基于C++的OpenCV3.3图像处理源码整理
OpenCV3.3.0配置完整教程请点击
VTK8.0配置完整教程请点击
本文章全部源码和用到的素材下载
目录:
实例1:opencv对单张DCM文件的读取并显示
实例2:opencv读取DCM图像并另存为JPG图像
实例3:opencv批量读取指定路径DCM图像并显示
实例4:opencv读取指定路径DCM并批量另存为JPG图像
实例5:opencv命名方式读取指定路径DCM并批量另存为JPG图像
实例6:opencv指定路径批量读取JPG图像并构建容器显示
实例7:opencv通过进度条阈值选定分割JPG图像并显示保存
实例8:opencv批量阈值分割JPG图像并显示保存
实例9:opencv区域增长算法分割JPG图像并显示保存
实例10:VTK格式文件的读取与渲染显示
实例11:基于VTK对MHD格式文件单张切片的鼠标滑动提取显示
实例12:基于VTK对MHA格式文件三维感兴趣区域裁剪及MHA格式保存
实例1:opencv对单张DCM文件的读取并显示
#include
#include // 当中含有_finddata_t
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// 读入一个CT图,返回它的像素矩阵,使用OpenCV的Mat类型返回
// VTK读取DICOM图像并将像素值转给OpenCV的Mat对象
void dicomread(string inputFilename, Mat& img, vtkSmartPointer& reader)
{
img.create(512, 512, CV_32SC1);
vtkSmartPointer imageCast =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
reader->SetFileName(inputFilename.c_str());
reader->Update();
imageCast->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
imageCast->SetOutputScalarTypeToInt();
imageCast->Update();
// 图像的基本信息
int dims[3];
reader->GetOutput()->GetDimensions(dims);
//图像的像素值
for (int k = 0; k < dims[2]; k++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dims[1]; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < dims[0]; i++)
{
//转换数据类型,使用imagecast转到double(或float)
int* pixel =
(int*)(imageCast->GetOutput()->GetScalarPointer(i, j, k)); // 第i列第j行的像素值
img.at(j, i) = int(*pixel); // 第j行第i列的像素值
}
}
}
}
//可视化DICOM图像
void showdicom(Mat I)
{
double maxx = 0, minn = 0;
double* max = &maxx;
double* min = &minn;
I.convertTo(I, CV_64FC1);
minMaxIdx(I, min, max);
for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; j++)
{
I.at(i, j) = 255 * (I.at(i, j) - minn) * 1 / (maxx - minn);
}
}
minMaxIdx(I, min, max);
for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; j++)
I.at(i, j) = (I.at(i, j) - minn) * 1 / (maxx - minn);
}
//cout << I < reader =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
// 读入dicom图
dicomread(filename, I1, reader);
//反转图像
flip(I1, I1, 0);
//显示得到的Mat对象I1的信息*(单通道 大小512*512)
cout << I1.channels() << " " << I1.size() << endl;
showdicom(I1);
} 要读取的dcm文件放在工程目录下:
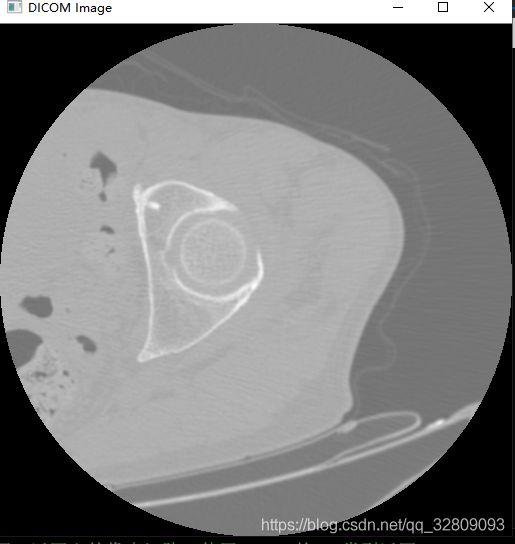
可见读取的为单通道的512*512像素大小的图像:
实例2:opencv读取DCM图像并另存为JPG图像
#include
#include // 当中含有_finddata_t
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// 读入一个CT图,返回它的像素矩阵,使用OpenCV的Mat类型返回
// VTK读取DICOM图像并将像素值转给OpenCV的Mat对象
void dicomread(string inputFilename, Mat& img, vtkSmartPointer& reader)
{
img.create(512, 512, CV_32SC1);
vtkSmartPointer imageCast =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
reader->SetFileName(inputFilename.c_str());
reader->Update();
imageCast->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
imageCast->SetOutputScalarTypeToInt();
imageCast->Update();
// 图像的基本信息
int dims[3];
reader->GetOutput()->GetDimensions(dims);
//图像的像素值
for (int k = 0; k < dims[2]; k++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dims[1]; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < dims[0]; i++)
{
//转换数据类型,使用imagecast转到double(或float)
int* pixel =
(int*)(imageCast->GetOutput()->GetScalarPointer(i, j, k)); // 第i列第j行的像素值
img.at(j, i) = int(*pixel); // 第j行第i列的像素值
}
}
}
}
//可视化DICOM图像
void showdicom(Mat I)
{
double maxx = 0, minn = 0;
double* max = &maxx;
double* min = &minn;
I.convertTo(I, CV_64FC1);
minMaxIdx(I, min, max);
for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; j++)
{
I.at(i, j) = 255 * (I.at(i, j) - minn) * 1 / (maxx - minn);
}
}
minMaxIdx(I, min, max);
for (int i = 0; i < I.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < I.cols; j++)
I.at(i, j) = (I.at(i, j) - minn) * 1 / (maxx - minn);
}
//cout << I < reader =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
// 读入dicom图
dicomread(filename, I1, reader);
//反转图像
flip(I1, I1, 0);
//显示得到的Mat对象I1的信息*(单通道 大小512*512)
cout << I1.channels() << " " << I1.size() << endl;
showdicom(I1);
//将DCM图像另存为JPG图像
imwrite("1.jpg", I1);
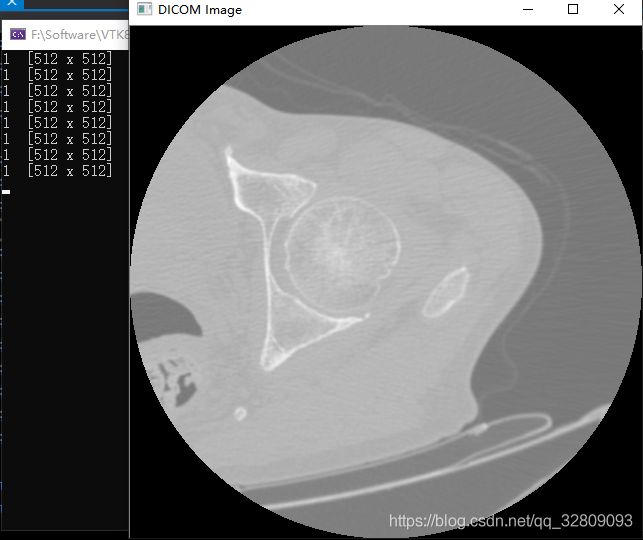
} 读取的为单通道的512*512像素大小的DCM图像:
生成的JPG图像:
实例3:opencv批量读取指定路径DCM图像并显示
#include
#include // 当中含有_finddata_t
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// 读入一个CT图,返回它的像素矩阵,使用OpenCV的Mat类型返回
// VTK读取DICOM图像并将像素值转给OpenCV的Mat对象
void dicomread(string inputFilename, Mat &img,vtkSmartPointer &reader)
{
img.create(512,512,CV_32SC1);
vtkSmartPointer imageCast =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
reader->SetFileName(inputFilename.c_str());
reader->Update();
imageCast->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
imageCast->SetOutputScalarTypeToInt();
imageCast->Update();
// 图像的基本信息
int dims[3];
reader->GetOutput()->GetDimensions(dims);
//图像的像素值
for(int k=0;kGetOutput()->GetScalarPointer(i,j,k)); // 第i列第j行的像素值
img.at(j,i) = int(*pixel); // 第j行第i列的像素值
}
}
}
}
//可视化DICOM图像
void showdicom(Mat I)
{
double maxx=0,minn=0;
double *max = &maxx;
double *min = &minn;
I.convertTo(I,CV_64FC1);
minMaxIdx(I,min,max);
for(int i=0;i(i,j) = 255*(I.at(i,j)-minn)*1/(maxx-minn);
}
}
minMaxIdx(I,min,max);
for(int i=0;i(i,j) = (I.at(i,j)-minn)*1/(maxx-minn);
}
//cout << I < reader =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
// 读入dicom图
dicomread(filename, I1, reader);
//翻转图像
flip(I1, I1, 0);
//显示得到的Mat对象I1的信息*(单通道 大小512*512)
cout << I1.channels() << " " << I1.size() << endl;
showdicom(I1);
}
} 读取DCM图像路径:
每按下空格,进行下一张图像读取和显示:
实例4:opencv读取指定路径DCM并批量另存为JPG图像
#include
#include // 当中含有_finddata_t
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// 读入一个CT图,返回它的像素矩阵,使用OpenCV的Mat类型返回
// VTK读取DICOM图像并将像素值转给OpenCV的Mat对象
void dicomread(string inputFilename, Mat &img,vtkSmartPointer &reader)
{
img.create(512,512,CV_32SC1);
vtkSmartPointer imageCast =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
reader->SetFileName(inputFilename.c_str());
reader->Update();
imageCast->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
imageCast->SetOutputScalarTypeToInt();
imageCast->Update();
// 图像的基本信息
int dims[3];
reader->GetOutput()->GetDimensions(dims);
//图像的像素值
for(int k=0;kGetOutput()->GetScalarPointer(i,j,k)); // 第i列第j行的像素值
img.at(j,i) = int(*pixel); // 第j行第i列的像素值
}
}
}
}
//可视化DICOM图像
void showdicom(Mat I)
{
double maxx=0,minn=0;
double *max = &maxx;
double *min = &minn;
I.convertTo(I,CV_64FC1);
minMaxIdx(I,min,max);
for(int i=0;i(i,j) = 255*(I.at(i,j)-minn)*1/(maxx-minn);
}
}
minMaxIdx(I,min,max);
for(int i=0;i(i,j) = (I.at(i,j)-minn)*1/(maxx-minn);
}
//cout << I < reader =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
// 读入dicom图
dicomread(filename, I1, reader);
//翻转图像
flip(I1, I1, 0);
//显示得到的Mat对象I1的信息*(单通道 大小512*512)
cout << I1.channels() << " " << I1.size() << endl;
showdicom(I1);
//指定路径对图像进行批量另存为JPG格式图像
//给的另存路径和文件格式
sprintf_s(ad, "F:\\Software\\VTK8.2.0\\vtk1\\helloVtk\\JPG_images\\%d.jpg", j);
//保存
imwrite(ad, I1);
}
} 每按下空格,进行下一张图像读取和显示:
程序运行完后,在F:\Software\VTK8.2.0\vtk1\helloVtk\JPG_images路径下便可以查看另存的JPG图像:
实例5:opencv命名方式读取指定路径DCM并批量另存为JPG图像
#include
#include // 当中含有_finddata_t
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define NUMBER 72//(CT文件数量为NUMBER-1)
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// 读入一个CT图,返回它的像素矩阵,使用OpenCV的Mat类型返回
// VTK读取DICOM图像并将像素值转给OpenCV的Mat对象
void dicomread(string inputFilename, Mat &img,vtkSmartPointer &reader)
{
img.create(512,512,CV_32SC1);
vtkSmartPointer imageCast =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
reader->SetFileName(inputFilename.c_str());
reader->Update();
imageCast->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
imageCast->SetOutputScalarTypeToInt();
imageCast->Update();
// 图像的基本信息
int dims[3];
reader->GetOutput()->GetDimensions(dims);
//图像的像素值
for(int k=0;kGetOutput()->GetScalarPointer(i,j,k)); // 第i列第j行的像素值
img.at(j,i) = int(*pixel); // 第j行第i列的像素值
}
}
}
}
//可视化DICOM图像
void showdicom(Mat I)
{
double maxx=0,minn=0;
double *max = &maxx;
double *min = &minn;
I.convertTo(I,CV_64FC1);
minMaxIdx(I,min,max);
for(int i=0;i(i,j) = 255*(I.at(i,j)-minn)*1/(maxx-minn);
}
}
minMaxIdx(I,min,max);
for(int i=0;i(i,j) = (I.at(i,j)-minn)*1/(maxx-minn);
}
//cout << I < images;
char ad[128] = { 0 };
for (int j = 1;j < NUMBER;j+=10) {
string filename = format("F:\\Software\\VTK8.2.0\\vtk1\\helloVtk\\CT\\1066244_20110617_CT_102_215_%03d.dcm", j);
Mat I1, G1;//I1为原图,G1为转化图
vtkSmartPointer reader =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
// 读入dicom图,并将像素值传递给Mat对象I1
dicomread(filename, I1, reader);
flip(I1, I1, 0);
//显示得到的Mat对象I1的信息*(单通道 大小512*512)
cout << I1.channels() << " " << I1.size() << endl;
showdicom(I1);
//保存图像
sprintf_s(ad, "F:\\Software\\VTK8.2.0\\vtk1\\helloVtk\\JPG_images\\%d.jpg", j);
imwrite(ad, I1);
}
} 每按下空格,进行下一张图像读取和显示:
程序运行完后,在F:\Software\VTK8.2.0\vtk1\helloVtk\JPG_images路径下便可以查看另存的JPG图像:
实例6:opencv指定路径批量读取JPG图像并构建容器显示
#include
#include // 当中含有_finddata_t
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define NUMBER 9 //(CT文件数量为NUMBER-1)
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
vector images;
for (int a = 1; a < NUMBER;a++) // a <=Count would do one too many...
{
string filename = format("F:\\Software\\VTK8.2.0\\vtk1\\helloVtk\\JPG_images\\%d.jpg", a);
Mat img = imread(filename); // pgm implies grayscale, maybe even: imread(name,0); to return CV_8U
if (img.empty()) // please, *always check* resource-loading.
{
cerr << "whaa " << filename << " can't be loaded!" << endl;
continue;
}
images.push_back(img);
}
//将读取在容器中的图像进行逐张显示
for(int k=1;k< NUMBER;k++)
{
imshow("vector", images[k-1]);
waitKey();//等待键盘输入
}
return 0;
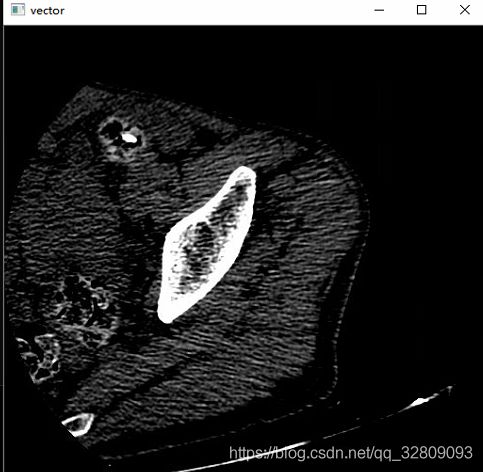
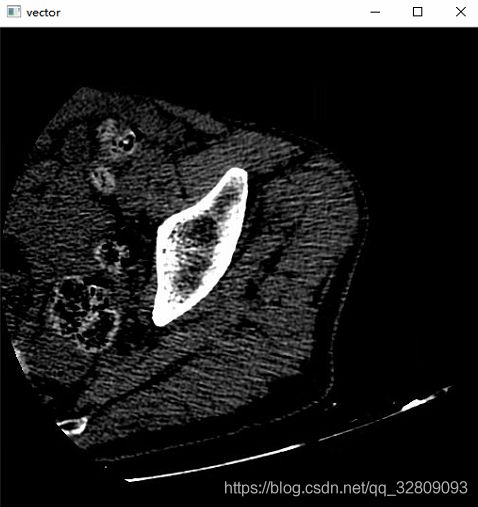
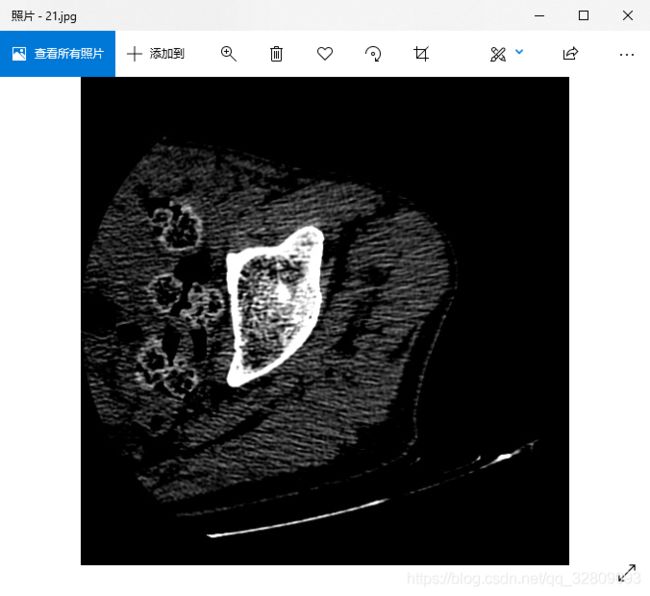
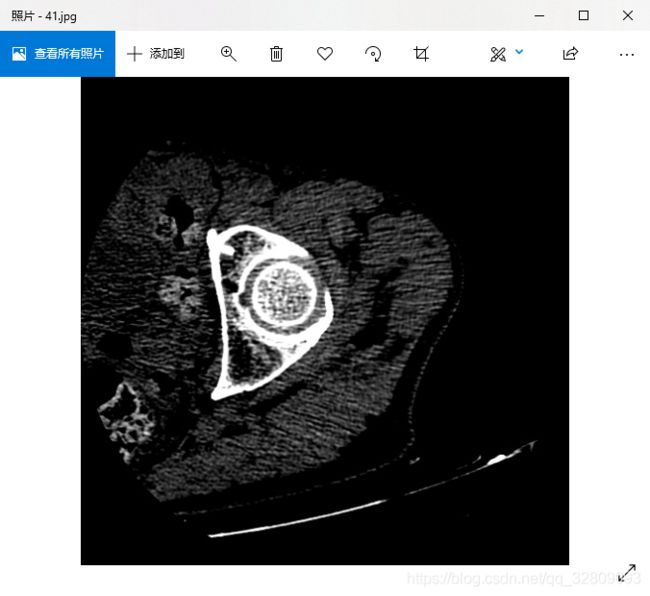
} 读取JPG图像路径:
图像显示:
实例7:opencv通过进度条阈值选定分割JPG图像并显示保存
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
Mat src, gray_src, dst;//定义Mat对象
int threshold_value = 178;//设置阈值 127
int threshold_max = 255;//RGB(0~255)最大值
int type_value = 2;
int type_max = 4;
const char* output_title = "binary image";//定义输出标题为二进制图像
void Threshold_Demo(int, void*);//定义函数
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
src = imread("1.jpg");//读入图像
if (!src.data) { //如果没有数据
printf("could not load image...\n");
return -1;
}
namedWindow("input image", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);//创建一个窗口,自动设置窗口大小
namedWindow(output_title, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow("input image", src);//在"input image"窗口显示原图像
//设置拖动棒 (手动拖动的阈值
createTrackbar("Threshold Value:", output_title, &threshold_value, threshold_max, Threshold_Demo);
createTrackbar("Type Value:", output_title, &type_value, type_max, Threshold_Demo);
Threshold_Demo(0, 0);
waitKey(0);//键盘任意键关闭
return 0;
}
void Threshold_Demo(int, void*) {
cvtColor(src, gray_src, CV_BGR2GRAY);//RGB图像对象src转换为灰度图像对象gray_src
//imshow("GRAY", gray_src);//显示灰度图像
//threshold(gray_src, dst, threshold_value, threshold_max, type_value);
threshold(gray_src, dst, threshold_value, threshold_max, THRESH_BINARY);
//保存阈值后图像
imwrite("threshold_1.jpg", dst);
imshow(output_title, dst);
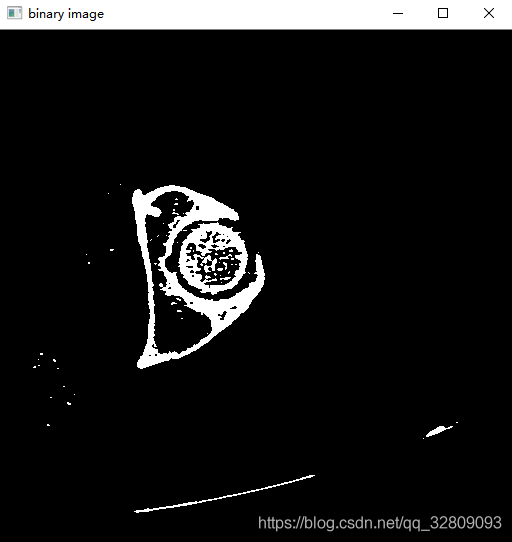
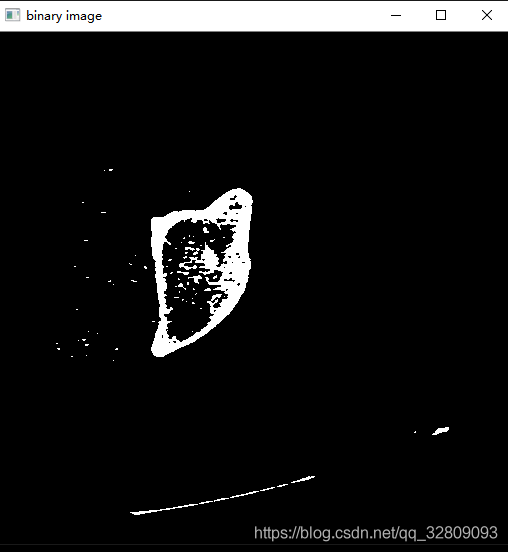
} 阈值通过进度条手动调整为106和178时的效果:
保存阈值分割后的图像:
实例8:opencv批量阈值分割JPG图像并显示保存
#include
#include // 当中含有_finddata_t
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define NUMBER 80 //(JPG文件数量为NUMBER-1)
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void Threshold_Demo(vector imag)
{
char ad[128] = { 0 };
Mat gray_src,dst;
const char* output_title = "binary image";//定义输出标题为二进制图像
for(int i=0;i images;
for (int a = 1; a < NUMBER;a+=10) // a <=Count would do one too many...
{
string filename = format("F:\\Software\\VTK8.2.0\\vtk1\\helloVtk\\JPG_images\\%d.jpg", a);//JPG文件的存储路径
Mat img = imread(filename); //读取图像
if (img.empty()) // 如果图像为空
{
cerr << "whaa " << filename << " can't be loaded!" << endl;
continue;
}
images.push_back(img);//图像保存进容器
}
//进行批量阈值分割与保存
Threshold_Demo(images);
return 0;
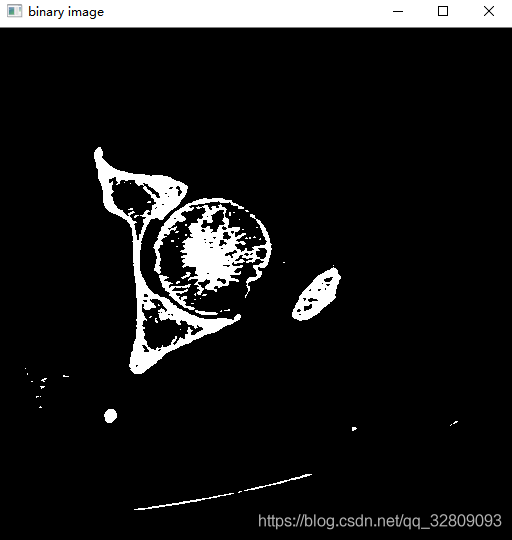
} 原图像和阈值设定阈值分割后的图像:
阈值分割后保存图像:
实例9:opencv区域增长算法分割JPG图像并显示保存
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
#include
#include "math.h"
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Point recent_Point, recent_Point1;
Mat RegionGrow(Mat src, Point2i pt, int th)
{
Point2i ptGrowing; //待生长点位置
int nGrowLable = 0; //标记是否生长过
int nSrcValue = 0; //生长起点灰度值
int nCurValue = 0; //当前生长点灰度值
Mat matDst = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC1); //创建一个空白区域,填充为黑色
//生长方向顺序数据
int DIR[8][2] = { { -1, -1 }, { 0, -1 }, { 1, -1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 0, 1 }, { -1, 1 }, { -1, 0 } };
vector vcGrowPt; //生长点栈
vcGrowPt.push_back(pt); //将生长点压入栈中
matDst.at(pt.y, pt.x) = 255; //标记生长点
nSrcValue = src.at(pt.y, pt.x); //记录生长点的灰度值
while (!vcGrowPt.empty()) //生长栈不为空则生长
{
pt = vcGrowPt.back(); //取出一个生长点
vcGrowPt.pop_back();
//分别对八个方向上的点进行生长
for (int i = 0; i < 9; ++i)
{
ptGrowing.x = pt.x + DIR[i][0];
ptGrowing.y = pt.y + DIR[i][1];
//检查是否是边缘点
if (ptGrowing.x < 0 || ptGrowing.y < 0 || ptGrowing.x >(src.cols - 1) || (ptGrowing.y > src.rows - 1))
continue;
nGrowLable = matDst.at(ptGrowing.y, ptGrowing.x); //当前待生长点的灰度值
if (nGrowLable == 0) //如果标记点还没有被生长
{
nCurValue = src.at(ptGrowing.y, ptGrowing.x);
if (abs(nSrcValue - nCurValue) < th) //在阈值范围内则生长
{
matDst.at(ptGrowing.y, ptGrowing.x) = 255; //标记为白色
vcGrowPt.push_back(ptGrowing); //将下一个生长点压入栈中
}
}
}
}
return matDst.clone();
}
void On_mouse(int event, int x, int y, int flags, void*)//每次点击左键,在相应位置画红点
{
if (event == EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN)
{
recent_Point = Point(x, y);
cout << "img_x" << " " << recent_Point.x << " " << "img_y" << " " << recent_Point.y << endl;
//circle(srcimg, recent_Point, 2, Scalar(0, 0, 255), -1);
//imshow("srcImg", srcimg);
}
}
int main() //区域生长
{
Mat binaryimg, greyimg;
Mat regiongrow, regiongrow1, regiongrow2;
Mat dst;
int th = 10;
Mat src = imread("1.jpg");
cvtColor(src, greyimg, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); //转化为灰度图
Mat temp_regiongrow = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC1); //创建一个空白区域,填充为黑色
//转化为二值图
threshold(greyimg, binaryimg, 200, 255, THRESH_BINARY);
namedWindow("srcImg", 0);
imshow("srcImg", src);
namedWindow("binaryImg", 0);
imshow("binaryImg", binaryimg);
cout << "select one point in binaryImg" << endl;
setMouseCallback("binaryImg", On_mouse);
for (int i = 0;i < 1;i++) {
char c = (char)waitKey(0);
cout << "select one point in binaryImg" << endl;
setMouseCallback("binaryImg", On_mouse);
if (c == 'b') {
regiongrow1 = RegionGrow(binaryimg, recent_Point, th);
bitwise_or(regiongrow1, temp_regiongrow, regiongrow); //和前一个分割的图做或运算
temp_regiongrow = regiongrow1.clone(); //保存前一个分割图
}
bitwise_and(greyimg, regiongrow, dst); //与原图做与运算
namedWindow("dstimg", 0);
imshow("dstimg", dst);
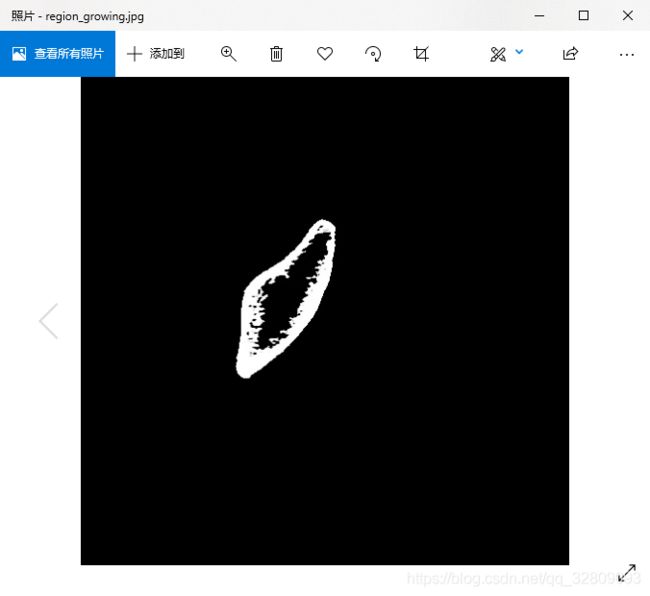
imwrite("region_growing.jpg", dst);
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
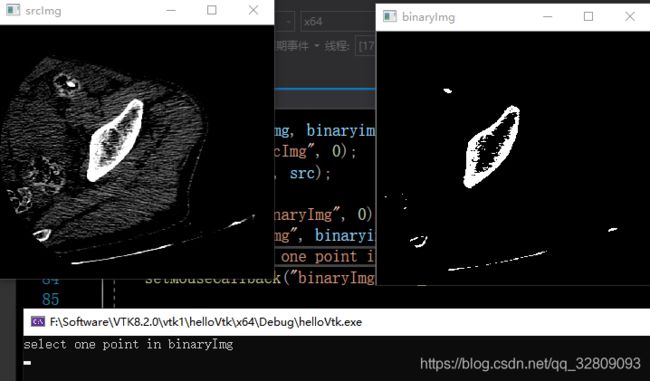
在binaryImag图像中选择区域增长的初始种子点(鼠标左键一下红色区域选取):
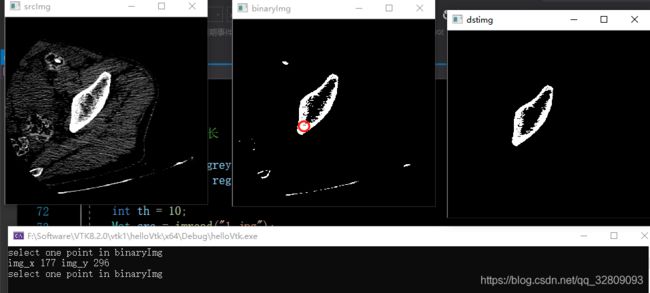
出现位置坐标后,键盘输入字母‘b'进行区域增长算法运行,dstimg为区域增长分割后图像:
实例10:VTK格式文件的读取与渲染显示
#include "vtkAutoInit.h"
VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2);
VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
#include "vtkRenderer.h"//绘制器
#include "vtkRenderWindow.h"//绘制窗口
#include "vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h"//加入交互机制类
#include "vtkDICOMImageReader.h"//DCM医学文件读取类
#include "vtkPolyDataMapper.h"//数据映射
#include "vtkActor.h"//演员
#include "vtkOutlineFilter.h"
#include "vtkCamera.h"//照相机
#include "vtkProperty.h"//属性设置类
#include "vtkPolyDataNormals.h"//vtkPolyData为多边形数据
#include "vtkContourFilter.h"//等值面提取类(可以接受任何的数据类型生成等值线或者等值面)
#include "vtkPolyDataWriter.h"//保存为.vtk图像类
#include "vtkPolyDataReader.h"//读取.vtk图像类
void main()
{
// Create the renderer, the render window, and the interactor. The renderer
// draws into the render window, the interactor enables mouse- and
// keyboard-based interaction with the data within the render window.
//创建渲染器、渲染窗口和交互器。
//绘制到渲染窗口,交互器启用,渲染窗口内的数据进行基于鼠标和键盘的交互。
vtkRenderer* aRenderer = vtkRenderer::New();
vtkRenderWindow* renWin = vtkRenderWindow::New();
renWin->AddRenderer(aRenderer);
vtkRenderWindowInteractor* iren = vtkRenderWindowInteractor::New();
iren->SetRenderWindow(renWin);
//读取vtk格式图像
vtkPolyDataReader* v16 = vtkPolyDataReader::New();
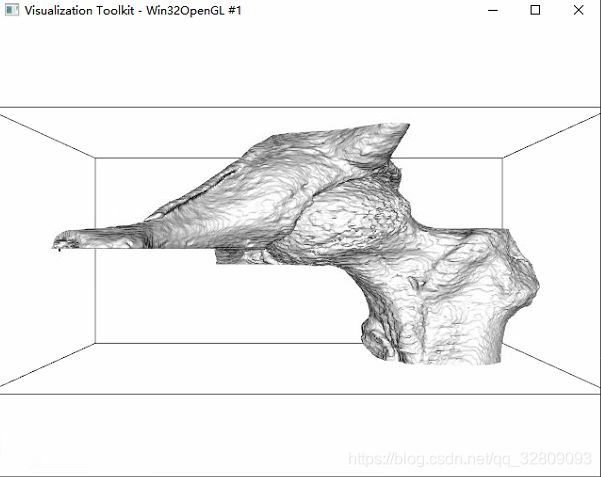
v16->SetFileName("spine.vtk");
vtkPolyDataMapper* skinMapper = vtkPolyDataMapper::New();
skinMapper->SetInputConnection(v16->GetOutputPort());
skinMapper->ScalarVisibilityOff();//这样不会带颜色
vtkActor* skin = vtkActor::New();
skin->SetMapper(skinMapper);
// An outline provides context around the data.
vtkOutlineFilter* outlineData = vtkOutlineFilter::New();
outlineData->SetInputConnection(v16->GetOutputPort());
vtkPolyDataMapper* mapOutline = vtkPolyDataMapper::New();
mapOutline->SetInputConnection(outlineData->GetOutputPort());
vtkActor* outline = vtkActor::New();
outline->SetMapper(mapOutline);
outline->GetProperty()->SetColor(0, 0, 0);
// It is convenient to create an initial view of the data. The FocalPoint
// and Position form a vector direction. Later on (ResetCamera() method)
// this vector is used to position the camera to look at the data in
// this direction.
//相机设置
vtkCamera* aCamera = vtkCamera::New();
aCamera->SetViewUp(0, 0, -1);
aCamera->SetPosition(0, 1, 0);
aCamera->SetFocalPoint(0, 0, 0);
aCamera->ComputeViewPlaneNormal();
// Actors are added to the renderer. An initial camera view is created.
// The Dolly() method moves the camera towards the FocalPoint,
// thereby enlarging the image.
//渲染
aRenderer->AddActor(outline);
aRenderer->AddActor(skin);
aRenderer->SetActiveCamera(aCamera);
aRenderer->ResetCamera();
aCamera->Dolly(1.5);
// Set a background color for the renderer and set the size of the
// render window (expressed in pixels).
//设置背景色和窗口大小
aRenderer->SetBackground(1, 1, 1);
renWin->SetSize(640, 480);
// Note that when camera movement occurs (as it does in the Dolly()
// method), the clipping planes often need adjusting. Clipping planes
// consist of two planes: near and far along the view direction. The
// near plane clips out objects in front of the plane; the far plane
// clips out objects behind the plane. This way only what is drawn
// between the planes is actually rendered.
aRenderer->ResetCameraClippingRange();
// Initialize the event loop and then start it.
iren->Initialize();
iren->Start();
// It is important to delete all objects created previously to prevent
// memory leaks. In this case, since the program is on its way to
// exiting, it is not so important. But in applications it is
// essential.
//释放内存
v16->Delete();
/*skinExtractor->Delete();
skinNormals->Delete();*/
skinMapper->Delete();
skin->Delete();
outlineData->Delete();
mapOutline->Delete();
outline->Delete();
aCamera->Delete();
iren->Delete();
renWin->Delete();
aRenderer->Delete();
}实例11:基于VTK对MHD格式文件单张切片的鼠标滑动提取显示
#include "vtkAutoInit.h"
VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2);
VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
class vtkImageInteractionCallback : public vtkCommand
{
public:
static vtkImageInteractionCallback* New()
{
return new vtkImageInteractionCallback;
}
vtkImageInteractionCallback()
{
this->Slicing = 0;
this->ImageReslice = 0;
this->Interactor = 0;
}
void SetImageReslice(vtkImageReslice* reslice)
{
this->ImageReslice = reslice;
}
void SetImageMapToColors(vtkImageMapToColors* mapToColors)
{
this->mapToColors = mapToColors;
}
vtkImageReslice* GetImageReslice()
{
return this->ImageReslice;
}
void SetInteractor(vtkRenderWindowInteractor* interactor)
{
this->Interactor = interactor;
}
vtkRenderWindowInteractor* GetInteractor()
{
return this->Interactor;
}
virtual void Execute(vtkObject*, unsigned long event, void*)
{
vtkRenderWindowInteractor* interactor = this->GetInteractor();
int lastPos[2];
interactor->GetLastEventPosition(lastPos);
int currPos[2];
interactor->GetEventPosition(currPos);
if (event == vtkCommand::LeftButtonPressEvent)
{
this->Slicing = 1;
}
else if (event == vtkCommand::LeftButtonReleaseEvent)
{
this->Slicing = 0;
}
else if (event == vtkCommand::MouseMoveEvent)
{
if (this->Slicing)
{
vtkImageReslice* reslice = this->ImageReslice;
// Increment slice position by deltaY of mouse
int deltaY = lastPos[1] - currPos[1];
reslice->Update();
double sliceSpacing = reslice->GetOutput()->GetSpacing()[2];
vtkMatrix4x4* matrix = reslice->GetResliceAxes();
// move the center point that we are slicing through
double point[4];
double center[4];
point[0] = 0.0;
point[1] = 0.0;
point[2] = sliceSpacing * deltaY;
point[3] = 1.0;
matrix->MultiplyPoint(point, center);
matrix->SetElement(0, 3, center[0]);
matrix->SetElement(1, 3, center[1]);
matrix->SetElement(2, 3, center[2]);
mapToColors->Update();
interactor->Render();
}
else
{
vtkInteractorStyle* style = vtkInteractorStyle::SafeDownCast(
interactor->GetInteractorStyle());
if (style)
{
style->OnMouseMove();
}
}
}
}
private:
int Slicing;
vtkImageReslice* ImageReslice;
vtkRenderWindowInteractor* Interactor;
vtkImageMapToColors* mapToColors;
};
int main()
{
vtkSmartPointer reader =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
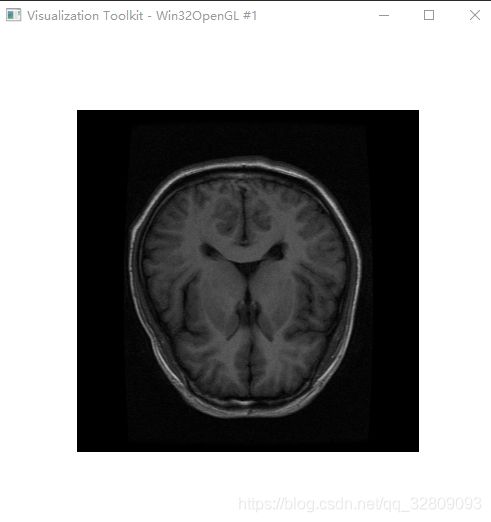
reader->SetFileName("brain.mhd");
reader->Update();
int extent[6];
double spacing[3];
double origin[3];
reader->GetOutput()->GetExtent(extent);
reader->GetOutput()->GetSpacing(spacing);
reader->GetOutput()->GetOrigin(origin);
double center[3];
center[0] = origin[0] + spacing[0] * 0.5 * (extent[0] + extent[1]);
center[1] = origin[1] + spacing[1] * 0.5 * (extent[2] + extent[3]);
center[2] = origin[2] + spacing[2] * 0.5 * (extent[4] + extent[5]);
static double axialElements[16] = {
1, 0, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, 0,
0, 0, 1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 1
};
vtkSmartPointer resliceAxes =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
resliceAxes->DeepCopy(axialElements);
resliceAxes->SetElement(0, 3, center[0]);
resliceAxes->SetElement(1, 3, center[1]);
resliceAxes->SetElement(2, 3, center[2]);
vtkSmartPointer reslice =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
reslice->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
reslice->SetOutputDimensionality(2);
reslice->SetResliceAxes(resliceAxes);
reslice->SetInterpolationModeToLinear();
vtkSmartPointer colorTable =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
colorTable->SetRange(0, 1000);
colorTable->SetValueRange(0.0, 1.0);
colorTable->SetSaturationRange(0.0, 0.0);
colorTable->SetRampToLinear();
colorTable->Build();
vtkSmartPointer colorMap =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
colorMap->SetLookupTable(colorTable);
colorMap->SetInputConnection(reslice->GetOutputPort());
colorMap->Update();
vtkSmartPointer imgActor =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
imgActor->SetInputData(colorMap->GetOutput());
vtkSmartPointer renderer =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
renderer->AddActor(imgActor);
renderer->SetBackground(1, 1, 1);
vtkSmartPointer renderWindow =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
renderWindow->SetSize(500, 500);
renderWindow->AddRenderer(renderer);
vtkSmartPointer renderWindowInteractor =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
vtkSmartPointer imagestyle =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
renderWindowInteractor->SetInteractorStyle(imagestyle);
renderWindowInteractor->SetRenderWindow(renderWindow);
renderWindowInteractor->Initialize();
vtkSmartPointer callback =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
callback->SetImageReslice(reslice);
callback->SetInteractor(renderWindowInteractor);
callback->SetImageMapToColors(colorMap);
imagestyle->AddObserver(vtkCommand::MouseMoveEvent, callback);
imagestyle->AddObserver(vtkCommand::LeftButtonPressEvent, callback);
imagestyle->AddObserver(vtkCommand::LeftButtonReleaseEvent, callback);
renderWindowInteractor->Start();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
} 用到的MHD文件:
效果(鼠标在切片区域左键一直按住右或左拖动(或上下拖动),即可更换不同切片显示):
注:此例程MHA和NII格式文件同样适用。
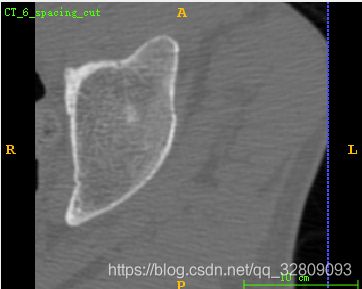
实例12:基于VTK对MHA格式文件三维感兴趣区域裁剪及MHA格式保存
#include "vtkAutoInit.h"
VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkRenderingOpenGL2);
VTK_MODULE_INIT(vtkInteractionStyle);
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //mha、mad图像读取类
#include mha、mad图像写入类
//测试图像:../data/lena.bmp
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
/*vtkSmartPointer reader =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
reader->SetFileName("lena.bmp");
reader->Update();*/
vtkSmartPointer reader = vtkSmartPointer::New();
//mhd与mha文件其实格式是一样的,记录mhd对应的raw文件应在同一目录
//mhd格式图像信息头与实际图像的存储分为两个文件(*.mhd文件记录图像信息头;*.raw或//*.zraw(zraw指有压缩)记录实际图像)
//mha格式将图像信息头与实际的像素值等数据写入到同一个文件中
//reader->SetFileName("test1.mhd");
//.mha和.raw文件需要在同一个文件夹
reader->SetFileName("CT_6_spacing.mha");
reader->Update();
int dims[3];
reader->GetOutput()->GetDimensions(dims);
vtkSmartPointer extractVOI =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
extractVOI->SetInputConnection(reader->GetOutputPort());
//设置感兴趣区域:X_min、X_max、Y_min、Y_max、Z_min、Z_max
extractVOI->SetVOI(dims[0] / 4., 3. * dims[0] / 4., dims[1] / 4., 3. * dims[1] / 4., 0, 5);//这里设置0~5,表示裁剪六张切片
extractVOI->Update();
vtkSmartPointer originalActor =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
originalActor->SetInputData(reader->GetOutput());
vtkSmartPointer voiActor =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
voiActor->SetInputData(extractVOI->GetOutput());
double originalViewport[4] = { 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0 };
double voiviewport[4] = { 0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0 };
vtkSmartPointer originalRenderer =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
originalRenderer->SetViewport(originalViewport);
originalRenderer->AddActor(originalActor);
originalRenderer->ResetCamera();
originalRenderer->SetBackground(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
vtkSmartPointer shiftscaleRenderer =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
shiftscaleRenderer->SetViewport(voiviewport);
shiftscaleRenderer->AddActor(voiActor);
shiftscaleRenderer->ResetCamera();
shiftscaleRenderer->SetBackground(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
vtkSmartPointer renderWindow =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
renderWindow->AddRenderer(originalRenderer);
renderWindow->AddRenderer(shiftscaleRenderer);
renderWindow->SetSize(900, 300);
renderWindow->Render();
renderWindow->SetWindowName("ExtractVOIExample");
vtkSmartPointer renderWindowInteractor =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
vtkSmartPointer style =
vtkSmartPointer::New();
//保存为mhd文件
//vtkMetaImageWriter* vtkWriter = vtkMetaImageWriter::New();
//vtkWriter->SetInputConnection(extractVOI->GetOutputPort());
以raw和mhd格式保存,去掉此句则以zraw保存
//vtkWriter->SetCompression(0);
//vtkWriter->SetFileName("BrainProtonDensity3Slices_1.mhd");
//vtkWriter->Write();
保存为mha文件
vtkMetaImageWriter* vtkWriter = vtkMetaImageWriter::New();
vtkWriter->SetInputConnection(extractVOI->GetOutputPort());
//以raw和mhd格式保存,去掉此句则以zraw保存
vtkWriter->SetCompression(0);
vtkWriter->SetFileName("CT_6_spacing_cut.mha");
vtkWriter->Write();
renderWindowInteractor->SetInteractorStyle(style);
renderWindowInteractor->SetRenderWindow(renderWindow);
renderWindowInteractor->Initialize();
renderWindowInteractor->Start();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
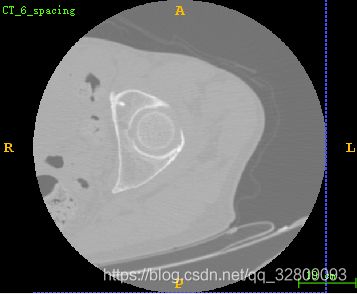
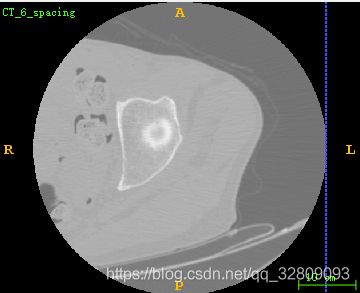
} 读取的MHA源文件:
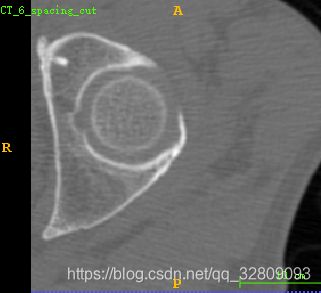
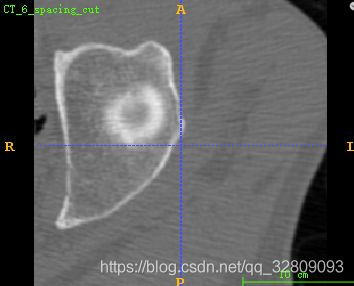
选定区域剪切后保存的MHA文件:
其中前四张剪切前后效果对比:
注:此例程MHD和NII格式文件同样适用。