用Pytorch从零复现YOLOv4网络推断部分 手撕代码#2
Ⅰ.实现目标
YOLO算法是目标检测算法中的经典算法,在two-stage目标检测领域独占鳌头。而YOLO算法的核心思想也是各大厂面试的考核点之一,理解从一代YOLO到第五代YOLO的技术演变对读者亦有颇大帮助。
此处复现的是YOLOv4,从零仅借助pytorch相关接口复现网络主体部分(不涉及训练部分)。适合读者练手提高代码能力。
文章目录
-
- Ⅰ.实现目标
- Ⅱ.开始代码寿司
-
- 一、CSPDarknet53实现
-
- ①Mish激活函数
- ②CBM
- ③ResBlock
- ④CSPX模块
- ⑤组合起来!
- ⑥验证结构
- 二、YoloBody实现
-
- ①CBL
- ②SPP组件
- ③CBL+UPSAMPLE
- ④五卷积
- ⑤三卷积
- ⑥输出头
- ⑦组合起来!
- ⑧验证结构
*参考资料:
YOLO-V4基于PyTorch从零复现(主要代码来源)
江大白讲解YOLO系列博文(主要图片来源)
Ⅱ.开始代码寿司
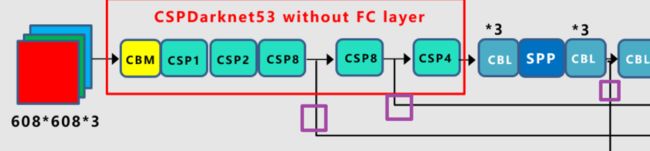
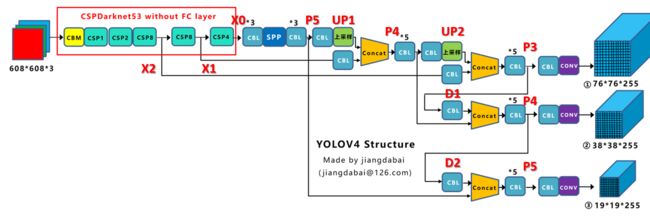
首先对整个模型有个大概的认知,此处借用江大白的网络结构图。
一、CSPDarknet53实现
具体而言就是Backbone前面的一部分。
①Mish激活函数
很简单,根据公式写即可。
Mish = x*tanh(ln(1+e^x))
class Mish(nn.Module):
'''
MISH activation function
'''
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x):
return x * torch.tanh(F.softplus(x))
②CBM
具体而言就是Conv + BN + Mish。
class CBM(nn.Module):
'''
CBM
CONV + BATCHNORM + MISH
'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1):
super().__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.activation = Mish()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
x = self.activation(x)
return x
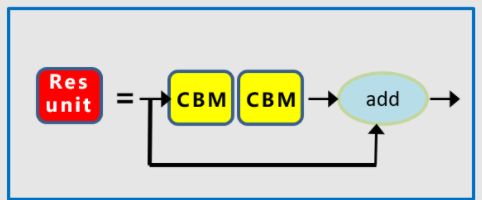
③ResBlock
仔细看模型会发现部分resblock会存在hidden_channels,故引入此参数,无hidden_channels的默认其值为channels,即无中间隐藏通道变换。
class Resblock(nn.Module):
'''
Resblock
CBM + CBM + SKIP CONNET
'''
def __init__(self, channels, hidden_channels=None):
super().__init__()
if hidden_channels is None:
hidden_channels = channels
self.block = nn.Sequential(
CBM(channels, hidden_channels, 1),
CBM(hidden_channels, channels, 3),
)
def forward(self, x):
return x + self.block(x)
④CSPX模块
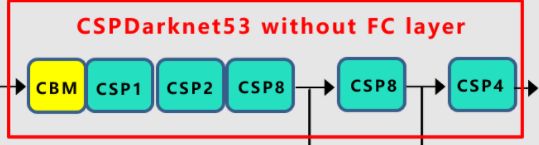
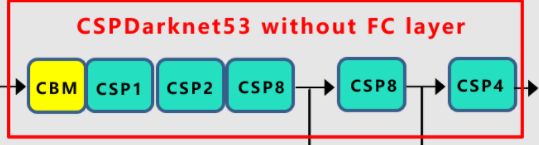
现在知道为何CSPX模块要放到最后来实现了吧,就是因为CSPX模块是在CBM和Resblock的基础上拼接构建的。
我们再回到yolov4的Darknet看看,其中CSP1表示其中包含一个红色的残差组件,CSP2则表示含有两个,以此类推。很明显,我们要将其设为参数传入,并按照1,2,8,8,4的顺序将其连接起来。
class CSPX(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, num_blocks, first):
super().__init__()
self.downsample_conv = CBM(in_channels, out_channels, 3, stride=2)
if first:
self.split_conv0 = CBM(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
self.split_conv1 = CBM(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
self.blocks_conv = nn.Sequential(
Resblock(channels=out_channels, hidden_channels=out_channels//2),
CBM(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
)
self.concat_conv = CBM(out_channels*2, out_channels, 1)
else:
self.split_conv0 = CBM(out_channels, out_channels//2, 1)
self.split_conv1 = CBM(out_channels, out_channels//2, 1)
self.blocks_conv = nn.Sequential(
*[Resblock(channels=out_channels//2) for _ in range(num_blocks)],
CBM(out_channels//2, out_channels//2, 1)
)
self.concat_conv = CBM(out_channels, out_channels, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.downsample_conv(x)
x0 = self.split_conv0(x)
x1 = self.split_conv1(x)
x1 = self.blocks_conv(x1)
x = torch.cat([x1, x0], dim=1)
x = self.concat_conv(x)
return x
⑤组合起来!
我们再看一眼结构图,是很简单的线性模型,将我们之前创建好的CBM以及CSPX模块串起来即可。特别注意最后forward需要返回三个输出,分别是第一个CSP8,第二个CSP8以及最后一个CSP4后的输出。
class CSPDarknet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, layers):
super().__init__()
self.inplanes = 32
self.conv1 = CBM(in_channels=3, out_channels=self.inplanes, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
self.feature_channels = [64, 128, 256, 512, 1024]
self.stages = nn.ModuleList([
CSPX(self.inplanes, self.feature_channels[0], layers[0], first=True),
CSPX(self.feature_channels[0], self.feature_channels[1], layers[1], first=False),
CSPX(self.feature_channels[1], self.feature_channels[2], layers[2], first=False),
CSPX(self.feature_channels[2], self.feature_channels[3], layers[3], first=False),
CSPX(self.feature_channels[3], self.feature_channels[4], layers[4], first=False)
])
self.num_features = 1
# weight initialize
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.stages[0](x)
x = self.stages[1](x)
out3 = self.stages[2](x)
out4 = self.stages[3](out3)
out5 = self.stages[4](out4)
return out3, out4, out5
⑥验证结构
当我们完整的按照以上1到5部完成构建后如何确保我们自己构建的模型结构正确呢?这里通过与权重模型进行维度检索匹配来检查,若维度匹配上了说明我们构建无误,反之有误。
其中检测权重模型方法如下:
def load_model_pth(model, pth):
print('Loading weights into state dict, name: %s'%(pth))
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model_dict = model.state_dict()
pretrained_dict = torch.load(pth, map_location=device)
matched_dict = {}
for k, v in model_dict.items():
if k.find('backbone') == -1:
key = 'backbone.'+k
if np.shape(pretrained_dict[key]) == np.shape(v):
matched_dict[k] = v
for key in matched_dict:
print('pretrained items:', key)
print('%d layers matched, %d layers miss'%(len(matched_dict.keys()), len(model_dict)-len(matched_dict.keys())))
model_dict.update(matched_dict)
model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
print('Finished!')
return model
def darknet53(pretrained):
model = CSPDarkNet([1, 2, 8, 8, 4])
if pretrained:
load_model_pth(model, pretrained)
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
backbone = darknet53('pth/yolo4_weights.pth')
二、YoloBody实现
简而言之,这一步就是要实现除了红色框第一步已经实现外的结构。并最后得到三个输出
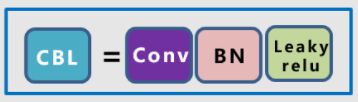
①CBL
具体而言就是Conv + BN + Leakyrelu,因为是很简单的线性关系,所以直接用nn.Sequantial即可
def CBL(filter_in, filter_out, kernel_size, stride=1):
'''
CBL
Conv + BN + Leakyrelu
'''
pad = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 if kernel_size else 0
return nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("conv", nn.Conv2d(filter_in, filter_out, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=pad, bias=False)),
("bn", nn.BatchNorm2d(filter_out)),
("relu", nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)),
]))
②SPP组件
具体而言就是三个Maxpool接一个skip connect,concat后为结果,这里需要注意的是三个Maxpool的尺寸并不一样,从上至下依次是13,9,5。详情见下图
注意代码中的maxpools[::-1]为取从后向前(相反)的元素。
class SPP(nn.Module):
'''
SPP
Concat[ n * Maxpool + direct ]
'''
def __init__(self, pool_sizes=[5, 9, 13]):
super(SPP, self).__init__()
self.maxpools = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(pool_size, 1, pool_size // 2) for pool_size in pool_sizes])
def forward(self, x):
features = [maxpool(x) for maxpool in self.maxpools[::-1]]
features = torch.cat(features + [x], dim=1)
return features
③CBL+UPSAMPLE
class CBL_UP(nn.Module):
'''
CBL + Upsample
'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(CBL_UP, self).__init__()
self.upsample = nn.Sequential(
CBL(in_channels, out_channels, 1),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.upsample(x)
return x
④五卷积
简单的五次卷积,注意输入输出维度的首尾匹配和size1-3-1-3-1的变化。
def make_five_conv(filters_list, in_filters):
'''
Five conv block
'''
m = nn.Sequential(
CBL(in_filters, filters_list[0], 1),
CBL(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 3),
CBL(filters_list[1], filters_list[0], 1),
CBL(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 3),
CBL(filters_list[1], filters_list[0], 1),
)
return m
⑤三卷积
大同小异,同样注意输入输出和size
def make_three_conv(filters_list, in_filters):
'''
Three conv block
'''
m = nn.Sequential(
CBL(in_filters, filters_list[0], 1),
CBL(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 3),
CBL(filters_list[1], filters_list[0], 1),
)
return m
⑥输出头
即主干部分用于输出的三个头,如图紫色框框所画。
def yolo_head(filters_list, in_filters):
'''
Final to get the output
'''
m = nn.Sequential(
CBL(in_filters, filters_list[0], 3),
nn.Conv2d(filters_list[0], filters_list[1], 1),
)
return m
⑦组合起来!
由于主体结构略显复杂,为了方便理解与构建,我们先在结构图上标记几个标志点。
其中输入输出维度需特别注意,根据权重文件中的记录进行匹配。
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
class YoloBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_anchors, num_classes):
super(YoloBody, self).__init__()
self.backbone = darknet53(None)
self.conv1 = make_three_conv([512,1024],1024)
self.SPP = SPP()
self.conv2 = make_three_conv([512,1024],2048)
self.upsample1 = CBL_UP(512,256)
self.conv_for_P4 = CBL(512,256,1)
self.make_five_conv1 = make_five_conv([256, 512],512)
self.upsample2 = CBL_UP(256,128)
self.conv_for_P3 = CBL(256,128,1)
self.make_five_conv2 = make_five_conv([128, 256],256)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
# 4+1+num_classes
final_out_filter2 = num_anchors * (5 + num_classes)
self.yolo_head3 = yolo_head([256, final_out_filter2],128)
self.down_sample1 = CBL(128,256,3,stride=2)
self.make_five_conv3 = make_five_conv([256, 512],512)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
final_out_filter1 = num_anchors * (5 + num_classes)
self.yolo_head2 = yolo_head([512, final_out_filter1],256)
self.down_sample2 = CBL(256,512,3,stride=2)
self.make_five_conv4 = make_five_conv([512, 1024],1024)
# 3*(5+num_classes)=3*(5+20)=3*(4+1+20)=75
final_out_filter0 = num_anchors * (5 + num_classes)
self.yolo_head1 = yolo_head([1024, final_out_filter0],512)
def forward(self, x):
x2, x1, x0 = self.backbone(x)
P5 = self.conv1(x0)
P5 = self.SPP(P5)
P5 = self.conv2(P5)
P5_upsample = self.upsample1(P5)
P4 = self.conv_for_P4(x1)
P4 = torch.cat([P4,P5_upsample],axis=1)
P4 = self.make_five_conv1(P4)
P4_upsample = self.upsample2(P4)
P3 = self.conv_for_P3(x2)
P3 = torch.cat([P3,P4_upsample],axis=1)
P3 = self.make_five_conv2(P3)
P3_downsample = self.down_sample1(P3)
P4 = torch.cat([P3_downsample,P4],axis=1)
P4 = self.make_five_conv3(P4)
P4_downsample = self.down_sample2(P4)
P5 = torch.cat([P4_downsample,P5],axis=1)
P5 = self.make_five_conv4(P5)
out2 = self.yolo_head3(P3)
out1 = self.yolo_head2(P4)
out0 = self.yolo_head1(P5)
return out0, out1, out2
⑧验证结构
这里依旧通过与权重模型进行维度检索匹配来检查,若维度匹配上了说明我们构建无误,反之有误。
其中检测权重模型方法如下:
def load_model_pth_yolov4(model, pth):
print('Loading weights into state dict, name: %s'%(pth))
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model_dict = model.state_dict()
pretrained_dict = torch.load(pth, map_location=device)
matched_dict = {}
for k,v in pretrained_dict.items():
if np.shape(model_dict[k]) == np.shape(v):
matched_dict[k] = v
else:
print('un matched layers: %s'%k)
print(len(model_dict.keys()), len(pretrained_dict.keys()))
print('%d layers matched, %d layers miss'%(len(matched_dict.keys()), len(model_dict)-len(matched_dict.keys())))
model_dict.update(matched_dict)
model.load_state_dict(model_dict)
print('Finished!')
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YoloBody(3, 80)
load_model_pth_yolov4(model, 'pth/yolo4_weights.pth')