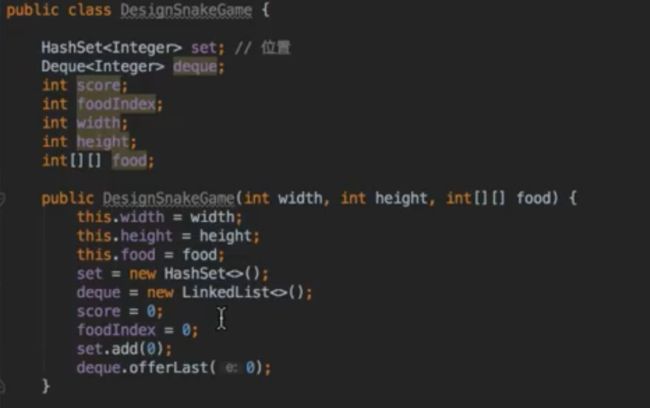
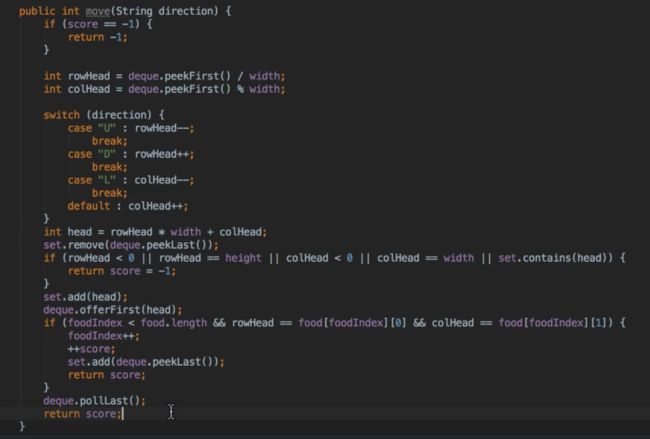
题目分析:
Move 会有以下几种情况:
- out of boarder =>
return -1- hit self =>
return -1
special case: 如果下一个点是 snake 的 tail, 是不会碰撞的。- eat food =>
return snake.size() - 1- just move by q =>
return snake.size() - 1
注意逻辑顺讯:1. remove and unmark tail first; 2. add and mark new head.
old tail 和 new head 可能是一个点。
Initial Solution
class SnakeGame {
Point[][] board;
LinkedList snake;
LinkedList foodList;
public SnakeGame(int width, int height, int[][] food) {
board = new Point[height][width];
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {
board[i][j] = new Point(i, j);
}
}
snake = new LinkedList<>();
board[0][0].isOccupied = true;
snake.add(board[0][0]);
foodList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int[] position: food) {
Point p = board[position[0]][position[1]];
foodList.add(p);
}
}
public int move(String direction) {
Point head = snake.getFirst();
int nextX = head.x;
int nextY = head.y;
switch (direction) {
case "U":
nextX = head.x - 1;
break;
case "L":
nextY = head.y - 1;
break;
case "R":
nextY = head.y + 1;
break;
case "D":
nextX = head.x + 1;
break;
default:
return -1;
}
// out of boarder
if (nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= board.length || nextY >= board[0].length) {
return -1;
}
Point nextPoint = board[nextX][nextY];
// hit self
if (nextPoint.isOccupied && !nextPoint.equals(snake.getLast())) {
return -1;
}
// eat food
if (foodList.size() > 0 && nextPoint.equals(foodList.getFirst())) {
snake.add(0, foodList.removeFirst());
nextPoint.isOccupied = true;
return snake.size() - 1;
}
// remove tail first, because tail can be the next head position
Point tail = snake.removeLast();
tail.isOccupied = false;
snake.add(0, nextPoint);
nextPoint.isOccupied = true;
return snake.size() - 1;
}
}
class Point {
int x;
int y;
boolean isOccupied;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.isOccupied = false;
}
}
TLE with case 1000 * 1000 board.
这里使用 Point isOccupied 来标记该 point 是否是 snake 的一部分,或者说已经被 snake 占用。也就不需要 HashSet 来就行标记。
这个 Test Case 中的 board 很大 1000 x1000,但只使用了很小一部分 3 x 3。因而 constructor 的时间复杂度为 weight x height,超出了test设置的时间限度。
下面的 Solution 是对上面 case 进行空间上的优化,只存使用过的 Point,而不对这个 board 进行 Point 初始化。但实际使用上来说,Initial Solution 还是更好一些,毕竟整个 board 对玩家来说都是可以使用的,在玩家游戏的过程中进行 Hash 运算,会慢一些。
Solution 2
tried to use LinkedHashSet, but LinkedHashSet does not support add(index, element), which is needed for the case of eating food. So used HashSet and LinkedList instead.
这里的 LinkedList 来表示 snake,实际上使用了 interface Deque. 头尾均可添加、删除。LinkedList implements Deque.
遇到知识盲点了,debug 了很长时间。对于 class Point, 要使用 HashSet 和 HashMap,需要 Override 两个 methods from class Object.
public boolean equals(Object o); // pay attention here
// WRONG: public boolean equals(Point p)
public int hashCode();
之前由于使用了 public boolean equals(Point p) 导致HashSet contains not working as expected:
// same point p1, p2
Point p1 = new Point(1, 2);
Point p2 = new Point(1, 2);
Set set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(p1);
set.contains(p2); // false
这也说明了使用 @Override 的重要性。
这里把纠正后的 class Point 写一下,下面的 Solution 都是用这个 implementation:
class Point {
int x;
int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Point)) {
return false;
}
Point p = (Point)o;
return this.x == p.x && this.y == p.y;
}
// WRONG
// public boolean equals(Point p) {
// return this.x == p.x && this.y == p.y;
// }
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (x + ";" + y).hashCode();
}
}
class SnakeGame {
int height, width;
LinkedList snake;
Set pointsInUse;
LinkedList foodList;
public SnakeGame(int width, int height, int[][] food) {
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
snake = new LinkedList<>();
pointsInUse = new HashSet<>();
Point head = new Point(0, 0);
snake.add(head);
pointsInUse.add(head);
foodList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int[] position: food) {
Point p = new Point(position[0], position[1]);
foodList.add(p);
}
}
public int move(String direction) {
Point head = snake.getFirst();
int nextX = head.x;
int nextY = head.y;
switch (direction) {
case "U":
nextX = head.x - 1;
break;
case "L":
nextY = head.y - 1;
break;
case "R":
nextY = head.y + 1;
break;
case "D":
nextX = head.x + 1;
break;
default:
return -1;
}
// out of boarder
if (nextX < 0 || nextY < 0 || nextX >= height || nextY >= width) {
return -1;
}
Point nextPoint = new Point(nextX, nextY);
// hit self
if (!nextPoint.equals(snake.getLast()) && pointsInUse.contains(nextPoint)) {
return -1;
}
// eat food
if (foodList.size() > 0 && nextPoint.equals(foodList.getFirst())) {
foodList.removeFirst();
snake.add(0, nextPoint);
pointsInUse.add(nextPoint);
return snake.size() - 1;
}
// remove tail first, because tail can be the next head position
Point tail = snake.removeLast();
pointsInUse.remove(tail);
snake.add(0, nextPoint);
pointsInUse.add(nextPoint);
return snake.size() - 1;
}
}
class Point {...}
Solution 3
从只是解题的角度来考虑,使用 x * height + y 来表达 Point 更为高效。Solution 1 & 2 are more Object Oriented!
Youtube Solution