李宏毅机器学习-HomeWork_01
Homework_01 主要涉及的用Deep Neural Networks(DNN)处理线性回归问题,更新参数的方法是梯度下降法。
是对COVID-19的结果预测,以下附上GoogleColab代码链接。https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1FzqsOU6NIydOz09FMshp9dDJ14gFJTtC#scrollTo=GrEbUxazQAAZ![]() https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1FzqsOU6NIydOz09FMshp9dDJ14gFJTtC#scrollTo=GrEbUxazQAAZ
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1FzqsOU6NIydOz09FMshp9dDJ14gFJTtC#scrollTo=GrEbUxazQAAZ
Download Data
tr_path = 'covid.train.csv' # path to training data
tt_path = 'covid.test.csv' # path to testing data
!gdown --id '19CCyCgJrUxtvgZF53vnctJiOJ23T5mqF' --output covid.train.csv
!gdown --id '1CE240jLm2npU-tdz81-oVKEF3T2yfT1O' --output covid.test.csvImport Some Package
# PyTorch
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
# For data preprocess
import numpy as np
import csv
import os
# For plotting
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure
myseed = 42069 # set a random seed for reproducibility
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True # 每次返回的卷积算法将会是固定的
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False # 若为True,会让每个卷积层搜索最适合的卷积算法,因而一开始比较费时间,会设置为False
np.random.seed(myseed)
torch.manual_seed(myseed) # 为CPU中设置种子,生成随机数
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(myseed) # 为GPU设置种子,生成随机数Some Utilities
def get_device():
''' Get device (if GPU is available, use GPU) '''
return 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
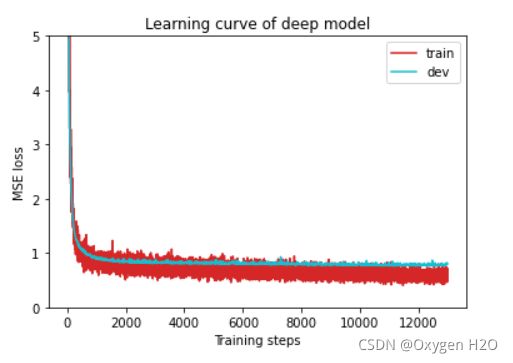
def plot_learning_curve(loss_record, title=''):
''' Plot learning curve of your DNN (train & dev loss) '''
total_steps = len(loss_record['train'])
x_1 = range(total_steps)
x_2 = x_1[::len(loss_record['train']) // len(loss_record['dev'])] # //表示 向下取整 并作为步长
figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.plot(x_1, loss_record['train'], c='tab:red', label='train')
plt.plot(x_2, loss_record['dev'], c='tab:cyan', label='dev')
plt.ylim(0.0, 5.) # 设置y轴数值范围
plt.xlabel('Training steps')
plt.ylabel('MSE loss')
plt.title('Learning curve of {}'.format(title))
plt.legend() # 为图中曲线设置解释性图标
plt.show()
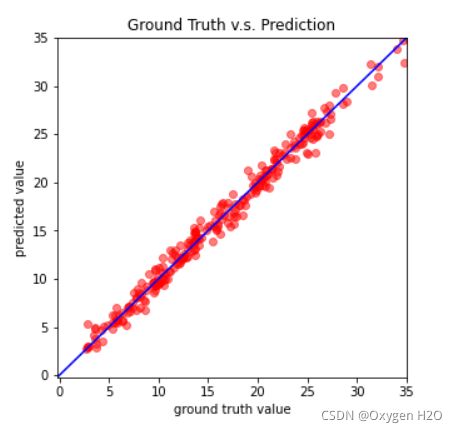
def plot_pred(dv_set, model, device, lim=35., preds=None, targets=None):
''' Plot prediction of your DNN '''
if preds is None or targets is None:
model.eval()
preds, targets = [], []
for x, y in dv_set:
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(x)
preds.append(pred.detach().cpu()) # pred为一个tensor,pred.detach()将Tensor分离,,并将x的require_grad改为False,最终将tensor添加至cpu
targets.append(y.detach().cpu())
preds = torch.cat(preds, dim=0).numpy() # 拼接函数,增加了行,
targets = torch.cat(targets, dim=0).numpy() # 将tensor转换为numpy中的数组
figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.scatter(targets, preds, c='r', alpha=0.5) # 绘制散点图,alpha表示透明度
plt.plot([-0.2, lim], [-0.2, lim], c='b')
plt.xlim(-0.2, lim)
plt.ylim(-0.2, lim)
plt.xlabel('ground truth value')
plt.ylabel('predicted value')
plt.title('Ground Truth v.s. Prediction')
plt.show()# **Preprocess**
We have three kinds of datasets:
* `train`: for training
* `dev`: for validation
* `test`: for testing (w/o target value)
## **Dataset**
The `COVID19Dataset` below does:
* read `.csv` files
* extract features
* split `covid.train.csv` into train/dev sets
* normalize featuresFinishing `TODO` below might make you pass medium baseline.
class COVID19Dataset(Dataset):
''' Dataset for loading and preprocessing the COVID19 dataset '''
def __init__(self,
path,
mode='train',
target_only=False):
self.mode = mode
# Read data into numpy arrays
with open(path, 'r') as fp:
data = list(csv.reader(fp)) #
data = np.array(data[1:])[:, 1:].astype(float)
if not target_only:
feats = list(range(93)) #
else:
# TODO: Using 40 states & 2 tested_positive features (indices = 57 & 75)
pass
if mode == 'test':
# Testing data
# data: 893 x 93 (40 states + day 1 (18) + day 2 (18) + day 3 (17))
data = data[:, feats] # 前93列数据
self.data = torch.FloatTensor(data) # 类型转换,将list,numpy转换为浮点类型的tensor
else:
# Training data (train/dev sets)
# data: 2700 x 94 (40 states + day 1 (18) + day 2 (18) + day 3 (18))
target = data[:, -1] # 最后一列
data = data[:, feats] # 前93列
# Splitting training data into train & dev sets 占比9:1
if mode == 'train':
indices = [i for i in range(len(data)) if i % 10 != 0]
elif mode == 'dev':
indices = [i for i in range(len(data)) if i % 10 == 0]
# Convert data into PyTorch tensors
self.data = torch.FloatTensor(data[indices])
self.target = torch.FloatTensor(target[indices])
# Normalize features (you may remove this part to see what will happen) 正则化数据至0-1
self.data[:, 40:] = \
(self.data[:, 40:] - self.data[:, 40:].mean(dim=0, keepdim=True)) \
/ self.data[:, 40:].std(dim=0, keepdim=True)
self.dim = self.data.shape[1]
print('Finished reading the {} set of COVID19 Dataset ({} samples found, each dim = {})'
.format(mode, len(self.data), self.dim))
def __getitem__(self, index):
# Returns one sample at a time
if self.mode in ['train', 'dev']:
# For training
return self.data[index], self.target[index]
else:
# For testing (no target)
return self.data[index]
def __len__(self):
# Returns the size of the dataset
return len(self.data) ## **DataLoader**
A `DataLoader` loads data from a given `Dataset` into batches.
def prep_dataloader(path, mode, batch_size, n_jobs=0, target_only=False):
''' Generates a dataset, then is put into a dataloader. '''
dataset = COVID19Dataset(path, mode=mode, target_only=target_only) # Construct dataset
dataloader = DataLoader(
dataset, batch_size,
shuffle=(mode == 'train'), drop_last=False, # 如果 mode == 'train' ,则 shuffle=True ,数据集则会打乱顺序
num_workers=n_jobs, pin_memory=True) # Construct dataloader
return dataloader# **Deep Neural Network**
`NeuralNet` is an `nn.Module` designed for regression.
The DNN consists of 2 fully-connected layers with ReLU activation.
This module also included a function `cal_loss` for calculating loss.
class NeuralNet(nn.Module):
''' A simple fully-connected deep neural network '''
def __init__(self, input_dim):
super(NeuralNet, self).__init__()
# Define your neural network here
# TODO: How to modify this model to achieve better performance?
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim, 64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(64, 1)
)
# Mean squared error loss, criterion 标准、尺度
self.criterion = nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean') # mean 是指返回差值的绝对值
def forward(self, x):
''' Given input of size (batch_size x input_dim), compute output of the network '''
return self.net(x).squeeze(1) # 指定删除的维度,但是这个维度必须为1,否则会报错
def cal_loss(self, pred, target):
''' Calculate loss '''
# TODO: you may implement L2 regularization here
return self.criterion(pred, target) # 计算 pred与target之间的MSELoss,并且返回绝对值# **Train/Dev/Test**
def train(tr_set, dv_set, model, config, device):
''' DNN training '''
n_epochs = config['n_epochs'] # Maximum number of epochs
# Setup optimizer
optimizer = getattr(torch.optim, config['optimizer'])(
model.parameters(), **config['optim_hparas']) #用于查找实例化对象torch.optim 中是否有属性 config['optimizer'] ,若没有,返回后面括号中内容
min_mse = 1000.
loss_record = {'train': [], 'dev': []} # for recording training loss
early_stop_cnt = 0
epoch = 0
while epoch < n_epochs:
model.train() # set model to training mode
for x, y in tr_set: # iterate through the dataloader
optimizer.zero_grad() # set gradient to zero
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device) # move data to device (cpu/cuda)
pred = model(x) # forward pass (compute output)
mse_loss = model.cal_loss(pred, y) # compute loss
mse_loss.backward() # compute gradient (backpropagation)
optimizer.step() # update model with optimizer, step()函数用于更新参数
loss_record['train'].append(mse_loss.detach().cpu().item()) # mse_loss为一个tensor,mse_loss.detach()将Tensor分离,,并将x的require_grad改为False,最终将tensor添加至cpu
# After each epoch, test your model on the validation (development) set.
dev_mse = dev(dv_set, model, device)
if dev_mse < min_mse:
# Save model if your model improved
min_mse = dev_mse
print('Saving model (epoch = {:4d}, loss = {:.4f})'
.format(epoch + 1, min_mse))
torch.save(model.state_dict(), config['save_path']) # Save model to specified path , state_dict变量存放训练过程中需要学习的权重和偏执系数
early_stop_cnt = 0
else:
early_stop_cnt += 1
epoch += 1
loss_record['dev'].append(dev_mse)
if early_stop_cnt > config['early_stop']:
# Stop training if your model stops improving for "config['early_stop']" epochs.
break
print('Finished training after {} epochs'.format(epoch))
return min_mse, loss_recorddef dev(dv_set, model, device):
model.eval() # set model to evalutation mode
total_loss = 0
for x, y in dv_set: # iterate through the dataloader
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device) # move data to device (cpu/cuda)
with torch.no_grad(): # disable gradient calculation
pred = model(x) # forward pass (compute output)
mse_loss = model.cal_loss(pred, y) # compute loss
total_loss += mse_loss.detach().cpu().item() * len(x) # accumulate loss
total_loss = total_loss / len(dv_set.dataset) # compute averaged loss
return total_lossdef test(tt_set, model, device):
model.eval() # set model to evalutation mode
preds = []
for x in tt_set: # iterate through the dataloader
x = x.to(device) # move data to device (cpu/cuda)
with torch.no_grad(): # disable gradient calculation
pred = model(x) # forward pass (compute output)
preds.append(pred.detach().cpu()) # collect prediction
preds = torch.cat(preds, dim=0).numpy() # concatenate all predictions and convert to a numpy array 数据拼接,增加行
return preds# **Setup Hyper-parameters**
`config` contains hyper-parameters for training and the path to save your model.
device = get_device() # get the current available device ('cpu' or 'cuda')
os.makedirs('models', exist_ok=True) # The trained model will be saved to ./models/
target_only = False # TODO: Using 40 states & 2 tested_positive features
# TODO: How to tune these hyper-parameters to improve your model's performance?
config = {
'n_epochs': 3000, # maximum number of epochs
'batch_size': 270, # mini-batch size for dataloader
'optimizer': 'SGD', # optimization algorithm (optimizer in torch.optim)
'optim_hparas': { # hyper-parameters for the optimizer (depends on which optimizer you are using)
'lr': 0.001, # learning rate of SGD
'momentum': 0.9 # momentum for SGD
},
'early_stop': 200, # early stopping epochs (the number epochs since your model's last improvement)
'save_path': 'models/model.pth' # your model will be saved here
}# **Load data and model**
tr_set = prep_dataloader(tr_path, 'train', config['batch_size'], target_only=target_only)
dv_set = prep_dataloader(tr_path, 'dev', config['batch_size'], target_only=target_only)
tt_set = prep_dataloader(tt_path, 'test', config['batch_size'], target_only=target_only)
model = NeuralNet(tr_set.dataset.dim).to(device) # Construct model and move to deviceStart training!!!
model_loss, model_loss_record = train(tr_set, dv_set, model, config, device)
plot_learning_curve(model_loss_record, title='deep model')del model
model = NeuralNet(tr_set.dataset.dim).to(device)
ckpt = torch.load(config['save_path'], map_location='cpu') # Load your best model
model.load_state_dict(ckpt)
plot_pred(dv_set, model, device) # Show prediction on the validation setTesting !!!
def save_pred(preds, file):
''' Save predictions to specified file '''
print('Saving results to {}'.format(file))
with open(file, 'w') as fp:
writer = csv.writer(fp)
writer.writerow(['id', 'tested_positive'])
for i, p in enumerate(preds):
writer.writerow([i, p])
preds = test(tt_set, model, device) # predict COVID-19 cases with your model
save_pred(preds, 'pred.csv') # save prediction file to pred.csv