【动手学基于Python+Tensorflow+CNN深度学习的轴承故障诊断(西储大学数据集)(含完整代码)】
项目名称
动手学基于Python+CNN深度学习的轴承故障诊断(西储大学数据集)(含完整代码)
项目介绍
该项目使用tensorflow和keras搭建深度学习CNN网络,并使用西储大学数据集作为训练集和测试集,对西储大学mat格式数据进行处理,将数据放入搭建好的网络中进行训练,最终得到相关故障诊断模型。
背景
最近在上故障诊断的课程,老师发给我们西储大学的轴承故障数据集,让我们自己去折腾。正巧前段时间学习了深度学习的课程,因此想着自己搭建一个深度学习的网络来进行相关故障的诊断。查阅相关文献,使用深度学习的故障诊断方法目前主要有两种形式,一种是直接将相关加速度一维数据放入深度学习网络中学习,另一种方式是使用相关变化将加速度数据转为二维图像,将二维图像放入深度学习网络进行学习。本文采用的是第一种方法,接下来对代码相关部分进行介绍,想要学习实践的也可以直接跳到最后有完整代码。
目录
-
- 项目名称
- 项目介绍
-
- 背景
- 项目相关展示
-
-
- 基本环境介绍
- 数据预处理
- 训练部分
- 完整源码下载地址
-
项目相关展示
基本环境介绍
电脑环境:
Windows10
Python环境:
Conda + python3.7
Tensorflow:1.7.1
keras
h5py==2.10.0
数据预处理
下面的代码可以实现数据的预处理,深度学习使用的数据需要我们进行随机划分训练集和测试集,并对相关的数据集打标签。一般我们使用的是0-1编码作为标签,这样做更有利于网络的计算。
from scipy.io import loadmat
import numpy as np
import os
from sklearn import preprocessing # 0-1编码
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit # 随机划分,保证每一类比例相同
def prepro(d_path, length=864, number=1000, normal=True, rate=[0.5, 0.25, 0.25], enc=True, enc_step=28):
"""对数据进行预处理,返回train_X, train_Y, valid_X, valid_Y, test_X, test_Y样本.
:param d_path: 源数据地址
:param length: 信号长度,默认2个信号周期,864
:param number: 每种信号个数,总共10类,默认每个类别1000个数据
:param normal: 是否标准化.True,False.默认True
:param rate: 训练集/验证集/测试集比例.默认[0.5,0.25,0.25],相加要等于1
:param enc: 训练集、验证集是否采用数据增强.Bool,默认True
:param enc_step: 增强数据集采样顺延间隔
:return: Train_X, Train_Y, Valid_X, Valid_Y, Test_X, Test_Y
```
import preprocess.preprocess_nonoise as pre
train_X, train_Y, valid_X, valid_Y, test_X, test_Y = pre.prepro(d_path=path,
length=864,
number=1000,
normal=False,
rate=[0.5, 0.25, 0.25],
enc=True,
enc_step=28)
```
"""
# 获得该文件夹下所有.mat文件名
filenames = os.listdir(d_path)
def capture(original_path):
"""读取mat文件,返回字典
:param original_path: 读取路径
:return: 数据字典
"""
files = {}
for i in filenames:
# 文件路径
file_path = os.path.join(d_path, i)
file = loadmat(file_path)
file_keys = file.keys()
for key in file_keys:
if 'DE' in key:
files[i] = file[key].ravel()
return files
def slice_enc(data, slice_rate=rate[1] + rate[2]):
"""将数据切分为前面多少比例,后面多少比例.
:param data: 单挑数据
:param slice_rate: 验证集以及测试集所占的比例
:return: 切分好的数据
"""
keys = data.keys()
Train_Samples = {}
Test_Samples = {}
for i in keys:
slice_data = data[i]
all_lenght = len(slice_data)
end_index = int(all_lenght * (1 - slice_rate))
samp_train = int(number * (1 - slice_rate)) # 700
Train_sample = []
Test_Sample = []
if enc:
enc_time = length // enc_step
samp_step = 0 # 用来计数Train采样次数
for j in range(samp_train):
random_start = np.random.randint(low=0, high=(end_index - 2 * length))
label = 0
for h in range(enc_time):
samp_step += 1
random_start += enc_step
sample = slice_data[random_start: random_start + length]
Train_sample.append(sample)
if samp_step == samp_train:
label = 1
break
if label:
break
else:
for j in range(samp_train):
random_start = np.random.randint(low=0, high=(end_index - length))
sample = slice_data[random_start:random_start + length]
Train_sample.append(sample)
# 抓取测试数据
for h in range(number - samp_train):
random_start = np.random.randint(low=end_index, high=(all_lenght - length))
sample = slice_data[random_start:random_start + length]
Test_Sample.append(sample)
Train_Samples[i] = Train_sample
Test_Samples[i] = Test_Sample
return Train_Samples, Test_Samples
# 仅抽样完成,打标签
def add_labels(train_test):
X = []
Y = []
label = 0
for i in filenames:
x = train_test[i]
X += x
lenx = len(x)
Y += [label] * lenx
label += 1
return X, Y
# one-hot编码
def one_hot(Train_Y, Test_Y):
Train_Y = np.array(Train_Y).reshape([-1, 1])
Test_Y = np.array(Test_Y).reshape([-1, 1])
Encoder = preprocessing.OneHotEncoder()
Encoder.fit(Train_Y)
Train_Y = Encoder.transform(Train_Y).toarray()
Test_Y = Encoder.transform(Test_Y).toarray()
Train_Y = np.asarray(Train_Y, dtype=np.int32)
Test_Y = np.asarray(Test_Y, dtype=np.int32)
return Train_Y, Test_Y
def scalar_stand(Train_X, Test_X):
# 用训练集标准差标准化训练集以及测试集
scalar = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit(Train_X)
Train_X = scalar.transform(Train_X)
Test_X = scalar.transform(Test_X)
return Train_X, Test_X
def valid_test_slice(Test_X, Test_Y):
test_size = rate[2] / (rate[1] + rate[2])
ss = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=1, test_size=test_size)
for train_index, test_index in ss.split(Test_X, Test_Y):
X_valid, X_test = Test_X[train_index], Test_X[test_index]
Y_valid, Y_test = Test_Y[train_index], Test_Y[test_index]
return X_valid, Y_valid, X_test, Y_test
# 从所有.mat文件中读取出数据的字典
data = capture(original_path=d_path)
# 将数据切分为训练集、测试集
train, test = slice_enc(data)
# 为训练集制作标签,返回X,Y
Train_X, Train_Y = add_labels(train)
# 为测试集制作标签,返回X,Y
Test_X, Test_Y = add_labels(test)
# 为训练集Y/测试集One-hot标签
Train_Y, Test_Y = one_hot(Train_Y, Test_Y)
# 训练数据/测试数据 是否标准化.
if normal:
Train_X, Test_X = scalar_stand(Train_X, Test_X)
else:
# 需要做一个数据转换,转换成np格式.
Train_X = np.asarray(Train_X)
Test_X = np.asarray(Test_X)
# 将测试集切分为验证集合和测试集.
Valid_X, Valid_Y, Test_X, Test_Y = valid_test_slice(Test_X, Test_Y)
return Train_X, Train_Y, Valid_X, Valid_Y, Test_X, Test_Y
if __name__ == "__main__":
path = r'data\0HP'
train_X, train_Y, valid_X, valid_Y, test_X, test_Y = prepro(d_path=path,
length=864,
number=1000,
normal=False,
rate=[0.5, 0.25, 0.25],
enc=False,
enc_step=28)
训练部分
数据处理完之后,就是我们的训练部分了,我们首先看一下我的CNN网络架构。
data_input=Input(shape=(4000,1))
#这相当于是第一段卷积
conv1=convolutional.Conv1D(128,3,strides=3,padding="same")(data_input)
conv1=BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(conv1)
conv1=MaxPool1D(pool_size=4)(conv1)
conv2=convolutional.Conv1D(128,3,strides=3,padding="same")(conv1)
conv2=BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(conv2)
conv2=MaxPool1D(pool_size=4)(conv2)
conv3=convolutional.Conv1D(128,3,strides=3,padding="same")(conv2)
conv3=BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8)(conv3)
conv3=MaxPool1D(pool_size=4)(conv3)
flatten=Flatten()(conv3)
dense_1=Dense(128)(flatten)
dense_1=Dropout(0.3)(dense_1)
output = Dense(3, activation='softmax')(dense_1)
cnn_model= Model(input=data_input, output=output)
cnn_model.summary() #打印模型结构与参数
上面的部分就是我们的网络架构,就是比较传统的CNN网络架构,如果有不太了解的小伙伴可以留言或者自行查阅相关资料,如果有想了解的朋友比较多,我也可以单独出一篇博客进行详细讲解。
有了网络模型和数据之后我们就可以进行训练了,训练部分代码如下:
def train(cnn_model):
# checkpoint
epoch = 50
filepath = "model\cnn-"+str(step)+"_weights"+str(epoch)+"-improvement-{epoch:02d}-{val_acc:.2f}.hdf5"
# 中途训练效果提升, 则将文件保存, 每提升一次, 保存一次
checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(filepath, monitor='val_acc', verbose=1, save_best_only=True, mode='max')
callbacks_list = [checkpoint]
cnn_model.compile(optimizer=Adam(lr=adam_lr),
loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
#下面是训练了
history = cnn_model.fit( X_train, y_train, batch_size=128, epochs=epoch, verbose=1, validation_data=[X_test,y_test],callbacks=callbacks_list)
# epochs = range(len(history.history['acc']))
epochs = range(epoch)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, history.history['acc'], 'b', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, history.history['val_acc'], 'r', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Traing and Validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig('model_'+str(step)+'_'+str(epoch)+'V0.1_acc.jpg')
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, history.history['loss'], 'b', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, history.history['val_loss'], 'r', label='Validation val_loss')
plt.title('Traing and Validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig('model_'+str(step)+'V1'+str(epoch)+'_loss.jpg')
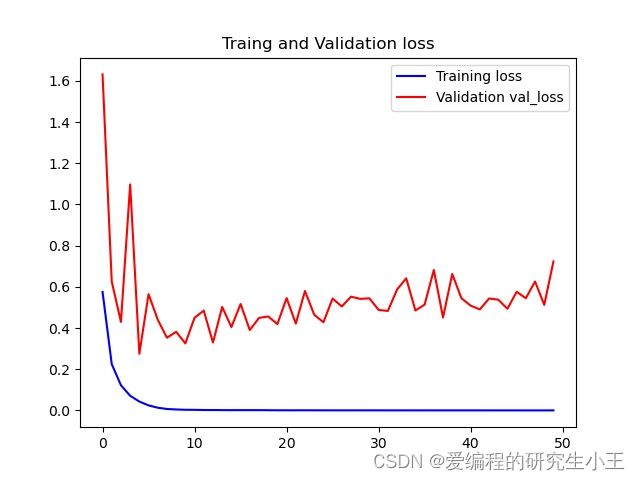
在上面的代码中,我使用了回调函数call_back_list,将该段函数加入后,模型训练中会帮我们保存所有有提升的模型。plot函数可以进行画图,我们可以画出我们训练过程中所有的准确率,损失函数值,得到我们的准确率图像和损失函数。准确率函数图像如下。因为电脑配置有限,因此我只选取了50次作为案例,如果希望图像更好可以尝试更多的次数。
完整源码下载地址
基于Python+CNN深度学习的轴承故障诊断 完整代码下载