深度强化学习笔记——DQN原理与实现(pytorch+gym)
概要
本文主要总结深度强化学习中无模型基于值方法的DQN算法,说明其算法原理并用该算法在gym提供的cartpole上进行实现。
有任何不准确或错误的地方望指正!
1. DQN(Deep Q-Network)基本原理
DQN算法相当于对传统Q-learning算法的改进,与之不同的是,DQN使用了神经网络(结构可以自行设计)对action value(即Q值)进行估计。
1.1 DQN算法的基本组成元素
DQN的伪代码如下,从中可以看出几个关键步骤:目标网络, ϵ \epsilon ϵ-greedy选择动作和经验重放机制。
(摘自《Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning》)
A. 目标网络(Target Network)
首先,目标网络解决的是一个回归问题(与分类问题中网络产生一个分布不同),其输入是环境的状态,输出是多个动作产生的不同值,也就是动作值。(实际过程中,我们需要通过索引来获取这个Q值,即 Q π θ ( s , a ) Q^{\pi_{\theta}}(s,a) Qπθ(s,a),这里的 θ \theta θ代表网络中的参数)。确定了网络的输入输出之后,就需要解决如何更新网络中的这些参数的问题。
其思路就是基于贝尔曼方程,并利用temporal difference的方法,让target network和用于训练的网络(这里就简记为agent网络)的差值尽可能近似于收益值,该收益值指的是从当前状态经过决策之后到达下一个状态所获取的收益。需要注明的是,DQN中的target network的参数就是直接拷贝agent网络的参数,使用的是一样的网络结构。但是在实际训练中,只能通过固定target network的输出来训练agent,而固定该网络的输出的方法就是延迟更新target network的参数,使其在固定步骤内输出不变,这样能够有效化agent网络的参数更新过程。
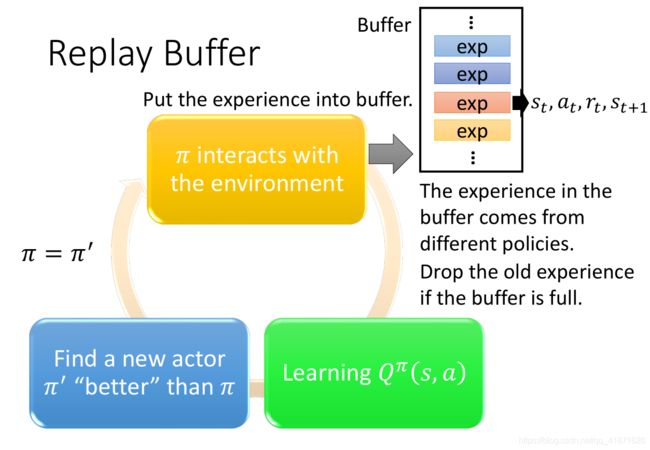
B. 经验重放(Experience Replay Buffer)
如果agent每次更新参数的时候都要与环境互动,这就大大降低了模型参数更新的效率,所以经验重放机制被提出。该机制就类似于一个有固定空间大小的存储器,把agent与环境互动所产生的部分结果( S t , a t , r t + 1 , S t + 1 S_{t}, a_t, r_{t+1}, S_{t+1} St,at,rt+1,St+1)进行存储,其每一行的维数就是 # (states) × 2 + 2 \# \text{(states)} \times2+2 #(states)×2+2(每次只能选取一个动作,得到的收益值也是一个标量)。等到了训练阶段的时候,每一次训练过程都会从该存储器中均匀采样出一批 (batch) 数量的样本(总量远小于存储器的最大容量),用于agent网络模型参数的更新。
C. ϵ \epsilon ϵ-greedy(策略的选择)
Q-learning中策略的选择(假设这里是确定性策略)就是选取能够使动作值达到最大的那个动作,用数学形式表示就是:
π ′ ( s ) = arg max a Q π ( s , a ) \pi'(s)=\argmax_{a}Q^{\pi}(s,a) π′(s)=aargmaxQπ(s,a)
而 ϵ \epsilon ϵ-greedy方法是贪心算法的一个变体。具体实现的方法就是先让程序由均匀分布生成一个 [ 0 , 1 ] [0,1] [0,1]区间内的随机数,如果该数值小于预设的 1 − ϵ 1-\epsilon 1−ϵ,则选取能够最大化动作值的动作,否则随机选取动作。
1.2 常用的提升DQN算法的技巧
A. Double DQN
DQN的实践过程中会出现一些问题,比如高估了动作值(overestimation),这时候研究人员就提出了Double DQN的技术。从下图可以看出,原先的DQN选用的target值其实还是由同一个网络生成的值,只是说这个网络所选用的参数是之前的参数。而Double DQN中将target的值做了小的改变,能够达到它是由“两个网络”生成的效果。从第二行的表达式可以看出,尽管这里依旧用的是agent含有旧参数的网络,但是这里的动作索引是通过agent当前参数网络得到的,取得该值的方法就是最大化agent当前参数的网络所输出的动作值(其输入值是环境返回的下一个状态),显然这样就解耦了动作的选取和动作值的计算,动作的选取(产生的是一系列大小为(batch_size, 1)的索引)是由新参数的agent网络获取,动作值的估算是由旧参数的agent网络所得到。
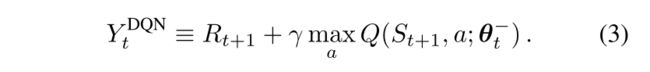

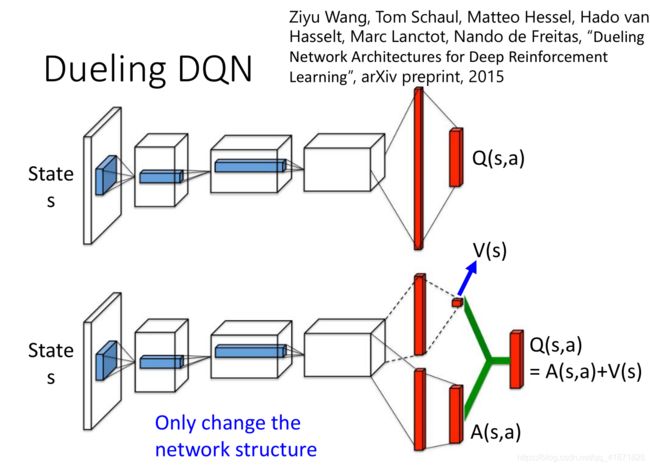
B. Dueling DQN
Dueling DQN最重要的一点就是改进了DQN中的网络结构,将Q值 Q π ( s , a ) Q^{\pi}(s,a) Qπ(s,a)拆分成状态值 V π ( s ) V^{\pi}(s) Vπ(s)和优势函数(Advantage Function) A π ( s , a ) A^{\pi}(s,a) Aπ(s,a)。该方法能够更有效率地对Q值进行更新,因为每一次V值更新之后,都要加在A函数的所有维度上(相当于一个bias),相当于其他动作的值也同时被更新了。
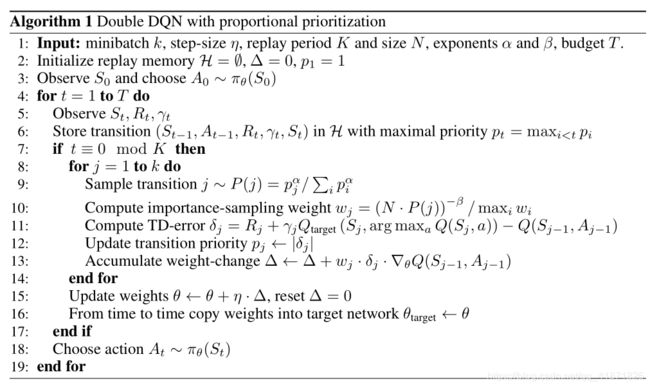
C. Prioritized Experience Replay
与经验重放机制不同的是,该技巧将有主次地对存储器中的经验进行采样,使参数更新过程更有效率。这个priority是基于target值与当前agent网络输出的差值(既为TD error),该误差越大,那么产生这个较大误差所对应的经验( S t , a t , r t + 1 , S t + 1 S_{t}, a_t, r_{t+1}, S_{t+1} St,at,rt+1,St+1)就有更高的概率被采样到。这里先把论文中《Prioritized Experience Replay》的伪代码放在这里,等实践完策略网络之后再来仔细学习一下~

2. DQN的pytorch实现
2.1 所需要的环境配置
gym
windows下gym的安装非常简单,conda activate到某个环境下使用pip install gym安装即可。
pytorch
windows下的快速pytorch安装可以参考我的这篇博客(简单来说就是找到版本所对应的.whl文件,然后本地进行pip install的安装)
2.2 DQN代码及详细注释
代码部分我就按莫烦pytorch教程重新码了一遍,并详细写明了注释(比如比较重要的变量的维度等)
基本流程就是:(第一步导入相关功能包就省略不写了)
- 定义超参数(batch_size,learning rate,discount等)
- 构建用于agent和target的网络架构(全连接或卷积或循环神经网络等)
- 开始构建DQN算法(初始化memory空间,定义损失函数和优化器,神经网络中的参数初始化;根据gym环境返回的状态信息选择动作,将得到的收益值和下一个状态的信息存储起来;对memory中的experiences进行采样,对agent网络参数进行更新,将agent网络输出的q值与目标值比较产生的均方差作为损失用梯度下降(Adam优化器)进行反向传播;在固定步数之后更新target网络。
(这里gym返回的状态信息是位置、角度和对应的速度和角速度,维度是4;其返回的动作只有两个,左或右)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# import the necessary packages
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
import gym
# 1. Define some Hyper Parameters
BATCH_SIZE = 32 # batch size of sampling process from buffer
LR = 0.01 # learning rate
EPSILON = 0.9 # epsilon used for epsilon greedy approach
GAMMA = 0.9 # discount factor
TARGET_NETWORK_REPLACE_FREQ = 100 # How frequently target netowrk updates
MEMORY_CAPACITY = 2000 # The capacity of experience replay buffer
env = gym.make("CartPole-v0") # Use cartpole game as environment
env = env.unwrapped
N_ACTIONS = env.action_space.n # 2 actions
N_STATES = env.observation_space.shape[0] # 4 states
ENV_A_SHAPE = 0 if isinstance(env.action_space.sample(), int) else env.action_space.sample().shape # to confirm the shape
# 2. Define the network used in both target net and the net for training
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
# Define the network structure, a very simple fully connected network
super(Net, self).__init__()
# Define the structure of fully connected network
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(N_STATES, 10) # layer 1
self.fc1.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.1) # in-place initilization of weights of fc1
self.out = nn.Linear(10, N_ACTIONS) # layer 2
self.out.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.1) # in-place initilization of weights of fc2
def forward(self, x):
# Define how the input data pass inside the network
x = self.fc1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
actions_value = self.out(x)
return actions_value
# 3. Define the DQN network and its corresponding methods
class DQN(object):
def __init__(self):
# -----------Define 2 networks (target and training)------#
self.eval_net, self.target_net = Net(), Net()
# Define counter, memory size and loss function
self.learn_step_counter = 0 # count the steps of learning process
self.memory_counter = 0 # counter used for experience replay buffer
# ----Define the memory (or the buffer), allocate some space to it. The number
# of columns depends on 4 elements, s, a, r, s_, the total is N_STATES*2 + 2---#
self.memory = np.zeros((MEMORY_CAPACITY, N_STATES * 2 + 2))
#------- Define the optimizer------#
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.eval_net.parameters(), lr=LR)
# ------Define the loss function-----#
self.loss_func = nn.MSELoss()
def choose_action(self, x):
# This function is used to make decision based upon epsilon greedy
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.FloatTensor(x), 0) # add 1 dimension to input state x
# input only one sample
if np.random.uniform() < EPSILON: # greedy
# use epsilon-greedy approach to take action
actions_value = self.eval_net.forward(x)
#print(torch.max(actions_value, 1))
# torch.max() returns a tensor composed of max value along the axis=dim and corresponding index
# what we need is the index in this function, representing the action of cart.
action = torch.max(actions_value, 1)[1].data.numpy()
action = action[0] if ENV_A_SHAPE == 0 else action.reshape(ENV_A_SHAPE) # return the argmax index
else: # random
action = np.random.randint(0, N_ACTIONS)
action = action if ENV_A_SHAPE == 0 else action.reshape(ENV_A_SHAPE)
return action
def store_transition(self, s, a, r, s_):
# This function acts as experience replay buffer
transition = np.hstack((s, [a, r], s_)) # horizontally stack these vectors
# if the capacity is full, then use index to replace the old memory with new one
index = self.memory_counter % MEMORY_CAPACITY
self.memory[index, :] = transition
self.memory_counter += 1
def learn(self):
# Define how the whole DQN works including sampling batch of experiences,
# when and how to update parameters of target network, and how to implement
# backward propagation.
# update the target network every fixed steps
if self.learn_step_counter % TARGET_NETWORK_REPLACE_FREQ == 0:
# Assign the parameters of eval_net to target_net
self.target_net.load_state_dict(self.eval_net.state_dict())
self.learn_step_counter += 1
# Determine the index of Sampled batch from buffer
sample_index = np.random.choice(MEMORY_CAPACITY, BATCH_SIZE) # randomly select some data from buffer
# extract experiences of batch size from buffer.
b_memory = self.memory[sample_index, :]
# extract vectors or matrices s,a,r,s_ from batch memory and convert these to torch Variables
# that are convenient to back propagation
b_s = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(b_memory[:, :N_STATES]))
# convert long int type to tensor
b_a = Variable(torch.LongTensor(b_memory[:, N_STATES:N_STATES+1].astype(int)))
b_r = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(b_memory[:, N_STATES+1:N_STATES+2]))
b_s_ = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(b_memory[:, -N_STATES:]))
# calculate the Q value of state-action pair
q_eval = self.eval_net(b_s).gather(1, b_a) # (batch_size, 1)
#print(q_eval)
# calculate the q value of next state
q_next = self.target_net(b_s_).detach() # detach from computational graph, don't back propagate
# select the maximum q value
#print(q_next)
# q_next.max(1) returns the max value along the axis=1 and its corresponding index
q_target = b_r + GAMMA * q_next.max(1)[0].view(BATCH_SIZE, 1) # (batch_size, 1)
loss = self.loss_func(q_eval, q_target)
self.optimizer.zero_grad() # reset the gradient to zero
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step() # execute back propagation for one step
'''
--------------Procedures of DQN Algorithm------------------
'''
# create the object of DQN class
dqn = DQN()
# Start training
print("\nCollecting experience...")
for i_episode in range(400):
# play 400 episodes of cartpole game
s = env.reset()
ep_r = 0
while True:
env.render()
# take action based on the current state
a = dqn.choose_action(s)
# obtain the reward and next state and some other information
s_, r, done, info = env.step(a)
# modify the reward based on the environment state
x, x_dot, theta, theta_dot = s_
r1 = (env.x_threshold - abs(x)) / env.x_threshold - 0.8
r2 = (env.theta_threshold_radians - abs(theta)) / env.theta_threshold_radians - 0.5
r = r1 + r2
# store the transitions of states
dqn.store_transition(s, a, r, s_)
ep_r += r
# if the experience repaly buffer is filled, DQN begins to learn or update
# its parameters.
if dqn.memory_counter > MEMORY_CAPACITY:
dqn.learn()
if done:
print('Ep: ', i_episode, ' |', 'Ep_r: ', round(ep_r, 2))
if done:
# if game is over, then skip the while loop.
break
# use next state to update the current state.
s = s_
2.3 训练结果
这里总共要训练400个episodes, 在300左右的时候已经可以训练的很好了,这里录了一小段结果,如下。
—待更新—
(DQN中的常见tips的代码实现)