Pytorch 使用Grad-CAM可视化网络模型的特征图
介绍
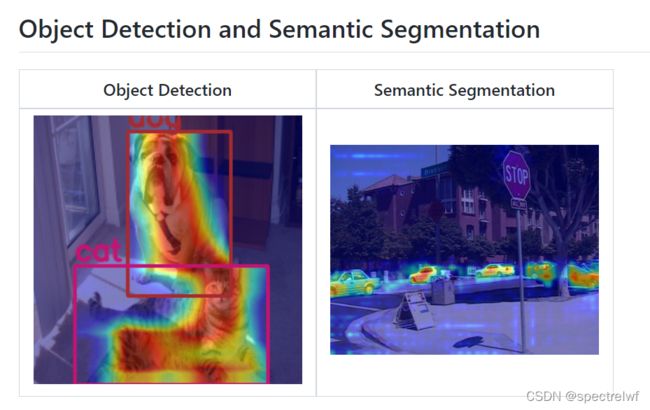
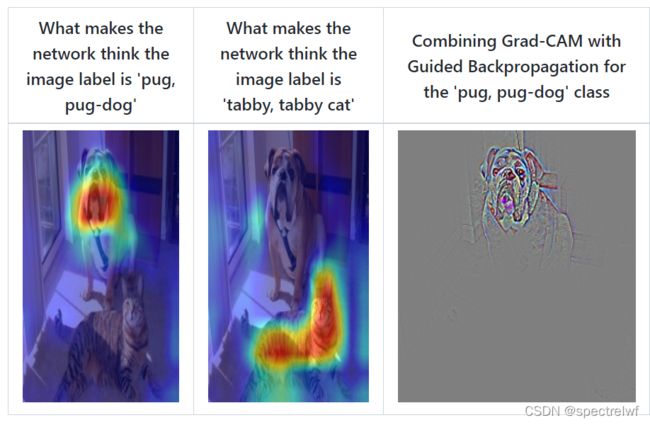
虽然说咱也不知道这个Grad-CAM的数学理论是如何推导的,但是在看论文的时候发现很多论文里面都用了Grad-CAM来可视化模型的特征图,用来显示网络对ROI区域的捕捉。想详细了解的话看一下B站大佬噼里啪啦的讲解视频。
推荐代码
code:https://github.com/jacobgil/pytorch-grad-cam
安装pytorch-grad-cam :pip install grad-cam
自己的尝试
我试着使用这个仓库来可视化我的vit模型,做的是一个五分类的病理图像分类,代码如下:
import argparse
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from pytorch_grad_cam import GradCAM, \
ScoreCAM, \
GradCAMPlusPlus, \
AblationCAM, \
XGradCAM, \
EigenCAM, \
EigenGradCAM, \
LayerCAM, \
FullGrad
from pytorch_grad_cam import GuidedBackpropReLUModel
from pytorch_grad_cam.utils.image import show_cam_on_image, \
preprocess_image
from pytorch_grad_cam.ablation_layer import AblationLayerVit
from vit_model import vit_base_patch16_224_in21k as create_model
def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--use-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
help='Use NVIDIA GPU acceleration')
parser.add_argument(
'--image-path',
type=str,
default='/home/lwf/Project/Datatset/数据集/肺癌和结肠癌组织病理学图像/archive/colon_aca/colonca1.jpeg',
help='Input image path')
parser.add_argument('--aug_smooth', action='store_true',
help='Apply test time augmentation to smooth the CAM')
parser.add_argument(
'--eigen_smooth',
action='store_true',
help='Reduce noise by taking the first principle componenet'
'of cam_weights*activations')
parser.add_argument(
'--method',
type=str,
default='fullgrad',
help='Can be gradcam/gradcam++/scorecam/xgradcam/ablationcam')
args = parser.parse_args()
args.use_cuda = args.use_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
if args.use_cuda:
print('Using GPU for acceleration')
else:
print('Using CPU for computation')
return args
def reshape_transform(tensor, height=14, width=14):
result = tensor[:, 1:, :].reshape(tensor.size(0),
height, width, tensor.size(2))
# Bring the channels to the first dimension,
# like in CNNs.
result = result.transpose(2, 3).transpose(1, 2)
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
""" python vit_gradcam.py -image-path
Example usage of using cam-methods on a VIT network.
"""
args = get_args()
methods = \
{"gradcam": GradCAM,
"scorecam": ScoreCAM,
"gradcam++": GradCAMPlusPlus,
"ablationcam": AblationCAM,
"xgradcam": XGradCAM,
"eigencam": EigenCAM,
"eigengradcam": EigenGradCAM,
"layercam": LayerCAM,
"fullgrad": FullGrad}
if args.method not in list(methods.keys()):
raise Exception(f"method should be one of {list(methods.keys())}")
# model = torch.hub.load('facebookresearch/deit:main',
# 'deit_tiny_patch16_224', pretrained=True)
model = create_model(num_classes=5, has_logits=False)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "/home/lwf/Project/vision-transformer-implemment/init_weights/lung_colon_weights/model-COVID12.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location='cpu'))
model.eval()
if args.use_cuda:
model = model.cuda()
target_layers = [model.blocks[-1].norm1]
if args.method not in methods:
raise Exception(f"Method {args.method} not implemented")
if args.method == "ablationcam":
cam = methods[args.method](model=model,
target_layers=target_layers,
use_cuda=args.use_cuda,
reshape_transform=reshape_transform,
ablation_layer=AblationLayerVit())
else:
cam = methods[args.method](model=model,
target_layers=target_layers,
use_cuda=args.use_cuda,
reshape_transform=reshape_transform)
rgb_img = cv2.imread(args.image_path, 1)[:, :, ::-1]
rgb_img = cv2.resize(rgb_img, (224, 224))
rgb_img = np.float32(rgb_img) / 255
input_tensor = preprocess_image(rgb_img, mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
# If None, returns the map for the highest scoring category.
# Otherwise, targets the requested category.
targets = None
# AblationCAM and ScoreCAM have batched implementations.
# You can override the internal batch size for faster computation.
cam.batch_size = 32
grayscale_cam = cam(input_tensor=input_tensor,
targets=targets ,
eigen_smooth=args.eigen_smooth,
aug_smooth=args.aug_smooth)
# Here grayscale_cam has only one image in the batch
grayscale_cam = grayscale_cam[0, :]
cam_image = show_cam_on_image(rgb_img, grayscale_cam)
cv2.imwrite(f'{args.method}_cam.jpg', cam_image)
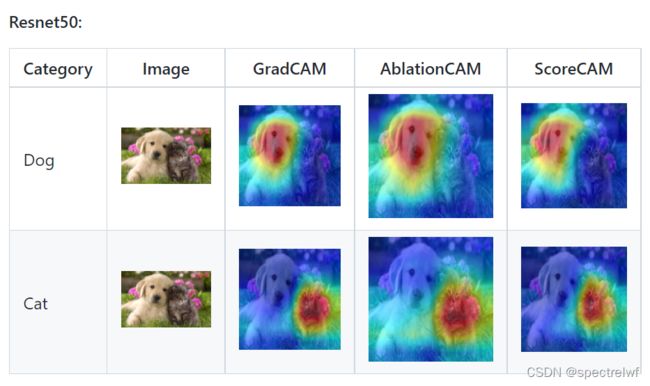
可以使用多种方法来可视化特征图,我的可视化结果如下:

一般来说:常用的模型通常可视化下面这些层:
FasterRCNN: model.backbone
Resnet18 and 50: model.layer4[-1]
VGG and densenet161: model.features[-1]
mnasnet1_0: model.layers[-1]
ViT: model.blocks[-1].norm1
SwinT: model.layers[-1].blocks[-1].norm1