Keras框架:Alexnet网络代码实现
网络思想:
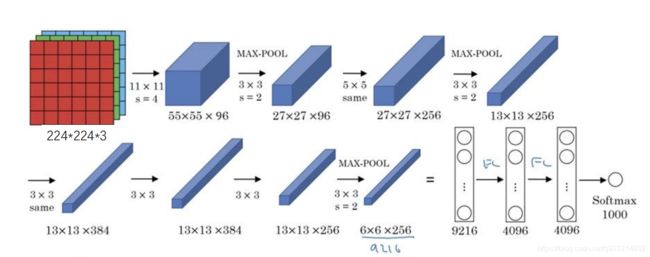
1、一张原始图片被resize到(224,224,3);
2、使用步长为4x4,大小为11的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为96层, 输出的shape为(55,55,96);
3、使用步长为2的最大池化层进行池化,此时输出的shape为(27,27,96)
4、使用步长为1x1,大小为5的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为256层, 输出的shape为(27,27,256);
5、使用步长为2的最大池化层进行池化,此时输出的shape为(13,13,256);
6、使用步长为1x1,大小为3的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为384层, 输出的shape为(13,13,384);
7、使用步长为1x1,大小为3的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为384层, 输出的shape为(13,13,384);
8、使用步长为1x1,大小为3的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为256层, 输出的shape为(13,13,256);
9、使用步长为2的最大池化层进行池化,此时输出的shape为(6,6,256);
10、两个全连接层,最后输出为1000类
细节部分举例:
第一层
第一层输入数据为原始图像的2242243的图像,这个图像被11113(3代表 深度,例如RGB的3通道)的卷积核进行卷积运算,卷积核对原始图像的每次 卷积都会生成一个新的像素。 卷积核的步长为4个像素,朝着横向和纵向这两个方向进行卷积。 由此,会生成新的像素; 第一层有96个卷积核,所以就会形成555596个像素层。 pool池化层:这些像素层还需要经过pool运算(池化运算)的处理,池化运 算的尺度由预先设定为33,运算的步长为2,则池化后的图像的尺寸为: (55-3)/2+1=27。即经过池化处理过的规模为2727*96.
代码实现:
网络主体部分:(AlexNet.py)
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense,Activation,Conv2D,MaxPooling2D,Flatten,Dropout,BatchNormalization
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.utils import np_utils
from keras.optimizers import Adam
# 注意,为了加快收敛,我将每个卷积层的filter减半,全连接层减为1024
def AlexNet(input_shape=(224,224,3),output_shape=2):
# AlexNet
model = Sequential()
# 使用步长为4x4,大小为11的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为96层,输出的shape为(55,55,96);
# 所建模型后输出为48特征层
model.add(
Conv2D(
filters=48,
kernel_size=(11,11),
strides=(4,4),
padding='valid',
input_shape=input_shape,
activation='relu'
)
)
model.add(BatchNormalization())
# 使用步长为2的最大池化层进行池化,此时输出的shape为(27,27,96)
# 所建模型后输出为48特征层
model.add(
MaxPooling2D(
pool_size=(3,3),
strides=(2,2),
padding='valid'
)
)
# 使用步长为1x1,大小为5的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为256层,输出的shape为(27,27,256);
# 所建模型后输出为128特征层
model.add(
Conv2D(
filters=128,
kernel_size=(5,5),
strides=(1,1),
padding='same',
activation='relu'
)
)
model.add(BatchNormalization())
# 使用步长为2的最大池化层进行池化,此时输出的shape为(13,13,256);
# 所建模型后输出为128特征层
model.add(
MaxPooling2D(
pool_size=(3,3),
strides=(2,2),
padding='valid'
)
)
# 使用步长为1x1,大小为3的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为384层,输出的shape为(13,13,384);
# 所建模型后输出为192特征层
model.add(
Conv2D(
filters=192,
kernel_size=(3,3),
strides=(1,1),
padding='same',
activation='relu'
)
)
# 使用步长为1x1,大小为3的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为384层,输出的shape为(13,13,384);
# 所建模型后输出为192特征层
model.add(
Conv2D(
filters=192,
kernel_size=(3,3),
strides=(1,1),
padding='same',
activation='relu'
)
)
# 使用步长为1x1,大小为3的卷积核对图像进行卷积,输出的特征层为256层,输出的shape为(13,13,256);
# 所建模型后输出为128特征层
model.add(
Conv2D(
filters=128,
kernel_size=(3,3),
strides=(1,1),
padding='same',
activation='relu'
)
)
# 使用步长为2的最大池化层进行池化,此时输出的shape为(6,6,256);
# 所建模型后输出为128特征层
model.add(
MaxPooling2D(
pool_size=(3,3),
strides=(2,2),
padding='valid'
)
)
# 两个全连接层,最后输出为1000类,这里改为2类(猫和狗)
# 缩减为1024
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1024, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Dense(1024, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Dense(output_shape, activation='softmax'))
return model
图像预处理部分:(utils.py)
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import numpy as np
import cv2
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
def load_image(path):
# 读取图片,rgb
img = mpimg.imread(path)
# 将图片修剪成中心的正方形
short_edge = min(img.shape[:2])
yy = int((img.shape[0] - short_edge) / 2)
xx = int((img.shape[1] - short_edge) / 2)
crop_img = img[yy: yy + short_edge, xx: xx + short_edge]
return crop_img
def resize_image(image, size):
with tf.name_scope('resize_image'):
images = []
for i in image:
i = cv2.resize(i, size)
images.append(i)
images = np.array(images)
return images
def print_answer(argmax):
with open("./data/model/index_word.txt","r",encoding='utf-8') as f:
synset = [l.split(";")[1][:-1] for l in f.readlines()]
# print(synset[argmax])
return synset[argmax]
训练部分:(train.py)
from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, EarlyStopping
from keras.utils import np_utils
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from model.AlexNet import AlexNet
import numpy as np
import utils
import cv2
from keras import backend as K
#K.set_image_dim_ordering('tf')
K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first'
def generate_arrays_from_file(lines,batch_size):
# 获取总长度
n = len(lines)
i = 0
while 1:
X_train = []
Y_train = []
# 获取一个batch_size大小的数据
for b in range(batch_size):
if i==0:
np.random.shuffle(lines)
name = lines[i].split(';')[0]
# 从文件中读取图像
img = cv2.imread(r".\data\image\train" + '/' + name)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = img/255
X_train.append(img)
Y_train.append(lines[i].split(';')[1])
# 读完一个周期后重新开始
i = (i+1) % n
# 处理图像
X_train = utils.resize_image(X_train,(224,224))
X_train = X_train.reshape(-1,224,224,3)
Y_train = np_utils.to_categorical(np.array(Y_train),num_classes= 2)
yield (X_train, Y_train)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 模型保存的位置
log_dir = "./logs/"
# 打开数据集的txt
with open(r".\data\dataset.txt","r") as f:
lines = f.readlines()
# 打乱行,这个txt主要用于帮助读取数据来训练
# 打乱的数据更有利于训练
np.random.seed(10101)
np.random.shuffle(lines)
np.random.seed(None)
# 90%用于训练,10%用于估计。
num_val = int(len(lines)*0.1)
num_train = len(lines) - num_val
# 建立AlexNet模型
model = AlexNet()
# 保存的方式,3代保存一次
checkpoint_period1 = ModelCheckpoint(
log_dir + 'ep{epoch:03d}-loss{loss:.3f}-val_loss{val_loss:.3f}.h5',
monitor='acc',
save_weights_only=False,
save_best_only=True,
period=3
)
# 学习率下降的方式,acc三次不下降就下降学习率继续训练
reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='acc',
factor=0.5,
patience=3,
verbose=1
)
# 是否需要早停,当val_loss一直不下降的时候意味着模型基本训练完毕,可以停止
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss',
min_delta=0,
patience=10,
verbose=1
)
# 交叉熵
model.compile(loss = 'categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer = Adam(lr=1e-3),
metrics = ['accuracy'])
# 一次的训练集大小
batch_size = 128
print('Train on {} samples, val on {} samples, with batch size {}.'.format(num_train, num_val, batch_size))
# 开始训练
model.fit_generator(generate_arrays_from_file(lines[:num_train], batch_size),
steps_per_epoch=max(1, num_train//batch_size),
validation_data=generate_arrays_from_file(lines[num_train:], batch_size),
validation_steps=max(1, num_val//batch_size),
epochs=50,
initial_epoch=0,
callbacks=[checkpoint_period1, reduce_lr])
model.save_weights(log_dir+'last1.h5')
#保存模型
预测部分:(predict.py)
import numpy as np
import utils
import cv2
from keras import backend as K
from model.AlexNet import AlexNet
# K.set_image_dim_ordering('tf')
K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first'
if __name__ == "__main__":
model = AlexNet()
model.load_weights("./logs/last1.h5")
img = cv2.imread("./test2.jpg")
img_RGB = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img_nor = img_RGB/255
img_nor = np.expand_dims(img_nor,axis = 0)
img_resize = utils.resize_image(img_nor,(224,224))
#utils.print_answer(np.argmax(model.predict(img)))
print('the answer is: ',utils.print_answer(np.argmax(model.predict(img_resize))))
cv2.imshow("ooo",img)
cv2.waitKey(0)