Leetcode SQL(一)
目录
613. 直线上的最近距离
182. 查找重复的电子邮箱
627. 交换工资
584. 寻找用户推荐人
1082. 销售分析 I
577. 员工奖金
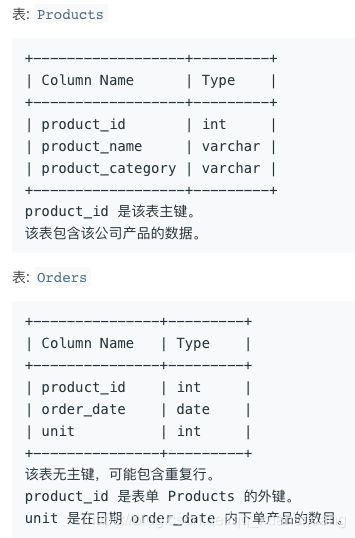
1327. 列出指定时间段内所有的下单产品
603. 连续空余座位
1407. 排名靠前的旅行者
1211. 查询结果的质量和占比
613. 直线上的最近距离
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shortest-distance-in-a-line/
表 point 保存了一些点在 x 轴上的坐标,这些坐标都是整数。
写一个查询语句,找到这些点中最近两个点之间的距离。
| x |
|-----|
| -1 |
| 0 |
| 2 |最近距离显然是 '1' ,是点 '-1' 和 '0' 之间的距离。所以输出应该如下:
| shortest|
|---------|
| 1 |注意:每个点都与其他点坐标不同,表 table 不会有重复坐标出现。
题解
一:我们知道最近的距离,必定是排序后的相邻元素差值的绝对值的最小值。那么是如何将每一行的数据与下一行的数据进行对比。在使用 row_number() over()函数时候,over()里头的分组以及排序的执行晚于 where 、group by、 order by 的执行。先生成两张临时表a和b,均是在原表的前面添加一个id字段,a的id从1开始,b的id从2开始。
select min(abs(a.x - b.x)) shortest from
(select ROW_NUMBER() over(order by x) as id, x from point)a
left join
(select ROW_NUMBER() over(order by x) + 1 as id, x from point)b
on a.id = b.id
where b.x is not null二:可以考虑将x中的值两两组合(当然不能和自己组合),这种可以用笛卡尔积来做。这种有一个缺点,我们必须排除与自身的组合,因为不然最小值肯定是0,但是若排出和自身值相等的组合,在有重复坐标,会出错,此时最小值应该是0,但这样做结果必然大于0。不过该题有给出注意事项,就是不会出现重复坐标,故而不会出现上述情况。
select min(abs(a.x - b.x)) shortest
from
point a
left join
point b
on a.x < b.x
182. 查找重复的电子邮箱
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/duplicate-emails/
编写一个 SQL 查询,查找 Person 表中所有重复的电子邮箱。
示例:
根据以上输入,你的查询应返回以下结果:
题解
一:group by 分组以及聚合函数的使用。当技术大于1的时候说明是重复的。
select Email from Person group by Email having count(Email) > 1627. 交换工资
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-salary/
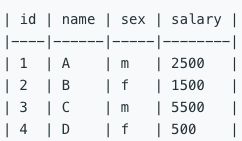
给定一个 salary 表,如下所示,有 m = 男性 和 f = 女性 的值。交换所有的 f 和 m 值(例如,将所有 f 值更改为 m,反之亦然)。要求只使用一个更新(Update)语句,并且没有中间的临时表。
注意,您必只能写一个 Update 语句,请不要编写任何 Select 语句。
例如:
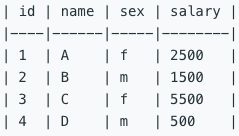
运行你所编写的更新语句之后,将会得到以下表:
题解
一:case when then else的使用。如何将字段的值按条件重新赋值。
Update salary set sex = (case when sex = "f" then "m" else "f" end)584. 寻找用户推荐人
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-customer-referee/
给定表 customer ,里面保存了所有客户信息和他们的推荐人。
写一个查询语句,返回一个编号列表,列表中编号的推荐人的编号都 不是 2。对于上面的示例数据,结果为:
题解
一:注意null的特殊处理。下面转自官方题解,https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-customer-referee/solution/xun-zhao-yong-hu-tui-jian-ren-by-leetcode/。MySQL 使用三值逻辑 —— TRUE, FALSE 和 UNKNOWN。任何与 NULL 值进行的比较都会与第三种值 UNKNOWN 做比较。这个“任何值”包括 NULL 本身!这就是为什么 MySQL 提供 IS NULL 和 IS NOT NULL 两种操作来对 NULL 特殊判断。因此,在 WHERE 语句中我们需要做一个额外的条件判断 `referee_id IS NULL'。
select name
from customer
where referee_id != 2 or referee_id is null下面的解法同样是错误的,错误原因同上。避免错误的秘诀在于使用 IS NULL 或者 IS NOT NULL 两种操作来对 NULL 值做特殊判断。
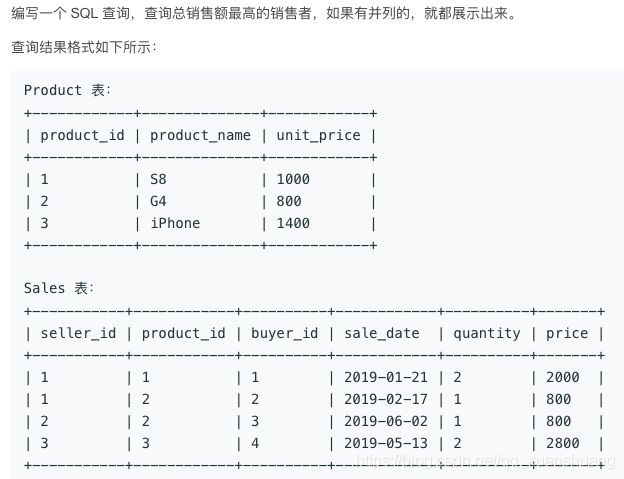
SELECT name FROM customer WHERE referee_id = NULL OR referee_id <> 2;1082. 销售分析 I
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sales-analysis-i/
题解
一:两张表join, 其中第二张表c拿到最大的销售总金额(b表,拿到每个销售的销售总金额),a表同b表,都是拿到每个销售的销售总金额,用金额join,条件销售总金额等于最大销售总金额。
select seller_id from
(select seller_id, sum(price) sum_price
from Sales
group by seller_id
)a
left join
(select max(sum_price) max_price from
(select seller_id, sum(price) sum_price
from Sales
group by seller_id
)b)c
on sum_price = max_price
where sum_price = max_price分步骤:拿到每个销售的销售总金额
select seller_id, sum(price) sum_price
from Sales
group by seller_id在拿到每个销售的销售总金额后,拿到最高的销售金额。
select max(sum_price) max_price from
(select seller_id, sum(price) sum_price
from Sales
group by seller_id
)b二:all的使用,max和all函数起到的作用是一样的, all和每一个进行比较(大于最大的或者小于最小的),any 则是大于任何一个都可以(大于最小的,小于最大的)
select seller_id from
Sales
group by
seller_id
having sum(price) >=
all(select sum(price) sum_price from Sales group by seller_id)三:窗口函数,ROW_NUMBER() VS dense_rank() ,dense_rank并列排名相同,即id不唯一;ROW_NUMBER()并列排名不相同,即id唯一。
select seller_id from
(select seller_id, dense_rank() over(order by sum(price) desc) id from Sales group by seller_id)a
where id = 1四、
select seller_id from Sales group by seller_id
having sum(price) >= (select max(sum_price) from (select sum(price) as sum_price from Sales group by seller_id) a )
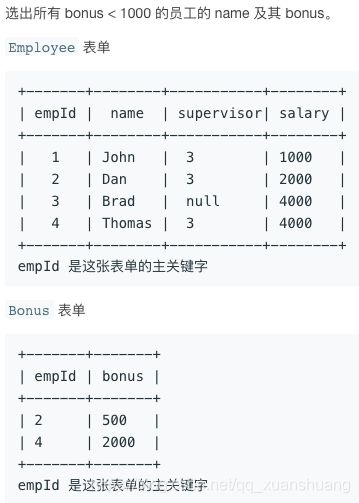
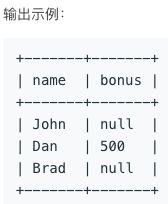
577. 员工奖金
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/employee-bonus/
题解
一:注意null值
select name, bonus
from Employee e left join Bonus b
on e.empId = b.empId
where b.empId is null or bonus < 10001327. 列出指定时间段内所有的下单产品
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/list-the-products-ordered-in-a-period/
写一个 SQL 语句,要求获取在 2020 年 2 月份下单的数量不少于 100 的产品的名字和数目。返回结果表单的顺序无要求。查询结果的格式如下:
题解
一:日期函数:提取月份month,提取年份year。
select product_name, sum(unit) unit
from
(
select o.product_id, product_name, unit
from Orders o left join Products p
on o.product_id = p.product_id
where month(order_date) = 2 and year(order_date) = 2020
)a
group by product_id, product_name
having sum(unit) >= 100二:当作字符串处理,like,
where order_date like "2020-02%"select product_name, sum(unit) as unit from
Orders o, Products p where o.product_id = p.product_id
and order_date like "2020-02%"
group by o.product_id
having unit >= 100603. 连续空余座位
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/consecutive-available-seats/
几个朋友来到电影院的售票处,准备预约连续空余座位。你能利用表 cinema ,帮他们写一个查询语句,获取所有空余座位,并将它们按照 seat_id 排序后返回吗?
对于如上样例,你的查询语句应该返回如下结果。
注意:seat_id 字段是一个自增的整数,free 字段是布尔类型('1' 表示空余, '0' 表示已被占据)。连续空余座位的定义是大于等于 2 个连续空余的座位。
题解
错解:left join会存在一个情况,只要左侧非空,右侧即使为空,也会返回结果,这带来一个不方便的例如值返回一条记录的,按理来说这不是所要求的解,但是却不好淘汰。例如只有一个座位且是空座位,符合and的第一个条件,以及第二个条件or后面的条件。还有当最后一张空闲,且前面均不空,这个座位也会被返回。
select a.seat_id
from cinema a
left join cinema b
on a.seat_id + 1 = b.seat_id
where a.free = 1 and (b.free = 1 or b.free is null)一:之前习惯了left join,left join会存在一个情况,只要左侧非空,右侧即使为空,也会返回结果,这带来一个不方便的例如值返回一条记录的,按理来说这不是所要求的解,但是却不好淘汰。join两边均非空才会出现,这边没像错解用a.seat_id + 1 = b.seat_id,这样会出现两次,故用distinct。
| seat_id | free | seat_id | free |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
select distinct a.seat_id
from cinema a join cinema b
on abs(a.seat_id - b.seat_id) = 1
and a.free = true and b.free = true
order by a.seat_id
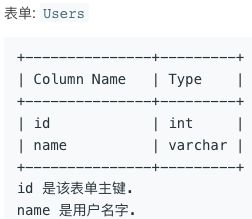
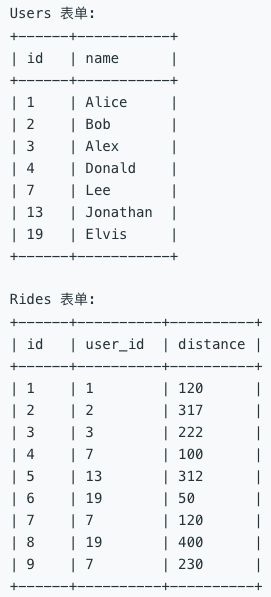
1407. 排名靠前的旅行者
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/top-travellers/
id 是该表单主键。user_id 是本次行程的用户的 id, 而该用户此次行程距离为 distance。写一段 SQL , 报告每个用户的旅行距离。返回的结果表单, 以 travelled_distance 降序排列, 如果有两个或者更多的用户旅行了相同的距离, 那么再以 name 升序排列。查询结果格式, 如下例所示。
Elvis 和 Lee 旅行了 450 英里, Elvis 是排名靠前的旅行者, 因为他的名字在字母表上的排序比 Lee 更小。Bob, Jonathan, Alex 和 Alice 只有一次行程, 我们只按此次行程的全部距离对他们排序。Donald 没有任何行程, 他的旅行距离为 0。
题解
一:case when then来进行判断,也可以处理给空值赋默认值的问题。
select name, case
when r.user_id is null then 0
else sum(distance) end travelled_distance
from Users u
left join Rides r
on u.id = r.user_id
group by u.id
order by travelled_distance desc, name asc二:ifnull来处理空值,当第一个参数为null,取第二个参数的值
select name, ifnull(sum(distance), 0) travelled_distance
from Users u
left join Rides r
on u.id = r.user_id
group by u.id
order by travelled_distance desc, name asc1211. 查询结果的质量和占比
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/queries-quality-and-percentage/
此表没有主键,并可能有重复的行。此表包含了一些从数据库中收集的查询信息。“位置”(position)列的值为 1 到 500 。“评分”(rating)列的值为 1 到 5 。评分小于 3 的查询被定义为质量很差的查询。
题解
一:纯粹的sql函数
select query_name, round(sum(rating / position) / count(rating), 2) quality,
round(sum(rating < 3) / count(rating) * 100, 2) poor_query_percentage
from Queries
group by query_name