前言
1992年扫雷被加入到windows3.1,成为早期windows的经典游戏。近来接触python的GUI(图形化)编程,于是通过编写扫雷来实践学习。有关程序的问题和想法欢迎大家指出。
一、基本思路
(1)程序的核心数据是二维列表control_list[16][16],值-1代表雷,0和其他数字代表四周雷的数目。函数randomization()随机40个雷的 位置
(2)生成16x16个按钮控件,根据control_list列表确定点击相应的按钮时执行的代码。如按照游戏规则:点击对应control_list列表值为0的按钮时,递归执行函数re()来扫雷,当点击对应的control_list列表值为-1时直接结束游戏,对应大于0的值则只需隐藏当前的按钮控件。
其他:本程序用到的GUI编程库为tkinter, 控件的布局统一采用place()方法
二、源代码
1.运行效果
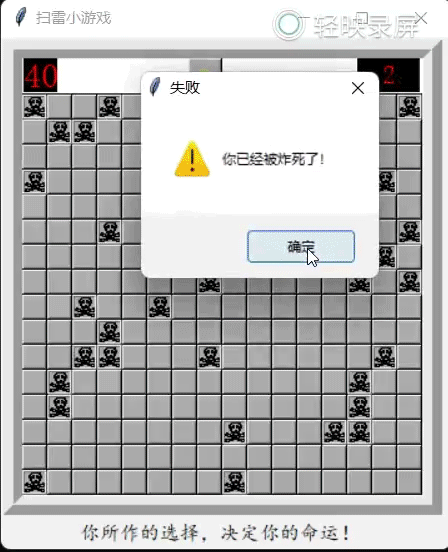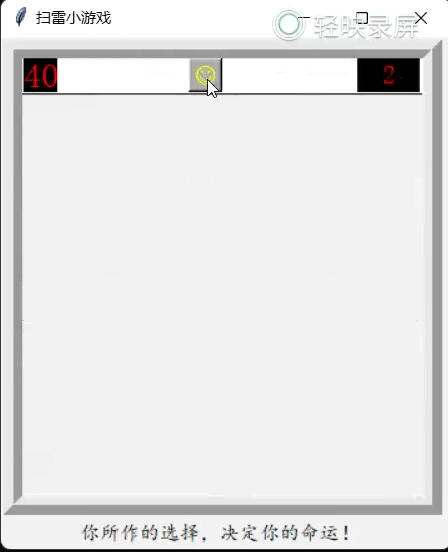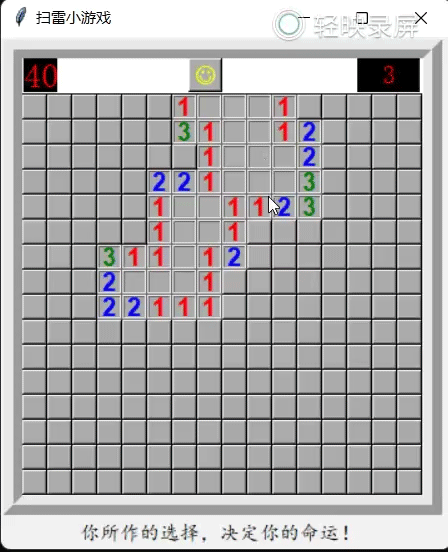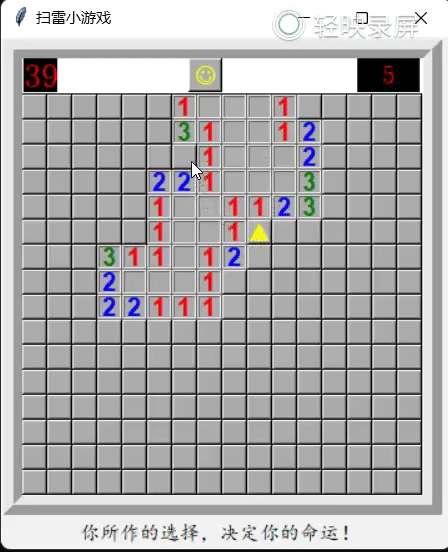
运行效果如下(示例):
2.上源码
"""
Created on Tuesday, April 5,2022
@author:I
"""
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import messagebox
import random
#定义五个二维数组,充当整个程序的数据
control_list=[[0 for i in range(16)] for j in range(16)]#二维列表,呈现雷和数字的分布。
show_list=[[0 for i in range(16)] for j in range(16)]#二维列表,控制遮住或显示雷和数字。(0--遮住,1--显示)
button_list=[[0 for i in range(16)] for j in range(16)]#二维的按钮列表(显示在上层)
label_list=[[0 for i in range(16)] for j in range(16)]#二维的标签列表(显示在下层)
mark_list=[[0 for i in range(16)] for j in range(16)]#二维标记列表
num_mine=40#控制游戏结束
counter=0#计时
T ,t= 1,0#游戏结束的判断
def randomization(c_list):#随机初始化雷的分布即初始化列表control_list
num=0
while num<40:
x=random.randint(0,15)
y=random.randint(0,15)
if(c_list[x][y]==0):
num+=1
c_list[x][y]=-1
for i in range(16):
for j in range(16):
if(c_list[i][j]>-1):
if (i>0 and c_list[i-1][j]==-1):
c_list[i][j]+=1
if (i<15 and c_list[i+1][j]==-1):
c_list[i][j]+=1
if (j>0 and c_list[i][j-1]==-1):
c_list[i][j]+=1
if (j<15 and c_list[i][j+1]==-1):
c_list[i][j]+=1
if (i>0 and j>0 and c_list[i-1][j-1]==-1):
c_list[i][j]+=1
if (i<15 and j<15 and c_list[i+1][j+1]==-1):
c_list[i][j]+=1
if (i>0 and j<15 and c_list[i-1][j+1]==-1):
c_list[i][j]+=1
if (i<15 and j>0 and c_list[i+1][j-1]==-1):
c_list[i][j]+=1
def game_core():
randomization(control_list)
for row in range(16):
for col in range(16):
if(control_list[row][col]==-1):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="☠",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="black",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==0):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==1):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="1",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="red",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==2):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="2",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="blue",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==3):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="3",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="green",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==4):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="4",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="white",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==5):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="5",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="red",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==6):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="6",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="blue",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==7):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="7",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="green",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
elif(control_list[row][col]==8):
label_list[row][col]=Label(root,text="8",font=('arial', 15, 'bold'),fg="white",bg="#AAAAAA",relief=RIDGE)
label_list[row][col].place(x=17+col*20,y=46+row*20,height=20,width=20)
for r in range(16):
for c in range(16):
s = str((r)*16+c)
button_list[r][c]=Button(root,text=s,activeforeground="#AAAAAA",bg="#AAAAAA",fg="#AAAAAA")
button_list[r][c].place(x=17+c*20,y=46+r*20,height=20,width=20)
button_list[r][c].bind("",button_control_l)#鼠标左击绑定函数
button_list[r][c].bind("",button_control_r)
def button_control_l(event):#扫雷控制函数.(开始函数直接用参数r和c,但是会产生问题)
r = int(event.widget["text"])//16
c = int(event.widget["text"])%16
global t
global T
if(control_list[r][c]>=1):
button_list[r][c].place_forget()
show_list[r][c]=1
t+=1
elif(control_list[r][c]==0):
rec(r,c)
elif(control_list[r][c]==-1 and T):
button_list[r][c].place_forget()
show_list[r][c]=1
T=0
for i in range(16):
for j in range(16):
if(control_list[i][j]==-1):
button_list[i][j].place_forget()
show_list[r][c]=1
button_restart["text"]="☹"
messagebox.showwarning("失败","你已经被炸死了!")
if t==216:
T=0
messagebox.showwarning("成功","恭喜你扫雷完成!")
def button_control_r(event):
r = int(event.widget["text"])//16
c = int(event.widget["text"])%16
mark_list[r][c]=Button(root,text="?",font=('楷体', 14),activeforeground="#AAAAAA",bg="#AAAAAA",fg="yellow")
mark_list[r][c].place(x=17+c*20,y=46+r*20,height=20,width=20)
mark_list[r][c].bind("",button_control_r_change)
def button_control_r_change(event):
global num_mine
if (event.widget["text"]=="?" and num_mine>0):
num_mine-=1
event.widget["text"]="▲"
cout_label["text"]=str(num_mine)
elif(event.widget["text"]=="▲"):
num_mine+=1
cout_label["text"]=str(num_mine)
event.widget.place_forget()
elif (event.widget["text"]=="?" and num_mine==0):
event.widget.place_forget()
def rec(r,c):#递归探测
global t
if control_list[r][c]>0 and show_list[r][c]==0:
button_list[r][c].place_forget()
show_list[r][c]=1
t+=1
return 0
elif control_list[r][c] ==0 and show_list[r][c]==0:
button_list[r][c].place_forget()
show_list[r][c]=1
t+=1
if r>0 and c>0:
rec(r-1,c-1)
if r>0:
rec(r-1,c)
if r>0 and c<15:
rec(r-1,c+1)
if c<15:
rec(r,c+1)
if r<15 and c<15:
rec(r+1,c+1)
if r<15:
rec(r+1,c)
if r<15 and c>0:
rec(r+1,c-1)
if c>0:
rec(r,c-1)
def time_counter(la): # la是标签,计时函数
def counting():
global counter
if T:
counter += 1
la["text"]=str(counter)
la.after(1000,counting) # 在1000毫秒后执行counting()函数,即循环执行counting
counting()
def restart():#重新开始函数
button_restart["text"]="☺"
cout_label["text"]="40"
#数据重置
for i in range(16):
for j in range(16):
control_list[i][j]=0
show_list[i][j]=0
button_list[i][j].place_forget()
button_list[i][j]=0
label_list[i][j].place_forget()
label_list[i][j]=0
if (mark_list[i][j]!=0):
mark_list[i][j].place_forget()
mark_list[i][j]=0
global num_mine
global counter
global T ,t
num_mine=40
counter=0
T ,t= 1,0
game_core()
if __name__ =="__main__":
root = Tk()#根窗体
root.title("扫雷小游戏")
root.geometry("360x410")#根窗体大小
cv1 = Canvas(root,bd=15,bg="#FFFFFF",relief=RIDGE,cursor="cross",width=321,height=350)
cv1.create_line(15,45,337,45)
cv1.place(x=0,y=0)
w=Label(root,text="你所作的选择,决定你的命运!",font=("楷体",12))
w.place(x=60,y=385)
button_restart=Button(root,text="☺",font=('楷体', 15),bg="#AAAAAA",fg="yellow",command=restart)
button_restart.place(x=150,y=17,height=27,width=27)
time_label = Label(root,bg="black",fg="red",text=str(counter),font=("LcdD",15))#计时标签
time_label.place(x=285,y=17,height=27,width=50)
cout_label = Label(root,bg="black",fg="red",text="40",font=("LcdD",20))#计数标签
cout_label.place(x=18,y=17,height=27,width=27)
game_core()
time_counter(time_label)
root.mainloop()#监控组件,组件发生变化或触发事件时,更新窗口
总结
扫雷的思路简单,但编写这个程序仍然花费了我比较长的时间,究其原因:初次接触python的GUI编程,对各个控件的方法等不熟悉,且没有能够充分的查找资料,在面对问题时处理思路局限。编程世界,道路漫长遥远。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。