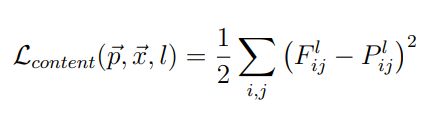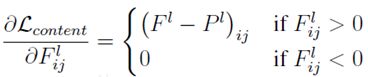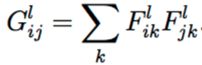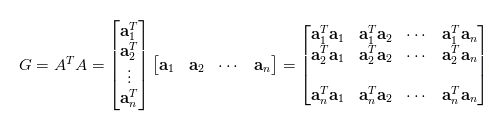图像风格迁移——pytorch实现
一、风格迁移的效果展示
先看一张效果图
二、风格迁移的基本原理:
1、损失函数方面:
损失函数有两部分组成:内容损失和风格损失:
图片内容:图片的主体,图片中比较突出的部分
图片风格:图片的纹理、色彩等
(1)内容损失content loss :原始图片的内容和生成图片的内容作欧式距离
其中,等式左侧表示在第l层中,原始图像(P)和生成图像(F)的举例,右侧是对应的最小二乘法表达式。Fij表示生成图像第 i 个feature map 的第 j 个输出值。
使用最小二乘法求导得出最小值,再让改的l层上生成的图片(F)逼近改层的原始图片(P)
(2)风格损失style loss使用类G矩阵代表图像的风格 :
当同一个维度上面的值相乘的时候原来越小相乘之后的值变得更小,原来越大相乘之后的中就变得越大;在不同维度上的关系也在相乘的表达当中表示出来。
因此,最终能够在保证内容的情况下,进行风格的迁移转换。
2、风格迁移的流程
输入风格图片和内容图片还有第三张图片,并改变第三张图片,使其与内容图片的内容间距和风格图片的风格间距最小化。最终得到生成的图片
三、代码部分:
from __future__ import print_function
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision.models as models
import copy
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # 来判断是否有可用的GPU
# 输出图像的所需尺寸
imsize = 512 if torch.cuda.is_available() else 128 # 如果没有GPU,请使用小尺寸
loader = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize(imsize), # 缩放导入的图像
transforms.ToTensor()]) # 将其转换为torch tensor
def image_loader(image_name):
image = Image.open(image_name)
image = loader(image).unsqueeze(0) # 需要伪造的批次尺寸以适合网络的输入尺寸
return image.to(device, torch.float)
# style_img = image_loader("./images/picasso.jpg")
# content_img = image_loader("./images/dancing.jpg")
style_img = image_loader(r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\styled_transfer\ori\18.jpg")
content_img = image_loader(r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\styled_transfer\ori\42.jpg")
assert style_img.size() == content_img.size(), \
"我们需要导入相同大小的样式和内容图像"
unloader = transforms.ToPILImage() # 重新转换为PIL图像
plt.ion()
def imshow(tensor, title=None):
image = tensor.cpu().clone() # 我们克隆张量不对其进行更改
image = image.squeeze(0) # 删除假批次尺寸
image = unloader(image)
plt.imshow(image)
if title is not None:
plt.title(title)
plt.pause(0.001) # 稍停一下,以便更新地块
plt.figure()
imshow(style_img, title='Style Image')
plt.figure()
imshow(content_img, title='Content Image')
class ContentLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, target, ):
super(ContentLoss, self).__init__()
# 我们将目标内容与所使用的树“分离”
# 动态计算梯度:这是一个规定值,
# 不是变量。 否则,准则的前进方法
# 将引发错误。
self.target = target.detach()
def forward(self, input):
self.loss = F.mse_loss(input, self.target)
return input
def gram_matrix(input):
a, b, c, d = input.size() # a=batch size(=1)
# b=特征图数量
# (c,d)=dimensions of a f. map (N=c*d)
features = input.view(a * b, c * d) # 将FXML调整为\ hat FXML
G = torch.matmul(features, features.t())
# 我们将gram矩阵的值“规范化”
# 除以每个要素图中的元素数量。
return G.div(a * b * c * d)
class StyleLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, target_feature):
super(StyleLoss, self).__init__()
self.target = gram_matrix(target_feature).detach()
def forward(self, input):
G = gram_matrix(input)
self.loss = F.mse_loss(G, self.target)
return input
cnn = models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features.to(device).eval()
cnn_normalization_mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]).to(device)
cnn_normalization_std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]).to(device)
# 创建一个模块来标准化输入图像,以便我们可以轻松地将其放入
# nn.Sequential
class Normalization(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, mean, std):
super(Normalization, self).__init__()
# 查看均值和标准差以使其为[C x 1 x 1],以便它们可以
# 直接使用形状为[B x C x H x W]的图像张量。
# B是批量大小。 C是通道数。 H是高度,W是宽度。
# self.mean = torch.tensor(mean).view(-1, 1, 1)
# self.std = torch.tensor(std).view(-1, 1, 1)
self.mean = mean.clone().detach().view(-1, 1, 1)
self.std = std.clone().detach().view(-1, 1, 1)
def forward(self, img):
# normalize img
return (img - self.mean) / self.std
# 所需的深度层以计算样式/内容损失:
content_layers_default = ['conv_4']
style_layers_default = ['conv_1', 'conv_2', 'conv_3', 'conv_4', 'conv_5']
def get_style_model_and_losses(cnn, normalization_mean, normalization_std,
style_img, content_img,
content_layers=content_layers_default,
style_layers=style_layers_default):
cnn = copy.deepcopy(cnn)
# 标准化模块
normalization = Normalization(normalization_mean, normalization_std).to(device)
# 只是为了获得对内容/样式的可迭代访问或列表
# losses
content_losses = []
style_losses = []
# 假设cnn是nn.Sequential,那么我们创建一个新的nn.Sequential
# 放入应该顺序激活的模块
model = nn.Sequential(normalization)
i = 0 # 每当转换时就增加
for layer in cnn.children():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d): #如果对象的类型与参数二的类型(classinfo)相同则返回 True,否则返回 False
i += 1
name = 'conv_{}'.format(i)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.ReLU):
name = 'relu_{}'.format(i)
# 旧版本与我们在下面插入的ContentLoss和StyleLoss不能很好地配合使用。
# 因此,我们在这里替换为不适当的。
layer = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.MaxPool2d):
name = 'pool_{}'.format(i)
elif isinstance(layer, nn.BatchNorm2d):
name = 'bn_{}'.format(i)
else:
raise RuntimeError('Unrecognized layer: {}'.format(layer.__class__.__name__))
model.add_module(name, layer)
if name in content_layers:
# 增加内容损失:
target = model(content_img).detach()
content_loss = ContentLoss(target)
model.add_module("content_loss_{}".format(i), content_loss)
content_losses.append(content_loss)
if name in style_layers:
# 增加样式损失:
target_feature = model(style_img).detach()
style_loss = StyleLoss(target_feature)
model.add_module("style_loss_{}".format(i), style_loss)
style_losses.append(style_loss)
# 现在我们在最后一次内容和样式丢失后修剪图层
for i in range(len(model) - 1, -1, -1):
if isinstance(model[i], ContentLoss) or isinstance(model[i], StyleLoss):
break
model = model[:(i + 1)]
return model, style_losses, content_losses
input_img = content_img.clone()
# 如果要使用白噪声,请取消注释以下行:
# input_img = torch.randn(content_img.data.size(), device=device)
# 将原始输入图像添加到图中:
plt.figure()
imshow(input_img, title='Input Image')
def get_input_optimizer(input_img):
# 此行显示输入是需要渐变的参数
optimizer = optim.LBFGS([input_img.requires_grad_()])
return optimizer
def run_style_transfer(cnn, normalization_mean, normalization_std,
content_img, style_img, input_img, num_steps=300,
style_weight=1000000, content_weight=1):
"""Run the style transfer."""
print('Building the style transfer model..')
model, style_losses, content_losses = get_style_model_and_losses(cnn,
normalization_mean, normalization_std, style_img,
content_img)
optimizer = get_input_optimizer(input_img)
print('Optimizing..')
run = [0]
while run[0] <= num_steps:
def closure():
# 更正更新后的输入图像的值
input_img.data.clamp_(0, 1)
optimizer.zero_grad()
model(input_img)
style_score = 0
content_score = 0
for sl in style_losses:
style_score += sl.loss
for cl in content_losses:
content_score += cl.loss
style_score *= style_weight
content_score *= content_weight
loss = style_score + content_score
loss.backward()
run[0] += 1
if run[0] % 50 == 0:
print("run {}:".format(run))
print('Style Loss : {:4f} Content Loss: {:4f}'.format(
style_score.item(), content_score.item()))
print()
return style_score + content_score
optimizer.step(closure)
# 最后更正...
input_img.data.clamp_(0, 1)
return input_img
output = run_style_transfer(cnn, cnn_normalization_mean, cnn_normalization_std,
content_img, style_img, input_img)
plt.figure()
imshow(output, title='Output Image')
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 4
plt.ioff()
plt.show()参考资料:
https://blog.puuuq.cn/index.php/2019/10/03/52.html
https://www.zhihu.com/question/49805962/answer/130549737
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoyh/p/11932095.html
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.09020