1.BeanFactoryPostProcessors和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的作用
2.spring源码prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)流程介绍
3.spring源码prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)源码解析
4.总结
1.BeanFactoryPostProcessors和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的作用
github源码地址(带注释):
https://github.com/su15967456...
spring源码执行流程图:
![]()
我们点到这个方法里,大致浏览一下代码,发现主要是围绕着这两个集合进行操作:
简而言之:
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法会把所有实现beanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的类进行实例化和调用。
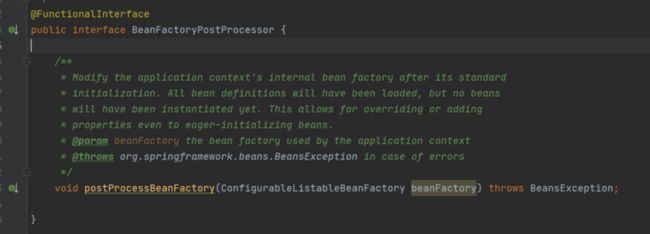
我们先来看一下beanFactoryPostProcessor的注释:
意思大致为:在bean definitions全部加载完毕,并且在初始化之前,beanFactoryPostProcessor可以对这些bd重写或者增加一些属性。
我们再来看一下BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的注释: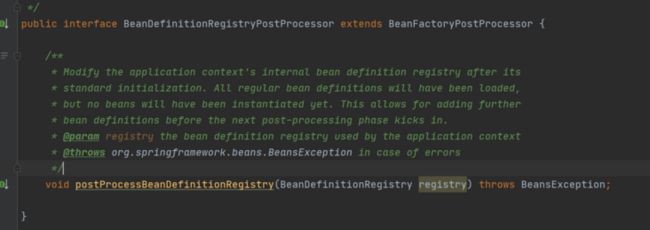
当bean definitions全部被加载完毕,并且在初始化之前,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor增加一些额外的bean definition。
我们得出结论:
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor:可以用来增加新的bean Difinition
beanFactoryPostProcessor:可以对bean Difinition的进行修改。
2.spring源码prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)流程介绍
从整体的执行顺序来看,这个方法的执行流程是这个样子的:
1)执行外部传进来的BeanFactoryPostProcessor类
2)执行实现子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类
3)执行实现父类BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类
从执行每一步的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor或者BeanFactoryPostProcessor,又可以分为以下几个逻辑:

1)执行实现了PriorityOrdered(高优先级)的类
2)执行实现了Ordered(有序)的类
3)执行什么都没有实现的普通类
3.spring源码prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)源码解析
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
//无论是什么情况,先执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
//将已经执行的BFPP存储在processBean中,防止重复执行
Set processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
//BeanDefinitionRegistry是对beanDefinition进行操作的类
// 判断beanFactory是不是 BeanDefinitionRegistry的实现,此处是DefaultListableBeanFactory,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,此处为true
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
//类型转换
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
//此时要做一个区分,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类
//BeanFactoryPostProcessor主要针对的对象是BeanFactory,
//BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor主要针对的对象是BeanDefinition
//存放BeanFactoryPostProcessor的集合类
List regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//存放BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的集合
List registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//首先处理入参中的beanFactoryPostProcessors,遍历所有的beanFactoryPostProcessors
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
//如果是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
//查找BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor中的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
//添加到registryProcessors
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
} else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
//用于保存本次要执行的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
List currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//调用所有实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现类
//找到所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口bean的beanName
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
//遍历所有符合规则的postProcessNames
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//检测是否实现了PriorityOrdered接口
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
//获取名字对应的bean实例,添加到currentRegistryProcessor
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
//将要被执行的BFPP添加到processedBeans中,防止重复执行
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
//按照优先顺序进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
//添加到registryProcessors中,用于最后执行postProcessBeanFactory方法
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//遍历currentRegistryProcessors,执行postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
//执行完毕后,清空
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
//调用所有实现Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现类
//找到所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口bean的beanName
//为什么要重新获取 :
//上面调用invoke方法的时候,可能会新增一些 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//检测是否实现了Order接口,并且还未执行过程
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
//获取名字的bean实例,添加到currentRegistryProcessors
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
//添加到已执行过的processedBeans
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
//按照优先顺序进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
//添加到registryProcessors中,用于最后执行postProcessBeanFactory方法
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//遍历currentRegistryProcessors,执行postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
//执行完毕后,清空
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
// 最后,调用剩下的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors,没有实现Order的
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
//找出所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors的接口类
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//如果还未执行过BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
//如果在中途过程中,可能会新增 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors,所以这里要为true
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
//执行postProcessBeanFactory
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
} else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
//获取实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor的所有类
//到目前为止,所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor已经全部实现完毕了,接下来开始BeanFactoryPostProcessor的类的处理
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 他们不重复执行是因为beanFactoryPostProcessor不会新增新Processor
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
//上面只执行了实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postprocessor,并没有实现
//有priorityOrdered的PostProcessors集合
List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//有ordered的PostProcessors集合 为什么下面两种存string,上面那种存类
//代码改掉还是可以运行的,猜测可能是省空间
List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
//没有order的PostProcessors集合
List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
} else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
} else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
} else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//根据priorityOrderedPostProcessors的集合先排序,后执行
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
} 以上的几个逻辑,除了执行顺序外,有几个重要的点:
1)为什么执行子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的时候,每次都要从容器中重新获取类?
因为实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的类可以增加新的bd,也就是说可以增加新的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,所以每次都要重新获取。
2)为什么执行父类BeanFactoryPostProcessor的时候,不用重新获取?
因为父类BeanFactoryPostProcessor,不能增加新的bd,所以就不用重新获取了。
3)
4.总结
我们可以看出,这个方法的执行逻辑还是比较简单和容易理解,而且都是由一个函数编写而成,封装地不是太厉害。