【Pytorch->ONNX->NCNN->NCNNfp16->vs编译】Windows NCNN部署
目录
- 前言
- 一、Pytorch2ONNX
-
- 1.1、具体操作
- 1.2、代码
- 二、ONNX2NCNN
-
- 2.1、下载、编译protobuf
- 2.2、下载编译ncnn
- 2.3、生成ncnn模型
- 2.4、优化ncnn
- 三、VS2019编译NCNN
-
- 3.1、VS2019环境配置
- 3.2、使用VS2019编译ncnn权重模型
- 四、结果比较
- 四、v5lites.cpp源码:
- Reference
前言
以YOLOv5为例子,在Windows下将权重文件进行这一整套的转换。
进行转换之前,首先得先安装以下环境:
- Visual Studio 2019 这个b站很多下载安装介绍,就不说了。
- OpenCV 注意它的安装配置:VS中opencv的配置.
- cmake 注意它的安装配置:windows下载安装cmake.
简单说说他们几个的关系:VS是美国微软公司的开发工具包系列产品,在该项目中有提供GCC、编译运行ncnn模型的C++程序的作用;CMake 是一个跨平台的,开源的构建系统,CMake可以通过CMakeLists.txt文件来产生特定平台的标准的构建文件,例如:为Unix平台生成makefiles文件(使用GCC编译),为Windows MSVC生成 projects/workspaces(使用VS IDE编译)或Makefile文件(使用nmake编译);OpenCV是一个基于BSD许可(开源)发行的跨平台计算机视觉和机器学习软件库,学习计算机视觉基本上离不开OpenCV。
一、Pytorch2ONNX
1.1、具体操作
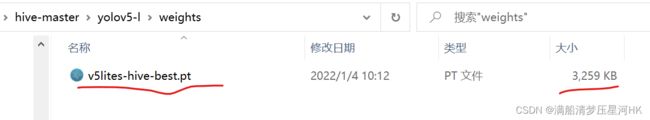
首先,我们对数据集进行训练,得到best的Pytorch权重文件:
在pycharm当前虚拟环境中执行
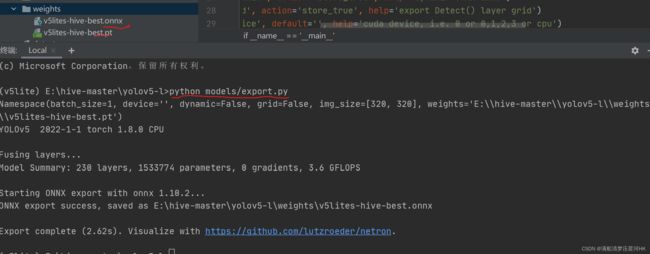
python models/export.py
会在同一个目录下生成onnx权重文件:
注意这里如果在pycharm里执行报如下错:

官网也有人提到过这个问题,应该是pycharm版本的问题,直接在 mini-conda 中执行这个文件即可:

注意export.py中的参数weights、img-size等还需要设置。
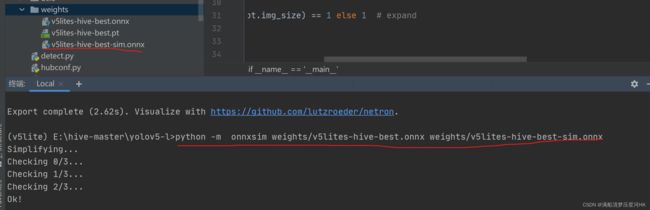
再简化ONNX,在当前环境下:
pip install onnx-simplifier
再执行
python -m onnxsim weights/v5lites-hive-best.onnx weights/v5lites-hive-best-sim.onnx
这一步如果不做,后面ONNX转NCNN可能会报错。
1.2、代码
export.py主要由两部分代码组成:加载模型、模型前传forward + ONNX Export
1、加载模型+forward:
...
model = attempt_load(opt.weights, map_location=device) # load FP32 model
...
y = model(img) # dry run forward
2、ONNX Export:
# 2、ONNX export
try:
import onnx
print('\nStarting ONNX export with onnx %s...' % onnx.__version__)
f = opt.weights.replace('.pt', '.onnx') # filename
# model: 由pt文件中读取的模型
# args: 模型的输入 这里只需要输入图片即可,其他全部为默认值
# f: onnx保存的文件名(地址)
# verbose: 如果指定True,我们将打印出转换的一些信息
# opset_version: ONNX的op(算子)版本
# input_names: 定义输入层名
# output_names: 定义输出层名
# dynamic_axes: 一般可以不用关这三个动态输入输出变量
torch.onnx.export(model, img, f, verbose=False, opset_version=12, input_names=['images'],
output_names=['classes', 'boxes'] if y is None else ['output'],
dynamic_axes={'images': {0: 'batch', 2: 'height', 3: 'width'}, # size(1,3,640,640)
'output': {0: 'batch', 2: 'y', 3: 'x'}} if opt.dynamic else None)
# Checks onnx weight file
onnx_model = onnx.load(f) # load onnx model
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model) # check onnx model
# print(onnx.helper.printable_graph(onnx_model.graph)) # print a human readable model
print('ONNX export success, saved as %s' % f)
except Exception as e:
print('ONNX export failure: %s' % e)
主要是调用了torch.onnx.export函数。这里注意要先在当前虚拟环境中 pip install onnx。
二、ONNX2NCNN
先在windows下搭建ncnn环境:
2.1、下载、编译protobuf
(1)下载 protobuf. 解压后最好和ncnn放在同一个目录。protobuf用于转换模型,protobuf(Google Protocol Buffers)是Google提供一个具有高效的协议数据交换格式工具库(类似Json),Protobuf 提供了C++、java、python语言的支持,提供了windows(proto.exe)和linux平台动态编译生成proto文件对应的源文件。
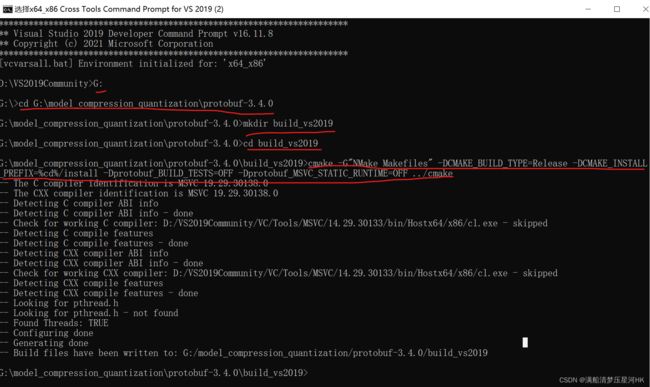
(2)在 vs2019 的本地工具命令提示符下编译 protobuf

指令:
> cd <protobuf-root-dir> #是指protobuf文件夹的根目录
> mkdir build_vs2019
> cd build_vs2019
> cmake -G"NMake Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%cd%/install -Dprotobuf_BUILD_TESTS=OFF -Dprotobuf_MSVC_STATIC_RUNTIME=OFF ../cmake
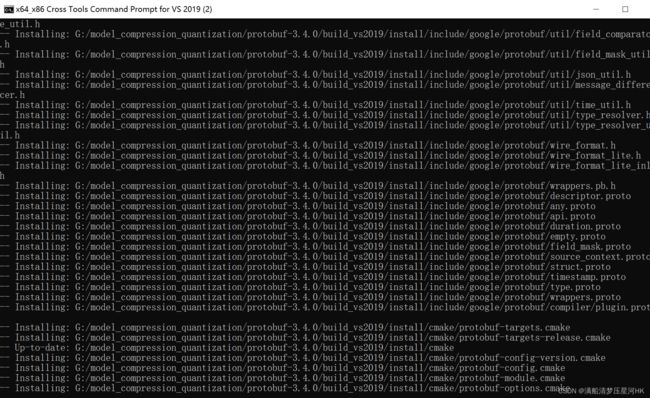
> nmake #编译cmake生成的Makefile文件
> nmake install #安装操作,把生成的文件复制到对应的目录中,并修改环境变量等。
2.2、下载编译ncnn
(1)下载 ncnn ,Git Bash指令如下(不能直接下载,那样就不是git格式的文件了)且这里下载的位置最好和上面的 protobuf 位置一样。
$ git clone https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn.git 或 git clone git://github.com/Tencent/ncnn.git 或 git clone https://gitee.com/Tencent/ncnn.git
# 更换代码版本 注意这里要看你的.cpp需要什么版本的ncnn 版本不对可能检测框会混乱
# cd ncnn
# git reset --hard f6c49523d2359ee598a8ba1793a8e958b52c20ca
$ cd ncnn
$ git submodule update --init # 这里最好是开启执行 很容易报错
(2)在 vs2019 的本地工具命令提示符下编译 ncnn
> cd <ncnn-root-dir> #是指ncnn的根目录
> mkdir build
> cd build
> cmake -G"NMake Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%cd%/install -DProtobuf_INCLUDE_DIR=G:\model_compression_quantization\protobuf-3.4.0\build_vs2019\install\include -DProtobuf_LIBRARIES=G:\model_compression_quantization\protobuf-3.4.0\build_vs2019\install\lib\libprotobuf.lib -DProtobuf_PROTOC_EXECUTABLE=G:\model_compression_quantization\protobuf-3.4.0\build_vs2019\install\bin\protoc.exe -DNCNN_VULKAN=OFF ..
> nmake
> nmake install
步骤和上面的编译 protobuf 步骤完全一样,就是cmake的命令下所有的DProtobuf开头的参数的值(路径)都要改为自己的 protobuf 路径(include、lib、bin三个)。
2.3、生成ncnn模型
将 v5lites-hive-best-sim.onnx 模型复制粘贴到 【ncnn-root-dir】\ build \ tools \ onnx 文件夹下面,如下图: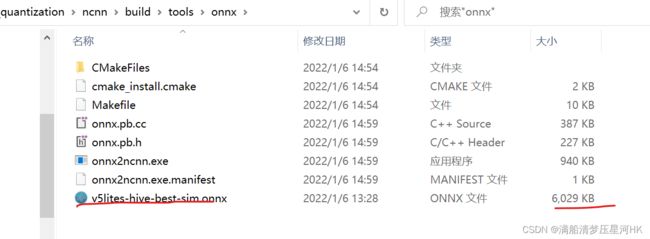
打开cmd,执行指令:
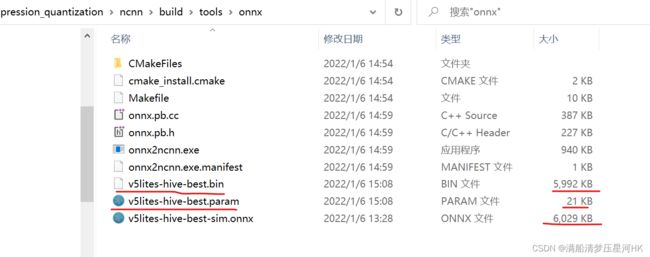
onnx2ncnn v5lites-hive-best-sim.onnx v5lites-hive-best.param v5lites-hive-best.bin
则生成ncnn权重文件,其中 .param 保存是模型的配置结构,.bin 文件保存模型的参数,如下图:
2.4、优化ncnn
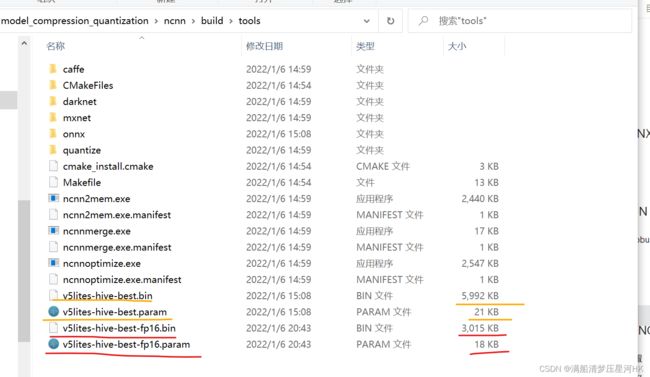
将上一步生成的ncnn模型(.param和.bin)一起从 ncnn/build/tools/onnx 复制到 ncnn/build/tools,并执行指令:
ncnnoptimize v5lites-hive-best.param v5lites-hive-best.bin v5lites-hive-best-fp16.param v5lites-hive-best-fp16.bin 65536
65536生成的是fp16模型。也可以用0、1指令,0指的是fp32 , 1指的是fp16。

生成fp16格式的NCNN模型:
三、VS2019编译NCNN
3.1、VS2019环境配置
(1)打开VS2019 -> 创建新项目 -> 控制台应用 -> 配置新项目 -> 创建,如图:

(2)模式选择 Release 和 x64,如图:
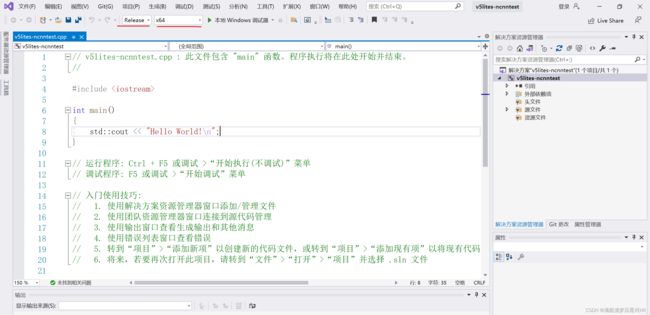
(3)打开属性管理器(没有就视图->其他窗口->属性管理器),找到Release|X64下的Microsoft.CPP.X64.user,如图:

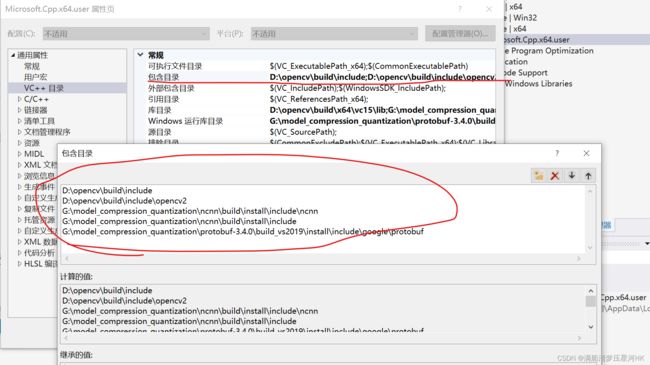
(4)双击Release|X64下的Microsoft.CPP.X64.user打开属性,选择VC++目录,配置包含目录(Include),配置如下属性:
(5)打开库目录(lib),配置如下属性:
(7)打开链接器->输入->附加依赖库,配置如下属性:

至此VS环境配置完毕!
3.2、使用VS2019编译ncnn权重模型
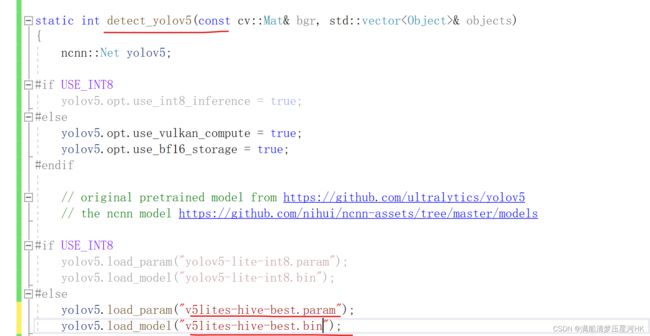
复制cpp_demo/ncnn/v5lite-s.cpp到新建的cpp上,因为源码是linux编程,所以还需要修改一些东西:
(3)记事本打开.param文件,3个Reshape都改为-1,如图:

(4)还是.param文件,3个permute的输出层ID也要和代码中的对齐,如图:
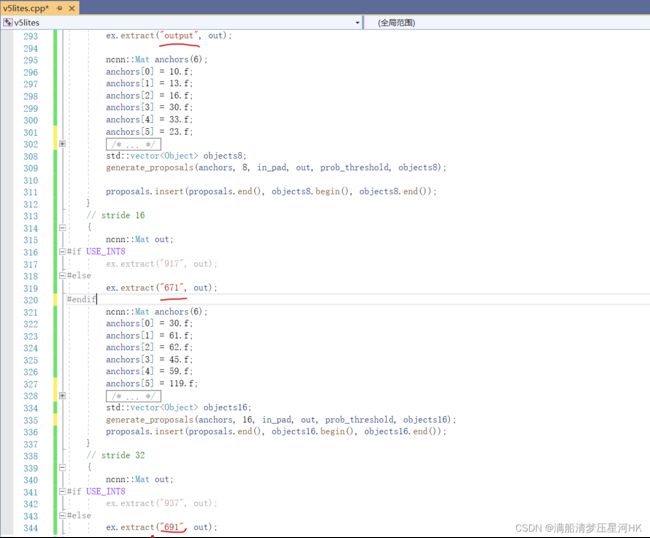
(5)还有就是如果训练改了anchor,需要在.cpp中3个输出层(stride=8、16、32)中改掉anchor,如图:
好了,然后直接按本地Windows调试器即可完成编译(注意上面环境配置了什么就要选什么样的调试器):

运行结果在项目/x64/Release生成.exe可执行文件:
再将exe文件复制到项目/v5lites下,如图有这些文件:
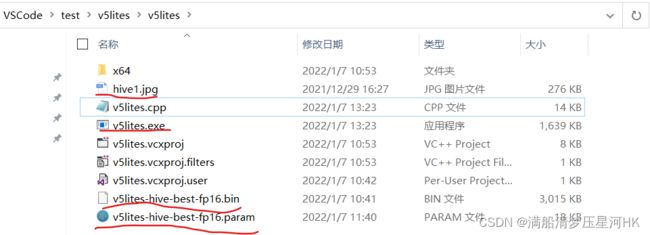
其实只需要上图画线的4个文件,就可以完成部署。
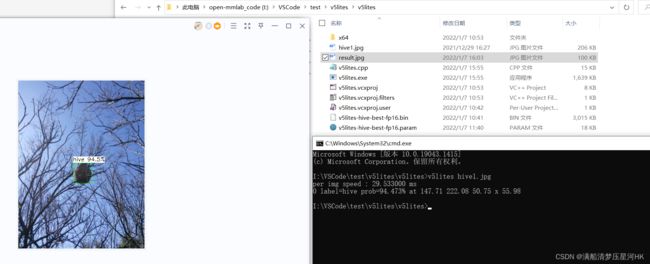
打开cmd,指令
v5lites hive1.jpg
四、结果比较
| ID | Computing backend | System | Input Size | Framework | speed(per img) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | @i5-10500 | Windows | 320x320 | pytorch | 33.5ms |
| 02 | @i5-10500 | Windows | 320x320 | ncnn fp16 | 29.5ms |
性能也会损失一点点(左边pytorch 右边ncnn fp16):


四、v5lites.cpp源码:
// Tencent is pleased to support the open source community by making ncnn available.
//
// Copyright (C) 2020 THL A29 Limited, a Tencent company. All rights reserved.
//
// Licensed under the BSD 3-Clause License (the "License"); you may not use this file except
// in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// https://opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed
// under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR
// CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
// specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
#include "layer.h"
#include "net.h"
#if defined(USE_NCNN_SIMPLEOCV)
#include "simpleocv.h"
#else
#include Reference
CSDN: Windows系统下把PyTorch模型转为ncnn模型流程.
zhihu nihui巨佬: 详细记录u版YOLOv5目标检测ncnn实现.
zhihu pogg大佬: ncnn+opencv+yolov5调用摄像头进行检测.
zhihu pogg大佬: NCNN+Int8+YOLOv4量化模型和实时推理.
CSDN pogg大佬: YOLOv5-Lite:NCNN+Int8部署和量化,树莓派也可实时.
Github pogg大佬: ONNX导出NCNN模型的问题解决+完整int8量化步骤 #53.