多传感器融合定位 第六章 惯性导航结算及误差模型
多传感器融合定位 第六章 惯性导航结算及误差模型
参考博客:深蓝学院-多传感器融合定位-第6章作业
代码下载:https://github.com/kahowang/sensor-fusion-for-localization-and-mapping/tree/main/%E7%AC%AC%E5%85%AD%E7%AB%A0%20%E6%83%AF%E6%80%A7%E5%AF%BC%E8%88%AA%E8%A7%A3%E7%AE%97%E5%8F%8A%E8%AF%AF%E5%B7%AE%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/catkin_ws
1.姿态更新-基于中值法的解算
1.1 基于四元数的姿态更新
获取等效旋转矢量
// get deltas:
size_t index_curr_ = 1;
size_t index_prev_ =0;
Eigen::Vector3d angular_delta = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero();
if(! (GetAngularDelta(index_curr_, index_prev_, angular_delta)) ){
std::cout << "GetAngularDelta(): index error" << std::endl; // 获取等效旋转矢量
}
/**********************************************************************************************************************/
bool Activity::GetAngularDelta(
const size_t index_curr, const size_t index_prev,
Eigen::Vector3d &angular_delta
) {
//
// TODO: this could be a helper routine for your own implementation
//
if (
index_curr <= index_prev ||
imu_data_buff_.size() <= index_curr
) {
return false;
}
const IMUData &imu_data_curr = imu_data_buff_.at(index_curr);
const IMUData &imu_data_prev = imu_data_buff_.at(index_prev);
double delta_t = imu_data_curr.time - imu_data_prev.time;
Eigen::Vector3d angular_vel_curr = GetUnbiasedAngularVel(imu_data_curr.angular_velocity); // omega_k
Eigen::Vector3d angular_vel_prev = GetUnbiasedAngularVel(imu_data_prev.angular_velocity); // omega_k-1
angular_delta = 0.5*delta_t*(angular_vel_curr + angular_vel_prev); // 中值法计算angular
return true;
}
更新四元数
// update orientation:
Eigen::Matrix3d R_curr_ = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
Eigen::Matrix3d R_prev_ = Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
UpdateOrientation(angular_delta,R_curr_, R_prev_); // 更新四元数
/*********************************************************************************************************************/
void Activity::UpdateOrientation(
const Eigen::Vector3d &angular_delta,
Eigen::Matrix3d &R_curr, Eigen::Matrix3d &R_prev
) {
//
// TODO: this could be a helper routine for your own implementation
//
// magnitude:
double angular_delta_mag = angular_delta.norm();
// direction:
Eigen::Vector3d angular_delta_dir = angular_delta.normalized();
// build delta q:
double angular_delta_cos = cos(angular_delta_mag/2.0);
double angular_delta_sin = sin(angular_delta_mag/2.0);
Eigen::Quaterniond dq(
angular_delta_cos,
angular_delta_sin*angular_delta_dir.x(),
angular_delta_sin*angular_delta_dir.y(),
angular_delta_sin*angular_delta_dir.z()
);
Eigen::Quaterniond q(pose_.block<3, 3>(0, 0));
// update:
q = q*dq;
// write back:
R_prev = pose_.block<3, 3>(0, 0);
pose_.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = q.normalized().toRotationMatrix();
R_curr = pose_.block<3, 3>(0, 0);
}
1.2 位置更新
更新速度
// get velocity delta:
double delta_t_;
Eigen::Vector3d velocity_delta_;
if(! (GetVelocityDelta(index_curr_, index_prev_, R_curr_, R_prev_, delta_t_, velocity_delta_)) ){
std::cout << "GetVelocityDelta(): index error" << std::endl; // 获取速度差值
}
/**********************************************************************************************************************/
bool Activity::GetVelocityDelta(
const size_t index_curr, const size_t index_prev,
const Eigen::Matrix3d &R_curr, const Eigen::Matrix3d &R_prev,
double &delta_t, Eigen::Vector3d &velocity_delta
) {
//
// TODO: this could be a helper routine for your own implementation
//
if (
index_curr <= index_prev ||
imu_data_buff_.size() <= index_curr
) {
return false;
}
const IMUData &imu_data_curr = imu_data_buff_.at(index_curr);
const IMUData &imu_data_prev = imu_data_buff_.at(index_prev);
delta_t = imu_data_curr.time - imu_data_prev.time;
Eigen::Vector3d linear_acc_curr = GetUnbiasedLinearAcc(imu_data_curr.linear_acceleration, R_curr);
Eigen::Vector3d linear_acc_prev = GetUnbiasedLinearAcc(imu_data_prev.linear_acceleration, R_prev);
velocity_delta = 0.5*delta_t*(linear_acc_curr + linear_acc_prev);
return true;
}
更新位置
// update position:
UpdatePosition(delta_t_, velocity_delta_);
/****************************************************************************************************/
void Activity::UpdatePosition(const double &delta_t, const Eigen::Vector3d &velocity_delta) {
//
// TODO: this could be a helper routine for your own implementation
//
pose_.block<3, 1>(0, 3) += delta_t*vel_ + 0.5*delta_t*velocity_delta;
vel_ += velocity_delta;
}
1.3 结果
roslaunch imu_integration imu_integration.launch
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-FtIJ7cCW-1633849406700)(/home/kaho/Pictures/chapter6/中值法解算/mid.png)]
2.姿态更新-基于欧拉法解算
bool Activity::GetAngularDelta( )
angular_delta = delta_t*angular_vel_prev; // 欧拉法
bool Activity::GetVelocityDelta( )
velocity_delta = delta_t*linear_acc_prev; // 欧拉法
结果:
roslaunch imu_integration imu_integration.launch
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-DICqGck0-1633849406702)(/home/kaho/Pictures/chapter6/欧拉法解算/euler.png)]
3.gnss-ins-sim仿真数据数据集,对比中值法和欧拉法得解算精度
3.1 gnss-ins-sim 使用
gnss-ins-sim github下载链接
使用示例教程, 基于Python的开源GNSS/INS仿真
使用要点:
1.定义仿真IMU的误差模型
可以选择 ‘low-accuracy’, ‘mid-accuracy’ and ‘high accuracy’ 三种不同精度的IMU模型,或自定义IMU模型
imu = imu_model.IMU(accuracy=imu_err, axis=6, gps=False)
imu = imu_model.IMU(accuracy='low accuracy', axis=9, gps=True)
imu_err = {
# gyro bias, deg/hr
'gyro_b': np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]),
# gyro angle random walk, deg/rt-hr
'gyro_arw': np.array([0.25, 0.25, 0.25]),
# gyro bias instability, deg/hr
'gyro_b_stability': np.array([3.5, 3.5, 3.5]),
# gyro bias instability correlation, sec.
# set this to 'inf' to use a random walk model
# set this to a positive real number to use a first-order Gauss-Markkov model
'gyro_b_corr': np.array([100.0, 100.0, 100.0]),
# accelerometer bias, m/s^2
'accel_b': np.array([0.0e-3, 0.0e-3, 0.0e-3]),
# accelerometer velocity random walk, m/s/rt-hr
'accel_vrw': np.array([0.03119, 0.03009, 0.04779]),
# accelerometer bias instability, m/s^2
'accel_b_stability': np.array([4.29e-5, 5.72e-5, 8.02e-5]),
# accelerometer bias instability correlation, sec. Similar to gyro_b_corr
'accel_b_corr': np.array([200.0, 200.0, 200.0]),
# magnetometer noise std, uT
'mag_std': np.array([0.2, 0.2, 0.2])
}
2.运动定义 command type
通过写入到csv中,进行运动定义,主要使用到两种指令格式, command type 1 和 command type 2
command type 1 定义在command duration 时间内的速率和角速率变化,可用于加速,匀速运动
command type 2 定义在command duration 时间内达到预设的角度(绝对) 和 速度
| Command type | Comment |
|---|---|
| 1 | Directly define the Euler angles change rate and body frame velocity change rate. The change rates are given by column 2~7. The units are deg/s and m/s/s. Column 8 gives how long the command will last. If you want to fully control execution time of each command by your own, you should always choose the motion type to be 1 |
| 2 | Define the absolute attitude and absolute velocity to reach. The target attitude and velocity are given by column 2~7. The units are deg and m/s. Column 8 defines the maximum time to execute the command. If actual executing time is less than max time, the remaining time will not be used and the next command will be executed immediately. If the command cannot be finished within max time, the next command will be executed after max time. |
3.2 prepare sim dataset
3.2.1 生成rosbag仿真数据集
通过参考recorder_node_allan_variance_analysis.py 和 Teamo 助教的GitHub写法,仿写生成dataset的代码 ,gnss-ins-sim 源码保存数据集的方式是csv,这里为了方便可视化,转为rosbag的方式保存,保存仿真的数据有,imu : gyro accel ; groundtruth : orientation(四元数)、position 、velocity。
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/src/recorder_node_sim.py
#!/usr/bin/python
import os
import rospkg
import rospy
import rosbag
import math
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from gnss_ins_sim.sim import imu_model
from gnss_ins_sim.sim import ins_sim
# from gnss_ins_sim.geoparams import geoparams
from std_msgs import msg
from std_msgs.msg import String
from sensor_msgs.msg import Imu
from nav_msgs.msg import Odometry
def get_gnss_ins_sim(motion_def_file, fs_imu, fs_gps):
# set origin x y z
origin_x = 2849886.61825
origin_y = -4656214.27294
origin_z = -3287190.60046
'''
Generate simulated GNSS/IMU data using specified trajectory.
'''
# set IMU model:
D2R = math.pi/180.0
# imu_err = 'low-accuracy'
imu_err = {
# 1. gyro:
# a. random noise:
# gyro angle random walk, deg/rt-hr
'gyro_arw': np.array([0., 0., 0.]),
# gyro bias instability, deg/hr
'gyro_b_stability': np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]),
# gyro bias isntability correlation time, sec
'gyro_b_corr': np.array([100.0, 100.0, 100.0]),
# b. deterministic error:
'gyro_b': np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]),
'gyro_k': np.array([1.0, 1.0, 1.0]),
'gyro_s': np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]),
# 2. accel:
# a. random noise:
# accel velocity random walk, m/s/rt-hr
'accel_vrw': np.array([0., 0., 0.]),
# accel bias instability, m/s2
'accel_b_stability': np.array([0., 0., 0.]),
# accel bias isntability correlation time, sec
'accel_b_corr': np.array([100.0, 100.0, 100.0]),
# b. deterministic error:
'accel_b': np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]),
'accel_k': np.array([1.0, 1.0, 1.0]),
'accel_s': np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]),
# 3. mag:
'mag_si': np.eye(3) + np.random.randn(3, 3)*0.0,
'mag_hi': np.array([10.0, 10.0, 10.0])*0.0,
'mag_std': np.array([0.1, 0.1, 0.1])
}
# generate GPS and magnetometer data:
imu = imu_model.IMU(accuracy=imu_err, axis=9, gps=True)
# init simulation:
sim = ins_sim.Sim(
# here sync GPS with other measurements as marker:
[fs_imu, fs_imu, fs_imu],
motion_def_file,
ref_frame=1,
imu=imu,
mode=None,
env=None,
algorithm=None
)
# run:
sim.run(1)
# get simulated data:
rospy.logwarn(
'Simulated data size: Gyro-{}, Accel-{}, pos-{}'.format(
len(sim.dmgr.get_data_all('gyro').data[0]),
len(sim.dmgr.get_data_all('accel').data[0]),
len(sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_pos').data)
)
)
# calibration stages:
step_size = 1.0 / fs_imu
for i, (gyro, accel, ref_q, ref_pos, ref_vel) in enumerate(
zip(
# a. gyro:
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('gyro').data[0],
# b. accel:
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('accel').data[0],
# c. gt_pose:
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_att_quat').data, # groundtruth
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_pos').data,
# d. true_vel :
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_vel').data
)
):
yield {
'stamp': i * step_size,
'data': {
# a. gyro:
'gyro_x': gyro[0],
'gyro_y': gyro[1],
'gyro_z': gyro[2],
# b. accel:
'accel_x': accel[0],
'accel_y': accel[1],
'accel_z': accel[2],
# c. true orientation:
'gt_quat_w': ref_q[0],
'gt_quat_x': ref_q[1],
'gt_quat_y': ref_q[2],
'gt_quat_z': ref_q[3],
# d. true position:
'gt_pos_x': ref_pos[0] + origin_x,
'gt_pos_y': ref_pos[1] + origin_y,
'gt_pos_z': ref_pos[2] + origin_z,
# d. true velocity:
'gt_vel_x': ref_vel[0],
'gt_vel_y': ref_vel[1],
'gt_vel_z': ref_vel[2]
}
}
sim.results()
sim.plot(['ref_pos', 'ref_vel'], opt={'ref_pos': '3d'})
def gnss_ins_sim_recorder():
"""
Record simulated GNSS/IMU data as ROS bag
"""
# ensure gnss_ins_sim_node is unique:
rospy.init_node('gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node')
# parse params:
motion_def_name = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/motion_file')
sample_freq_imu = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/sample_frequency/imu')
sample_freq_gps = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/sample_frequency/gps')
topic_name_imu = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/topic_name_imu')
topic_name_gt = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/topic_name_gt')
## save scv
output_path = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/output_path')
output_name = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/output_name')
## save rosbag
rosbag_output_path = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/output_path')
rosbag_output_name = rospy.get_param('/gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node/output_name')
# generate simulated data:
motion_def_path = os.path.join(
rospkg.RosPack().get_path('gnss_ins_sim'), 'config', 'motion_def', motion_def_name
)
imu_simulator = get_gnss_ins_sim(
# motion def file:
motion_def_path,
# gyro-accel/gyro-accel-mag sample rate:
sample_freq_imu,
# GPS sample rate:
sample_freq_gps
)
# write as csv:
# data = pd.DataFrame(
# list(imu_simulator)
# )
# data.to_csv(
# os.path.join(output_path, output_name)
# )
#write rosbag
with rosbag.Bag(
os.path.join(rosbag_output_path, rosbag_output_name), 'w'
) as bag:
# get timestamp base:
timestamp_start = rospy.Time.now()
for measurement in imu_simulator:
# init:
msg_imu = Imu()
# a. set header:
msg_imu.header.frame_id = 'inertial'
msg_imu.header.stamp = timestamp_start + rospy.Duration.from_sec(measurement['stamp'])
# b. set orientation estimation:
msg_imu.orientation.x = 0.0
msg_imu.orientation.y = 0.0
msg_imu.orientation.z = 0.0
msg_imu.orientation.w = 1.0
# c. gyro:
msg_imu.angular_velocity.x = measurement['data']['gyro_x']
msg_imu.angular_velocity.y = measurement['data']['gyro_y']
msg_imu.angular_velocity.z = measurement['data']['gyro_z']
msg_imu.linear_acceleration.x = measurement['data']['accel_x']
msg_imu.linear_acceleration.y = measurement['data']['accel_y']
msg_imu.linear_acceleration.z = measurement['data']['accel_z']
# write:
bag.write(topic_name_imu, msg_imu, msg_imu.header.stamp)
# write:
bag.write(topic_name_imu, msg_imu, msg_imu.header.stamp)
# init : groundtruth
msg_odom = Odometry()
# a.set header:
msg_odom.header.frame_id = 'inertial'
msg_odom.header.stamp = msg_imu.header.stamp
# b.set gt_pose
msg_odom.pose.pose.position.x = measurement['data']['gt_pos_x']
msg_odom.pose.pose.position.y = measurement['data']['gt_pos_y']
msg_odom.pose.pose.position.z = measurement['data']['gt_pos_z']
msg_odom.pose.pose.orientation.w = measurement['data']['gt_quat_w']
msg_odom.pose.pose.orientation.x = measurement['data']['gt_quat_x']
msg_odom.pose.pose.orientation.y = measurement['data']['gt_quat_y']
msg_odom.pose.pose.orientation.z = measurement['data']['gt_quat_z']
#c.set gt_vel
msg_odom.twist.twist.linear.x = measurement['data']['gt_vel_x']
msg_odom.twist.twist.linear.y = measurement['data']['gt_vel_y']
msg_odom.twist.twist.linear.z = measurement['data']['gt_vel_z']
# write
bag.write(topic_name_gt, msg_odom, msg_odom.header.stamp)
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
gnss_ins_sim_recorder()
except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
pass
3.2.2 自定义motion 运动状态
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/config/motion_def
根据 gnss-ins-sim 的command type 定义和各量纲单位,修改csv,生成对应的rosbag,配置文件在config中
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/config/recorder_gnss_ins_sim.yaml
# motion def:
motion_file: recorder_gnss_ins_sim_speedup_down.csv
# IMU params:
imu: 1
# sample frequency of simulated GNSS/IMU data:
sample_frequency:
imu: 100.0
gps: 10.0
# topic name:
topic_name_imu: /sim/sensor/imu
topic_name_gt: /pose/ground_truth
# output rosbag path:
output_path: /home/kaho/catkin_ws/src/data/gnss_ins_sim/recorder_gnss_ins_sim
# output name:
output_name: speedup_down.bag
motion1 : 绕“8”字
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/config/motion_def/recorder_gnss_ins_sim_8circle.csv
| ini lat (deg) | ini lon (deg) | ini alt (m) | ini vx_body (m/s) | ini vy_body (m/s) | ini vz_body (m/s) | ini yaw (deg) | ini pitch (deg) | ini roll (deg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.224361 | 121.46917 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| command type | yaw (deg) | pitch (deg) | roll (deg) | vx_body (m/s) | vy_body (m/s) | vz_body (m/s) | command duration (s) | GPS visibility |
| 1 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 1 |
| 1 | -10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 1 |
| 1 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 1 |
| 1 | -10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 1 |
motion2: 静止
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/config/motion_def/recorder_gnss_ins_sim_static.csv
| ini lat (deg) | ini lon (deg) | ini alt (m) | ini vx_body (m/s) | ini vy_body (m/s) | ini vz_body (m/s) | ini yaw (deg) | ini pitch (deg) | ini roll (deg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.224361 | 121.46917 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| command type | yaw (deg) | pitch (deg) | roll (deg) | vx_body (m/s) | vy_body (m/s) | vz_body (m/s) | command duration (s) | GPS visibility |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 |
motion3:匀速
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/config/motion_def/recorder_gnss_ins_sim_speedconstant.csv
| ini lat (deg) | ini lon (deg) | ini alt (m) | ini vx_body (m/s) | ini vy_body (m/s) | ini vz_body (m/s) | ini yaw (deg) | ini pitch (deg) | ini roll (deg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.224361 | 121.46917 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| command type | yaw (deg) | pitch (deg) | roll (deg) | vx_body (m/s) | vy_body (m/s) | vz_body (m/s) | command duration (s) | GPS visibility |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60 | 1 |
motion4: 加速
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/config/motion_def/recorder_gnss_ins_sim_speedup.csv
| ini lat (deg) | ini lon (deg) | ini alt (m) | ini vx_body (m/s) | ini vy_body (m/s) | ini vz_body (m/s) | ini yaw (deg) | ini pitch (deg) | ini roll (deg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.224361 | 121.46917 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| command type | yaw (deg) | pitch (deg) | roll (deg) | vx_body (m/s) | vy_body (m/s) | vz_body (m/s) | command duration (s) | GPS visibility |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 60 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 60 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 60 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 60 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 60 | 1 |
motion5: 先加速后减速
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/config/motion_def/recorder_gnss_ins_sim_speedup_down.csv
| ini lat (deg) | ini lon (deg) | ini alt (m) | ini vx_body (m/s) | ini vy_body (m/s) | ini vz_body (m/s) | ini yaw (deg) | ini pitch (deg) | ini roll (deg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.224361 | 121.46917 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| command type | yaw (deg) | pitch (deg) | roll (deg) | vx_body (m/s) | vy_body (m/s) | vz_body (m/s) | command duration (s) | GPS visibility |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | -2 | -2 | -2 | 60 | 1 |
注意
在和大家讨论中,发现静止时,gt为在原点静止不动,但是estimate产生竖直向上的方向,产生原因有两个:
1.没使用无噪声的IMU数据
2.程序中没有修改适应的重力加速度系数
roslaunch imu_integration imu_ins_gnss.launch
rosbag play static.bag
现象:groundtruth(红色)在原点不动,estimator(蓝色)竖直向上移动
解决:
1.修改为无噪声模型 gyro 修改 ref_gyro 、 accel 修改为 ref_accel
for i, (gyro, accel, ref_q, ref_pos, ref_vel) in enumerate(
zip(
# a. gyro:
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_gyro').data,
# b. accel:
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_accel').data,
# c. gt_pose:
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_att_quat').data, # groundtruth
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_pos').data,
# d. true_vel :
sim.dmgr.get_data_all('ref_vel').data
)
):
通过plot sim_imu 的 gyro和accel数据,观察得知,在静止时,数据恒定不变,此时数据是无噪声的。
2.修改重力,在FILE: catkin_ws/src/imu_integration/config/estimator.yaml 文件中,默认gravity为9.81,需要修改为传感器实际的初始重力加速度
可通过rqt_bag 去查看话题 /sim/sensor/imu 第一帧的accel_z
rqt_bag static.bag
linear_accerleration z : -9.7942164704
修改到 catkin_ws/src/imu_integration/config/estimator.yaml
imu:
topic_name: /sim/sensor/imu
gravity:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: -9.7942164704
bias:
angular_velocity:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
linear_acceleration:
x: 0.0
y: 0.0
z: 0.0
pose:
frame_id: inertial
topic_name:
ground_truth: /pose/ground_truth
estimation: /pose/estimation
launch 文件中记得调用上步已修改的estimator.yaml
FILE: catkin_ws/src/imu_integration/launch/imu_ins_gnss.launch
>
>
>
<!-- load default params -->
>
-d $(find imu_integration)/rviz/imu_integration.rviz" required="true" />
>
3.2.3 使用
roslaunch gnss_ins_sim recorder_gnss_ins_sim.launch
FILE: catkin_ws/src/gnss_ins_sim/launch/recorder_gnss_ins_sim.launch
<launch>
<node name="gnss_ins_sim_recorder_node" pkg="gnss_ins_sim" type="recorder_node_sim.py">
<rosparam command="load" file="$(find gnss_ins_sim)/config/recorder_gnss_ins_sim.yaml" />
node>
launch>
运行后,在 catkin_ws/src/data/gnss_ins_sim/recorder_gnss_ins_sim 目录下会生成相应的rosbag
3.3 evo 格式存储 pose
FILE:catkin_ws/src/imu_integration/src/evo_evaluate/evaluate.cpp
使用evo工具进行精度评估,evo format 使用TUM格式,参考了eamo 助教的GitHub写法,为了方便后续调用,将保存文件格式写成ROS Node的方式,通过订阅:
/sim/sensor/imu /pose/ground_truth 两个话题,存储到对应格式的文件中,进行 evo 评估。
evo的使用方式可参考:
SLAM轨迹精度评估工具evo使用方法
evo测评TUM数据集
evo安装、evo使用方法详细介绍使用教程,SLAM轨迹精度评估工具,如何用来评估ORB-SLAM2生成的轨迹精度,评估激光雷达SLAM与视觉SLAM的轨迹精度,量化SLAM的误差
3.3.1 evo TUM格式存储
常用的evo KITTI pose format是美誉timestamp的,通过固定序列数来进行精度评估比较,TUM 数据集 format中有时间戳,通过时间戳来比较,会比较准,所以本次存储的evo数据格式为TUM
evo TUM需要pose 存储格式为 timestamp x y z q_x q_y q_z q_w ;具体参考evo 官档Formats
存储写法
/* write2txt format TUM*/
void WriteText(std::ofstream& ofs, pose data){
ofs << std::fixed << data.timestamp << " " << data.pos.x() << " " << data.pos.y() << " " << data.pos.z() << " "
<< data.q.x() << " " << data.q.y() <<" " << data.q.z() << " " << data.q.w() << std::endl;
}
3.3.1 TUM timestamps时间对齐
一开始,给gt.txt 和 ins.txt 中写上timestamps时,时间戳都是各自的ROS topic的时间戳,运行evo_rpe 分段评估时,报错,找不到两个文件中时间戳相差0.01s的数据,经过观察,因为estimate imu惯性解算节点是先通过订阅imu_sim topic 数据才进行解算,会比groundtruth topic 时间戳显示慢一点,因此将各自当前时间戳减去第一帧的数据时间戳,就可以对齐各自的时间。
if(flag_ins){
stamp_ins_init = msg->header.stamp.toSec();
flag_ins = 0;
}
pose_ins.timestamp = msg->header.stamp.toSec() - stamp_ins_init; //把时间戳转化成浮点型格式
/******************************************************************************************************/
if(flag_gt){
stamp_gt_init = msg->header.stamp.toSec();
flag_gt = 0;
}
pose_gt.timestamp = msg->header.stamp.toSec() - stamp_gt_init;
3.3.3 evo TUM ROS_Node 完整实现
FILE:catkin_ws/src/imu_integration/src/evo_evaluate/evaluate.cpp
#include
#include 3.4 不同运动场景下,中值法和欧拉法IMU解算对比
启动imu 惯性解算节点
roslaunch imu_integration imu_ins_gnss.launch
rosbag play 8circle.bag
evo 评估
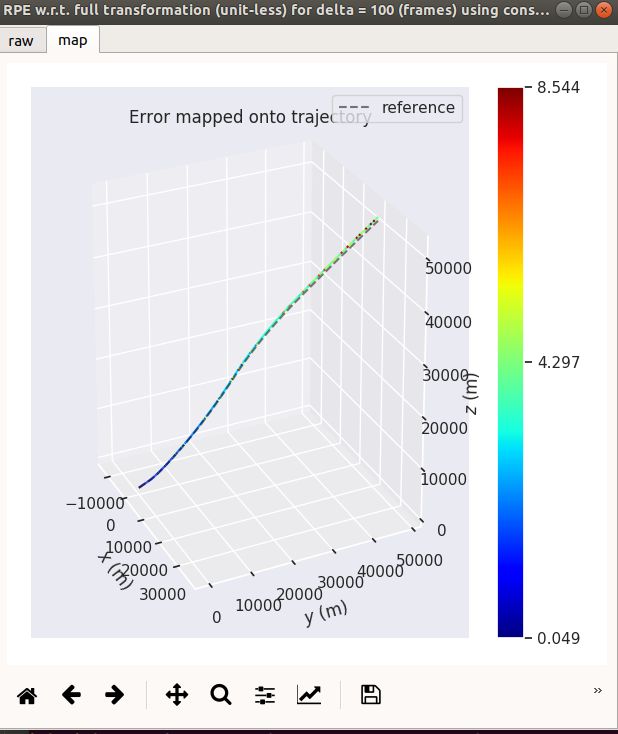
evo_rpe tum gt.txt ins.txt -r full --delta 100 --plot --plot_mode xyz
剧烈运动:绕‘8’字
| 中值法 | 欧拉法 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
静止状态下 STATIC
| 中值法 | 欧拉法 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
匀速运动 speedconstant
| 中值法 | 欧拉法 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
加速运动 speedup
| 中值法 | 欧拉法 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
先加速后减速 speedup_down
| 中值法 | 欧拉法 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3.5 结论:
一般说来,imu的角速度精度高,线性加速度精度低
3.5.1 对于静止和匀速运动(加速度为0),中值法精度比欧拉法低
原因:imu测得的线性加速度和角速度并不为0,由于imu的角速度变化量小,所以
误差较小,欧拉法和中值法效果差不多。而通过线性加速度计算得到的速度会累
积误差,中值法取平均值会加大位置的误差(相对欧拉法)。
3.5.2 对于加减速运动,中值法精度比欧拉法高
原因:在变速运动下中值法取平均值就比较合理,而且角加速度和线性加速度绝
对值越大,欧拉法误差会越大。
edited by kaho 2021.10.1













