大话设计模式——策略模式
1)商场收银系统
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.DefaultListModel;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JList;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
/**
* 商场收银系统
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class Mall implements ActionListener {
private static JLabel unitPriceLabel;
private static JTextField unitPriceValue;
private static JLabel numLabel;
private static JTextField numValue;
private double totalPrice = 0;
private static JList<String> jList;
private static DefaultListModel<String> listModel;
private static JLabel totalNum;
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("商城收银系统");
frame.setSize(450, 400);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
frame.add(panel);
placeComponents(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
private static void placeComponents(JPanel panel) {
panel.setLayout(null);
Mall mainFrame = new Mall();
// 第一行
unitPriceLabel = new JLabel("单价:");
unitPriceLabel.setBounds(10, 20, 80, 25);
panel.add(unitPriceLabel);
unitPriceValue = new JTextField(20);
unitPriceValue.setBounds(100, 20, 165, 25);
panel.add(unitPriceValue);
JButton confirmButton = new JButton("确定");
confirmButton.setBounds(280, 20, 80, 25);
confirmButton.addActionListener(mainFrame);
confirmButton.setActionCommand("confirm");
panel.add(confirmButton);
// 第二行
numLabel = new JLabel("数量:");
numLabel.setBounds(10, 50, 80, 25);
panel.add(numLabel);
numValue = new JTextField(20);
numValue.setBounds(100, 50, 165, 25);
panel.add(numValue);
JButton resetButton = new JButton("重置");
resetButton.setBounds(280, 50, 80, 25);
resetButton.addActionListener(mainFrame);
resetButton.setActionCommand("reset");
panel.add(resetButton);
// 第三行
listModel = new DefaultListModel<String>();
jList = new JList<String>(listModel);
jList.setBounds(10, 90, 400, 180);
panel.add(jList);
// 第四行
JLabel totalLabel = new JLabel("总计:");
totalLabel.setBounds(10, 300, 80, 25);
panel.add(totalLabel);
totalNum = new JLabel("0.00");
totalNum.setBounds(100, 300, 80, 25);
panel.add(totalNum);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
if (event.getActionCommand().equals("confirm")) {
double unitPrice = Double.parseDouble(unitPriceValue.getText());
double num = Double.parseDouble(numValue.getText());
double total = unitPrice * num;
listModel.addElement("单价:"+unitPriceValue.getText()+" 数量:"+numValue.getText() +" 合计:"+total);
totalPrice +=total;
totalNum.setText(totalPrice+"");
} else if(event.getActionCommand().equals("reset")) {
unitPriceValue.setText("");
numValue.setText("");
listModel.clear();
totalPrice=0;
totalNum.setText(totalPrice+"");
}
}
}
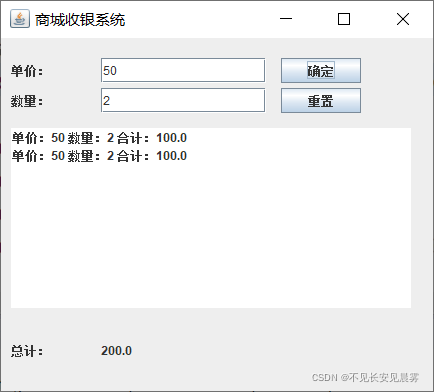
执行效果
2)增加打折功能
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.DefaultListModel;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JList;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
/**
* 需求:增加打折功能
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class Mall implements ActionListener {
private static JLabel unitPriceLabel;
private static JTextField unitPriceValue;
private static JLabel numLabel;
private static JTextField numValue;
private double totalPrice = 0;
private static JList<String> jList;
private static DefaultListModel<String> listModel;
private static JLabel totalNum;
private static JLabel calcType;
private static JComboBox<String> jComboBox;
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("商城收银系统");
frame.setSize(450, 400);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
frame.add(panel);
placeComponents(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
private static void placeComponents(JPanel panel) {
panel.setLayout(null);
Mall mainFrame = new Mall();
// 第一行
unitPriceLabel = new JLabel("单价:");
unitPriceLabel.setBounds(10, 20, 80, 25);
panel.add(unitPriceLabel);
unitPriceValue = new JTextField(20);
unitPriceValue.setBounds(100, 20, 165, 25);
panel.add(unitPriceValue);
JButton confirmButton = new JButton("确定");
confirmButton.setBounds(280, 20, 80, 25);
confirmButton.addActionListener(mainFrame);
confirmButton.setActionCommand("confirm");
panel.add(confirmButton);
// 第二行
numLabel = new JLabel("数量:");
numLabel.setBounds(10, 50, 80, 25);
panel.add(numLabel);
numValue = new JTextField(20);
numValue.setBounds(100, 50, 165, 25);
panel.add(numValue);
JButton resetButton = new JButton("重置");
resetButton.setBounds(280, 50, 80, 25);
resetButton.addActionListener(mainFrame);
resetButton.setActionCommand("reset");
panel.add(resetButton);
// 第三行
calcType = new JLabel("计算方式:");
calcType.setBounds(10, 90, 80, 25);
panel.add(calcType);
jComboBox = new JComboBox<String>();
jComboBox.insertItemAt("正常收费", 0);
jComboBox.insertItemAt("打八折", 1);
jComboBox.insertItemAt("打七折", 2);
jComboBox.insertItemAt("打五折", 3);
jComboBox.setSelectedIndex(0);
jComboBox.setBounds(100, 90, 80, 25);
panel.add(jComboBox);
// 第四行
listModel = new DefaultListModel<String>();
jList = new JList<String>(listModel);
jList.setBounds(10, 120, 400, 180);
panel.add(jList);
// 第五行
JLabel totalLabel = new JLabel("总计:");
totalLabel.setBounds(10, 300, 80, 25);
panel.add(totalLabel);
totalNum = new JLabel("0.00");
totalNum.setBounds(100, 300, 80, 25);
panel.add(totalNum);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
if (event.getActionCommand().equals("confirm")) {
double unitPrice = Double.parseDouble(unitPriceValue.getText());
double num = Double.parseDouble(numValue.getText());
int selectedIndex = jComboBox.getSelectedIndex();
double total = 0;
switch (selectedIndex) {
case 0:
total = unitPrice * num;
break;
case 1:
total = unitPrice * num * 0.8;
break;
case 2:
total = unitPrice * num * 0.7;
break;
case 3:
total = unitPrice * num * 0.5;
break;
}
totalPrice += total;
listModel.addElement("单价:" + unitPriceValue.getText() + " 数量:" + numValue.getText() + " "
+ jComboBox.getSelectedItem() + " 合计:" + total);
totalNum.setText(totalPrice + "");
} else if (event.getActionCommand().equals("reset")) {
unitPriceValue.setText("");
numValue.setText("");
listModel.clear();
totalPrice = 0;
totalNum.setText(totalPrice + "");
}
}
}
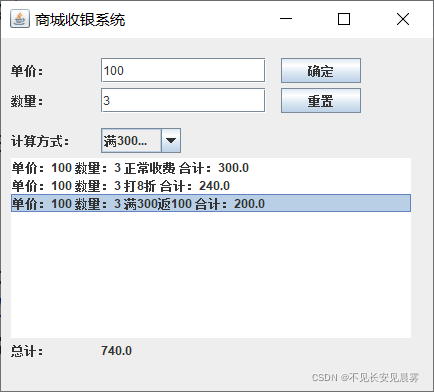
执行效果
3)简单工厂实现
问题:如果增加满300返100的促销算法,该如何处理?
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.DefaultListModel;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JList;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class Mall implements ActionListener {
private static JLabel unitPriceLabel;
private static JTextField unitPriceValue;
private static JLabel numLabel;
private static JTextField numValue;
private double totalPrice = 0;
private static JList<String> jList;
private static DefaultListModel<String> listModel;
private static JLabel totalNum;
private static JLabel calcType;
private static JComboBox<String> jComboBox;
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("商城收银系统");
frame.setSize(450, 400);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
frame.add(panel);
placeComponents(panel);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
private static void placeComponents(JPanel panel) {
panel.setLayout(null);
Mall mainFrame = new Mall();
// 第一行
unitPriceLabel = new JLabel("单价:");
unitPriceLabel.setBounds(10, 20, 80, 25);
panel.add(unitPriceLabel);
unitPriceValue = new JTextField(20);
unitPriceValue.setBounds(100, 20, 165, 25);
panel.add(unitPriceValue);
JButton confirmButton = new JButton("确定");
confirmButton.setBounds(280, 20, 80, 25);
confirmButton.addActionListener(mainFrame);
confirmButton.setActionCommand("confirm");
panel.add(confirmButton);
// 第二行
numLabel = new JLabel("数量:");
numLabel.setBounds(10, 50, 80, 25);
panel.add(numLabel);
numValue = new JTextField(20);
numValue.setBounds(100, 50, 165, 25);
panel.add(numValue);
JButton resetButton = new JButton("重置");
resetButton.setBounds(280, 50, 80, 25);
resetButton.addActionListener(mainFrame);
resetButton.setActionCommand("reset");
panel.add(resetButton);
// 第三行
calcType = new JLabel("计算方式:");
calcType.setBounds(10, 90, 80, 25);
panel.add(calcType);
jComboBox = new JComboBox<String>();
jComboBox.insertItemAt("正常收费", 0);
jComboBox.insertItemAt("打8折", 1);
jComboBox.insertItemAt("满300返100", 2);
jComboBox.setSelectedIndex(0);
jComboBox.setBounds(100, 90, 80, 25);
panel.add(jComboBox);
// 第四行
listModel = new DefaultListModel<String>();
jList = new JList<String>(listModel);
jList.setBounds(10, 120, 400, 180);
panel.add(jList);
// 第五行
JLabel totalLabel = new JLabel("总计:");
totalLabel.setBounds(10, 300, 80, 25);
panel.add(totalLabel);
totalNum = new JLabel("0.00");
totalNum.setBounds(100, 300, 80, 25);
panel.add(totalNum);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
if (event.getActionCommand().equals("confirm")) {
double unitPrice = Double.parseDouble(unitPriceValue.getText());
double num = Double.parseDouble(numValue.getText());
CashSuper cashSuper = CashFactory.createashAccept(jComboBox.getSelectedItem().toString());
double total = cashSuper.acceptCash(unitPrice * num);
totalPrice += total;
listModel.addElement("单价:" + unitPriceValue.getText() + " 数量:" + numValue.getText() + " "
+ jComboBox.getSelectedItem() + " 合计:" + total);
totalNum.setText(totalPrice + "");
} else if (event.getActionCommand().equals("reset")) {
unitPriceValue.setText("");
numValue.setText("");
listModel.clear();
totalPrice = 0;
totalNum.setText(totalPrice + "");
}
}
}
/**
* 现金收费抽象类
*/
public abstract class CashSuper {
/**
* 现金收取超类的抽象方法,收取现金,参数为原价,返回为当前价
*/
public abstract double acceptCash(double money);
}
/**
* 正常收费子类
*/
public class CashNormal extends CashSuper{
/**
* 正常收费,原价返回
*/
public double acceptCash(double money) {
return money;
}
}
/**
* 打折收费子类
*/
public class CashRebate extends CashSuper {
private double moneyRebate = 1d;
public CashRebate(String moneyRebate) {
this.moneyRebate = Double.parseDouble(moneyRebate);
}
/**
* 打折收费,初始化时,必须要输入折扣率,如八折,就是0.8
*/
public double acceptCash(double money) {
return money * moneyRebate;
}
}
/**
* 返利收费子类
*/
public class CashReturn extends CashSuper {
private double moneyCondition = 0.0d;
private double moneyReturn = 0.0d;
/**
* 初始化时必须要输入返利条件和返回值,比如满300返100
*
* @param moneyCondition 300
* @param moneyReturn 100
*/
public CashReturn(String moneyCondition, String moneyReturn) {
this.moneyCondition = Double.parseDouble(moneyCondition);
this.moneyReturn = Double.parseDouble(moneyReturn);
}
public double acceptCash(double money) {
double result = money;
// 若大于返利条件,则需要减去返利值
if (money >= moneyCondition) {
result = money - Math.floor(money / moneyCondition) * moneyReturn; // 向下取整
}
return result;
}
}
/**
* 收费对象生成工厂
*/
public class CashFactory {
public static CashSuper createashAccept(String type) {
CashSuper cs = null;
switch (type) {
case "正常收费":
cs = new CashNormal();
break;
case "满300返100":
cs = new CashReturn("300", "100");
break;
case "打8折":
cs = new CashRebate("0.8");
break;
}
return cs;
}
}
执行效果
问题:如果增加满100积分10点,该如何做?
1)增加一个积分算法,构造方法有两个参数:条件和返点
2)在收费对象生成工厂里增加满100积分10点的分支条件,再到界面稍加改动
*
简单工厂模式虽然也能解决这个问题,但这个模式只是解决对象的创建问题,而且由于工厂本身包括了所有的收费模式,商场是可能经常性地更改打折额度和返利额度,每次维护或扩展收费方式都要改动这个工厂,以致代码需重新编译部署,所以这不是最好的办法,面对算法的时常变动,应该使用策略模式。
商场收银时如何促销,用打折还是返利,其实都是一些算法,用工厂来生成算法,这没有错,但算法本身只是一种策略,最重要的是这些算法随时都可能互相替换,这就是变化点,而封装变化点是面向对象很重要的思维方式。
4)策略模式
/**
* 抽象算法类
*/
public abstract class Strategy {
// 算法方法
public abstract void AlgorithmInterface();
}
/**
* 具体算法A
*/
public class ConcreteStrategyA extends Strategy{
@Override
public void AlgorithmInterface() {
System.out.println("算法A实现");
}
}
/**
* 具体算法B
*/
public class ConcreteStrategyB extends Strategy{
@Override
public void AlgorithmInterface() {
System.out.println("算法B实现");
}
}
/**
* 具体算法C
*/
public class ConcreteStrategyC extends Strategy{
@Override
public void AlgorithmInterface() {
System.out.println("算法C实现");
}
}
/**
* 上下文
*/
public class Context {
Strategy strategy;
// 初始化时,传入具体的策略对象
public Context(Strategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 上下文接口
public void ContextInterface() {
// 根据具体的策略对象,调用其算法的方法
strategy.AlgorithmInterface();
}
}
客户端
/**
* 客户端对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 由于实例化不同的策略,所以最终在调用context.ContextInterface()时,所获得的结果就不尽相同
Context context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyA());
context.ContextInterface();
context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyB());
context.ContextInterface();
context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyC());
context.ContextInterface();
}
}
5)策略模式实现
只需要增加一个CashContext 类,再改写一下界面即可。
public class CashContext {
private CashSuper cs;
// 通过构造方法,传入具体的收费策略
public CashContext(CashSuper csuper) {
this.cs = csuper;
}
public double getResult(double money) {
// 根据收费策略的不同,获得计算结果
return cs.acceptCash(money);
}
}
界面逻辑修改
if (event.getActionCommand().equals("confirm")) {
double unitPrice = Double.parseDouble(unitPriceValue.getText());
double num = Double.parseDouble(numValue.getText());
CashContext cashContext = null;
// 根据下拉选择框,将相应的策略对象作为参数传入CashContext的对象中
switch (jComboBox.getSelectedItem().toString()) {
case "正常收费":
cashContext = new CashContext(new CashNormal());
break;
case "满300返100":
cashContext = new CashContext(new CashReturn("300", "100"));
break;
case "打8折":
cashContext = new CashContext(new CashRebate("0.8"));
break;
}
// 通过对Context的getResult方法的调用,可以得到收取费用的结果,让具体算法与客户进行了隔离。
double total = cashContext.getResult(unitPrice*num);
totalPrice += total;
listModel.addElement("单价:" + unitPriceValue.getText() + " 数量:" + numValue.getText() + " "
+ jComboBox.getSelectedItem() + " 合计:" + total);
totalNum.setText(totalPrice + "");
}
执行效果
6)策略模式+简单工厂
将界面中判断的过程转义到CashContext中。
public class CashContext {
private CashSuper cs;
// 注意参数不是具体的收费策略对象,而是一个字符串,表示收费类型
public CashContext(String type) {
switch (type) {
case "正常收费":
// 将实例化具体策略的过程由客户端转移到Context类中,简单工厂的应用
cs = new CashNormal();
break;
case "满300返100":
cs = new CashReturn("300", "100");
break;
case "打8折":
cs = new CashRebate("0.8");
break;
}
}
public double getResult(double money) {
// 根据收费策略的不同,获得计算结果
return cs.acceptCash(money);
}
}
界面代码
if (event.getActionCommand().equals("confirm")) {
double unitPrice = Double.parseDouble(unitPriceValue.getText());
double num = Double.parseDouble(numValue.getText());
CashContext cashContext = new CashContext(jComboBox.getSelectedItem().toString());
double total = cashContext.getResult(unitPrice*num);
totalPrice += total;
listModel.addElement("单价:" + unitPriceValue.getText() + " 数量:" + numValue.getText() + " "
+ jComboBox.getSelectedItem() + " 合计:" + total);
totalNum.setText(totalPrice + "");
}
简单工厂与策略模式的区别
// 简单工厂模式
CashSuper cashSuper = CashFactory.createashAccept(jComboBox.getSelectedItem().toString());
double total = cashSuper.acceptCash(unitPrice*num);
// 策略模式与简单工厂结合的用法
CashContext cashContext = new CashContext(jComboBox.getSelectedItem().toString());
double total = cashContext.getResult(unitPrice*num);
简单工厂模式,客户端需要认识CashSuper和CashFactory两个类。
而策略模式与简单工厂结合的用法,客户端只需要认识一个类CashContext就可以了。耦合更加降低。
策略模式解析
策略模式是一种定义一系列算法的方法,从概念上来看,所有这些算法完成的都是相同的工作,只是实现不同,它可以以相同的方式调用所有的算法,减少了各种算法类与使用算法类之间的耦合。
策略模式的Strategy类层次为Context定义了一系列的可供重用的算法或行为。继承有助于析取出这些算法中的公共功能。
策略模式的优点是简化了单元测试,因为每个算法都有自己的类,可以通过自己的接口单独测试。
当不同的行为堆砌在一个类中时,就很难避免使用条件语句来选择合适的行为。将这些行为封装在一个个独立的Strategy类中,可以在使用这些行为的类中消除条件语句。即策略模式封装了变化。
策略模式就是用来封装算法的,但在实践中,我们发现可以用它来封装几乎任何类型的规则,只要在分析过程中听到需要在不同时间应用不同的业务规则,就可以考虑使用策略模式处理这种变化的可能性。
在基本的策略模式中,选择所用具体实现的职责由客户端对象承担,并转给策略模式的Context对象。这本身并没有解除客户端需要选择判断的压力,而策略模式与简单工厂模式结合后,选择具体实现的职责也可以由Context来承担,这就最大化地减轻了客户端的职责。