前言
文章中的代码是参考基于Pytorch的特征图提取编写的代码本身很简单这里只做简单的描述。
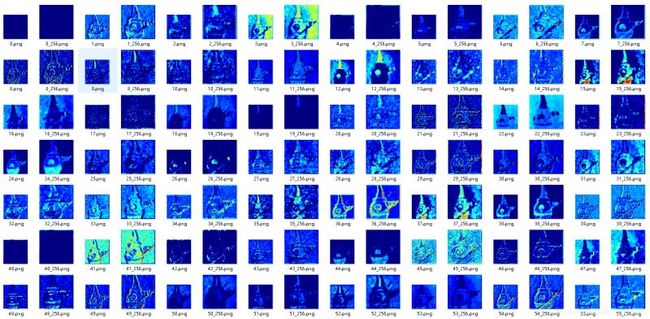
1. 效果图
先看效果图(第一张是原图,后面的都是相应的特征图,这里使用的网络是resnet50,需要注意的是下面图片显示的特征图是经过放大后的图,原图是比较小的图,因为太小不利于我们观察):
2. 完整代码
import os
import torch
import torchvision as tv
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import argparse
import skimage.data
import skimage.io
import skimage.transform
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.models as models
from PIL import Image
import cv2
class FeatureExtractor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, submodule, extracted_layers):
super(FeatureExtractor, self).__init__()
self.submodule = submodule
self.extracted_layers = extracted_layers
def forward(self, x):
outputs = {}
for name, module in self.submodule._modules.items():
if "fc" in name:
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = module(x)
print(name)
if self.extracted_layers is None or name in self.extracted_layers and 'fc' not in name:
outputs[name] = x
return outputs
def get_picture(pic_name, transform):
img = skimage.io.imread(pic_name)
img = skimage.transform.resize(img, (256, 256))
img = np.asarray(img, dtype=np.float32)
return transform(img)
def make_dirs(path):
if os.path.exists(path) is False:
os.makedirs(path)
def get_feature():
pic_dir = './images/2.jpg'
transform = transforms.ToTensor()
img = get_picture(pic_dir, transform)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 插入维度
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
img = img.to(device)
net = models.resnet101().to(device)
net.load_state_dict(torch.load('./model/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pt'))
exact_list = None
dst = './feautures'
therd_size = 256
myexactor = FeatureExtractor(net, exact_list)
outs = myexactor(img)
for k, v in outs.items():
features = v[0]
iter_range = features.shape[0]
for i in range(iter_range):
#plt.imshow(x[0].data.numpy()[0,i,:,:],cmap='jet')
if 'fc' in k:
continue
feature = features.data.numpy()
feature_img = feature[i,:,:]
feature_img = np.asarray(feature_img * 255, dtype=np.uint8)
dst_path = os.path.join(dst, k)
make_dirs(dst_path)
feature_img = cv2.applyColorMap(feature_img, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
if feature_img.shape[0] < therd_size:
tmp_file = os.path.join(dst_path, str(i) + '_' + str(therd_size) + '.png')
tmp_img = feature_img.copy()
tmp_img = cv2.resize(tmp_img, (therd_size,therd_size), interpolation = cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
cv2.imwrite(tmp_file, tmp_img)
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_path, str(i) + '.png')
cv2.imwrite(dst_file, feature_img)
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_feature()
3. 代码说明
下面的模块是根据所指定的模型筛选出指定层的特征图输出,如果未指定也就是extracted_layers是None则以字典的形式输出全部的特征图,另外因为全连接层本身是一维的没必要输出因此进行了过滤。
class FeatureExtractor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, submodule, extracted_layers):
super(FeatureExtractor, self).__init__()
self.submodule = submodule
self.extracted_layers = extracted_layers
def forward(self, x):
outputs = {}
for name, module in self.submodule._modules.items():
if "fc" in name:
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = module(x)
print(name)
if self.extracted_layers is None or name in self.extracted_layers and 'fc' not in name:
outputs[name] = x
return outputs
这段主要是存储图片,为每个层创建一个文件夹将特征图以JET的colormap进行按顺序存储到该文件夹,并且如果特征图过小也会对特征图放大同时存储原始图和放大后的图。
for k, v in outs.items():
features = v[0]
iter_range = features.shape[0]
for i in range(iter_range):
#plt.imshow(x[0].data.numpy()[0,i,:,:],cmap='jet')
if 'fc' in k:
continue
feature = features.data.numpy()
feature_img = feature[i,:,:]
feature_img = np.asarray(feature_img * 255, dtype=np.uint8)
dst_path = os.path.join(dst, k)
make_dirs(dst_path)
feature_img = cv2.applyColorMap(feature_img, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
if feature_img.shape[0] < therd_size:
tmp_file = os.path.join(dst_path, str(i) + '_' + str(therd_size) + '.png')
tmp_img = feature_img.copy()
tmp_img = cv2.resize(tmp_img, (therd_size,therd_size), interpolation = cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
cv2.imwrite(tmp_file, tmp_img)
dst_file = os.path.join(dst_path, str(i) + '.png')
cv2.imwrite(dst_file, feature_img)
这里主要是一些参数,比如要提取的网络,网络的权重,要提取的层,指定的图像放大的大小,存储路径等等。
net = models.resnet101().to(device)
net.load_state_dict(torch.load('./model/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pt'))
exact_list = None#['conv1']
dst = './feautures'
therd_size = 256
4. 可视化梯度,feature
上面的办法只是简单的将经过网络计算的图片的输出的feature进行图片,github上有将CNN的梯度等全部进行可视化的代码:pytorch-cnn-visualizations,需要注意的是如果只是简单的替换成自己的网络可能无法运行,大概率会报model没有features或者classifier等错误,这两个是进行分类网络定义时的Sequential,其实就是索引网络的每一层,自己稍微修改用model.children()等方法进行替换即可,我自己修改之后得到的代码grayondream-pytorch-visualization(本来想稍微封装一下成为一个更加通用的结构,暂时没时间以后再说吧!),下面是效果图:
总结
到此这篇关于使用pytorch提取卷积神经网络的特征图可视化的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关pytorch提取特征图可视化内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!