大家都知道,每一个应用程序都有一个唯一的入口(即main函数),那么对于Java语言开发的tomcat服务器也不例外,找到这个入口,了解各个组件加载的具体过程,对理解整个应用的实现过程有很大的帮助。
tomcat启动相关的类位于catalina.startup包路径下,入口是类Bootstrap中的main()函数。Bootstrap启动类主要完成了三方面的内容,分别如下:
①在静态代码块中设置catalinaHome和catalinaBase两个路径;
②common、server、shared三个类加载器的初始化;
③利用反射机制实例化org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina类。
一、设置catalinaHome和catalinaBase
catalinaHome是tomcat的安装目录,catalinaBase是tomcat的工作目录;这两个目录的主要功能是当在同一台机器上部署多个tomcat实例时,可以不用安装多个tomcat副本,而是通过共享tomcat代码的方式实现。例如在同一台机器上部署两个tomcat实例时,只需要创建两个base目录,base1和base2,然后将tomcat安装目录下的共享目录拷贝到这两个目录下。分别修改conf目录下的server.xml文件中的端口号,就可以同时启动两个tomcat服务器,此时tomcat安装目录(即tomcatHome)下的bin和lib目录是共享的。
代码清单(Bootstrap中设置catalinaHome和catalinaBase的代码)
static {
//获取tomcat的安装目录
String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String home = System.getProperty(Globals.CATALINA_HOME_PROP);
File homeFile = null;
if (home != null) {
File f = new File(home);
try {
homeFile = f.getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
homeFile = f.getAbsoluteFile();
}
}
if (homeFile == null) {
//bootstrap.jar的根目录,其实就是tomcat按照路径下的bin文件夹
File bootstrapJar = new File(userDir, "bootstrap.jar");
if (bootstrapJar.exists()) {
File f = new File(userDir, "..");
try {
homeFile = f.getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
homeFile = f.getAbsoluteFile();
}
}
}
if (homeFile == null) {
// Second fall-back. Use current directory
File f = new File(userDir);
try {
homeFile = f.getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
homeFile = f.getAbsoluteFile();
}
}
catalinaHomeFile = homeFile;
System.setProperty(
Globals.CATALINA_HOME_PROP, catalinaHomeFile.getPath());
// Then base
String base = System.getProperty(Globals.CATALINA_BASE_PROP);
if (base == null) {
catalinaBaseFile = catalinaHomeFile;
} else {
File baseFile = new File(base);
try {
baseFile = baseFile.getCanonicalFile();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
baseFile = baseFile.getAbsoluteFile();
}
catalinaBaseFile = baseFile;
}
System.setProperty(
Globals.CATALINA_BASE_PROP, catalinaBaseFile.getPath());
}
二、初始化类加载器 common、server、shared
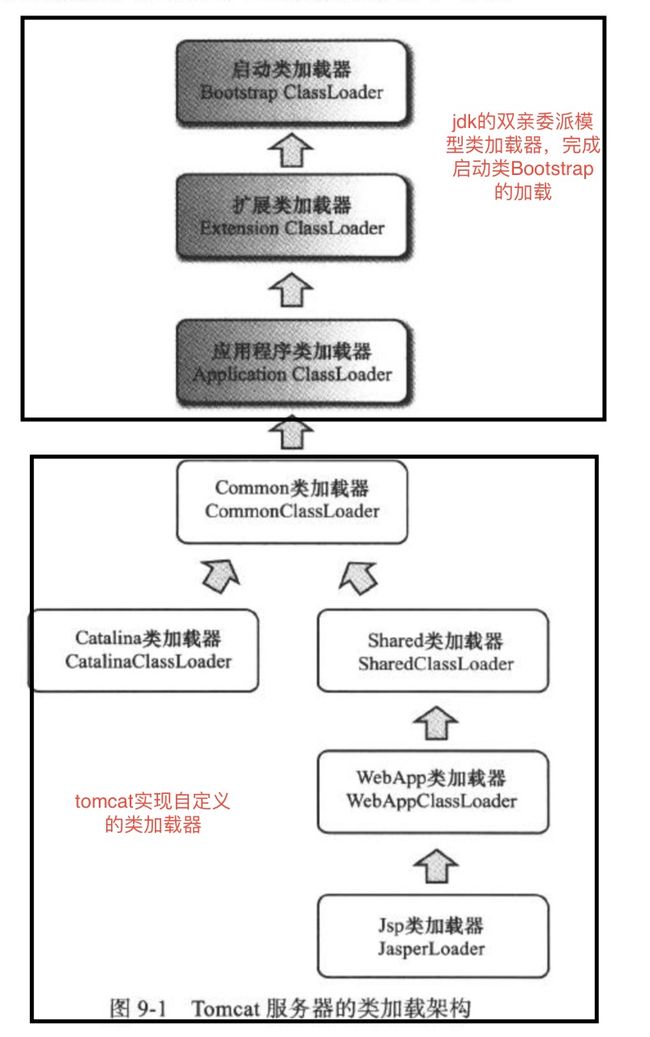
tomcat自定义的类加载器主要有三类:common、server和shared,用来加载不同位置的类和jar文件,实现不同web应用程序以及tomcat系统之间类文件的分离和共享。主要解决的问题有:部署在同一个tomcat服务器上多个web应用程序所使用的Java类库可以实现相互分离(同一个类库的不同版本);部署在同一个tomcat服务器上多个web应用程序所使用的Java类库可以实现相互共享;服务器保证自身的安全不受部署的web应用程序的影响(tomcat系统类只能通过server类加载器加载,web应用程序由shared类加载器下的WebAppClassLoader加载);实现HotSwap功能(通过替换JsperLoader类加载器实现)。
commonClassLoader
commonClassLoader在catalina.properties中的定义是:common.loader="${catalina.base}/lib","${catalina.base}/lib/*.jar","${catalina.home}/lib","${catalina.home}/lib/*.jar"
可以看出它加载的类库是catalina.base和catalina.home下lib中的文件。common是服务器和web应用程序共用的类加载器,也是server和shared的父加载器。在Bootstrap中的实现如下
private void initClassLoaders() {
try {
commonLoader = createClassLoader("common", null);
if( commonLoader == null ) {
commonLoader=this.getClass().getClassLoader();
}
catalinaLoader = createClassLoader("server", commonLoader); //设置commonLoader为catalinaLoader和sharedLoader的父加载器。
sharedLoader = createClassLoader("shared", commonLoader);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
log.error("Class loader creation threw exception", t);
System.exit(1);
}
}
继续跟踪createClassLoader的源码如下:
private ClassLoader createClassLoader(String name, ClassLoader parent)
throws Exception {
String value = CatalinaProperties.getProperty(name + ".loader");
if ((value == null) || (value.equals("")))
return parent;
value = replace(value);
List repositories = new ArrayList<>();
String[] repositoryPaths = getPaths(value);
for (String repository : repositoryPaths) {
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
URL url = new URL(repository);
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.URL));
continue;
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// Ignore
}
if (repository.endsWith("*.jar")) {
repository = repository.substring
(0, repository.length() - "*.jar".length());
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.GLOB));
} else if (repository.endsWith(".jar")) {
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.JAR));
} else {
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.DIR));
}
}
return ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader(repositories, parent);
}
catalinaClassLoader
catalinaClassLoader在catalina.properties中设置的路径为空 server.loader,所以它的类加载路径和它的父加载器commonClassLoader一样。初始化catalinaClassLoader后在init方法中设置为当前线程的类加载器,然后完成对org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina类的加载。
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
Class startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
sharedClassLoader
catalinaClassLoader在catalina.properties中设置的路径也为空,所以其默认类加载路径和它的父加载器commonClassLoader一样。
利用反射机制实例化org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina类
Catalina类在tomcat启动中有着比较重要的作用,作为tomcat生命周期的一个开始类,Catalina主要职责是解析server.xml文件,完成Server,Service,Connector等组件的启动和关闭,接受tomcat停止指令,关闭tomcat服务器。在Bootstrap中通过反射机制生成org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina实例,代码如下
Class startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
在Catalina类中是通过创建Digester的方式解析server.xml并且生成Server,Service,Connector和Container实例的,xml中只配置了Engine和Host两种Container。
protected String configFile = "conf/server.xml"; //设置server.xml的路径
...
protected Digester createStartDigester() {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
Digester digester = new Digester();
digester.setValidating(false);
digester.setRulesValidation(true);
Map, List> fakeAttributes = new HashMap<>();
List attrs = new ArrayList<>();
attrs.add("className");
fakeAttributes.put(Object.class, attrs);
digester.setFakeAttributes(fakeAttributes);
digester.setUseContextClassLoader(true);
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
//省略一大段设置其他组件的代码,形式和StandardServer的生成一样,关于Digester类解析xml生成Java实例可参考《深入剖析tomcat》第15章。
}
Catalina类的入口同样是start方法,在Bootstrap中通过反射的方式调用了Catalina的start方法
public void start()
throws Exception {
if( catalinaDaemon==null ) init();
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [] )null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null);
}
start方法中又调用load方法进行创建Digester,生成各个组件;load类的定义如下:
public void load() {
if (loaded) {
return;
}
loaded = true;
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
initDirs();
// Before digester - it may be needed
initNaming();
// Create and execute our Digester
Digester digester = createStartDigester();
InputSource inputSource = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
File file = null;
try {
try {
file = configFile(); //获取到server.xml 文件并解析
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail", file), e);
}
}
if (inputStream == null) {
try {
inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(getConfigFile());
inputSource = new InputSource
(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResource(getConfigFile()).toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
getConfigFile()), e);
}
}
}
// This should be included in catalina.jar
// Alternative: don't bother with xml, just create it manually.
if (inputStream == null) {
try {
inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("server-embed.xml");
inputSource = new InputSource
(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResource("server-embed.xml").toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
"server-embed.xml"), e);
}
}
}
if (inputStream == null || inputSource == null) {
if (file == null) {
log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
getConfigFile() + "] or [server-embed.xml]"));
} else {
log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
file.getAbsolutePath()));
if (file.exists() && !file.canRead()) {
log.warn("Permissions incorrect, read permission is not allowed on the file.");
}
}
return;
}
try {
inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream); //对server.xml数据流解析
digester.push(this);
digester.parse(inputSource);
} catch (SAXParseException spe) {
log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " +
spe.getMessage());
return;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " , e);
return;
}
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
getServer().setCatalina(this); //配置server,启动类为当前Catalina类,Home和base在Bootstrap中定义
getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());
getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile());
// Stream redirection
initStreams();
// 启动server
try {
getServer().init();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) {
throw new java.lang.Error(e);
} else {
log.error("Catalina.start", e);
}
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Initialization processed in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
}
}
tomcat启动是通过server.xml配置文件实现Server、Service、Connector和Container组件,那么这些组件具体是如何实现的,后面几篇文章将继续跟进tomcat各组件的具体实现。
tomcat源码分析(第一篇 tomcat源码分析(第一篇 从整体架构开始))
tomcat源码分析(第三篇 tomcat请求原理解析--Connector源码分析)
tomcat源码分析(第四篇 tomcat请求处理原理解析--Container源码分析)