《数据结构与算法分析:C语言描述》复习——第十章“算法设计技巧”——Huffman编码
2014.07.06 16:47
简介:
给定一段有固定符号集合S构成的文本T,集合S中总共有n种符号。如果对于每种符号,使用一种不同的由‘0’和‘1’构成的位字符串来代替,比如:
‘a’->‘01’
‘c’->'101'
'd'->‘11’
...
例如,文本“acd”经过这种编码就变成了“0110111”。
这样,就可以把文本T中的符号全部替换为‘0’‘1’构成的二进制串,这样就能以二进制文件的形式保存信息了。并且,一个ASCII字符默认占用一个字节,也就是8位。但使用这种不定长的编码方式一个字符占用的位数可能小于8位,于是可能达到压缩数据的效果。Huffman编码的规则,就是通过选定合适的编码,使得这段文本经过编码转换后的二进制串的长度最短。
图示:
用算法描述Huffman编码的过程还是比较简单的:
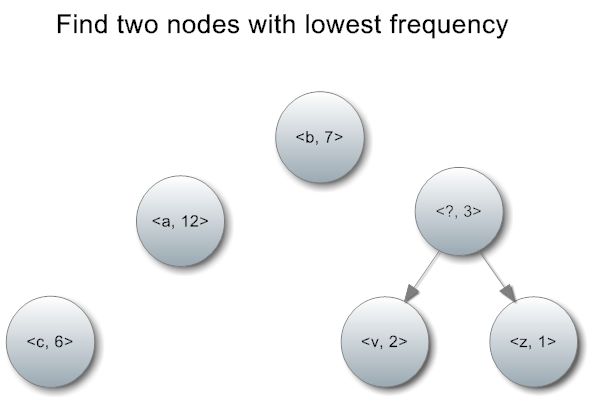
1. 定义键值对<字符, 出现频率>,比如<a, 12>表示a字符出现了12次。
2. 每次选出出现频率最低的两个字符,组合成一个字符(字符当然不能组合,但频率是可以相加的),重新放入候选集中。
3. 这个组合的过程,其实就是构建二叉树的过程
新结点的频率等于两个子节点的频率之和,而新节点上对应的字符没有实际意义,所以我们姑且标记为‘?’。
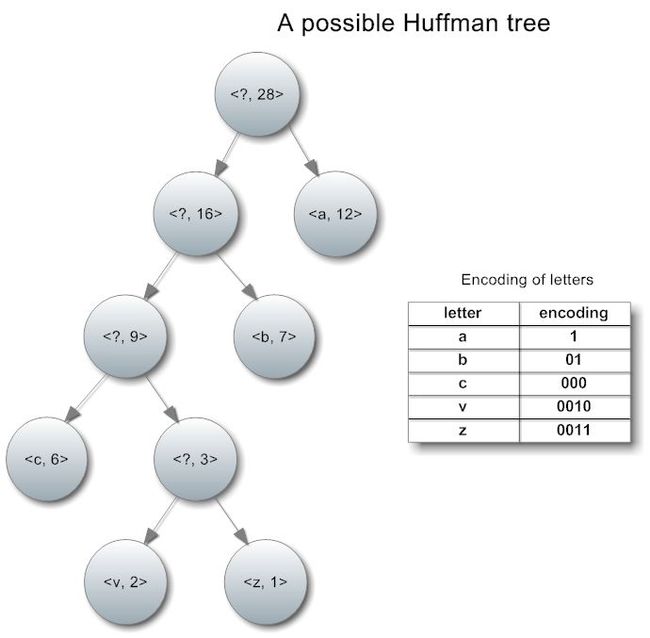
每经过一轮这样的操作,我们取出两个结点,放回一个结点,所以要经过n-1轮才能得到一棵完整的树,比如这样:
上图中给出了这棵树对应的字符编码方式,其实每个字符的编码对应于从根结点到叶结点的路径,‘0’向左,‘1’向右。
由于组合两个结点时,左右次序可以调换,因此同一套文本与字符可以构建出2^(n-1)种的Huffman树。任何一种的效果都是相同的,目的只有一个:压缩数据。
如何每次选出最小的两个呢?最小堆。
问题是:为什么每次选出最小的,结果就是最好的呢?贪婪。
实现:
1 // A simple illustration for 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <queue> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <unordered_map> 6 #include <vector> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 // The character statistics type 10 typedef unordered_map<char, int> StatType; 11 // The character encoding type 12 typedef unordered_map<char, string> EncodeType; 13 14 struct TreeNode { 15 char ch; 16 int weight; 17 TreeNode *left; 18 TreeNode *right; 19 20 TreeNode(char _ch, int _weight): ch(_ch), weight(_weight), 21 left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 22 }; 23 24 struct GreaterFunctor { 25 bool operator () (const TreeNode *x, const TreeNode *y) { 26 return x->weight > y->weight; 27 } 28 }; 29 30 void deleteTree(TreeNode *&root) 31 { 32 if (root == nullptr) { 33 return; 34 } else { 35 deleteTree(root->left); 36 deleteTree(root->right); 37 delete root; 38 root = nullptr; 39 } 40 } 41 42 void calculateEncoding(const TreeNode *root, EncodeType &encoding, string &path) 43 { 44 if (root == nullptr) { 45 return; 46 } 47 48 if (root->ch != '\0') { 49 encoding[root->ch] = path; 50 return; 51 } 52 53 path.push_back('0'); 54 calculateEncoding(root->left, encoding, path); 55 path.pop_back(); 56 57 path.push_back('1'); 58 calculateEncoding(root->right, encoding, path); 59 path.pop_back(); 60 } 61 62 void huffmanEncoding(const StatType &statistics, EncodeType &encoding) 63 { 64 priority_queue<TreeNode *, vector<TreeNode *>, GreaterFunctor> pq; 65 66 int n; 67 68 n = 0; 69 for (StatType::const_iterator sta_it = statistics.begin(); 70 sta_it != statistics.end(); ++sta_it) { 71 pq.push(new TreeNode(sta_it->first, sta_it->second)); 72 ++n; 73 } 74 75 TreeNode *p1, *p2, *p3; 76 int i; 77 for (i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) { 78 p1 = pq.top(); 79 pq.pop(); 80 p2 = pq.top(); 81 pq.pop(); 82 83 p3 = new TreeNode('\0', p1->weight + p2->weight); 84 p3->left = p1; 85 p3->right = p2; 86 pq.push(p3); 87 } 88 89 TreeNode *root = pq.top(); 90 pq.pop(); 91 92 string code = ""; 93 calculateEncoding(root, encoding, code); 94 deleteTree(root); 95 } 96 97 int main() 98 { 99 int i, n; 100 string s; 101 int weight; 102 StatType statistics; 103 EncodeType encoding; 104 105 while (cin >> n && n > 0) { 106 for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 107 cin >> s >> weight; 108 statistics[s[0]] = weight; 109 } 110 huffmanEncoding(statistics, encoding); 111 112 for (EncodeType::const_iterator enc_it = encoding.begin(); 113 enc_it != encoding.end(); ++enc_it) { 114 cout << enc_it->first << ':' << enc_it->second << endl; 115 } 116 cout << endl; 117 118 statistics.clear(); 119 encoding.clear(); 120 } 121 122 return 0; 123 }