}
}
偷偷摸摸的干活
public class SubtleMethod extends StealingMethod {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SubtleMethod.class);
@Override
protected String pickTarget() {
return "shop keeper";
}
@Override
protected void confuseTarget(String target) {
LOGGER.info("Approach the {} with tears running and hug him!", target);
}
@Override
protected void stealTheItem(String target) {
LOGGER.info("While in close contact grab the {}'s wallet.", target);
}
}
测试
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HalflingThief thief = new HalflingThief(new HitAndRunMethod());
thief.steal();
thief.changeMethod(new SubtleMethod());
thief.steal();
}
}
源码中的体现
JDBCTemplate
JdbcTemplate#query()
public T query(
PreparedStatementCreator psc, final PreparedStatementSetter pss, final ResultSetExtractor rse)
throws DataAccessException {
Assert.notNull(rse, "ResultSetExtractor must not be null");
logger.debug("Executing prepared SQL query");
return execute(psc, new PreparedStatementCallback() {
@Override
public T doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException {
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
if (pss != null) {
pss.setValues(ps);
}
rs = ps.executeQuery();
ResultSet rsToUse = rs;
if (nativeJdbcExtractor != null) {
rsToUse = nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeResultSet(rs);
}
return rse.extractData(rsToUse);
}
finally {
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(rs);
if (pss instanceof ParameterDisposer) {
((ParameterDisposer) pss).cleanupParameters();
}
}
}
});
}
public List extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
List results = (this.rowsExpected > 0 ? new ArrayList(this.rowsExpected) : new ArrayList());
int rowNum = 0;
while (rs.next()) {
results.add(this.rowMapper.mapRow(rs, rowNum++));
}
return results;
}
可以看到固定的代码都已经帮我们写好了,帮我们做了获取连接,获取驱动,获取statement,关闭连接等。
我们只需要自己来实现对应的RowMapper做结果集映射就行了。
AbstractList
AbstractList中定义了很多抽象方法能够让子类不用重复写
例如add方法
public boolean add(E e) {
add(size(), e);
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
子类可以重写来实现自己的逻辑
HttpServlet
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
可以看到service方法就是模板方法,具体的DoGet和DoPost等方法就交给子类来实现,子类不需要重写这段冗长的代码了。
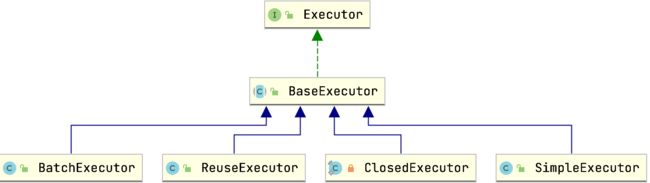
Mybatis BaseExecute
Executor是一个基础的SQL执行类,他实现了大部分的SQL执行逻辑,然后把几个方法交给子类定制化来完成。
例如
- doUpdate
- doFlushStatement
- doQuery
- doQueryCursor
查询方法
看到org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecutor#commit他的提交方法会调用刷新也就是提交到数据库去,但是具体的实现可能提交的时机是不一样的,例如SimpleExecutor是立即提交,但是BatchExecutor是存一堆然后一起提交。
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed");
}
clearLocalCache();
flushStatements();
if (required) {
transaction.commit();
}
}
public List flushStatements(boolean isRollBack) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
return doFlushStatements(isRollBack);
}
protected abstract List doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback)
throws SQLException;
此时查看具体的类的doFlushStatements
ReuseExecutor
org.apache.ibatis.executor.ReuseExecutor#doFlushStatements
private final Map statementMap = new HashMap<>();
public List doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) {
for (Statement stmt : statementMap.values()) {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
statementMap.clear();
return Collections.emptyList();
}
ReuseExecutor因为需要重用相同语句的Statement所以在提交的时候需要把那些都清空
SimpleExecutor
org.apache.ibatis.executor.SimpleExecutor#doQuery
@Override
public List doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
SimpleExecutor则不需要做任何操作
BatchExecutor
org.apache.ibatis.executor.BatchExecutor#doQuery
public List doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
try {
List results = new ArrayList<>();
if (isRollback) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
for (int i = 0, n = statementList.size(); i < n; i++) {
Statement stmt = statementList.get(i);
applyTransactionTimeout(stmt);
BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(i);
try {
batchResult.setUpdateCounts(stmt.executeBatch());
MappedStatement ms = batchResult.getMappedStatement();
List BatchExecutor则需要一批一批的来提交
所以可以看到公共的方法在父类中实现了,具体的差异性的内容都交给子类来实现钩子方法了
总结
模板和策略模式的区别
模板子类能干预实现,但是基础流程已经定下来了
策略不能干预流程,实现方式只能去选择
优缺点
优点
- 封装不变部分,扩展可变部分
- 新增功能,只需要一个新的子类来实现对应的功能方法就行了
- 提取公共部分代码,便于维护
- 不然维护人员为了 修正一个缺陷,需要到处查找类似的代码!
- 行为由父类控制,子类实现
- 基本方法是由子类实现的,因此子类可以通过扩展的方式增加相应 的功能,符合开闭原则。
缺点
- 类数目的增加,每一个抽象类都需要一个子类来实现,这样导致类的个数增加。
- 类数量的增加,间接地增加了系统实现的复杂度。
- 继承关系自身缺点,如果父类添加新的抽象方法,所有子类都要改一遍
适用场景
- 一多个子类有公有的方法,并且逻辑基本相同时。
- 重要、复杂的算法,可以把核心算法设计为模板方法,周边的相 关细节功能则由各个子类实现。
- 重构时,模板方法模式是一个经常使用的模式,把相同的代码抽 取到父类中,然后通过钩子函数来约束行为
其他的问题
父类怎么调用子类的方法
- 把子类传递到父类的有参构造中,然后调用。
- 使用反射的方式调用,你使用了反射还有谁不能调用的
- 父类调用子类的静态方法。
我的笔记仓库地址gitee 快来给我点个Star吧