pytorch实现VGG16 (2)
VGG16Net.py
from torch import nn
class Vgg16_net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Vgg16_net, self).__init__()
self.layer1=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,out_channels=64,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(32-3+2)/1+1=32 32*32*64
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
#inplace-选择是否进行覆盖运算
#意思是是否将计算得到的值覆盖之前的值,比如
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
#意思就是对从上层网络Conv2d中传递下来的tensor直接进行修改,
#这样能够节省运算内存,不用多存储其他变量
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64,out_channels=64,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(32-3+2)/1+1=32 32*32*64
#Batch Normalization强行将数据拉回到均值为0,方差为1的正太分布上,
# 一方面使得数据分布一致,另一方面避免梯度消失。
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,stride=2) #(32-2)/2+1=16 16*16*64
)
self.layer2=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64,out_channels=128,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(16-3+2)/1+1=16 16*16*128
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128,out_channels=128,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(16-3+2)/1+1=16 16*16*128
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2,2) #(16-2)/2+1=8 8*8*128
)
self.layer3=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128,out_channels=256,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(8-3+2)/1+1=8 8*8*256
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256,out_channels=256,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(8-3+2)/1+1=8 8*8*256
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256,out_channels=256,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(8-3+2)/1+1=8 8*8*256
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2,2) #(8-2)/2+1=4 4*4*256
)
self.layer4=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256,out_channels=512,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(4-3+2)/1+1=4 4*4*512
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512,out_channels=512,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(4-3+2)/1+1=4 4*4*512
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512,out_channels=512,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(4-3+2)/1+1=4 4*4*512
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2,2) #(4-2)/2+1=2 2*2*512
)
self.layer5=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512,out_channels=512,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(2-3+2)/1+1=2 2*2*512
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512,out_channels=512,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(2-3+2)/1+1=2 2*2*512
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512,out_channels=512,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1), #(2-3+2)/1+1=2 2*2*512
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(2,2) #(2-2)/2+1=1 1*1*512
)
self.conv=nn.Sequential(
self.layer1,
self.layer2,
self.layer3,
self.layer4,
self.layer5
)
self.fc=nn.Sequential(
#y=xA^T+b x是输入,A是权值,b是偏执,y是输出
#nn.Liner(in_features,out_features,bias)
#in_features:输入x的列数 输入数据:[batchsize,in_features]
#out_freatures:线性变换后输出的y的列数,输出数据的大小是:[batchsize,out_features]
#bias: bool 默认为True
#线性变换不改变输入矩阵x的行数,仅改变列数
nn.Linear(512,512),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(512,256),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(256,10)
)
def forward(self,x):
x=self.conv(x)
#这里-1表示一个不确定的数,就是你如果不确定你想要reshape成几行,但是你很肯定要reshape成512列
# 那不确定的地方就可以写成-1
#如果出现x.size(0)表示的是batchsize的值
# x=x.view(x.size(0),-1)
x = x.view(-1, 512)
x=self.fc(x)
return x
train.py
import time
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def load_dataset(batch_size):
train_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root="../../../data_hub/cifar10/data_1", train=True,
download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor()
)
test_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root="../../../data_hub/cifar10/data_1", train=False,
download=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor()
)
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4
)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
test_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4
)
return train_iter, test_iter
def train(net, train_iter, criterion, optimizer, num_epochs, device, num_print, lr_scheduler=None, test_iter=None):
net.train()
record_train = list()
record_test = list()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
print("========== epoch: [{}/{}] ==========".format(epoch + 1, num_epochs))
total, correct, train_loss = 0, 0, 0
start = time.time()
for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter):
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
output = net(X)
loss = criterion(output, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_loss += loss.item()
total += y.size(0)
correct += (output.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().item()
train_acc = 100.0 * correct / total
if (i + 1) % num_print == 0:
print("step: [{}/{}], train_loss: {:.3f} | train_acc: {:6.3f}% | lr: {:.6f}" \
.format(i + 1, len(train_iter), train_loss / (i + 1), \
train_acc, get_cur_lr(optimizer)))
if lr_scheduler is not None:
lr_scheduler.step()
print("--- cost time: {:.4f}s ---".format(time.time() - start))
if test_iter is not None:
record_test.append(test(net, test_iter, criterion, device))
record_train.append(train_acc)
return record_train, record_test
def test(net, test_iter, criterion, device):
total, correct = 0, 0
net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
print("*************** test ***************")
for X, y in test_iter:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
output = net(X)
loss = criterion(output, y)
total += y.size(0)
correct += (output.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().item()
test_acc = 100.0 * correct / total
print("test_loss: {:.3f} | test_acc: {:6.3f}%"\
.format(loss.item(), test_acc))
print("************************************\n")
net.train()
return test_acc
def get_cur_lr(optimizer):
for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
return param_group['lr']
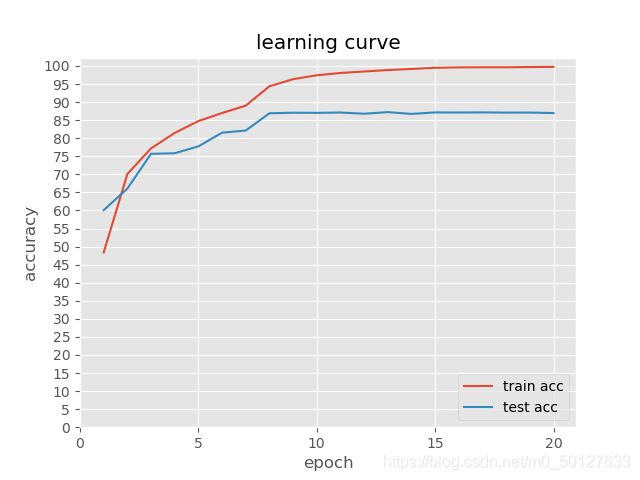
def learning_curve(record_train, record_test=None):
plt.style.use("ggplot")
plt.plot(range(1, len(record_train) + 1), record_train, label="train acc")
if record_test is not None:
plt.plot(range(1, len(record_test) + 1), record_test, label="test acc")
plt.legend(loc=4)
plt.title("learning curve")
plt.xticks(range(0, len(record_train) + 1, 5))
plt.yticks(range(0, 101, 5))
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("accuracy")
plt.show()
import torch.optim as optim
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NUM_EPOCHS = 20
NUM_CLASSES = 10
LEARNING_RATE = 0.02
MOMENTUM = 0.9
WEIGHT_DECAY = 0.0005
NUM_PRINT = 100
DEVICE = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
from VggNet import *
def main():
net = Vgg16_net()
net = net.to(DEVICE)
train_iter, test_iter = load_dataset(BATCH_SIZE)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(
net.parameters(),
lr=LEARNING_RATE,
momentum=MOMENTUM,
weight_decay=WEIGHT_DECAY,
nesterov=True
)
lr_scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=7, gamma=0.1)
record_train, record_test = train(net, train_iter, criterion, optimizer, \
NUM_EPOCHS, DEVICE, NUM_PRINT, lr_scheduler, test_iter)
learning_curve(record_train, record_test)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
这篇和上篇基本差不多,只不过训练模板不一样,上篇链接。
训练模板参考自:https://blog.csdn.net/cp1314971/article/details/104396169?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501