【 web高级 01vue 】 vue直播课01 vue组件化实践
课堂目标
- 深入理解Vue的组件化机制
- 掌握Vue组件化常用技术
- 能够设计并实现多种类型的组件
- 加深对一些Vue原理的理解
- 学会看开源组件库源码
知识要点
- 组件通信方式盘点
- 组件复合
- 递归组件
- 组件构造函数和实例
- 渲染函数
- 组件挂载
- …
运行环境
- node 12.x
- vue.js 2.6.x
- vue-cli 4.x
知识点
组件化
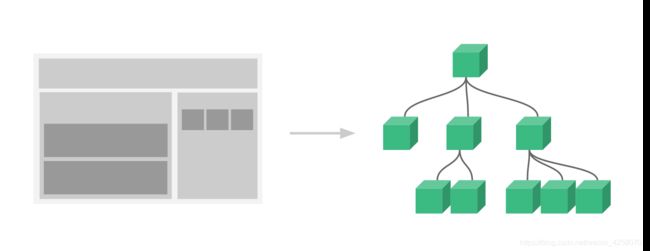
vue组件系统提供了一种抽象,让我们可以使用独立可复用的组件来构建大型应用,任意类型的应用界面都可以抽象为一个组件树。组件化能提高开发效率,方法重复使用,简化调试步骤,提升项目可维护性,便于多人协同开发。
一、组件通信
组件通信常用方式
- props
- eventbus
- vuex
- 自定义事件
- 边界情况
- $parent
- $children
- $root
- $refs
- provide/inject
- 非prop特性
- $attrs
- $listeners
- 边界情况
1.1 props
父给子传值
//child
props:{msg:String}
//parent 属性
<Helloworld msg="welcome to Your Vue.js App">
1.2 自定义事件
子给父传值
//child
this.$emit('add',good);
//perent
<Cart @add="cartAdd($event)">Cart >
//完整代码
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>组件通信h2>
<Child1 msg="some msg frpm parent" @some-event="onSomeEvent">Child1>
div>
template>
<script>
import Child1 from "@/components/communication/Child1";
export default {
components:{
Child1
},
methods:{
onSomeEvent(msg){
console.log('communication',msg)
}
}
};
script>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Child1.vue
<template>
<div>
<div @click="$emit('some-event','msg from child1')">
<h3>child1h3>
<p>{{msg}}p>
div>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
props:{
msg:{
type:String,
default:''
}
},
}
script>
1.3 事件总线
任意两个组件之间传值常用事件总线 或 vuex的方式。
//Bus:事件派发、监听和回调管理
class Bus {
constructor(){
this.callbacks = {}
}
$on(name, fn){
this.callbacks[name] = this.callbacks[name] || []
this.callbacks[name].push(fn)
}
$emit(name, args){
if(this.callbacks[name]){
this.callbacks[name].forEach(cb => cb(args))
}
}
}
// main.js
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Bus()
// child1
this.$bus.$on('foo', handle)
// child2
this.$bus.$emit('foo')
//完整代码
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 事件总线
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Vue()
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>组件通信h2>
<Child1>Child1>
<Child2>Child2>
div>
template>
<script>
import Child1 from "@/components/communication/Child1";
import Child2 from "@/components/communication/Child2";
export default {
components:{
Child1,
Child2
},
};
script>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Child1.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>
Child1
div>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
mounted(){
//child1接收来自child2的消息
//利用事件总线接收事件
this.$bus.$on('event-from-child2',msg=>{
console.log('Child1',msg);
})
}
}
script>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Child2.vue
<template>
<div>
child2
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
sendToChild1(){
//child2给child1发送消息
//利用事件总线派发事件
this.$bus.$emit('event-from-child2','some msg form child2')
}
},
};
script>
1.4 vuex
创建唯一的全局数据管理者store,通过它管理数据并通知组件状态变更。
1.5 $parent/$root
兄弟组件之间通信可通过共同祖辈搭桥,$parent或$root。
// brother1
this.$parent.$on('foo', handle)
// brother2
this.$parent.$emit('foo')
//完整代码
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>组件通信h2>
<Child1>Child1>
<Child2>Child2>
div>
template>
<script>
import Child1 from "@/components/communication/Child1";
import Child2 from "@/components/communication/Child2";
export default {
components:{
Child1,
Child2
},
};
script>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Child1.vue
<template>
<div>
<div>
Child1
div>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
mounted(){
//child1接收来自child2的消息
//利用事件总线接收事件
// this.$bus.$on('event-from-child2',msg=>{
// console.log('Child1:',msg);
// });
this.$parent.$on('event-from-child2',msg=>{
console.log('Child1:',msg);
})
}
}
script>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Child2.vue
<template>
<div>
child2
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
sendToChild1(){
//child2给child1发送消息
//利用事件总线派发事件
// this.$bus.$emit('event-from-child2','some msg form child2')
//事件的派发和监听者是同一个 发布订阅模式
this.$parent.$emit('event-from-child2','some msg form child2')
}
},
};
script>
1.6 $children
父组件可以通过$children访问子组件实现父子通信。
// parent
this.$children[0].xx = 'xxx'
注意:
$children 并不保证顺序,也不是响应式的
完整代码
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>组件通信h2>
<Child1>Child1>
<Child2>Child2>
<button @click="goHome">回家吃饭button>
div>
template>
<script>
import Child1 from "@/components/communication/Child1";
import Child2 from "@/components/communication/Child2";
export default {
components:{
Child1,
Child2
},
methods:{
goHome(){
//父组件利用$children,直接调用子元素的实例方法
this.$children[0].eat();
console.log('所有子元素的数组',this.$children);
}
}
};
script>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Child1.vue
<template>
<div>
child1
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
methods:{
eat(){
console.log('这就回家!')
}
}
}
script>
1.7 $attrs / $listeners
$attrs
代码
index.vue
<Child2 msg="some msg frpm parent">Child2>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Child2.vue
<p>{{msg}}p>
包含了父作用域中不作为 prop 被识别 (且获取) 的特性绑定 ( class 和 style 除外)。当一个组件没有 声明任何 prop 时,这里会包含所有父作用域的绑定 ( class 和 style 除外),并且可以通过 vbind="$attrs" 传入内部组件——在创建高级别的组件时非常有用。
// child:并未在props中声明foo
<p>{{$attrs.foo}}p>
// parent
<HelloWorld foo="foo"/>
index.vue
<Child2 msg="some msg frpm parent">Child2>
Child2.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>child2h3>
<p>{{$attrs.msg}}p>
div>
template>
$listeners
包含了父作用域中的 (不含 .native 修饰器的) v-on 事件监听器。它可以通过 v-on="$listeners" 传入内部组件——在创建更高层次的组件时非常有用。
完整代码
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>组件通信h2>
<Child2 msg="some msg frpm parent" @click="onClick">Child2>
div>
template>
<script>
import Child2 from "@/components/communication/Child2";
export default {
components:{
Child2
},
methods:{
onClick(){
console.log('来自父组件的回调函数的处理',this);//this指的是老爹
}
}
};
script>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Child2.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3 v-on="$listeners">child2h3>
div>
template>
1.8 refs
获取子节点引用
// parent
<HelloWorld ref="hw"/>
<script>
mounted() {
this.$refs.hw.xx = 'xxx'
}
script>
1.9 provide/inject
主要在开发高阶插件/组件库时使用。并不推荐用于普通应用程序代码中。
能够实现祖先和后代之间传值。— 跨层级
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>组件通信h2>
<Child2>Child2>
div>
template>
<script>
import Child2 from "@/components/communication/Child2";
export default {
provide() {
return {
foo: "fooooooo",
};
},
components: {
Child2,
},
};
script>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Child2.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>child2h3>
<p>{{foo}}p>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
inject: ["foo"],
};
script>
二、插槽
插槽语法是Vue 实现的内容分发 API,用于复合组件开发。该技术在通用组件库开发中有大量应用。
2.1 匿名插槽
// comp1 子组件
<div>
<slot>slot> //占位
div>
// parent
<comp>hellocomp>
完整代码
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>插槽h2>
<Layout2>
<template>匿名插槽template>
Layout2>
div>
template>
<script>
import Layout2 from "./Layout2.vue";
export default {
components: {
Layout2
},
};
script>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Layout2.vue
<template>
<div>
<div class="body">
<slot>slot>
div>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
};
script>
<style scoped>
.body {
display: flex;
background-color: rgb(144, 250, 134);
min-height: 100px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
style>
2.2 具名插槽
将内容分发到子组件指定位置
// comp2
<div>
<slot name="content">slot> //name的值对应的是 v-slot: 后面的值
div>
// parent
<Comp2>
<template v-slot:content>内容...template> //template 模板
Comp2>
完整代码
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>插槽h2>
<Layout2>
<template v-slot:header>具名插槽template>
Layout2>
div>
template>
<script>
import Layout2 from "./Layout2.vue";
export default {
components: {
Layout2
},
};
script>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Layout2.vue
<template>
<div>
<div class="header">
<slot name="header">slot>
div>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
};
script>
<style scoped>
.header {
background-color: rgb(252, 175, 175);
}
style>
2.3 作用域插槽
分发内容要用到子组件中的数据
怎么区分具名插槽、作用域插槽
在声明的template里面的数据,
来自当前的父元素,父组件
还是来自于子组件
// comp3
<div>
<slot :foo="foo">slot>
div>
// parent
<Comp3>
<template v-slot:default="slotProps">
来自子组件数据:{{slotProps.foo}}
template>
Comp3>
完整代码
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>插槽h2>
<Layout2>
<template v-slot:footer="{fc}">{{fc}}template> //v-slot 后面又赋了值,就说明需要的值来自子组件
<template v-slot:footer="ctx">{{ctx.fc}}template> //ctx 上下文 子组件传出来多个参的时候
Layout2>
div>
template>
<script>
import Layout2 from "./Layout2.vue";
export default {
components: {
Layout2
},
};
script>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Layout2.vue
<template>
<div>
<div class="footer">
<slot name="footer" :fc="footerContent" abc >slot> //将footerContent的值传出去,值是fc 可以传多个参
div>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
remark: [ //名言警句
'好好学习,天天向上',
'学习永远不晚',
'学习知识要善于思考,思考,再思考',
'学习的敌人是自己的满足,要认真学习一点东西,必须从不自满开始',
'构成我们学习最大障碍的是已知的东西,而不是未知的东西',
'在今天和明天之间,有一段很长的时间;趁你还有精神的时候,学习迅速办事',
'三人行必有我师焉;择其善者而从之,其不善者而改之'
]
}
},
computed: {
footerContent() {
return this.remark[new Date().getDay() - 1]
}
},
};
script>
<style scoped>
.footer {
background-color: rgb(114, 116, 255);
}
style>
三、组件化实战
3.1 通用表单组件
收集数据、校验数据并提交。
需求分析
-
实现KForm
- 指定数据、校验规则. KformItem
- 执行校验
- 显示错误信息 KInput
- 维护数据
最终效果:Element表单
范例代码查看components/form/ElementTest.vue
完整代码
npm i element-ui -S
---------------------------------------------------------------------
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import './plugins/element.js'
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
---------------------------------------------------------------------
/plugins/element.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Element from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css'
Vue.use(Element)
---------------------------------------------------------------------
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<ElementTest>ElementTest>
div>
template>
<script>
import ElementTest from './ElementTest';
export default {
components: {
ElementTest,
},
};
script>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
ElementTest.vue
<template>
<div>
<el-form
:model="userInfo"
:rules="rules"
ref="loginForm"
>
<el-form-item label="用户名" prop="name">
<el-input v-model="userInfo.name">el-input>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="password">
<el-input v-model="userInfo.password" type="password">el-input>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button @click="login">登录el-button>
el-form-item>
el-form>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
userInfo: {
name: "",
password: ""
},
rules: {
name: [
{ required: true, message: "请输入用户名称" }
],
password: [
{ required: true, message: "请选择活动区域", trigger: "change" },
],
},
};
},
methods: {
submitForm(formName) {
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
alert("submit!");
} else {
console.log("error submit!!");
return false;
}
});
},
resetForm(formName) {
this.$refs[formName].resetFields();
},
},
};
script>
3.2 实现KInput 自定义组件的双向绑定
3.2.1 创建components/form/KInput.vue
<template>
<div>
<input :type="type" :value="value" @input="onInput">
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
value: {
type: String,
default: ''
},
type:{
type: String,
default: 'text'
}
},
methods: {
onInput(e) {
//派发一个input事件即可
this.$emit('input',e.target.value);
}
},
}
script>
3.2.2 使用KInput
创建components/form/index.vue,添加如下代码:
<template>
<div>
<KInput v-model="userInfo.username">KInput>
{{userInfo.username}}
div>
template>
<script>
// import ElementTest from './ElementTest';
import KInput from './KInput'
export default {
components: {
// ElementTest,
KInput
},
data() {
return {
userInfo: {
username: "tom",
password: ""
},
rules: {
name: [
{ required: true, message: "请输入用户名称" }
],
password: [
{ required: true, message: "请选择活动区域", trigger: "change" },
],
},
};
},
};
script>
3.3 实现KFormItem
3.3.1 创建components/form/KFormItem.vue
<template>
<div>
<label v-if="label">{{ label }}label>
<slot>slot>
<p v-if="error">{{ error }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
error: "", //error为空说明校验通过
};
},
props: {
label: {
type: String,
default: "",
},
},
};
script>
3.3.2 components/form/index.vue,添加基础代码:
<template>
<div>
<KformItem label="用户名">
<KInput v-model="userInfo.username">KInput>
KformItem>
<KformItem label="密码">
<KInput v-model="userInfo.password" type="password">KInput>
KformItem>
div>
template>
<script>
// import ElementTest from './ElementTest';
import KInput from "./KInput";
import KformItem from "./KformItem";
export default {
components: {
// ElementTest,
KInput,
KformItem,
},
data() {
return {
userInfo: {
username: "tom",
password: "",
},
rules: {
name: [{ required: true, message: "请输入用户名称" }],
password: [
{ required: true, message: "请选择活动区域", trigger: "change" },
],
},
};
},
};
script>
3.4 实现KForm
3.4.1 创建components/form/KForm .vue
<template>
<div>
<slot>slot>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
provide() {
return {
form: this,
};
},
props: {
model: {
type: Object,
required: true,
},
rules: {
type: Object,
},
},
};
script>
3.4.2 使用KForm
components/form/index.vue,添加基础代码:
<template>
<div>
<KForm :model="userInfo" :rules="rules">
<KformItem label="用户名">
<KInput v-model="userInfo.username">KInput>
KformItem>
<KformItem label="密码">
<KInput v-model="userInfo.password" type="password">KInput>
KformItem>
KForm>
div>
template>
<script>
// import ElementTest from './ElementTest';
import KInput from "./KInput";
import KformItem from "./KformItem";
import KForm from "./KForm";
export default {
components: {
// ElementTest,
KInput,
KformItem,
KForm,
},
data() {
return {
userInfo: {
username: "tom",
password: "",
},
rules: {
name: [{ required: true, message: "请输入用户名称" }],
password: [
{ required: true, message: "请选择活动区域", trigger: "change" },
],
},
};
},
};
script>
3.5 数据校验
inheritAttrs:false, //设置为false,避免设置到根元素上
index.vue
<KInput v-model="userInfo.username" placeholder="请输入用户名">KInput>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
KInput.vue
<input :type="type" :value="value" @input="onInput" v-bind="$attrs">
<script>
export default {
inheritAttrs:false,//设置weifalse,避免$attrs设置到根元素上,比较干净
}
script>
3.5.1 input通知校验
KInput.vue
onInput(e) {
//派发一个input事件即可
this.$emit('input',e.target.value);
//通知父级执行校验
// this.$emit KInput在KformItem中是slot,是一个占位坑
// $parent指FormItem
this.$parent.$emit('validate');
}
3.5.2 FormItem监听校验通知,获取规则并执行校验
FormItem.vue
mounted() {
//监听 校验
//使用 created,还是 mounted ?
//建议 mounted
//mounted:确定子组件都存在
this.$on("validate", () => {
this.validate();
});
},
methods: {
validate() {
// 获取对应FormItem校验规则
console.log(this.form.rules[this.prop]);
// 获取校验值
console.log(this.form.model[this.prop]);
}
}
3.5.3 安装async-validator 在验证的时候,使用 这个库
npm i async-validator
FormItem.vue
methods: {
validate() {
//获取对应FormItem校验规则
const rules = this.form.rules[this.prop];
// 获取校验值
const value = this.form.model[this.prop];
//校验描述对象 [this.prop] username password
const desc = { [this.prop]: rules }; //校验rules ,为了创建Schema
//创建 Schema 实例 创建校验器
const schema = new Schema(desc);
//validate 方法返回的是promise,可以return出去
// 返回Promise,没有触发catch就说明验证通过
//校验数据源
return schema.validate({ [this.prop]: value }, (errors) => {
if (errors) {
//validation failed
this.error = errors[0].message;
} else {
//校验通过 validation passed
this.error = "";
}
});
-----------start-----------------------------
官网例子:
validator.validate({ name: 'muji' }, (errors, fields) => {
if (errors) {
validation failed, errors is an array of all errors //
fields is an object keyed by field name with an array of //
errors per field //
return handleErrors(errors, fields);
}
validation passed //
});
// PROMISE USAGE
validator.validate({ name: 'muji', age: 16 }).then(() => {
validation passed or without error message //
}).catch(({ errors, fields }) => {
validation passed //
return handleErrors(errors, fields);
});
then(), validation passed //
catch({ errors, fields }), validation failed, //
-----------end-----------------------------
},
},
3.5.4 表单全局验证,为Form提供validate方法
KForm.vue
<script>
methods: {
//这个方法,是有一个回调函数的
validate(cb) {
//1.获取所有的孩子 KformItem
//[resultPromise]
const tasks = this.$children
.filter((item) => item.prop) //过滤掉没有prop属性的item
.map((item) => item.validate());
//统一处理所有的promise结果 Promise.all
//如果then,一定是校验通过
//如果catch,说明校验失败,任何一个失败,都会进入catch
Promise.all(tasks)
.then(() => {
cb(true);
})
.catch(() => {
cb(false);
});
},
},
</script>
---------------------------------------------------------------------
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- KForm -->
<!-- 跨层级传数据 -->
<KForm :model="userInfo" :rules="rules" ref="loginForm">
......
<!-- 提交按钮 -->
<KformItem >
<button @click="login">登录</button>
</KformItem>
</KForm>
</div>
</template>
<script>
......
export default {
......
methods: {
login() {
// loginForm 组件,需要一个全局校验方法: validate
// 接受一个回调函数,返回一个 boolean 值,根据 boolean 去进行操作
this.$refs["loginForm"].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
alert("submit!");
} else {
console.log("error submit!!");
return false;
}
});
}
},
};
</script>
3.6 完整代码
KInput .vue
<template>
<div>
<input :type="type" :value="value" @input="onInput" v-bind="$attrs">
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
inheritAttrs:false,//设置weifalse,避免$attrs设置到根元素上,比较干净
props: {
value: {
type: String,
default: ''
},
type:{
type: String,
default: 'text'
}
},
methods: {
onInput(e) {
//派发一个input事件即可
this.$emit('input',e.target.value);
//通知父级执行校验
// this.$emit KInput在KformItem中是slot,是一个占位坑
// $parent指FormItem
this.$parent.$emit('validate');
}
},
}
script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
style>
KformItem .vue
<template>
<div>
<label v-if="label">{{ label }}label>
<slot>slot>
<p v-if="error" class="error">{{ error }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
// Async-validator 官网
import Schema from "async-validator"; //Schema 名称自定义
export default {
inject: ["form"], //form 表单的组件实例
data() {
return {
error: "", //error为空说明校验通过
};
},
props: {
label: {
type: String,
default: "",
},
prop: {
type: String,
},
},
mounted() {
//监听 校验
//使用 created,还是 mounted ?
//建议 mounted
//mounted:确定子组件多存在
this.$on("validate", () => {
this.validate();
});
},
methods: {
validate() {
//当前的规则
const rules = this.form.rules[this.prop];
//当前的值
const value = this.form.model[this.prop];
//校验的描述对象 [this.prop] username password
const desc = { [this.prop]: rules }; //校验规则,创建Schema
//创建 Schema 实例
const schema = new Schema(desc);
//validate 方法返回的是promise,可以return出去
//校验数据源
return schema.validate({ [this.prop]: value }, (errors) => {
if (errors) {
//validation failed
this.error = errors[0].message;
} else {
//校验通过 validation passed
this.error = "";
}
});
},
},
};
script>
<style scoped>
.error {
color: red;
}
style>
KForm.vue
<template>
<div>
<slot>slot>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
provide() {
return {
form: this,
};
},
props: {
model: {
type: Object,
required: true,
},
rules: {
type: Object,
},
},
methods: {
//这个方法,是有一个回调函数的
validate(cb) {
//1.获取所有的孩子 KformItem
//[resultPromise]
const tasks = this.$children
.filter((item) => item.prop) //过滤掉没有prop属性的item
.map((item) => item.validate());
//统一处理所有的promise结果 Promise.all
//如果then,一定是校验通过
//如果catch,说明校验失败,任何一个失败,都会进入catch
Promise.all(tasks)
.then(() => {
cb(true);
})
.catch(() => {
cb(false);
});
},
},
};
script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>style>
index.vue
<template>
<div>
<KForm :model="userInfo" :rules="rules" ref="loginForm">
<KformItem label="用户名" prop="username">
<KInput v-model="userInfo.username" placeholder="请输入用户名">KInput>
KformItem>
<KformItem label="密码" prop="password">
<KInput v-model="userInfo.password" type="password">KInput>
KformItem>
<KformItem >
<button @click="login">登录button>
KformItem>
KForm>
div>
template>
<script>
// import ElementTest from './ElementTest';
import KInput from "./KInput";
import KformItem from "./KformItem";
import KForm from "./KForm";
export default {
components: {
// ElementTest,
KInput,
KformItem,
KForm,
},
data() {
return {
userInfo: {
username: "",
password: "",
},
rules: {
username: [{ required: true, message: "请输入用户名称" }],
password: [
{ required: true, message: "请选择活动区域", trigger: "change" },
],
},
};
},
methods: {
login() {
// loginForm 组件,需要一个全局校验方法: validate
// 接受一个回调函数,返回一个 boolean 值,根据 boolean 去进行操作
this.$refs["loginForm"].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
alert("submit!");
} else {
console.log("error submit!!");
return false;
}
});
}
},
};
script>
四、实现弹窗组件
弹窗这类组件的特点是它们在当前vue实例之外独立存在,通常挂载于body;它们是通过JS动态创建 的,不需要在任何组件中声明。常见使用姿势:
this.$create(Notice, {
title: '社会你杨哥喊你来搬砖',
message: '提示信息',
duration: 1000
}).show();
4.1 create函数
新建src/utils/create.js
create.js
import Vue from 'vue'
//改成插件
//创建函数接收要创建组件定义
/**
*
* @param {*} Component 组件
* @param {*} props 参数
* {
title: '社会你杨哥喊你来搬砖',
message: '提示信息',
duration: 1000
}
*/
function create(Component, props) {
//Helloorld 是构造函数吗? 不是,export出去的是一个对象,只是一个配置对象,需要变成构造函数
//Component 变成 构造函数
//组件构造函数如何获取?
//1. Vue.extend()
//2. render
const vm = new Vue({
// h 是createElement,返回VNode 是虚拟dom
// 需要挂载才能变成真实dom
render: h => h(Component, { props }),
}).$mount();//不指定宿主元素,则会创建真实dom,不会做dom的追加操作 里面不可以写body,会将body中的其他内容全部覆盖
//可以通过 vm.$el 获取 真实dom
document.body.appendChild(vm.$el); //将真实的dom追加到body
const comp = vm.$children[0];//在当前的vue里面,只管了一个组件,就是 Component
//销毁自己
comp.remove = function(){
document.body.removeChild(vm.$el);
vm.$destroy();//实例销毁
}
//返回组件实例
return comp;
}
export default create;
另一种创建组件实例的方式: Vue.extend(Component)
4.2 通知组件
建通知组件,src/components/Notice.vue
Notice.vue
<template>
<div class="box" v-if="isShow">
<h3>{{title}}h3>
<p class="box-content">{{message}}p>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
title: {
type: String,
default: ""
},
message: {
type: String,
default: ""
},
duration: {
type: Number,
default: 1000
}
},
data() {
return {
isShow: false
};
},
methods: {
show() {
this.isShow = true;
setTimeout(this.hide, this.duration);
},
hide() {
this.isShow = false;
// 清除自己
this.remove();
}
}
};
script>
<style>
.box {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
top: 16px;
left: 0;
text-align: center;
pointer-events: none;
background-color: #fff;
border: grey 3px solid;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.box-content {
width: 200px;
margin: 10px auto;
font-size: 14px;
padding: 8px 16px;
background: #fff;
border-radius: 3px;
margin-bottom: 8px;
}
style>
4.2 使用create api
测试,components/form/index.vue
components/form/index.vue
<script>
import Notice from "@/components/Notice.vue";
export default {
methods: {
login() {
// loginForm 组件,需要一个全局校验方法: validate
// 接受一个回调函数,返回一个 boolean 值,根据 boolean 去进行操作
this.$refs["loginForm"].validate((valid) => {
const notice = this.$create(Notice, {
title: "提示",
message: valid ? "请求登录!" : "校验失败!",
duration: 2000,
});
notice.show();
// if (valid) {
// alert("submit!");
// } else {
// console.log("error submit!!");
// return false;
// }
});
},
},
};
</script>
五、遗留问题
1. 修正input中$parent写法的问题
1.element的minxins方法
element/src/mixins/emitter.js
function broadcast(componentName, eventName, params) {
this.$children.forEach(child => {
var name = child.$options.componentName;
if (name === componentName) {
child.$emit.apply(child, [eventName].concat(params));
} else {
broadcast.apply(child, [componentName, eventName].concat([params]));
}
});
}
export default {
methods: {
dispatch(componentName, eventName, params) {
var parent = this.$parent || this.$root;
var name = parent.$options.componentName;
while (parent && (!name || name !== componentName)) {
parent = parent.$parent;
if (parent) {
name = parent.$options.componentName;
}
}
if (parent) {
parent.$emit.apply(parent, [eventName].concat(params));
}
},
broadcast(componentName, eventName, params) {
broadcast.call(this, componentName, eventName, params);
}
}
};
其实这里的broadcast与dispatch
实现了一个定向的多层级父子组件间的事件广播及事件派发功能。
完成多层级分发对应事件的组件间通信功能。
2.input组件中的使用

element/packages/input/src/input.vue
this.dispatch('ElFormItem', 'el.form.blur', [this.value]);
element/packages/form/src/form-item.vue
this.$on('el.form.change', this.onFieldChange);
2. 使用Vue.extend方式实现create方法
const Ctor = Vue.extend(Component)
const comp = new Ctor({propsData: props})
comp.$mount();
document.body.appendChild(comp.$el)
comp.remove = () => {
// 移除dom
document.body.removeChild(comp.$el)
// 销毁组件
comp.$destroy();
}
3. 使用插件进一步封装便于使用,create.js
create.js
import Vue from 'vue'
改成插件
1.引入Notice组件
import Notice from '@/components/Notice.vue';
//创建函数接收要创建组件定义
/**
*
* @param {*} Component 组件
* @param {*} props 参数
* {
title: '社会你杨哥喊你来搬砖',
message: '提示信息',
duration: 1000
}
*/
function create(Component, props) {
//Hellwoorld 是构造函数吗? 不是,export出去的是一个对象,只是一个配置对象,需要变成构造函数
//Component 变成 构造函数
//组件构造函数如何获取?
//1. Vue.extend()
//2. render
const vm = new Vue({
// h 是createElement,返回VNode 是虚拟dom
// 需要挂载才能变成真实dom
render: h => h(Component, { props }),
}).$mount();//不指定宿主元素,则会创建真实dom,不会做dom的追加操作 里面不可以写body,会将body中的其他内容全部覆盖
//可以通过 vm.$el 获取 真实dom
document.body.appendChild(vm.$el); //将真实的dom追加到body
const comp = vm.$children[0];//在当前的vue里面,只管了一个组件,就是 Component
//销毁自己
comp.remove = function(){
document.body.removeChild(vm.$el);
vm.$destroy();//实例销毁
}
//返回组件实例
return comp;
}
// export default create;
改成插件
2.改成install
export default {
install(Vue){
Vue.prototype.$notice = function(options){
return create(Notice,options);
}
}
};
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import './plugins/element.js'
import create from './utils/create'
//----------------------使用弹窗插件start-----------------------------------------
1.注释
//弹窗----原来的
// Vue.prototype.$create = create;
2.注册插件
Vue.use(create);
3.在index.vue使用插件
3.1原来的 导出的是create方法
import Notice from "@/components/Notice.vue";
const notice = this.$create(Notice, {
title: "提示",
message: valid ? "请求登录!" : "校验失败!",
duration: 2000,
});
3.2使用插件 现在导出的是插件,一个对象
不用引入Notice : import Notice from "@/components/Notice.vue"; 注释
const notice = this.$notice({
title: "提示",
message: valid ? "请求登录!" : "校验失败!",
duration: 2000,
});
//------------------------使用弹窗插件end---------------------------------------
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app');
六、element框架form组件源码分析以及dispatch原理
6.1 form和form-item组件
先给出一个官网使用代码
<template>
<el-form :model="ruleForm" status-icon :rules="rules" ref="ruleForm" label-width="100px" class="demo-ruleForm">
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="pass">
<el-input type="password" v-model="ruleForm.pass" autocomplete="off">el-input>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="确认密码" prop="checkPass">
<el-input type="password" v-model="ruleForm.checkPass" autocomplete="off">el-input>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="年龄" prop="age">
<el-input v-model.number="ruleForm.age">el-input>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm('ruleForm')">提交el-button>
<el-button @click="resetForm('ruleForm')">重置el-button>
el-form-item>
el-form>
template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
var checkAge = (rule, value, callback) => {
if (!value) {
return callback(new Error('年龄不能为空'));
}
setTimeout(() => {
if (!Number.isInteger(value)) {
callback(new Error('请输入数字值'));
} else {
if (value < 18) {
callback(new Error('必须年满18岁'));
} else {
callback();
}
}
}, 1000);
};
var validatePass = (rule, value, callback) => {
if (value === '') {
callback(new Error('请输入密码'));
} else {
if (this.ruleForm.checkPass !== '') {
this.$refs.ruleForm.validateField('checkPass');
}
callback();
}
};
var validatePass2 = (rule, value, callback) => {
if (value === '') {
callback(new Error('请再次输入密码'));
} else if (value !== this.ruleForm.pass) {
callback(new Error('两次输入密码不一致!'));
} else {
callback();
}
};
return {
ruleForm: {
pass: '',
checkPass: '',
age: ''
},
rules: {
pass: [
{ validator: validatePass, trigger: 'blur' }
],
checkPass: [
{ validator: validatePass2, trigger: 'blur' }
],
age: [
{ validator: checkAge, trigger: 'blur' }
]
}
};
},
methods: {
submitForm(formName) {
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
alert('submit!');
} else {
console.log('error submit!!');
return false;
}
});
},
resetForm(formName) {
this.$refs[formName].resetFields();
}
}
}
script>
- 父组件先执行created,但是没有挂载
- 接着子组件执行created,然后mounted。
- 父组件接着mounted
6.1.1 form组件在created时做了什么?
做了两件事:
created() {
this.$on('el.form.addField', (field) => {
if (field) {
this.fields.push(field);
}
});
/* istanbul ignore next */
this.$on('el.form.removeField', (field) => {
if (field.prop) { // 表单form-item的属性
this.fields.splice(this.fields.indexOf(field), 1);
}
});
}
组件o n 监 听 当 前 实 例 上 的 自 定 义 事 件 。 事件可以由‘vm.emit` 触发。回调函数会接收所有传入事件触发函数的额外参数。
所以两件事:
-
监听el.form.addField自定义事件,如果这个事件被触发,就将field(子组件form-item实例对象)添加到组件data的fields数组中
-
监听el.form.removeField自定义事件,如果事件被触发,就执行函数,函数中判断如果form-item实例对象还有prop属性。form-item的props中prop,这个属性在element官网中的可以查询到。prop:表单域 model 字段,在使用 validate、resetFields方法的情况下,该属性是必填的。如果在form-item组件销毁的时候会触发(比如v-if为false)
form-item组件中的beforeDestory中做的事情。
beforeDestroy() {
this.dispatch('ElForm', 'el.form.removeField', [this]);
}
这里有个dispatch,是element的自己实现的,据说的是vue1.x中dispatch的阉割版。
具体dispatch怎么实现的,请看本文中的element的dispatch实现原理。
6.1.2 form-item组件在mounted组件中做了什么?
form-item在created没有操作,但是在mounted做了些操作
mounted() {
if (this.prop) {
this.dispatch('ElForm', 'el.form.addField', [this]);
let initialValue = this.fieldValue;
if (Array.isArray(initialValue)) {
initialValue = [].concat(initialValue);
}
Object.defineProperty(this, 'initialValue', {
value: initialValue
});
this.addValidateEvents();
}
}
- 如果这个组件有props中的prop属性有值,那么dispatch到父组件触发el.form.addField事件。这个addField,上面有提到过,是将子组件实例对象form-item添加到form组件实例对象的fields数组中。
待补全
6.2 element中emitter.js
6.2.1 dispatch
使用过vuex的肯定知道vuex中也有dispatch, vuex中的disaptch是对action的派发,进入到mutation的变更。
dispatch(componentName, eventName, params) {
var parent = this.$parent || this.$root; //找到组件的父组件,或者这个组件本就是根组件。
var name = parent.$options.componentName;//获取到组件的componentName的值
while (parent && (!name || name !== componentName)) {
//只要parent为true,并且有name为false,或者name和componentName不全等,就一直循环。
parent = parent.$parent; //获取上一层组件实例对象
if (parent) {//如果上层组件存在,重新将上层组件的componentName的值赋值给他
name = parent.$options.componentName;
}
}
if (parent) {
parent.$emit.apply(parent, [eventName].concat(params));
}
}
单从dispatch的函数参数名中就可以看出是是对事件的派发,函数中使用vm.$emit触发事件。其中的componentName是element组件自定义的一个属性.
//element的form组件
export default {
name: 'ElForm',
componentName: 'ElForm'
//...
}
我们先看一个调用dispatch方法的例子
//form-item中mounted执行了这句话。this是form-item实例对象
this.dispatch('ElForm', 'el.form.addField', [this]);
那么这个dispatch一共做了两件事:
- 找到这个组件指定的父组件
- 使用vm.$emit触发这个父组件的事件(包括自定义事件)
还有就是那个while循环干了啥,为啥要循环:
- 原因就在于你要找的父组件不是直接父组件,如:
<el-form >
<el-row>
<el-col :span="24">
<el-form-item prop="checkPass">
<el-tag>标签一el-tag>
el-form-item>
el-col>
el-row>
el-form>
如上,我el-form-item组件要触发el-form中的自定义事件,但是el-form不是直接父组件。所有while循环做了一件事情,就是层层往上找,直到找到这个父组件或者直到根组件也没有找到想要的,那么这个parent就是undefined。undefined也就不会执行下面的$emit了。
七、Vue动态创建组件实例
Vue动态创建组件实例并挂载到body
方式一
import Vue from 'vue'
/**
* @param Component 组件实例的选项对象
* @param props 组件实例中的prop
*/
export function create(Component, props) {
const comp = new (Vue.extend(Component))({ propsData: props }).$mount()
document.body.appendChild(comp.$el)
comp.remove = () => {
document.body.removeChild(comp.$el)
comp.$destroy()
}
return comp
}
方式二
import Vue from 'vue'
export function create(Component, props) {
// 借鸡生蛋new Vue({render() {}}),在render中把Component作为根组件
const vm = new Vue({
// h是createElement函数,它可以返回虚拟dom
render(h) {
console.log(h(Component,{ props }));
// 将Component作为根组件渲染出来
// h(标签名称或组件配置对象,传递属性、事件等,孩子元素)
return h(Component, { props })
}
}).$mount() // 挂载是为了把虚拟dom变成真实dom
// 不挂载就没有真实dom
// 手动追加至body
// 挂载之后$el可以访问到真实dom
document.body.appendChild(vm.$el)
console.log(vm.$children);
// 实例
const comp = vm.$children[0]
// 淘汰机制
comp.remove = () => {
// 删除dom
document.body.removeChild(vm.$el)
// 销毁组件
vm.$destroy()
}
// 返回Component组件实例
return comp
}
使用
A组件(要动态创建的组件)
<template>
<div class="a">
<h2>{{ title }}h2>
<p>{{ data }}p>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
title: {
type: String,
default: "hello world!"
},
message: {
type: String,
default: "o(∩_∩)o 哈哈"
},
duration: {
type: Number,
default: 1000
}
},
data() {
return {
data: "我是a组件",
};
},
created() {
let num = 1
const timer = setInterval(() => {
this.data = num++
}, this.duration)
this.$once("hook: beforeDestroy", () => clearInterval(timer))
}
};
script>
<style>
.a {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
top: 16px;
left: 0;
text-align: center;
pointer-events: none;
background-color: #fff;
border: grey 3px solid;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
style>
B组件(操作动态创建组件的地方)
<template>
<div class="b">
<button @click="createA">创建button>
div>
template>
<script>
import A from "@/components/A.vue"
import { create } from "@/utils/create.js"
export default {
components: {
A,
},
methods: {
createA() {
// 创建A组件,并挂载到body上
create(A, { title: "vue", message: "么么哒" })
}
},
};
script>