数据结构 Java数据结构 ---- 堆(优先级队列)
文章目录
- 堆(优先级队列)
-
- 1.二叉树的顺序存储
-
- 1.1 存储方式
- 1.2 下标的关系
- 2.堆
-
- 2.1 概念
- 3.模拟实现PriorityQueue
-
- ①基本操作
- ②向下调整
- ③建堆
- ④入队列
- ⑤出队列
- ⑥堆排序
- 4.堆的应用-优先级队列
-
- 4.1 java 中的优先级队列
- 4.2 java 中堆的使用
- 5. 集合框架中PriorityQueue的比较方式
- 6.堆的其他应用-TopK 问题
-
- 用堆的思路:
- 画图解析:
- 代码实现:
- 运行结果:
- 7.面试题---查找和最小的K对数字
-
- 解题思路:
- 代码实现:
堆(优先级队列)
1.二叉树的顺序存储
1.1 存储方式
使用数组保存二叉树结构,方式即将二叉树用层序遍历方式放入数组中。
一般只适合表示完全二叉树,因为非完全二叉树会有空间的浪费。
这种方式的主要用法就是堆的表示。

1.2 下标的关系
- 如果 已知双亲下标(parent) ,则:
左孩子的下标(left child) = 2 * parent + 1;
右孩子的下标(right child) = 2 * parent + 2; - 如果 已知任意孩子下标(child),则:
双亲的下标(parent) = ( child - 1 ) / 2;

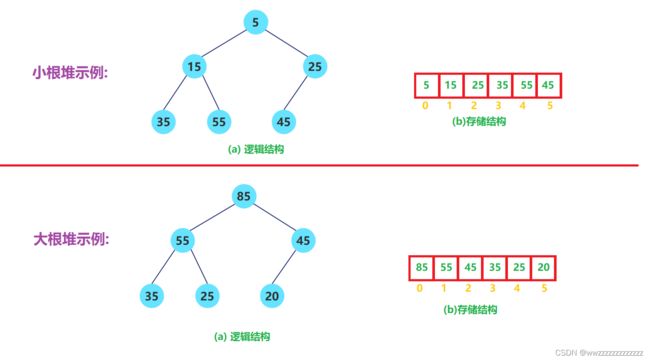
2.堆
2.1 概念
- 堆逻辑上是一棵完全二叉树
- 堆物理上是保存在数组中
- 满足任意结点的值都大于其子树中结点的值,叫做大堆,或者大根堆,或者最大堆
- 反之,则是小堆,或者小根堆,或者最小堆
- 堆的基本作用是,快速找集合中的最值
3.模拟实现PriorityQueue
①基本操作
class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public TestHeap(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
}
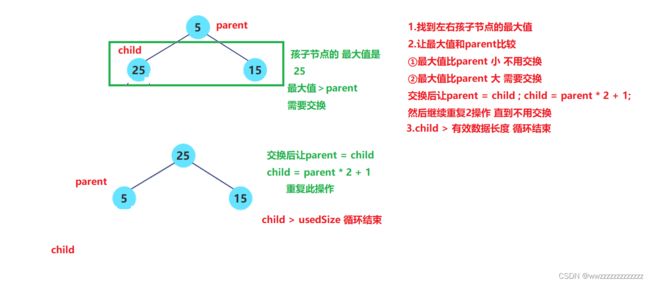
②向下调整
//len是有效数据长度
public void adjustDown(int root,int len) {
int parent = root;
int child = 2 * parent + 1;
while(child < len){
//找到左右孩子的最大值
//1. 没有右孩子,左孩子就是最大.child下标下就是最大
//2. 有右孩子,但是左孩子更大,即左孩子是最大.child下标下就是最大
//3. 有右孩子,但是右孩子更大,即右孩子是最大.child+1 下标下就是最大
if(child+1 < len && this.elem[child] < this.elem[child+1]){
child++;
}
//此时child下标下就是最大值.
if(this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
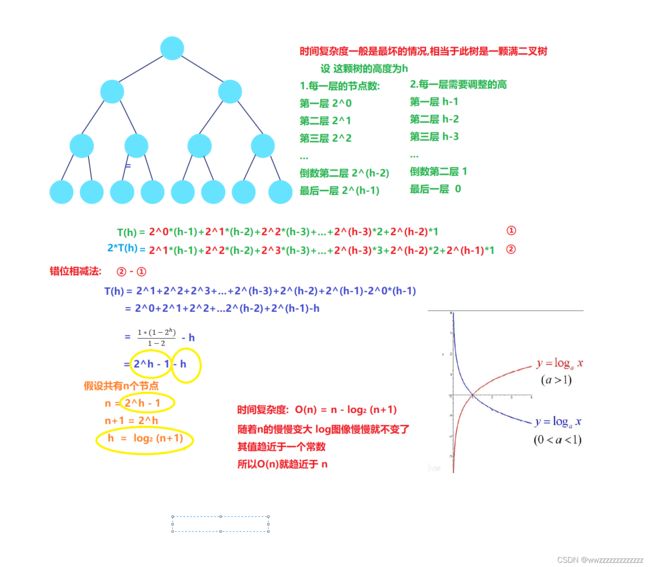
③建堆
建大堆 - 思路:
从最后一个数据的 双亲开始 向下调整. 每次调整完 让parent-- 直到调整到parent = 0;
/**
* 建大堆
* @param array
*/
public void createHeap(int[] array){
//这一步相当于 数组的拷贝
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
this.elem[i] = array[i];
this.usedSize++;
}
//parent 就代表每颗子树的根节点
for (int parent = (array.length-1-1)/2;parent >= 0; parent--) {
adjustDown(parent,this.usedSize);
}
}
④入队列
思路:从队尾入,每次入队列都要进行向上调整
向上调整:
① 如果插入的child比parent大 则需要交换
② 交换后需要让child = parent; parent = (child - ) / 2;
③ 如果插入的child比parent小 则不需要交换
④循环①②③操作,直到不需要交换或则 child<0结束循环.
代码实现:
public void adjustUp(int child){
//parent等于child的双亲
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//child>0进入循环
while(child > 0) {
if (this.elem[child] > this.elem[parent]){
int tmp = this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent] = this.elem[child];
this.elem[child] = tmp;
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}else {
//不需要交换直接跳出循环
break;
}
}
}
入队思路:
1.首先判断是否需要扩容
2.如果需要扩容则要先扩容然后插入,不需要扩容直接插入
3.插入后进行向上调整
代码实现:
public void push(int val){
if(isFull()){
//扩容
Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
//插入 向上调整
this.elem[this.usedSize++] = val;
adjustUp(usedSize - 1);
}
//判断是否满
public boolean isFull(){
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
⑤出队列
出队列思路:
1.首先需要判断是否为空
2.为空直接返回
3.不为空,首先交换队首元素和队尾元素,然后从0下标开始进行向下调整.
代码实现:
//判断是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
public void pop(){
if(!isEmpty()){
//不为空首先进行交换
int tmp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[usedSize - 1];
this.elem[usedSize - 1] = tmp;
this.usedSize--;
//然后进行向下调整
adjustDown(0,this.usedSize);
}
}
⑥堆排序
堆排序思路:
1.让end指向队尾元素
2.让队首元素和end交换
3.从0下标位置进行向下调整 然后end–;
4.重复以上操作直到end=0;
代码实现:
/**
* 前提是要先创建大堆
*/
public void heapSort() {
int end = this.usedSize - 1;
while(end > 0) {
int tmp = this.elem[0];
this.elem[0] = this.elem[end];
this.elem[end] = tmp;
adjustDown(0,end--);
}
}
4.堆的应用-优先级队列
4.1 java 中的优先级队列
PriorityQueue implements Queue
| 错误处理 | 抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 |
|---|---|---|
| 入队列 | add(e) | offer(e) |
| 出队列 | remove() | poll() |
| 队首元素 | element() | peek() |
4.2 java 中堆的使用
注意:
1. 堆的默认大小是 11 默认为小堆
2. 可以指定堆的大小,可以指定堆为大小堆.
public static void main (String[] args) {
//堆 默认是大小为11
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
//默认是 小堆
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
priorityQueue.add(3);
System.out.println(priorityQueue);
}
5. 集合框架中PriorityQueue的比较方式
集合框架中的PriorityQueue底层使用堆结构,因此其内部的元素必须要能够比大小,PriorityQueue采用了:
Comparble和Comparator两种方式。
- Comparble是默认的内部比较方式,如果用户插入自定义类型对象时,该类对象必须要实现Comparble接
口,并覆写compareTo方法 - 用户也可以选择使用比较器对象,如果用户插入自定义类型对象时,必须要提供一个比较器类,让该类实现
Comparator接口并覆写compare方法。

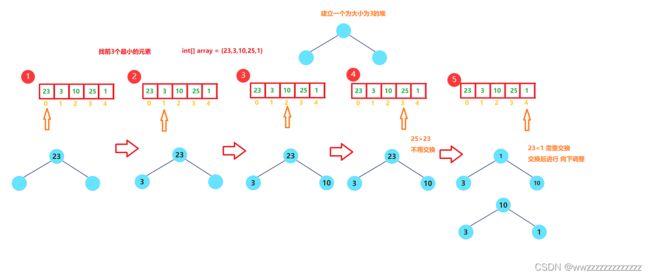
6.堆的其他应用-TopK 问题
TopK问题,找前K个最大(最小)的数.
用堆的思路:
- 放入k个元素到堆中
①找前k个最大的数,建小堆.
②找前k个最小的数,建大堆. - 如果找的是前k个最大的数,先建小堆将k个元素放入堆中,然后让堆顶元素 和 后面的数比较,如果小于后面的数,就和堆顶元素交换,然后变成小堆继续此操作.
- 反之则是找前k个最小的数.
- 遍历结束后,堆中的元素就是要找的数
画图解析:
代码实现:
/**
* 找前k个最大的元素
* @param array
* @param k
*/
public static void topk2(int[] array,int k){
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2;//大堆
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (maxHeap.size() < k) {
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
} else {
int top = maxHeap.peek();//获取队顶元素
if (top < array[i]) {
maxHeap.poll();
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
System.out.println(maxHeap);
}
/**
* 找前k个最小的元素
* @param array
* @param k
*/
public static void topk1(int[] array,int k){
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;//大堆
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (maxHeap.size() < k) {
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
} else {
int top = maxHeap.peek();//获取队顶元素
if (top > array[i]) {
maxHeap.poll();
maxHeap.offer(array[i]);
}
}
}
System.out.println(maxHeap);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
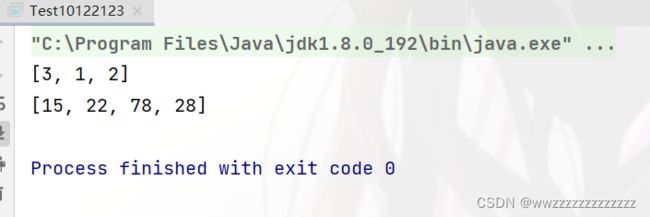
int[] array = {1,3,2,6,5,78,22,15,28};//找前3个最大的数据.
topk1(array,3);
topk2(array,4);
}
运行结果:
7.面试题—查找和最小的K对数字
LeetCode 373: 查找和最小的K对数字
描述:
给定两个以升序排列的整数数组 nums1 和 nums2 , 以及一个整数 k 。
定义一对值 (u,v),其中第一个元素来自 nums1,第二个元素来自 nums2 。
请找到和最小的 k 个数对 (u1,v1), (u2,v2) … (uk,vk) 。
示例 1:
输入: nums1 = [1,7,11], nums2 = [2,4,6], k = 3
输出: [1,2],[1,4],[1,6]
解释: 返回序列中的前 3 对数:
[1,2],[1,4],[1,6],[7,2],[7,4],[11,2],[7,6],[11,4],[11,6]
解题思路:
- 根据题意找最小的k对数字,建立大小为k的大堆
- 如果堆没放满,直接放入堆中.
- 如果堆放满了,每次需要和堆顶比较,如果小于堆顶,需要交换.
- 遍历时注意,如果数组过大,遍历会超时,所以遍历次数可以优化为 只最多遍历到 k,而且要满足小于数组长度的要求.(i
- 在遍历结束后,将数据插入list中的时候注意.可能堆没满.
代码实现:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
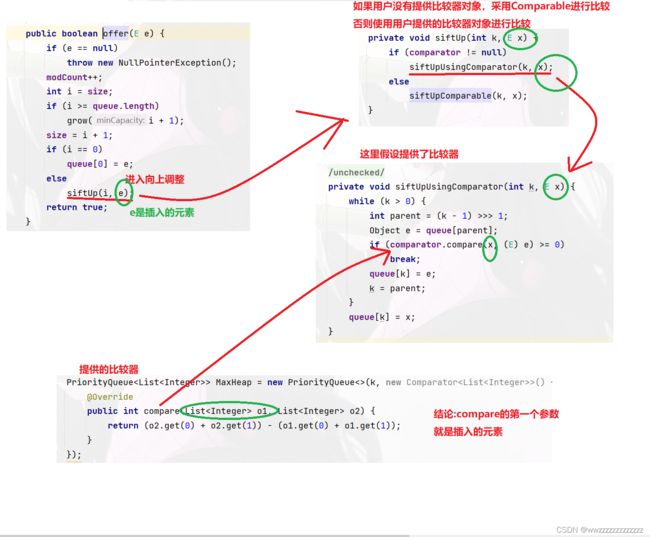
PriorityQueue<List<Integer>> MaxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(k, new Comparator<List<Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(List<Integer> o1, List<Integer> o2) {
return (o2.get(0) + o2.get(1)) - (o1.get(0) + o1.get(1));
}
});
// 只最多遍历到 k,而且要满足小于数组长度的要求
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length && i < k; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums2.length && j < k; j++) {
// 堆没满 首先放入堆中
if (MaxHeap.size() < k){
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(nums1[i]);
list1.add(nums2[j]);
MaxHeap.offer(list1);
}else {
List<Integer> top = MaxHeap.peek();
int topValue = top.get(0) + top.get(1);
//堆满了后要进行比较,大于堆顶的值要出队然后把大于的数据入队
if(topValue > nums1[i] + nums2[j]){
MaxHeap.poll();
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(nums1[i]);
list1.add(nums2[j]);
MaxHeap.offer(list1);
}
}
}
}
//将数据放入ret中要注意 可能堆没放满
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k && !MaxHeap.isEmpty(); i++) {
ret.add(MaxHeap.poll());
}
return ret;
}
}