【CSAPP随笔】CH3:Bits, Bytes, and Integers
![]()
前言
《深入理解操作系统》个人用学习笔记。
目录
0x00 Binary Representations - 二进制表示
0x01 Representing Information - 信息表示
0x02 Encoding Byte Values
0x03 Example Data Representations - 数据表示的例子
0x04 Representations for Integers - 整数的表示
0x05 Two’s Complement Encoding - 二进制补码
0x06 Signed Integer Representation
0x07 Principle of using Complements as Negative Numbers
0x08 Two-complement Encoding Example (Cont.)
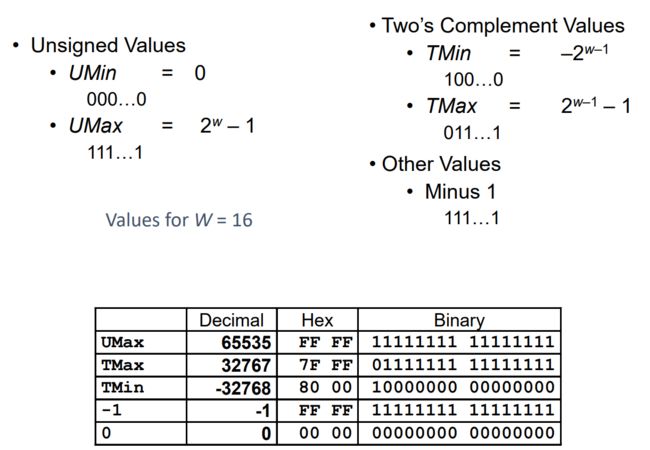
0x09 Numeric Ranges
0x0A Values for Different Word Sizes
0x0B Unsigned & Signed Numeric Values
0x0C Conversion Visualized
0x0D Sign Extension
0x0E Visualizing Unsigned Addition
0x0F Visualizing 2’s Complement Addition - 二进制补码加法
0x10 Unsigned Multiplication in C - 无符号乘法
0x11 Signed Multiplication in C 0 有符号乘法
0x12 Boolean Algebra - 布尔代数
0x13 General Boolean Algebras
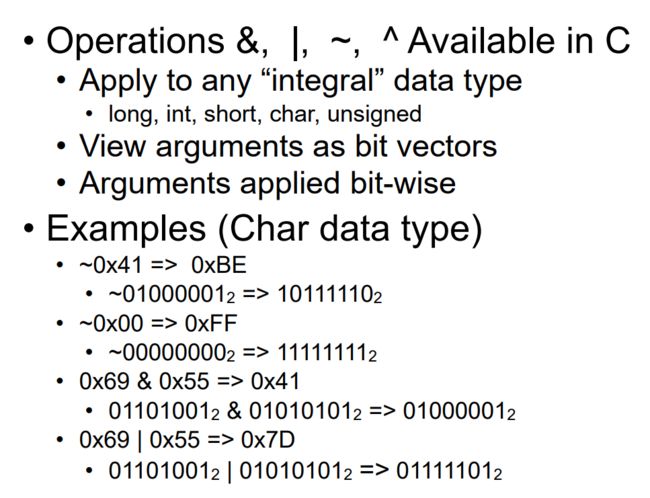
0x14 Bit-Level Operations in C
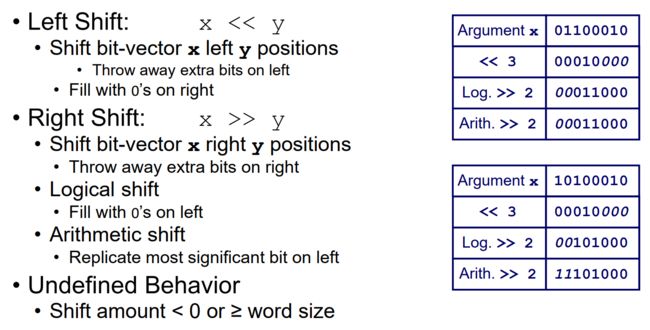
0x15 Shift Operations
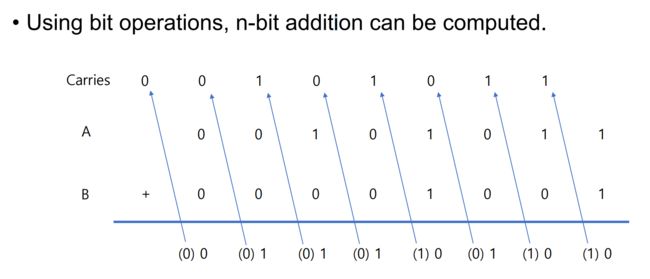
0x16 Adder
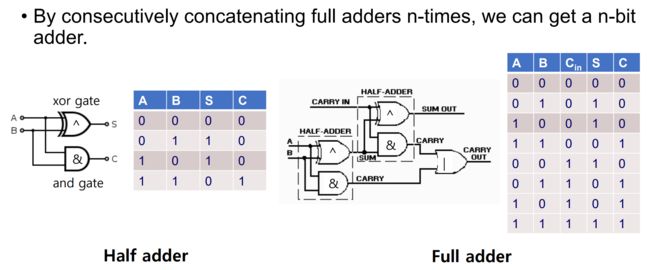
0x17 Implementation of Adder
0x18 4-bit integer adder
0x00 Binary Representations - 二进制表示
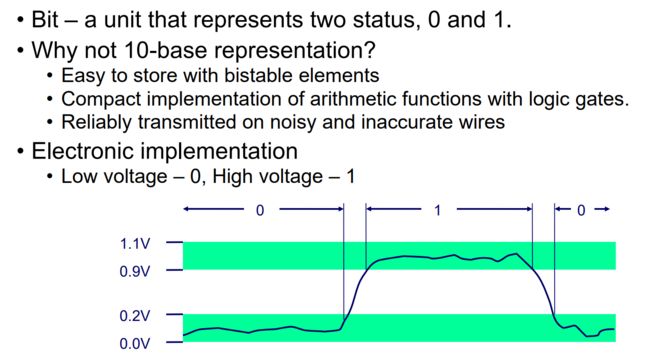
位 —— 代表两种状态的单位,即0和1。
为什么不用10进制表示?
① 已与存储
② 用逻辑门紧凑地实现算术功能。
③ 抗干扰,可靠传输。
(电子实现:低电压-0,高电压-1)
0x01 Representing Information - 信息表示
信息=比特+上下文+表示方法
① 信息以比特形式写在存储器上。
② 上下文表示一组比特的数据类型。
③ 表征将赋予比特以意义。
N个比特可以代表多少信息?
2n个东西
如何代表不同类型的信息?
每种信息类型都有其数据表示。
字符、数字(整数和浮点数)、像素、机器指令
0x02 Encoding Byte Values
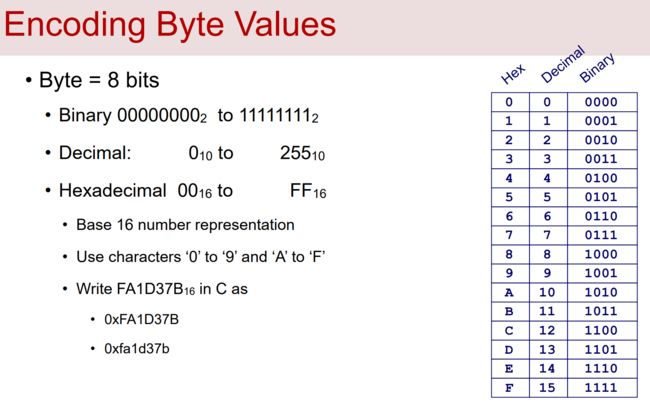
一个字节包括8位。
① 在二进制表示法中,它的值域是 ![]()
② 换成十进制,它的值域就是![]()
③ 用十六进制,一个字节的取值范围就是 ![]()
十六进制(简写为Hex),使用数字 0~9 以及字符 A ~ F 来表示 16个可能的值。
在C中,以 0x 开头的数字常量被认为是十六进制的值。
A~F 既可以写成大写也可以是小写(甚至可以大小写混合)
比如 FA1D37B_16 可以在C语言中写作 0xFA1D37B、0xfa1d37b……
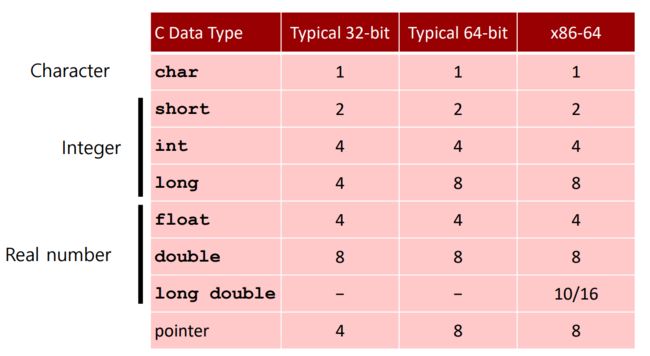
0x03 Example Data Representations - 数据表示的例子
0x04 Representations for Integers - 整数的表示
分为无符号整数表示和有符号整数表示。
0x05 Two’s Complement Encoding - 二进制补码
0x06 Signed Integer Representation
无符号数(unsigned),有符号数(signed)。
符号位:最高位0表示正数,最高位1表示负数。
有符号 char 的范围是: -128 ~ 127
无符号 char 的范围是: 0 ~ 255
![]()
0x07 Principle of using Complements as Negative Numbers
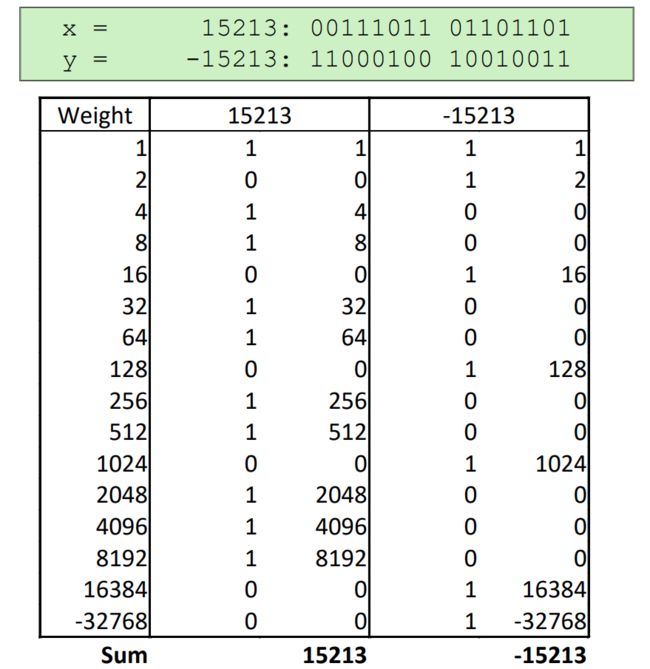
0x08 Two-complement Encoding Example (Cont.)
0x09 Numeric Ranges
0x0A Values for Different Word Sizes
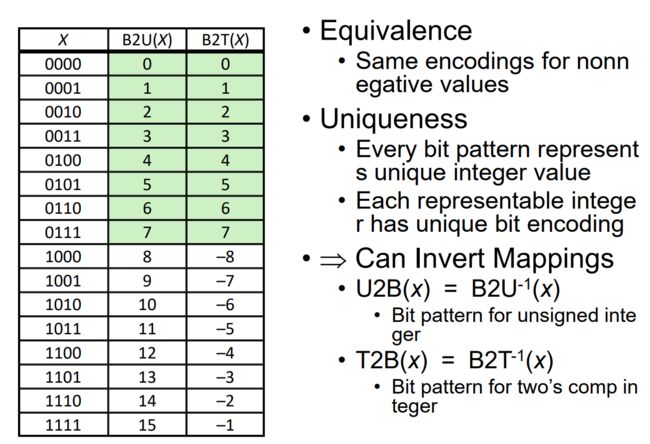
0x0B Unsigned & Signed Numeric Values
等效性 - 非整数值的编码相同 - 唯一性 - 每个比特模式都代表唯一的整数值 - 每个可表示的整数都有唯一的比特编码 - ⇒可以反转映射 - U2B(x) = B2U-1(x) - 无符号整数的比特模式 - T2B(x) = B2T-1(x) - 整数中二的比特模式
0x0C Conversion Visualized
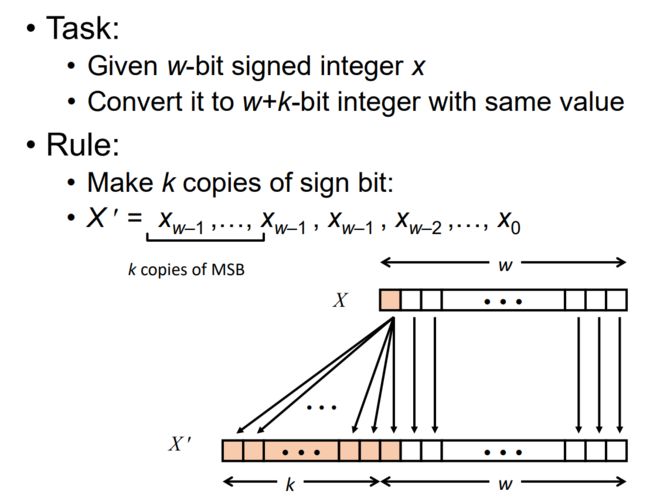
0x0D Sign Extension
例子:
从较小的整数数据类型转换到较大的整数数据类型
C自动进行符号扩展。
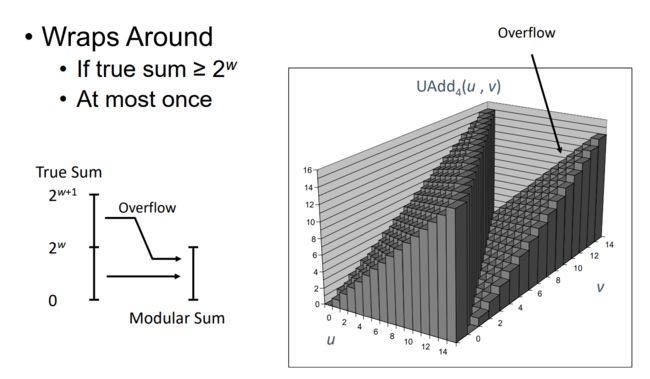
0x0E Visualizing Unsigned Addition
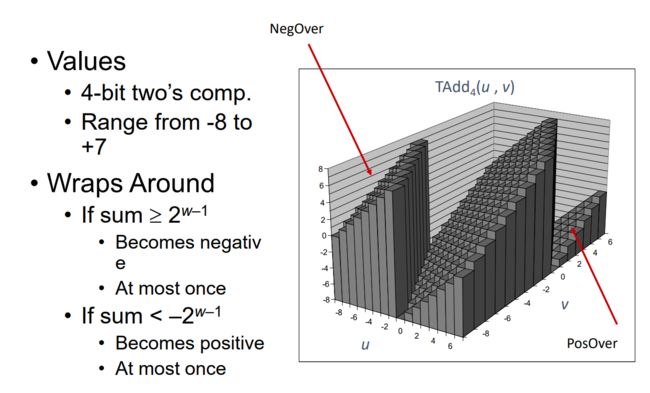
0x0F Visualizing 2’s Complement Addition - 二进制补码加法
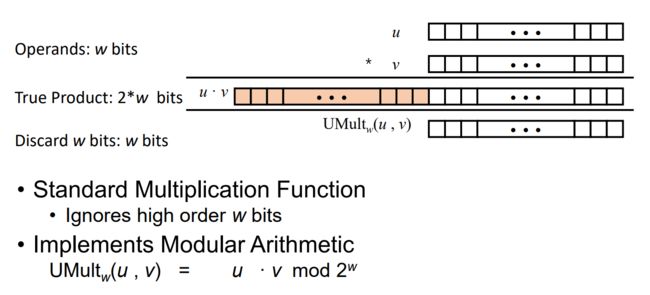
0x10 Unsigned Multiplication in C - 无符号乘法
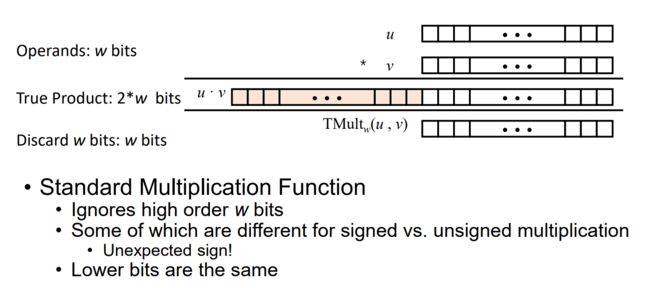
0x11 Signed Multiplication in C 0 有符号乘法
0x12 Boolean Algebra - 布尔代数
计算机是如何操作比特的?由乔治 - 布尔在19世纪开发
逻辑的代数表示 —— 将 "真 "编码为1,"假 "编码为0
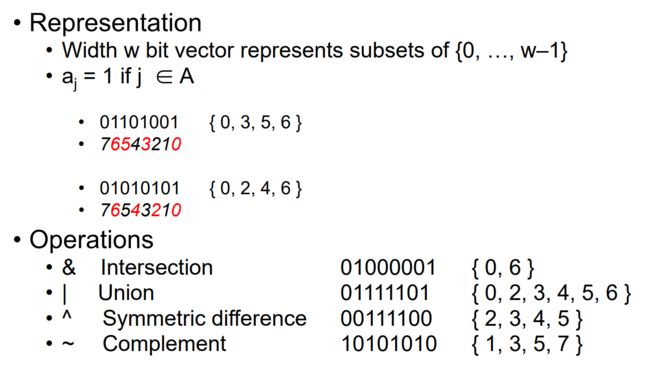
0x13 General Boolean Algebras
Example: Representing & Manipulating Sets
0x14 Bit-Level Operations in C
0x15 Shift Operations
0x16 Adder
0x17 Implementation of Adder
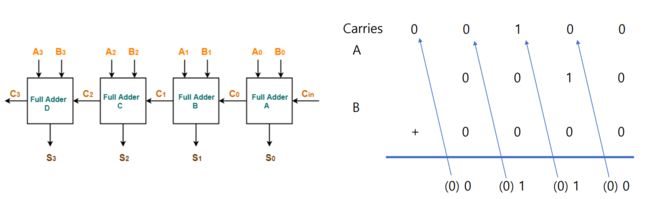
0x18 4-bit integer adder
A computer encodes, stores, and manipulates information in bits.
Representing negative numbers as 2’s complements
Use the same logic hardware for unsigned and signed integers.
If the true result is out of scope, the result is not valid.
参考资料
Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective (3rd Edition)