(代码已更新)QT 环境下 用opencv 进行骨架细化(骨架提取)得到图像中心线
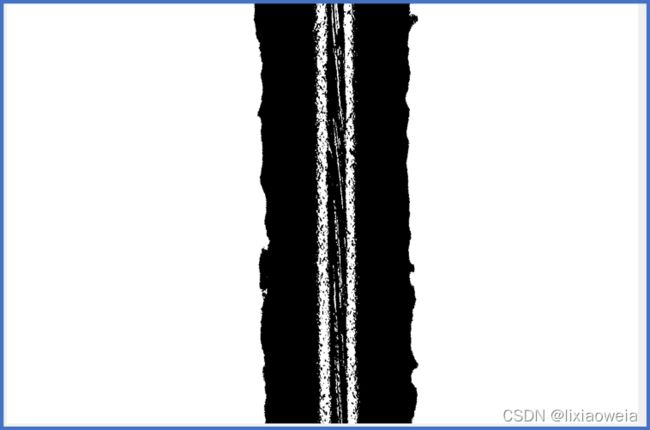
之前的任务是把如下的一个直钢管图像进行处理,提取出中心线,用到了骨架细化算法以及一些常用的opencv处理。思路就是:
预处理通过灰度得到二值图像——二值图形态学处理——骨架细化提取中心线——霍夫概率检测直线——画出目标直线。
骨架细化算法程序是直接用的下面这个转载的博客的,
csdn搜索【7】OPencv骨架细化算法。
亲自测试了可以直接用,不需要调整,但是要注意:
(1)输入的二值图像目标区域是白色,背景是黑色
(2)可能直接输入原图会加载不出来或者要等很久,可以先压缩图像然后细化,细化后放大。
在opencv中压缩图像有金字塔的方法:pyrDown(); pyrUp();以及resize函数的方法。压缩次数越多,细化后得到的线越粗
下面贴一下我输入图像的代码:
①预处理过程函数
目的是将输入的图像进行二值化以及形态学处理,为后续处理做准备:
/************预处理函数:将直/弯钢管图像进行预处理,并等比例显示在窗口中,并等比例显示在窗口中*****************************************************************************************/
/***************************************************************************************************************************************/
void MainWindow::pipe_predeal()
{
//imageMat = imread("E:\\AProject\\project1\\ziliao\\IFOVImages1014\\21.bmp");
Mat medianimg,threshold_img,gray,medianimg1;
channnlnumber= imageMat.type();
if(channnlnumber==0)
{
imageMat.copyTo(gray);
}
if(channnlnumber==16)
{
cvtColor(imageMat,gray,COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
}
imageMat.copyTo(img);
medianBlur(gray,medianimg,3);//中值滤波
//二值化
threshold(medianimg,threshold_img,20,255,THRESH_OTSU);
medianBlur(threshold_img,medianimg1,3);
//imshow("threshold", medianimg1);
bitwise_not(medianimg1,medianimg1);
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(6, 6), Point(-1, -1));//定义闭运算算子
morphologyEx(medianimg1, close, MORPH_CLOSE, kernel,Point(-1,-1),9);
//imshow("xingtaixue",close);
//等比列显示预处理后的图片
// qImg1 = cvMat2QImage(close);
// QPixmap pixmap1 = QPixmap::fromImage(qImg1);//转化成可以显示的格式
// int with1 = ui->dealimage->width();
// int height1 = ui->dealimage->height();
// QPixmap fitpixmap1 = pixmap1.scaled(with1, height1, Qt::KeepAspectRatio, Qt::SmoothTransformation); // 按比例缩放
// ui->dealimage->setPixmap(fitpixmap1);
}
②预处理之后,细化骨架提取中心线并显示,一定要先压缩图像,不然细化不出来。
这里检测直线用的是霍夫概率检测,虽然参数也很难调!!!!但是比霍夫直线检测要好一点。
void MainWindow::middelline()
{ Mat thin1 = close.clone();
//二值图去除毛疵
imshow("thin1",thin1);
//bitwise_not(thin1,thin1);
delete_jut(thin1,thin1, 50,50, 1);
imageblur(thin1,thin1, Size(10,10), 200);
imshow("xihuaqian",thin1);
//骨架细化
pyrDown(thin1,thin1);
pyrDown(thin1,thin1);
Mat thin2;
Rosenfeld(thin1,thin2);
thin2.copyTo(thin1);
pyrUp(thin1, thin1);
pyrUp(thin1, thin1);
thin1 = thin1 * 255;
imshow("xihuahou",thin1);
//腐蚀一下,骨架更细
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_ELLIPSE, Size(3, 3), Point(-1, -1));//定义闭运算算子
erode(thin1,thin1,kernel,Point(-1,-1),3);
//imshow("gujiafushi",thin1);
//检测边缘
Mat canny;
Canny(thin1,canny,20,255);
//imshow("canny",canny);
//剪裁出中间区域,去除细化干扰
int h1=canny.rows;
int w1=canny.cols;
Mat roi = canny(Range(25, h1-25), Range(25, w1-25));
//imshow("roi",roi);
//霍夫概率检测直线
vector plines;//保存霍夫变换检测到的直线
vector fitpoint;//保存拟合点
Vec4f fitline;//保存拟合直线
HoughLinesP(roi, plines, 1, CV_PI / 180,0, 10, 0);//提取边缘时,会造成有些点不连续,所以maxLineGap设大点
//画出检测直线
Scalar color = Scalar(0, 0, 255);
Mat hough = imageMat.clone();
for (size_t i = 0; i < plines.size(); i++)
{
Vec4f hline = plines[i];
int x1 = hline[0];
int y1 = hline[1];
int x2 = hline[2];
int y2 = hline[3];
Point p1=Point(x1+26, y1+26);
Point p2=Point(x2+26, y2+26);
fitpoint.push_back(p1);
fitpoint.push_back(p2);
line(hough, p1, p2, color, 1, LINE_AA);
}
fitLine(fitpoint, fitline, DIST_L2, 0, 0.01, 0.01);
double k = fitline[1]/(fitline[0]+0.0000001);
double b = fitline[3]-k*fitline[2];
double h = img.rows;double w = img.cols;
double imgk = h/w;
if(channnlnumber==0)
{
Mat m_Img = Mat(img.rows, img.cols, CV_8UC3);
cvtColor(img, m_Img, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
m_Img.copyTo(img);
}
if(abs(k)>abs(imgk))
{
Point pa,pb;
pa.x = -b/k;
pa.y = 0;
pb.x = (h-b)/k;
pb.y = h;
line(img,pb,pa,Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, LINE_AA );
}
if(abs(k)dealimage->width();
int height1 = ui->dealimage->height();
QPixmap fitpixmap1 = pixmap1.scaled(with1, height1, Qt::KeepAspectRatio, Qt::SmoothTransformation); // 按比例缩放
ui->dealimage->setPixmap(fitpixmap1);
} ③这个是②中程序调用的骨架细化、骨架提取算法
void MainWindow:: Rosenfeld(Mat& src, Mat& dst)//输入的目标像素为1,背景像素为0
{if (src.type() != CV_8UC1)
{
printf("只能处理二值或灰度图像\n");
return;
}
//非原地操作时候,copy src到dst
if (dst.data != src.data)
{
src.copyTo(dst);
}
int i, j, n;
int width, height;
//之所以减1,是方便处理8邻域,防止越界
width = src.cols-1 ;
height = src.rows-1 ;
int step = src.step;
int p2, p3, p4, p5, p6, p7, p8, p9;
uchar* img;
bool ifEnd;
Mat tmpimg;
int dir[4] = { -step, step, 1, -1 };
while (1)
{
//分四个子迭代过程,分别对应北,南,东,西四个边界点的情况
ifEnd = false;
for (n = 0; n < 4; n++)
{
dst.copyTo(tmpimg);
img = tmpimg.data;
for (i = 1; i < height; i++)
{
img += step;
for (j = 1; j < width; j++)
{
uchar* p = img + j;
//如果p点是背景点或者且为方向边界点,依次为北南东西,继续循环
if (p[0] == 0 || p[dir[n]] > 0) continue;
p2 = p[-step] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
p3 = p[-step + 1] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
p4 = p[1] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
p5 = p[step + 1] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
p6 = p[step] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
p7 = p[step - 1] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
p8 = p[-1] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
p9 = p[-step - 1] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
//8 simple判定
int is8simple = 1;
if (p2 == 0 && p6 == 0)
{
if ((p9 == 1 || p8 == 1 || p7 == 1) && (p3 == 1 || p4 == 1 || p5 == 1))
is8simple = 0;
}
if (p4 == 0 && p8 == 0)
{
if ((p9 == 1 || p2 == 1 || p3 == 1) && (p5 == 1 || p6 == 1 || p7 == 1))
is8simple = 0;
}
if (p8 == 0 && p2 == 0)
{
if (p9 == 1 && (p3 == 1 || p4 == 1 || p5 == 1 || p6 == 1 || p7 == 1))
is8simple = 0;
}
if (p4 == 0 && p2 == 0)
{
if (p3 == 1 && (p5 == 1 || p6 == 1 || p7 == 1 || p8 == 1 || p9 == 1))
is8simple = 0;
}
if (p8 == 0 && p6 == 0)
{
if (p7 == 1 && (p3 == 9 || p2 == 1 || p3 == 1 || p4 == 1 || p5 == 1))
is8simple = 0;
}
if (p4 == 0 && p6 == 0)
{
if (p5 == 1 && (p7 == 1 || p8 == 1 || p9 == 1 || p2 == 1 || p3 == 1))
is8simple = 0;
}
int adjsum;
adjsum = p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9;
//判断是否是邻接点或孤立点,0,1分别对于那个孤立点和端点
if (adjsum != 1 && adjsum != 0 && is8simple == 1)
{
dst.at(i, j) = 0; //满足删除条件,设置当前像素为0
ifEnd = true;
}
}
}
}
if (!ifEnd) break;
}
}
④这个是二值图去除毛刺的算法
目的是使图像更加平滑,这样骨架细化的时候不会因为方向性出现许多分岔。
//去除二值图像边缘的突出部
//uthreshold、vthreshold分别表示突出部的宽度阈值和高度阈值
//type代表突出部的颜色,0表示黑色,1代表白色
void MainWindow::delete_jut(Mat& src, Mat& dst, int uthreshold, int vthreshold, int type)
{
src.copyTo(dst);
int height = dst.rows;
int width = dst.cols;
int k; //用于循环计数传递到外部
for (int i = 0; i < height - 1; i++)
{
uchar* p = dst.ptr(i);
for (int j = 0; j < width - 1; j++)
{
if (type == 0)
{
//行消除
if (p[j] == 255 && p[j + 1] == 0)
{
if (j + uthreshold >= width)
{
for (int k = j + 1; k < width; k++)
p[k] = 255;
}
else
{
for (k = j + 2; k <= j + uthreshold; k++)
{
if (p[k] == 255) break;
}
if (p[k] == 255)
{
for (int h = j + 1; h < k; h++)
p[h] = 255;
}
}
}
//列消除
if (p[j] == 255 && p[j + width] == 0)
{
if (i + vthreshold >= height)
{
for (k = j + width; k < j + (height - i)*width; k += width)
p[k] = 255;
}
else
{
for (k = j + 2 * width; k <= j + vthreshold*width; k += width)
{
if (p[k] == 255) break;
}
if (p[k] == 255)
{
for (int h = j + width; h < k; h += width)
p[h] = 255;
}
}
}
}
else //type = 1
{
//行消除
if (p[j] == 0 && p[j + 1] == 255)
{
if (j + uthreshold >= width)
{
for (int k = j + 1; k < width; k++)
p[k] = 0;
}
else
{
for (k = j + 2; k <= j + uthreshold; k++)
{
if (p[k] == 0) break;
}
if (p[k] == 0)
{
for (int h = j + 1; h < k; h++)
p[h] = 0;
}
}
}
//列消除
if (p[j] == 0 && p[j + width] == 255)
{
if (i + vthreshold >= height)
{
for (k = j + width; k < j + (height - i)*width; k += width)
p[k] = 0;
}
else
{
for (k = j + 2 * width; k <= j + vthreshold*width; k += width)
{
if (p[k] == 0) break;
}
if (p[k] == 0)
{
for (int h = j + width; h < k; h += width)
p[h] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
//图片边缘光滑处理
//size表示取均值的窗口大小,threshold表示对均值图像进行二值化的阈值
void MainWindow::imageblur(Mat& src, Mat& dst, Size size, int threshold)
{
int height = src.rows;
int width = src.cols;
blur(src, dst, size);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
uchar* p = dst.ptr(i);
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
if (p[j] < threshold)
p[j] = 0;
else p[j] = 255;
}
}
}
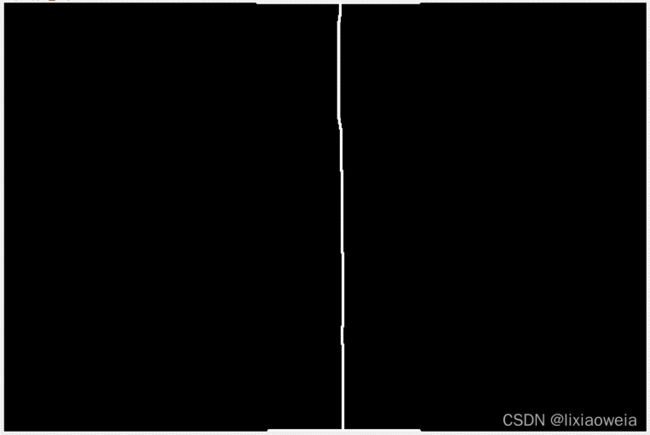
⑤最后看一下成果吧:
效果还可以,对你有用的话希望可以点个赞哦!!